Abstract
Background
The search for natural products as potential cytotoxic agents has yielded promising candidates. However multidrug resistance (MDR) is still a major hurdle for patients receiving chemotherapy. In the present study, we evaluated the cytotoxicity of the methanol extracts of four dietary Aframomum plant species (A. arundinaceum, A. alboviolaceum, A. kayserianum and A. polyanthum) against nine sensitive and MDR cancer cell lines. We have also identified the bioactive constituents of A. arundinaceum.
Methods
The cytotoxicity of the methanol extracts of the above plants was determined using a resazurin reduction assay. Chromatographic techniques were used to isolate the constituents of A. arundinaceum.
Results
A preliminary experiment on leukemia CCRF-CEM cells at 40 μg/mL showed that the extracts from A. kayserianum and A. alboviolaceum as well as the isolated compounds namely compounds aframodial (1), 8(17),12-labdadien-15,16-dial (2), galanolactone (3), 1-p-menthene-3,6-diol (6) and 1,4-dimethoxybenzene (7) were less active, inducing more than 50% growth of this cell line contrary to A. polyanthum and A. arundinaceum extracts, galanals A (4) and B (5), naringenin (8) and kaempferol-3,7,4’-trimethylether (9). The IC50 values below or around 30 μg/mL were recorded with A. arundinaceum extract against eight of the nine tested cancer cell lines. This extract as well as compound 8 displayed IC50 values below 40 μg/mL towards the nine tested cancer cell lines whilst A. polyanthum extract, compounds 4, 5 and 9 showed selective activities. Collateral sensitivity (hypersensitivity) was observed with A. arundinaceum extract towards leukemia CEM/ADR5000 cells and glioblastoma U87MG.ΔEGFR compared to their respective sensitive counterparts CEM/CEM and U87MG.
Conclusion
The results of this study provide evidence of the cytotoxicity selected Aframomum species as well as a baseline information for the potential use of Aframomum arundinaceum in the fight against drug sensitive and otherwise drug-resistant cancers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Chemotherapy remains the major treatment of cancers but often fails due to cells multidrug resistance (MDR) [1, 2]. MDR is displayed by many cancer cells to withstand increasingly higher doses of antineoplastic compounds [3]. Investigation for naturally occurring molecules as potential cytotoxic drugs has yielded promising candidates [3–7]. However, MDR is still considered a major hurdle for patients receiving chemotherapy [8, 9]. Various Cameroonian dietary plants including those from the family Zinziberaceae are used in traditional medicine to manage various ailments [5, 10–13]. The genus Aframomum, belonging to the Zingiberaceae family have 40 species and is most common in tropical and subtropical regions [14]. Twenty species are found in Cameroon, where they are widely used as spices and in traditional medicine [14]. The Seeds of Aframomum arundinaceum K. Schum are used as laxative and as anti-helmintic. The fresh juice of the rhizomes is used against body odor. The rhizomes are used against toothache and the crushed seeds against fungal infections [10]. The decoction of the leaves Aframomum melegueta K. Schum together with the leaves of Momordica charantia and Sorghum arundinaceum cereal in local dry gin (alcohol) is recommended to be taken one dose daily against cholera [15]. Several Aframomum species such as Aframomum angustifolium, A. danielli, A. sanguineum, and A. sulcatum are also traditionally used to treat fevers in Africa [16], and recently, the antiplasmodial activity of some labdanes from A. sceptrum and A. latifolium was demonstrated [17]. The antibacterial activities of Aframomum kayserianum[12] and Aframomum polyanthum[13] were also reported on Gram-negative multidrug-resistant phenotypes. The cytotoxicity of other Afromomum species such as A. citratum and A. melegueta towards leukemia CCRF-CEM and ADR5000 cell lines was also reported [5]. The present study was designed to investigate the cytotoxicity of four dietary Aframomum species commonly used as spices in Cameroon, Aframomum alboviolaceum (Ridl.) K. Schum, A. arundinaceum (Oliver & Hanbury) K. Schum, Aframomum kayserianum K. Schum and Aframomum polyanthum K. Schum towards sensitive and multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cell lines. The study was extended to the identification of the bioactive constituents of A. arundinaceum.
Methods
Plant material and extraction
The tested Aframomum species, A. alboviolaceum, A. kayserianum and A. polyanthum were purchased from Bafoussam local market (West region of Cameroon) in January 2012. Aframomum arundinaceum was collected in Yaoundé (Centre region) in March 2012. The plants were further identified at the National Herbarium (Yaoundé, Cameroon) where voucher specimens were deposited under the reference numbers 11704/SFR/CAM (A. arundinaceum), 34888/HNC (A. alboviolaceum), 18884/SRFC (A. kayserianum) and 3981/SRFK (A. polyanthum). The air dried fruits of A. kayserianum, A. polyanthum (100 g) and A. arundinaceum (3000 g) as well as the roots of A. alboviolaceum (100 g) were powdered and macerated with methanol for 48 h at room temperature. The methanol extract was concentrated in vacuo to give 18.7 g, 21.2 g, 25.3 and 100 g of the crude extracts of A. kayserianum, A. polyanthum, A. alboviolaceum and A. arundinaceum respectively. The extracts were then conserved at 4°C until further use.
Isolation of compounds from Aframomum arundinaceum
Crude extract of A. arundinaceum (100 g) was successively extracted with petroleum ether, chloroform and methanol at room temperature. The petroleum ether fraction (25 g) was column chromatographed on 100 g of silica gel (Merck, 0.040-0.063 mm) using hexane and hexane-choloroform mixture with increasing polarity. Fractions of 300 mL were collected, concentrated, and pooled on the basis of their thin layer chromatography (TLC) profile. The obtained fractions (frs) directly afforded a yellow oil (1; frs 4 to 9; 30 mg) and amorphous powders 2 ( frs 13 to 16; 25 mg), 3 (frs 20 to 27; 40 mg), 4 (frs 30 to 33) and 5 (frs 36 to 38; 10 mg). The chloroform extract (20 g) was also column chromatographed on 250 g of silica gel (Merck, 0.040-0.063 mm) using hexane (Hex) and mixture of hexane-chloroform (Hex-CHCl3). Fractions of 400 mL were collected, concentrated and pooled after TLC analysis to give five sub-fractions (sub-frs A-E).
Sub-fraction B (Hex-CHCl3; 10 to 25; 6 g) was subjected to column chromatography (CC) to afford a white crystal (6; 20 mg). Sub-fraction C (8.0 g) obtained with Hexane-CHCl3 4:6 was subjected to CC (silica gel 60, 50 g) and eluted with Hex-CHCl3 mixtures of increasing polarity to give 6 new sub-fractions (C1-C6). Sub-fraction C4 obtained with Hex-CHCl3 6:4. afforded a yellow oil (7; 10 mg). Sub-fraction C5 (Hex-CHCl3 4:6) and C6 (Hex-CHCl3 8:2) were repeatedly filtered through Sephadex LH-20 (CHCl3-MeOH 7:3) to give yellow powders, 8 (sub-frs 3 to 6; 10.0 mg) and 9 (sub-frs 15 to 19; 15 mg).
General procedure
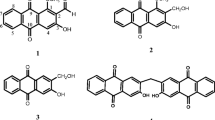
Aluminum sheet pre-coated with silica gel 60 F 254 nm (Merck) was used for thin layer chromatography; the spots were visualized using both ultraviolet light (254 and 366 nm) and 50% H2SO4 spray reagent. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 300 (Billerica, MA, USA) at 300 MHz (1H) and 75 MHz (13C), with the residual solvent peaks as internal references. Mass spectra were recorded with API QSTAR pulsar mass (Milford, MA, USA). Melting points (m.p) were recorded using a Stuart Scientific (Redhill, Surrey, UK) melting point apparatus (SMP1) and are uncorrected. The chemical structures of the compounds were confirmed by comparing with reference data from available literature (Figure 1).
Chemicals
Doxorubicin 98.0% were provided by the University Pharmacy of the Johannes Gutenberg University (Mainz, Germany) and dissolved in PBS (Invitrogen, Eggenstein, Germany) at a concentration of 10 mM. Geneticin >98% (72.18 mM; Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany).
Cell cultures
The cell lines used the present work, their origins and their treatments were previously reported [18, 19]. They include drug-sensitive CCRF-CEM and multidrug-resistant P-glycoprotein over-expressing CEM/ADR5000 leukemia cells [20–22], the MDA-MB-231-pcDNA3 breast cancer cells and its resistant subline MDA-MB-231-BCRP clone 23) [23], the HCT116 (p53 +/+) colon cancer cells and its knockout clones HCT116 (p53 -/-), the U87MG glioblastoma cells and its resistant subline U87MG.ΔEGFR, HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cells and AML12 normal hepatocytes [6, 19, 24]. The CCRF-CEM and CEM/ADR5000 leukemia cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. Sensitive and resistant cells were kindly provided by Dr. Axel Sauerbrey (Department of Pediatrics, University of Jena, Jena, Germany). The generation of the resistant subline was previously described [6, 19, 24]. Breast cancer cells, transduced with control vector (MDA-MB-231-pcDNA3) or with cDNA for the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (MDA-MB-231-BCRP clone 23), were maintained under standard conditions as described above for CCRF-CEM cells. Human wild-type HCT116 (p53 +/+) colon cancer cells as well as knockout clones HCT116 (p53 -/-) derived by homologous recombination were a generous gift from Dr. B. Vogelstein and H. Hermeking (Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Baltimore, MD). Human glioblastoma multiforme U87MG cells (non-transduced) and U87MG cell line transduced with an expression vector harboring an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene with a genomic deletion of exons 2 through 7 (U87MG.ΔEGFR) were kindly provided by Dr. W. K. Cavenee (Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, San Diego, CA). MDA-MB-231-BCRP, U87MG.ΔEGFR and HCT116 (p53 -/- ) were maintained in DMEM medium containing 10% FBS (Invitrogen) and 1% penicillin (100 U/mL)-streptomycin (100 μg/mL) (Invitrogen) and were continuously treated with 800 ng/mL and 400 μg/mL geneticin, respectively. Human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells and normal AML12 heptocytes were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, USA). The above medium without geneticin was used to maintain MDA-MB-231, U87MG, HCT116 (p53 +/+), HepG2 and AML12 cell lines. The cells were passaged twice weekly. All experiments were performed with cells in the logarithmic growth phase.
Resazurin reduction assay
The cytotoxicity of the studied samples was performed by resazurin reduction assay as we previously described [6, 18, 19, 24–26]. Briefly, adherent cells at 1x104 cells were allowed to attach overnight and then treated with different studied samples. Samples were preliminary tested at 40 μg/mL (extract and isolated compounds) and doxorubicin (20 μg/mL) against the sensitive leukemia CCRF-CEM cell line and those inducing less than 50% growth proliferation were further tested for IC50 determinations towards all the studied cell lines. For suspension cells, aliquots of 2 × 104 cells per well were seeded in 96-well-plates in a final volume of 200 μL. Extracts and compounds were prior diluted in DMSO and tested in a final concentration below 0.1% (A final concentration of 0.1% DMSO was used as negative control and did not show any effect on cell growth). The tested concentrations ranges were 0.16 μg/mL to 40 μg/mL for crude extracts and isolated compounds and 0.08 μg/mL to 20 μg/mL for doxorubicin. After 72 h incubation and a resazurin (Sigma-Aldrich, Schnelldorf, Germany) staining, fluorescence was measured on an Infinite M2000 Pro™ plate reader (Tecan, Crailsheim, Germany) using an excitation wavelength of 544 nm and an emission wavelength of 590 nm. Each assay was done at least two times, with six replicates each. IC50 values represent the sample’s concentrations required to inhibit 50% of cell proliferation and were calculated from a calibration curve by linear regression using Microsoft Excel [5, 6].
Results and discussion
The structures of the compounds isolated from Aframomum arundinaceum were established using spectroscopic analysis, especially, NMR spectra in conjunction with 2D experiments, COSY, HMQC, HMBC, and direct comparison with published information and with authentic specimens obtained in our research group for some cases. The compounds isolated from the fruits of A. arundinaceum (Figure 1) were identified as Aframodial C20H30O3 (1; m/z 318.2) [27], 8(17),12-labdadien-15,16-dial C20H30O2 (2; m/z 302.2) [17], galanolactone C20H30O3 (3; m/z 318.2) [27], galanal A C20H30O3 (4; 15 mg, m/z 318.2) [28], and galanal B C20H30O3 (5; m/z 318.2) [29], 1-p-menthene-3,6-diol C10H18O2 (6; m/z 170.1; m.p:165-167°C) [30], 1,4-dihydroxybenzene C6H6O2 (7; m/z 110.0) [31], naringenin C15H12O5 (8; m/z 272.0; 245-248°C) [32] and kaempferol-3,7,4’-trimethylether C18H16O6 (9; m/z 328.0; 157-158°C) [33]. The cytotoxicity of compounds 1-9 as well as the crude extracts was determined towards drug sensitive and resistant cancer cell lines.
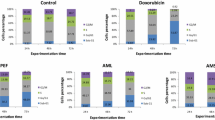
In a preliminary investigation of the four studied Aframomum species and compounds isolated from A. arundinaceum, we tested a single concentration of 40 μg/mL for each sample and 20 μg/mL for doxorubicin against the sensitive CCRF-CEM leukemia cell line (Figure 2). The extracts from A. kayserianum and A. alboviolaceum were less active and induced respectively 50.33% and 54.36% growth proliferation of CCRF-CEM cells. Compounds 1, 2, 3, 6 and 7 also induced more than 50% growth of this cell line. The extracts from A. polyanthum (36.28%) and A. arundinaceum (24.68%) as well as compounds 4 (47.78%), 5 (49.81%), 8 (38.49%) and 9 (39.58%) displayed less than 50% growth proliferation of CCRF-CEM cells. The IC50 values of the above samples were further determined on nine cancer cell lines, including both sensitive and MDR phenotypes (Table 1). Aframomum. arundinaceum extract as well as compound 8 and doxorubucin induced less than 50% proliferation of all tested cancer cell lines, with IC50 values below 40 μg/mL. A. polyanthum extract, compounds 9, 4 and 5 showed selective activities, the IC50 values <40 μg/mL being obtained on 5/9, 4/9, 2/9 and 1/9 tested cell lines respectively (Table 1). According to the National Cancer Institute (USA), 30 μg/mL is the upper IC50 limit considered promising for purification of a crude extract [34]. We therefore, tested a slightly higher concentration of 40 μg/mL in our preliminary assay. Also, the IC50 threshold value of 4 μg/ml or 10 μM [35, 36] after 48 and 72 h incubations has been set to identify good cytotoxic compounds. Considering these thresholds, the IC50 values below or around 30 μg/mL were recorded with A. arundinaceum extract against eight of the nine tested cancer cell lines (Table 1) explaining why it was considered further for purification. Nonetheless, the extract from A. polyanthum also showed activities with IC50 values <30 μg/mL on four of the nine tested cancer cell lines. Though Compound 8 was active on all the tested cancer cell lines, no IC50 below 4 μg/ml was recorded, the lowest values being 7.86 μg/mL against CEM/ADR5000 cells. Interestingly, none of the selected extracts and compounds was more toxic towards AML12 normal hepatocytes (IC50 > 40 Mg/mL) than cancer cell lines, suggesting their good selectivity. Importantly, collateral sensitivity (hypersensitivity) was also observed with A. arundinaceum extract towards CEM/ADR5000 cells (degree of resistance of 0.76) and U87MG.ΔEGFR (degree of resistance of 0.95) compared to their respective sensitive counterparts CEM/CEM and U87MG. This extract was also more active against hepatocarcinoma HepG2 as compared to AML12 normal hepatocytes, confirming its selectivity to cancer cells (Table 1). Despite the fact that compound 8 showed moderate activities, it also displayed better collateral sensitivity of MDR cell lines compared to doxorubicin. The use of natural products to fight multidrug resistance is an attractive strategy in chemotherapy [37–39]. P-gp-expressing CEM/ADR5000 as well as p53 knock out HCT116 (p53 -/-) and BCRP- expressing U87MG.ΔEGFR cells were less cross-resistant towards the best samples namely A. arundinaceum and compound 8 than towards the positive drug, doxorubicin, highlighting their possible therapeutic potential in the fight against multidrug resistance. This report also highlights the importance of the plants of the genus Aframomum as potential source of cytotoxic compounds. The results obtained collaborate with previous investigations. In effect, Aframomum melegueta previously inhibited the proliferation of the leukemia ADR5000 cell lines with a reported IC50 value of 7.80 μg/mL [5]. Also, naringenin (8) has shown cytotoxicity in various human cancer cell lines and induced apoptosis via a transient induction of caspase-3/CPP32 activity, in the human promyeloleukemia cell line HL-60 [40–42]. The moderate cytotoxicity of galanals A (4; IC50 of 18 μM or 5.62 μg/mL) and B (5; IC50 of 32 μM or 12.21 μg/mL) towards human T lymphoma Jurkat cells was also reported [29].
Growth percentage (%) of leukemia CCRF-CEM cancer cell line treated with plant extracts and isolated compounds at 40 μg/mL and doxorubicin (20 μg/mL). 1: aframodial; 2: 8(17),12-labdadien-15,16-dial; 3: galanolactone; 4: galanal A; 5: galanal B; 6: 1-p-menthene-3,6-diol; 7: 1,4-dihydroxybenzene; 8: naringenin; 9: kaempferol-3,7,4’-trimethylether.
Conclusions
Finally, this work provides further evidence of the cytotoxic potential of Aframomum species and highlights the good activity of Aframomum arundinaceum on sensitive and drug-resistant cancer cell lines. Bioactive constituents of this plant include galanals A and B, naringenin and kaempferol-3,7,4’-trimethylether. Aframomum arundinaceum could be explored in more detail in the future to develop novel anticancer drugs against sensitive and resistant phenotypes.
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA-Cancer J Clin. 2011, 61 (2): 69-90. 10.3322/caac.20107.
Chen Z, Zhang L, Xia L, Jin Y, Wu Q, Guo H, Shang X, Dou J, Wu K, Nie Y, Fan D: Genomic analysis of drug resistant gastric cancer cell lines by combining mRNA and microRNA expression profiling. Cancer Lett. 2014, 350 (1–2): 43-51.
Marchini S, Marrazzo E, Bonomi R, Chiorino G, Zaffaroni M, Weissbach L, Hornicek FJ, Broggini M, Faircloth GT, D’Incalci M: Molecular characterisation of two human cancer cell lines selected in vitro for their chemotherapeutic drug resistance to ET-743. Eur J Cancer. 2005, 41 (2): 323-333. 10.1016/j.ejca.2004.10.021.
Kuete V, Mbaveng AT, Tsaffack M, Beng VP, Etoa FX, Nkengfack AE, Meyer JJ, Lall N: Antitumor, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Bersama engleriana (Melianthaceae). J Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115 (3): 494-501. 10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.027.
Kuete V, Krusche B, Youns M, Voukeng I, Fankam AG, Tankeo S, Lacmata S, Efferth T: Cytotoxicity of some Cameroonian spices and selected medicinal plant extracts. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134 (3): 803-812. 10.1016/j.jep.2011.01.035.
Kuete V, Sandjo L, Nantchouang Ouete J, Fouotsa H, Wiench B, Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of three naturally occuring xanthones (8-hydroxycudraxanthone G, morusignin I and cudraxanthone I) against sensitive and multidrug-resistant cancer cell lines. Phytomedicine. 2013, 21 (3): 315-322.
Kuete V, Sandjo LP, Kwamou GM, Wiench B, Nkengfack AE, Efferth T: Activity of three cytotoxic isoflavonoids from Erythrina excelsa and Erythrina senegalensis (neobavaisoflavone, sigmoidin H and isoneorautenol) toward multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2014, 21 (5): 682-688. 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.10.017.
Goldstein LJ, Galski H, Fojo A, Willingham M, Lai S-L, Gazdar A, Pirker R, Green A, Crist W, Brodeur GM, Lieber M, Cossman J, Gottesman MM, Pastan I: Expression of multidrug resistance gene in human cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989, 81 (2): 116-124. 10.1093/jnci/81.2.116.
Kuwazuru Y, Yoshimura A, Hanada S, Ichikawa M, Saito T, Uozumi K, Utsunomiya A, Arima T, Akiyama S-I: Expression of the multidrug transporter, P-glycoprotein, in chronic myelogenous leukaemia cells in blast crisis. Brit J Haematol. 1990, 74 (1): 24-29. 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02533.x.
Tane P, Tatsimo S, Ayimele G, Connolly J: Bioactive metabolites from Aframomum species. 11th NAPRECA Symposium Book of Proceedings. 2005, Antananarivo, Madagascar: NAPRECA, 214-223.
Dzoyem JP, Guru SK, Pieme CA, Kuete V, Sharma A, Khan IA, Saxena AK, Vishwakarma RA: Cytotoxic and antimicrobial activity of selected Cameroonian edible plants. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013, 13: 78-10.1186/1472-6882-13-78.
Djeussi DE, Noumedem JA, Seukep JA, Fankam AG, Voukeng IK, Tankeo SB, Nkuete AH, Kuete V: Antibacterial activities of selected edible plants extracts against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013, 13 (1): 164-10.1186/1472-6882-13-164.
Seukep JA, Fankam AG, Djeussi DE, Voukeng IK, Tankeo SB, Noumdem JA, Kuete AH, Kuete V: Antibacterial activities of the methanol extracts of seven Cameroonian dietary plants against bacteria expressing MDR phenotypes. Springerplus. 2013, 2: 363-10.1186/2193-1801-2-363.
Thomas D, Thomas J, Bromley W, Mbenkum F: Korup ethnobotany survey, final report to: The World Wide Fund for Nature. 1989, Weyside Park, Godalming, Surrey, UK: Penda House
Ndukwu B, Ben-Nwadibia N: Ethnomedicinal aspects of plants used as spices and condiments in the Niger delta area of Nigeria. 2010, Port Harcourt, Nigeria: University of Port Harcourt PMB
Iwu M: Handbook of African Medicinal Plants. 1993, Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press
Duker-Eshun G, Jaroszewski JW, Asomaning WA, Oppong-Boachie F, Olsen CE, Christensen SB: Antiplasmodial activity of labdanes from Aframomum latifolium and Aframomum sceptrum. Planta Med. 2002, 68 (7): 642-644. 10.1055/s-2002-32888.
O’Brien J, Wilson I, Orton T, Pognan F: Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur J Biochem. 2000, 267 (17): 5421-5426. 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01606.x.
Kuete V, Tchakam PD, Wiench B, Ngameni B, Wabo HK, Tala MF, Moungang ML, Ngadjui BT, Murayama T, Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of four naturally occuring benzophenones: 2,2′,5,6′-tetrahydroxybenzophenone, guttiferone E, isogarcinol and isoxanthochymol. Phytomedicine. 2013, 20 (6): 528-536. 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.02.003.
Kimmig A, Gekeler V, Neumann M, Frese G, Handgretinger R, Kardos G, Diddens H, Niethammer D: Susceptibility of multidrug-resistant human leukemia cell lines to human interleukin 2-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1990, 50 (21): 6793-6799.
Efferth T, Sauerbrey A, Olbrich A, Gebhart E, Rauch P, Weber HO, Hengstler JG, Halatsch ME, Volm M, Tew KD, Ross DD, Funk JO: Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 2003, 64 (2): 382-394. 10.1124/mol.64.2.382.
Gillet J, Efferth T, Steinbach D, Hamels J, de Longueville F, Bertholet V, Remacle J: Microarray-based detection of multidrug resistance in human tumor cells by expression profiling of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes. Cancer Res. 2004, 64 (24): 8987-8993. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1978.
Doyle LA, Yang W, Abruzzo LV, Krogmann T, Gao Y, Rishi AK, Ross DD: A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998, 95 (26): 15665-15670. 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15665.
Kuete V, Sandjo L, Wiench B, Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of four Cameroonian dietary spices ethno-medically used to treat Cancers: Echinops giganteus, Xylopia aethiopica, Imperata cylindrica and Piper capense. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149 (1): 245-253. 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.029.
Kuete V, Fankam AG, Wiench B, Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of the methanol extracts of six Cameroonian medicinal plants against multidrug-resistant tumor cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013, 2013: 285903-
Kuete V, Tankeo SB, Saeed ME, Wiench B, Tane P, Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of five Cameroonian medicinal plants against multi-factorial drug resistance of tumor cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153 (1): 207-219. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.025.
Kamdem Wabo H, Tane P, Connolly J: Diterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids from Aframomum arundinaceum. Biochem Syst Ecol. 2006, 34: 603-605. 10.1016/j.bse.2006.02.001.
Morita H, Itokawa H: Cytotoxic and antifungal diterpenes from the seeds of Alpinia galanga. Planta Med. 1988, 54 (2): 117-120. 10.1055/s-2006-962365.
Miyoshi N, Nakamura Y, Ueda Y, Abe M, Ozawa Y, Uchida K, Osawa T: Dietary ginger constituents, galanals A and B, are potent apoptosis inducers in Human T lymphoma Jurkat cells. Cancer Lett. 2003, 199 (2): 113-119. 10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00381-1.
Bousetla A, Konuklugil B, Bouacida S, Zellagui A, Rhouati S, Akkal S: Phytochemical study of Algerian Foeniculum vulgare Mill (Apiaceae). Der Pharmacia Lettre. 2013, 5 (6): 9-11.
Rogerson FSS, Azevedo Z, Fortunato N, de Freitas VAP: 1,3-Dimethoxybenzene, a newly identified component of port wine. J Sci Food Agric. 2002, 82 (11): 1287-1292. 10.1002/jsfa.1182.
Nilupa R, Lalith J, Noriyuki H, Yoshinori F: Chemical constituents of the fruits of Artocarpus altilis. Biochem Syst Ecol. 2007, 36: 323-325.
Pizzolatti M, Verdi L, Brighente I, Neiva T, Schripsema J, Braz Filho R: Anticoagulant effect and constituents of Baccharis illinita. Nat Prod Commun. 2006, 1 (1): 37-42.
Suffness M, Pezzuto J: Assays related to cancer drug discovery. 1990, London: Academic Press
Boik J: Natural compounds in cancer therapy. 2001, Minnesota USA: Oregon Medical Press
Brahemi G, Kona FR, Fiasella A, Buac D, Soukupova J, Brancale A, Burger AM, Westwell AD: Exploring the structural requirements for inhibition of the ubiquitin E3 ligase breast cancer associated protein 2 (BCA2) as a treatment for breast cancer. J Med Chem. 2010, 53 (7): 2757-2765. 10.1021/jm901757t.
Efferth T: The human ATP-binding cassette transporter genes: from the bench to the bedside. Curr Mol Med. 2001, 1 (1): 45-65. 10.2174/1566524013364194.
Gottesman MM, Ling V: The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: the early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580 (4): 998-1009. 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.12.060.
Gillet JP, Efferth T, Remacle J: Chemotherapy-induced resistance by ATP-binding cassette transporter genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007, 1775 (2): 237-262.
Chen YC, Shen SC, Lin HY: Rutinoside at C7 attenuates the apoptosis-inducing activity of flavonoids. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003, 66 (7): 1139-1150. 10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00455-6.
Kanno S, Shouji A, Asou K, Ishikawa M: Effects of naringin on hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in P388 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003, 92 (2): 166-170. 10.1254/jphs.92.166.
Wang BD, Yang ZY, Wang Q, Cai TK, Crewdson P: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxic activities, and DNA-binding properties of the La(III) complex with Naringenin Schiff-base. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006, 14 (6): 1880-1888. 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.10.031.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/340/prepub
Acknowledgements
VK is very grateful to the Alexander von Humboldt foundation for an 18 months’ fellowship in Germany through the “Georg Foster Research Fellowship for Experienced Researcher” program; PYA is grateful to the Network of Analytical and Bioassay Services in Africa (NABSA) for a 2-months maintenance grant to the University of Botswana.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
VK, PYA and ATM carried out the study; PYA, ATM, SOY, RM, GDWF and BTN contributed to plant’s collection, compound’s isolation and/or identification. VK and TE designed the experiments. VK wrote the manuscript; TE supervised the work, provided the facilities for the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Kuete, V., Ango, P.Y., Yeboah, S.O. et al. Cytotoxicity of four Aframomum species (A. arundinaceum, A. alboviolaceum, A. kayserianum and A. polyanthum) towards multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cell lines. BMC Complement Altern Med 14, 340 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-340
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-340