Abstract
Background
Dietary fat exerts numerous complex effects on proinflammatory and immunologic pathways. Several epidemiological studies have examined the relationships between intake of fatty acids and/or foods high in fat and allergic rhinitis, but have provided conflicting findings. The current cross-sectional study investigated such relationships in Japan.
Methods
Study subjects were 1745 pregnant women. The definition of rhinoconjunctivitis was based on criteria from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood. Information on dietary factors was collected using a validated self-administered diet history questionnaire. Adjustment was made for age; gestation; region of residence; number of older siblings; number of children; smoking; secondhand smoke exposure at home and at work; family history of asthma, atopic eczema, and allergic rhinitis; household income; education; and body mass index.
Results
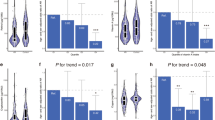
The prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in the past 12 months was 25.9%. Higher meat intake was significantly associated with an increased prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis: the adjusted odds ratio between extreme quartiles was 1.71 (95% confidence interval: 1.25-2.35, P for trend = 0.002). No measurable association was found between fish intake and rhinoconjunctivitis. Intake of total fat, saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, and cholesterol and the ratio of n-3 to n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake were not evidently related to the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis.
Conclusions
The current results suggest that meat intake may be positively associated with the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in young adult Japanese women.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Allergic rhinitis is one of the most common disorders in Japan. In a study of 1540 Japanese aged 20 to 49 years, the prevalence of allergic rhinitis was 44.2%, and 89.6% of the subjects with allergic rhinitis were sensitized to Japanese cedar pollen [1]. The prevalence of Japanese cedar pollinosis increased 2.6-fold between 1980 and 2000 [2]. Such an increase may be a consequence of dietary change: a study of Japanese men showed an increase in intake of fat from 5% to 20%, of fish from 56 g/day to 71 g/day, and of meat from 13 g/day to 92 g/day from 1958 to 1999 [3].
Dietary fat exerts numerous complex effects on proinflammatory and immunologic pathways [4]. Several epidemiological studies have examined the relationships between intake of fatty acids and/or foods high in fat and allergic rhinitis in children [5–12] and adults [13–18], but have provided conflicting findings. Such epidemiological evidence in Japan, where fish intake is high, is scarce. A significant inverse relationship was observed between arachidonic acid intake and the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in schoolchildren aged 6-15 years [11], while the sum of intake of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids was significantly associated with a lower prevalence of allergic rhinitis in pregnant women [16]. Another cross-sectional study of female university students showed a significant inverse association between seafood intake and pollen allergy [17].
To accumulate further epidemiological evidence, we performed a cross-sectional study to investigate the relationship between consumption of meat, fish, and specific types of fatty acids and the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in pregnant Japanese women using baseline data from the Kyushu Okinawa Maternal and Child Health Study (KOMCHS).
Methods
Study population
The KOMCHS is an ongoing prospective prebirth cohort study that investigates risk and preventive factors for maternal and child health problems such as allergic disorders. From April 2007 to March 2008, the KOMCHS requested that 131 obstetric hospitals in Fukuoka Prefecture, the largest prefecture on Kyushu Island in southern Japan with a total population of approximately 5.04 million, provide as many pregnant women as possible with a set of leaflets explaining the KOMCHS, an application form to participate in the study, and a self-addressed and stamped return envelope. From May 2007 to March 2008, the KOMCHS also requested that forty obstetric hospitals in Okinawa Prefecture, an island in the southernmost area in Japan with a total population of nearly 1.37 million, provide pregnant women with a similar set of materials. In addition, to increase the sample size, from August 2007 to March 2008, pregnant women living in six prefectures on Kyushu Island (other than Fukuoka Prefecture), with a total population of approximately 8.22 million, were provided with a similar set of materials at 252 obstetric hospitals. Pregnant women who intended to participate in the KOMCHS returned the application form to the data management center. When all responses were tallied, a total of 1757 pregnant women between the 5th and 39th weeks of pregnancy had provided their fully informed written consent to participate and had completed the baseline survey. Incomplete data on the variables under study caused the exclusion of 12 pregnant women; in the end, data on 1745 pregnant women were available for analysis. The ethics committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka University approved the KOMCHS.
Measurements
In the baseline survey, each participant filled out a set of two self-administered questionnaires and mailed them to the data management center. Research technicians clarified missing or illogical data by telephone interview.
A self-administered, semi-quantitative, comprehensive diet history questionnaire (DHQ) was used to assess dietary habits during the preceding month [19, 20]. Estimates of daily intake of foods (total of 150 foods), energy, and selected nutrients were calculated using an ad hoc computer algorithm for the DHQ based on the Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan [21]. Information on dietary supplements was not used in the calculation of dietary intake. Detailed descriptions of the methods used for calculating dietary intake and the validity of the DHQ were published elsewhere [19, 20]. The correlation coefficients for nutrient intake between those estimated from the DHQ and those observed by a three-day dietary record were 0.75, 0.50, 0.37, and 0.49 for saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and cholesterol, respectively, in women [19]. A highly positive correlation was also observed between marine-origin n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake estimated by the DHQ and the corresponding concentration in the serum phospholipid fraction in women (r = 0.69) [20]. Energy-adjusted intake by the residual method was used for the analyses [22]. Body weight and height were self-reported as part of the DHQ. Body mass index was calculated as weight (kg) divided by the square of height (m).
A second self-administered questionnaire included questions on rhinoconjunctivitis based on the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) [23]. The presence of rhinoconjunctivitis was defined as a positive response to the following two questions: 'In the last 12 months, have you had a problem with sneezing or a runny or blocked nose when you did not have a cold or flu?' and 'In the last 12 months, has this nose problem been accompanied by itchy-watery eyes?' The questionnaire also elicited information on age; gestation; region of residence; number of older siblings; number of children; smoking habits; secondhand smoke exposure at home and at work; family history of asthma, atopic eczema, and allergic rhinitis; household income; and education. A family history of asthma, atopic eczema, or allergic rhinitis (including Japanese cedar pollinosis) was considered to be present if one or more parents or siblings of the study subjects had been diagnosed by a physician as having any of these allergic disorders.
Statistical analysis
Intake of the dietary factors under study was divided into quartile ranges based on distribution among all study subjects. Age; gestation; region of residence; number of older siblings; number of children; smoking; secondhand smoke exposure at home and at work; family history of asthma, atopic eczema, and allergic rhinitis; household income; education; and body mass index were selected a priori as potential confounding factors. Because values of dietary intake under study were energy-adjusted according to the residual method, estimated energy from protein and carbohydrates and alcohol intake were not included in the multivariate model.
Logistic regression analysis was performed to estimate crude odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of rhinoconjunctivitis according to the quartile of dietary factors under study, with the lowest quartile as the reference. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to adjust for potential confounding factors. Trend of association was assessed by a logistic regression model assigning consecutive integers (1 to 4) to the quartiles of the exposure variables. All statistical analyses were carried out using the SAS software package version 9.2 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
The prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in the past 12 months was 25.9% among the 1745 pregnant women. The mean age of the participants and gestation at baseline were 31.2 years and 18.5 weeks, respectively (Table 1). Many more women had a family history of allergic rhinitis than a family history of asthma or atopic eczema. Mean daily total energy consumption, mean daily energy-adjusted intake of meat, and mean daily energy-adjusted intake of total fat during pregnancy were 7434.2 kJ, 64.4 g, and 58.0 g, respectively (Table 2).
Table 3 presents ORs and 95% CIs for the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis by quartiles of dietary intake of meat and fish. Compared with being in the lowest quartile, being in the highest quartile for meat intake was significantly related to a higher prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis, and the positive linear trend was also significant in crude analysis. Adjustment for confounders under study did not materially alter the positive relationship: the adjusted OR between extreme quartiles was 1.71 (95% CI: 1.25-2.35, P for trend = 0.002). No measurable association was found between fish intake and rhinoconjunctivitis.
Results for intake of specific types of fatty acids and cholesterol are given in Table 4. Intake of total fat, saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, α-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, and cholesterol and the ratio of n-3 to n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake were not significantly related to the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in the multivariate model.
Discussion
The current cross-sectional study of pregnant Japanese women revealed that higher meat intake was independently associated with a higher prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis. There were no significant associations between intake of total fat, saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, or cholesterol or the ratio of n-3 to n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis.
Our results are not consistent with the hypothesis that decreased intake of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and increased intake of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids might have contributed to the recent increase in the prevalence of allergic disorders [4], a hypothesis that is supported by several other studies. In two cross-sectional studies of German children, a significant positive association was observed between margarine intake and allergic rhinitis [5, 6]. A significant inverse association between fish intake and allergic rhinitis was shown in two cohort studies of children in Norway [9] and Sweden [10]. A recent prebirth cohort study in Finland found that higher maternal α-linolenic acid intake during pregnancy was significantly related to a reduced risk of allergic rhinitis in children by 5 years of age, while a significant positive association was found between the ratio of n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake during pregnancy and childhood allergic rhinitis [12]. On the other hand, there was no relationship between fish intake and allergic rhinitis in a cross-sectional study of Italian children [8]. In a Finnish study, the differences in consumption of margarine and fish were not significant between children with allergic rhinitis and those without [7]. With regard to studies in adults, a cross-sectional study of German adults showed significant positive associations between margarine intake and the ratio of n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and hay fever in men, but not in women [14]. In a case-control study of German adults, higher eicosapentaenoic acid intake was significantly associated with a reduced risk of hay fever [13]. In young adult Japanese women, a significant inverse relationship was observed between intake of marine origin n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids [16] or seafood [17] and allergic rhinitis. A significant inverse relationship between α-linolenic acid intake and the prevalence of allergic rhinitis was found in German adults [15]. The discrepancies among studies may be explained, at least in part, by differences in the study populations and designs, dietary assessment methods, definitions of allergic rhinitis, and confounders.
Japanese people eat considerably more fish than do people in Western countries. The mean values for daily intake of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in this population were 0.17 g and 0.29 g, respectively. In many parts of Europe, the daily combined intake of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid by adults is < 100 mg [24]. A beneficial association between n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and rhinoconjunctivitis might be detected among populations whose fish intake is low. Alternatively, unknown active agents in fish might have interfered with the beneficial effect of marine-origin n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in rhinoconjunctivitis. For example, methylmercury and dioxins are accumulated in fish and shellfish through the marine food web. A significant correlation between fish consumption and hair mercury levels was found, and hair mercury levels were much higher in Japanese women residing in Canada than in Canadian women [25].
To our knowledge, this study is the first to show a significant positive association between meat intake and the prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis. The current findings regarding meat intake are in partial agreement with those of a previously cited Japanese study of female university students that showed a significant positive relationship between meat intake and the prevalence of wheeze, but not between meat intake and pollen allergy [17]. The present findings are also partially consistent with those of a prebirth cohort study in Japan that reported that higher maternal meat intake during pregnancy was significantly associated with an increased risk of suspected atopic eczema, which was based on a physician's diagnosis of atopic eczema or possible atopic eczema, in infants aged 3-4 months [26], although such intake was not related to the risk of wheeze or eczema based on the ISAAC criteria in the children aged 16-24 months [27]. In reports using baseline data from the prebirth cohort study in Japan, there were no associations between meat intake and the prevalence of asthma, atopic eczema, or allergic rhinitis in pregnant women [16, 28, 29]. Several studies showed no relationships between meat intake and wheeze and/or asthma in children [30–36] and adults [37]. Furthermore, a significant inverse association was found between red meat intake and doctor-diagnosed asthma in a cross-sectional study of young Australian adults [38]. These observations are at variance with the current results. The positive association between meat intake and rhinoconjunctivitis in this study is not ascribed to saturated fatty acid intake because saturated fatty acid intake was not related to rhinoconjunctivitis. The other constituents in meat may affect the development of rhinoconjunctivitis. Cooking meat at high temperatures results in the formation of carcinogenic compounds, such as heterocyclic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [39]. Also, meat intake results in exposures to N-nitroso compounds, which can form endogenously [40] and exogenously in nitrite-preserved meats [41]. Our results regarding meat intake might be ascribed to these possible carcinogens; however, there is no epidemiological evidence for relationships between these carcinogens and allergic disorders. Alternatively, meat intake might be a marker of a dietary pattern that is related to rhinoconjunctivitis. Or, some unknown non-dietary factors related to meat intake may have confounded the observed association. Higher meat intake is likely to be linked to a westernized lifestyle which may be related to rhinoconjunctivitis among Japanese.
This study has methodological advantages. Study subjects were homogeneous in that they were all pregnant. We took into consideration extensive information on potential confounders. Adjustment was not made for external factors such as aeroallergens and air pollution, however. The definition of rhinoconjunctivitis was based on the questions of the ISAAC, although validation tests of these questions have not been performed for young Japanese adults.
There are methodological limitations, however. Our DHQ could only approximate consumption. The validity of our DHQ seems reasonable, as described above, although the correlation coefficient for polyunsaturated fatty acids was 0.37 [19]. The possibility of exposure misclassification would bias the estimates of the associations toward the null. Our DHQ was designed to assess dietary intake for one month prior to completing the questionnaire. Information on dietary supplements that included eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid was not available; however, it might not be necessary to take such supplements into consideration among our study subjects because pregnant Japanese women are generally not advised to take such supplements. Only a small number of our participants used vitamin C (4.6%), multivitamin (5.5%), and calcium (5.6%) supplements at least once a week, although 26.2% used vitamin B complex at least once a week. Substantial changes in diet in the previous month were experienced by 502 pregnant women because of nausea gravidarum (473 women), maternal and fetal health (27 women), and other reasons (2 women). The results of a sensitivity analysis excluding these 502 women were similar to those in the overall analysis: the adjusted OR for rhinoconjunctivitis in the highest quartile of meat intake was 1.47 (95% CI: 1.01-2.15, P for trend = 0.04).
The participation rate could not be calculated because the exact number of eligible pregnant women who were provided with a set of leaflets explaining the KOMCHS, an application form, and a self-addressed and stamped return envelope by the 423 collaborating obstetric hospitals was not available. We were not able to analyze the differences between participants and non-participants, because information on personal characteristics such as age, socioeconomic status, and history of allergic disorders was not available for non-participants. It is likely, however, that our subjects were not a representative sample of Japanese women in the general population. In fact, educational levels in the present study population were higher than in the general population. According to the 2000 population census of Japan, the proportions of women aged 30 to 34 years in Fukuoka Prefecture with < 13, 13-14, ≥ 15, and an unknown number of years of education were 52.0%, 31.5%, 11.8%, and 4.8%, respectively [42]. The corresponding figures for the current study were 24.5%, 33.1%, 42.4%, and 0.0%, respectively. The present population might therefore have had greater awareness of health topics than did the general population.
The cross-sectional nature of the study did not permit the assessment of causality because of the uncertain temporality of the association. Therefore, the findings from the present cross-sectional study do not necessarily indicate a causal relationship between meat intake and rhinoconjunctivitis.
The interface between allergy/immunology and pregnancy should be discussed, as it may have an influence on the association of interest. It has been suggested that pregnancy involves a shift to the Th2 side of the immune response [43] although Chaouat et al. have pointed out the importance of the role of natural killer cells and IL-12, IL-15, and IL-18 tripods in successful or failed pregnancies in humans beyond the Th1/Th2 paradigm [44]. The hormonal changes in pregnancy are often invoked to explain the apparent association between rhinitis symptoms and pregnancy. However, rhinitis ascribed solely to pregnancy may not be a distinct entity because most pregnant women do not have significant nasal symptoms [43].
Conclusion
The current results suggest that higher meat intake may be associated with an increased prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in young adult Japanese women. This finding warrants further epidemiological investigation of diet and allergic rhinitis, especially in prospective cohort studies.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DHQ:
-
Diet history questionnaire
- ISAAC:
-
International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood
- KOMCHS:
-
Kyushu Okinawa Maternal and Child Health Study
- OR:
-
Odds ratio.
References
Sakashita M, Hirota T, Harada M, Nakamichi R, Tsunoda T, Osawa Y, Kojima A, Okamoto M, Suzuki D, Kubo S, Imoto Y, Nakamura Y, Tamari M, Fujieda S: Prevalence of allergic rhinitis and sensitization to common aeroallergens in a Japanese population. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010, 151: 255-261. 10.1159/000242363.
Kaneko Y, Motohashi Y, Nakamura H, Endo T, Eboshida A: Increasing prevalence of Japanese cedar pollinosis: a meta-regression analysis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005, 136: 365-371. 10.1159/000084256.
Adachi H, Hino A: Trends in nutritional intake and serum cholesterol levels over 40 years in Tanushimaru, Japanese men. J Epidemiol. 2005, 15: 85-89. 10.2188/jea.15.85.
Devereux G, Seaton A: Diet as a risk factor for atopy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005, 115: 1109-1117. 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.12.1139.
von Mutius E, Weiland SK, Fritzsch C, Duhme H, Keil U: Increasing prevalence of hay fever and atopy among children in Leipzig, East Germany. Lancet. 1998, 351: 862-866. 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)10100-3.
Bolte G, Frye C, Hoelscher B, Meyer I, Wjst M, Heinrich J: Margarine consumption and allergy in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001, 163: 277-279.
Dunder T, Kuikka L, Turtinen J, Räsänen L, Uhari M: Diet, serum fatty acids, and atopic diseases in childhood. Allergy. 2001, 56: 425-428. 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2001.056005425.x.
Farchi S, Forastiere F, Agabiti N, Corbo G, Pistelli R, Fortes C, Dell'Orco V, Perucci CA: Dietary factors associated with wheezing and allergic rhinitis in children. Eur Respir J. 2003, 22: 772-780. 10.1183/09031936.03.00006703.
Nafstad P, Nystad W, Magnus P, Jaakkola JJ: Asthma and allergic rhinitis at 4 years of age in relation to fish consumption in infancy. J Asthma. 2003, 40: 343-348. 10.1081/JAS-120018633.
Kull I, Bergström A, Lilja G, Pershagen G, Wickman M: Fish consumption during the first year of life and development of allergic diseases during childhood. Allergy. 2006, 61: 1009-1015. 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01115.x.
Miyake Y, Tanaka K, Sasaki S, Arakawa M: Polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and prevalence of eczema and rhinoconjunctivitis in Japanese children: the Ryukyus Child Health Study. BMC Publ Health. 2011, 11: 358-10.1186/1471-2458-11-358.
Nwaru BI, Erkkola M, Lumia M, Kronberg-Kippilä C, Ahonen S, Kaila M, Ilonen J, Simell O, Knip M, Veijola R, Virtanen SM: Maternal intake of fatty acids during pregnancy and allergies in the offspring. Br J Nutr.
Nagel G, Nieters A, Becker N, Linseisen J: The influence of the dietary intake of fatty acids and antioxidants on hay fever in adults. Allergy. 2003, 58: 1277-1284. 10.1046/j.1398-9995.2003.00296.x.
Trak-Fellermeier MA, Brasche S, Winkler G, Koletzko B, Heinrich J: Food and fatty acid intake and atopic disease in adults. Eur Respir J. 2004, 23: 575-582. 10.1183/09031936.04.00074404.
Hoff S, Seiler H, Heinrich J, Kompauer I, Nieters A, Becker N, Nagel G, Gedrich K, Karg G, Wolfram G, Linseisen J: Allergic sensitisation and allergic rhinitis are associated with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the diet and in red blood cell membranes. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005, 59: 1071-1080. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602213.
Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Ohya Y, Miyamoto S, Matsunaga I, Yoshida T, Hirota Y, Oda H, The Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study Group: Fish and fat intake and prevalence of allergic rhinitis in Japanese females: the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. J Am Coll Nutr. 2007, 26: 279-287.
Takaoka M, Norback D: Diet among Japanese female university students and asthmatic symptoms, infections, pollen and furry pet allergy. Respir Med. 2008, 102: 1045-1054. 10.1016/j.rmed.2008.01.023.
Schnappinger M, Sausenthaler S, Linseisen J, Hauner H, Heinrich J: Fish consumption, allergic sensitisation and allergic diseases in adults. Ann Nutr Metab. 2009, 54: 67-74. 10.1159/000207357.
Sasaki S, Yanagibori R, Amano K: Self-administered diet history questionnaire developed for health education: a relative validation of the test-version by comparison with 3-day diet record in women. J Epidemiol. 1998, 8: 203-215. 10.2188/jea.8.203.
Sasaki S, Ushio F, Amano K, Morihara M, Todoriki T, Uehara Y, Toyooka T: Serum biomarker-based validation of a self-administered diet history questionnaire for Japanese subjects. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. 2000, 46: 285-296. 10.3177/jnsv.46.285.
Science and Technology Agency: Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan, Fifth Revised and Enlarged Edition. 2005, Tokyo: Printing Bureau of the Ministry of Finance, (in Japanese)
Willett W, Stampfer MJ: Total energy intake: implications for epidemiologic analyses. Am J Epidemiol. 1986, 124: 17-27.
Strachan D, Sibbald B, Weiland S, Aït-Khaled N, Anabwani G, Anderson HR, Asher MI, Beasley R, Björkstén B, Burr M, Clayton T, Crane J, Ellwood P, Keil U, Lai C, Mallol J, Martinez F, Mitchell E, Montefort S, Pearce N, Robertson C, Shah J, Stewart A, von Mutius E, Williams H: Worldwide variations in prevalence of symptoms of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis in children: the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1997, 8: 161-176. 10.1111/j.1399-3038.1997.tb00156.x.
Ian Givens D, Gibbs RA: Current intakes of EPA and DHA in European populations and the potential of animal-derived foods to increase them. Proc Nutr Soc. 2008, 67: 273-280. 10.1017/S0029665108007167.
Schoeman K, Tanaka T, Bend JR, Koren G: Hair mercury levels of women of reproductive age in Ontario, Canada: implications to fetal safety and fish consumption. J Pediatr. 2010, 157: 127-131. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.01.020.
Saito K, Yokoyama T, Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Ohya Y, Hirota Y: Maternal meat and fat consumption during pregnancy and suspected atopic eczema in Japanese infants aged 3-4 months: the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21: 38-46. 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2009.00897.x.
Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Ohfuji S, Hirota Y: Maternal fat consumption during pregnancy and risk of wheeze and eczema in Japanese infants aged 16-24 months: the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Thorax. 2009, 64: 815-821. 10.1136/thx.2009.115931.
Miyamoto S, Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Ohya Y, Matsunaga I, Yoshida T, Oda H, Ishiko O, Hirota Y, The Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study Group: Fat and fish intake and asthma in Japanese women: baseline data from the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007, 11: 103-109.
Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Ohya Y, Matsunaga I, Yoshida T, Hirota Y, Oda H: Relationship between dietary fat and fish intake and the prevalence of atopic eczema in pregnant Japanese females: baseline data from the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2008, 17: 612-619.
Wickens K, Barry D, Friezema A, Rhodius R, Bone N, Purdie G, Crane J: Fast foods-are they a risk factor for asthma?. Allergy. 2005, 60: 1537-1541. 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00945.x.
Kim JL, Elfman L, Mi Y, Johansson M, Smedje G, Norbäck D: Current asthma and respiratory symptoms among pupils in relation to dietary factors and allergens in the school environment. Indoor Air. 2005, 15: 170-182. 10.1111/j.1600-0668.2005.00334.x.
Hong SJ, Lee MS, Lee SY, Ahn KM, Oh JW, Kim KE, Lee JS, Lee HB, the Korean ISAAC Study Group, Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease, Seoul, Korea: High body mass index and dietary pattern are associated with childhood asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006, 41: 1118-1124. 10.1002/ppul.20372.
Tsai HJ, Tsai AC: The association of diet with respiratory symptoms and asthma in schoolchildren in Taipei, Taiwan. J Asthma. 2007, 44: 599-603. 10.1080/02770900701539509.
Chatzi L, Torrent M, Romieu I, Garcia-Esteban R, Ferrer C, Vioque J, Kogevinas M, Sunyer J: Mediterranean diet in pregnancy is protective for wheeze and atopy in childhood. Thorax. 2008, 63: 507-513. 10.1136/thx.2007.081745.
Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Perea JM, Jiménez AI, Rodríguez-Rodríguez P, López-Sobaler AM, Ortega RM: Fat intake and asthma in Spanish schoolchildren. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010, 64: 1065-1071. 10.1038/ejcn.2010.127.
Nagel G, Weinmayr G, Kleiner A, Garcia-Marcos L, Strachan DP, ISAAC Phase Two Study Group: Effect of diet on asthma and allergic sensitisation in the International Study on Allergies and Asthma in Childhood (ISAAC) Phase Two. Thorax. 2010, 65: 516-522. 10.1136/thx.2009.128256.
Nagel G, Linseisen J: Dietary intake of fatty acids, antioxidants and selected food groups and asthma in adults. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005, 59: 8-15. 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602025.
Woods RK, Walters EH, Raven JM, Wolfe R, Ireland PD, Thien FC, Abramson MJ: Food and nutrient intakes and asthma risk in young adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003, 78: 414-421.
Sinha R, Norat T: Meat cooking and cancer risk. IARC Sci Publ. 2002, 156: 181-186.
Hughes R, Cross AJ, Pollock JR, Bingham S: Dose-dependent effect of dietary meat on endogenous colonic N-nitrosation. Carcinogenesis. 2001, 22: 199-202. 10.1093/carcin/22.1.199.
Mirvish SS, Haorah J, Zhou L, Clapper ML, Harrison KL, Povey AC: Total N-nitroso compounds and their precursors in hot dogs and in the gastrointestinal tract and feces of rats and mice: possible etiologic agents for colon cancer. J Nutr. 2002, 132 (Suppl): 3526S-3529S.
Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications: 2000 Population Census of Japan, Vol. 3-2-40, Labour Force Status of Population, Industry (Major Groups) of Employed Persons, and Education: Fukuoka-ken. 2002, Tokyo: Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications, in Japanese
Palmer GW, Claman HN: Pregnancy and immunology: selected aspects. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002, 89: 350-359. 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62034-0.
Chaouat G, Ledée-Bataille N, Dubanchet S, Zourbas S, Sandra O, Martal J: TH1/TH2 paradigm in pregnancy: paradigm lost? Cytokines in pregnancy/early abortion: reexamining the TH1/TH2 paradigm. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2004, 134: 93-119. 10.1159/000074300.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Kyushu Branch of the Japan Allergy Foundation, the Fukuoka Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Okinawa Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Miyazaki Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Oita Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Kumamoto Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Nagasaki Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Kagoshima Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Saga Association of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, the Fukuoka Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the Okinawa Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the Fukuoka City Government, and the Fukuoka City Medical Association for their valuable support.
This study was supported by KAKENHI (19590606, 20791654, 21590673, and 22592355), by Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants, Research on Allergic Disease and Immunology from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Japan, by Meiji Co. Ltd., and by the Food Science Institute Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
YM, KT, and MA contributed to the study concept and design and the acquisition of data. HO and SS were responsible for the estimation of dietary factors. YM was responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data and the drafting of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Miyake, Y., Tanaka, K., Okubo, H. et al. Dietary meat and fat intake and prevalence of rhinoconjunctivitis in pregnant Japanese women: baseline data from the Kyushu Okinawa Maternal and Child Health Study. Nutr J 11, 19 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-11-19
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-11-19