Abstract
Background
A wide range of outcomes have been assessed in trials of interventions for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), however there appears to be little consensus on what constitutes the most relevant outcomes. The purpose of this systematic review was to identify the outcomes assessed in randomized clinical trials of surgical interventions for CTS and to compare these to the concepts contained in the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF).
Methods
The bibliographic databases Medline, AMED and CINAHL were searched for randomized controlled trials of surgical treatment for CTS. The outcomes assessed in these trials were identified, classified and linked to the different domains of the ICF.
Results
Twenty-eight studies were retrieved which met the inclusion criteria. The most frequently assessed outcomes were self-reported symptom resolution, grip or pinch strength and return to work. The majority of outcome measures employed assessed impairment of body function and body structure and a small number of studies used measures of activity and participation.
Conclusion
The ICF provides a useful framework for identifying the concepts contained in outcome measures employed to date in trials of surgical intervention for CTS and may help in the selection of the most appropriate domains to be assessed, especially where studies are designed to capture the impact of the intervention at individual and societal level. Comparison of results from different studies and meta-analysis would be facilitated through the use of a core set of standardised outcome measures which cross all domains of the ICF. Further work on developing consensus on such a core set is needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common peripheral entrapment neuropathy and a frequent cause of disability in the upper extremity[1]. Surgical release or decompression rates in the USA amount to 400,000 to 500,000 per year [2] and 43 to 74 per 100,000 in the UK[3]. Conservative treatment of CTS also accounts for a large proportion of resources and includes splinting, nerve gliding, ultrasound and carpal bone mobilisation[2]. Whilst the reported success rates of carpal tunnel release range from 70 to 90 percent there is little agreement on how results should be evaluated[4].
The evidence from trials evaluating the outcomes from surgical and non-surgical interventions is extensive[2, 5], however the pooling of results as required for meta-analysis has been impeded by the wide range of outcome measures used. Outcomes from carpal tunnel release have been assessed in many different ways including objective nerve conduction studies, clinical measures of sensibility, muscle function and dexterity, patient-reported symptoms and perceived function and the impact on daily activity, work and leisure. It has also been noted, that there is a lack of consensus among clinicians over what constitutes the most reliable, valid and responsive instruments to evaluate outcomes in carpal tunnel syndrome[4, 6].
Outcome measures should not only capture the impact of the disorder on body structure (impairments) but also on activities and participation as defined in the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF)[7]. The ICF is part of the family of International Classifications developed by the World Health Organisation[7]. It provides a framework which uses unifying terminology for the classification of diseases and their effect on body structure and functioning, activities and participation. The ICF complements existing classifications systems such as the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and related health problems – ICD-10. The ICF is particularly useful to understand and measure health outcomes which look beyond mortality and morbidity [7] as it reflects a biopsychosocial perspective describing the impact of disease from an individual and societal perspective. Its applications in health are manifold, including outcome evaluation and work is underway linking the measurement of health status in different patient populations with the ICF[8].
Given the wide range of outcomes that have been employed in trials of surgical interventions for CTS and the lack of consensus among clinicians on what are considered the most relevant outcomes to assess [4]it was hypothesised that linking the outcomes to the ICF would highlight where outcome measures overlap in the concepts and domains which they assess and whether the existing outcomes assessed encompass all aspects of functioning as conceptualised by the ICF. The results of such a review may inform the selection of outcome domains and respective instruments for future trials on interventions in CTS. Similar work has already been undertaken in the fields of back pain, osteoarthritis [9] and stroke [10] and this in turn has resulted in the development of consensus on core sets for outcome assessment in these populations.
Methods
A systematic review was performed to identify the outcomes assessed and concepts contained in the measures used in trials of interventions for CTS, and to relate these concepts to the ICF as a reference tool.
Search strategy
The bibliographic databases Medline (January 1966 to July 2005), CINAHL (January 1982 to July 2005), AMED (January 1985 to July 2005) were searched using the following MeSH terms: randomized controlled trial, controlled clinical trial, carpal tunnel decompression, carpal tunnel release, carpal tunnel surgery. The titles and abstracts of articles retrieved through the search were checked applying the eligibility criteria as defined below. In order to crosscheck the sensitivity of the search strategy and identify any studies not retrieved through the search the bibliographies of a Cochrane review on surgical interventions for CTS were also examined[5].
Study selection criteria and procedures
The review considered all published studies if they met the following eligibility criteria: randomized or quasi-randomized trials, the interventions were surgical, the patients had a diagnosis of CTS made through clinical symptoms with or without confirmatory electrodiagnostic testing, and the outcomes assessed were described. Studies designed solely for the purpose of evaluating the effectiveness of different local anaesthesia on pain during or within 48 hours of surgery were excluded.
English language publications only were included and regardless of the time of the publication. The purpose of this review was not to assess the methodological quality of these trials as this has been done previously[5, 11, 12], but to identify the outcome domains assessed and the instruments or scales employed for this purpose, irrespective of whether these were standardised or not. Outcome measures extraction was carried out using a standard form to obtain data on the following aspects: study design, experimental and control interventions, length of follow-up, sample size, the outcome domains assessed pre- and post-operatively and respective instruments or scales employed. Each article was independently read by two reviewers and a data extraction form completed. Any discrepancies between reviewers were discussed and agreed.
Results
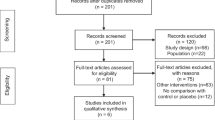
137 studies were identified through the initial search. After checking the abstracts and further review of the full-text article a total of 28 studies which met inclusion criteria were identified [13–40] A summary of the main study characteristics is shown in Table 1.
Review of studies and outcome domains assessed
The studies, conducted between 1985 and 2005, were all designed to evaluate the relative effectiveness of different surgical techniques such as endoscopic carpal tunnel release (ECTR) or open carpal tunnel release with or without epineurotomy. Standard open carpal tunnel release (OCTR) was the control intervention in 27 of the 28 trials. A total of 2558 hands in 2232 patients were studied in 28 studies. The length of follow-up after decompression varied greatly between the studies, ranging from 4 weeks to 2 years. The mean follow-up time was 37 weeks with 13 studies reporting follow-up at 1 year or longer. There was no apparent association between the type of outcomes assessed and other study characteristics such as the type of intervention studied, the length of follow-up or the country of the study.
A wide range of outcomes were reported and these were classified according to the three ICF domains: i) measures of impairment of body function and body structure; ii) measurers of activity limitations and iii) measures of participation restriction (see Tables 2 and 3). The most commonly assessed outcome domain was symptom resolution (27 studies) using either non-standardised methods (19 studies) or the standardised and disease-specific instrument, the Symptom Severity Scale of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ)[41]. The second most commonly assessed outcomes were complications (including scar adhesions, pillar pain and wound infection) and motor function, measured either as composite power grip (19 studies) and/or pinch grip (14 studies) with dynamometry and/or using manual muscle testing (MMT) and/or presence or absence of wasting of the thenar muscles. Sensibility was assessed in 15 studies and included touch threshold with monofilaments or the pressure specifying device (PSSD), two-point discrimination and vibration. Other outcomes within the impairment domain included range of movement of wrist or fingers, nerve conduction studies and interstitial pressures of the carpal canal.
At the level of activity limitations, hand function was assessed with timed dexterity tests in three studies or through self-reported use of hand in activities of daily living including the Functional Status Score of the BCTQ (12 studies). Measures of participation used in the trials were return to work which featured as a primary or secondary outcome measure in 15 studies and satisfaction (7 studies).
The level of reporting on the actual methods of assessment varied between studies. In several studies standardised outcome measures were used but with none or minimal detail on the actual instrument used, method of administration or reference to literature on standardised protocols. For example, 11 studies assessed two-point discrimination with only 4 studies stating the instrument used and one study describing the method (Table 4).
The BCTQ, a standardised patient-based outcome measure for use in CTS, started to feature only in studies published in 2000 and later, despite the original paper by Levine dating back to 1993. Non-standardised methods of assessing symptom resolution continued to be reported in 6 studies post 2000 and included assessing a range of symptoms which patients were asked to rate on a 3 or 4 point ordinal scale or to indicate as present or absent.
For some domains there were inconsistencies in the methods of quantifying the outcome. Return to work was a primary or secondary outcome in 15 studies and was often reported as the number of the days from surgery to resumption of employment. However, this is likely to vary between studies and depends on factors such as type of work undertaken (manual versus non-manual) employment status (self-employed versus employee) and variations in healthcare systems and how 'sick notes' are issued. The time taken to return to work also does not indicate whether someone is able to resume the activities without pain or discomfort and to the satisfaction of the individual and/or his employer. Furthermore, work as a measure of participation is not relevant to those patients who are not in employment or retired.
Linking outcomes assessed in CTS trials with the ICF
Current understanding of the pathophysiology of CTS together with the clinical manifestation of signs and symptoms allows the specific body structures and functions to be identified which are implicated in this disease. Depending on the severity of their symptoms, patients are also affected in their ability to carry out activities (activity limitations) and participation in work or leisure (participation restrictions). These in turn are also influenced by personal and environmental factors [7].
Using the ICF as a framework, firstly the codes and categories within health and health-related domains relevant to CTS were identified (see figure 1). Secondly the outcomes assessed in the 28 studies retrieved were mapped to the relevant domains and categories of the ICF. Where instruments contained subscales and several items these were individually assigned to the relevant category (see table 5). The frequency with which the domains and categories of the ICF were assessed in all 28 studies is presented in Figure 2.
The outcomes assessed in the 28 studies together covered all three domains of the ICF, that is, impairments of body structure and function, activity limitations and participation restrictions. However the majority of outcomes assessed focused on impairments of body structure and function, that is, sensory functions, sensations of pain, motor functions and sleep functions. Activity limitations and participation restrictions were assessed far less frequently in trials and included the patient-rated Functional Status Scale of the BCTQ, timed hand dexterity tests and self-reported time taken to resume activities of daily living, mostly self-care and household chores. Number of days taken to return to work or satisfaction were the only measures of participation restrictions.
Discussion
This systematic review has identified a wide range of outcome domains which were assessed in trials of surgical interventions and using a variety of methods and instruments. Based on the total count of studies which assessed different domains, self-reported resolution of symptoms, grip strength and return to work were the most frequently assessed outcomes.
The focus of these trials on assessing outcomes at the level of body function and structure and lesser use of measures of activity and participation concurs with findings from Gummerson et al [42] who reviewed trials of upper extremity disorders published in 4 journals over 11 years and totalling 92 studies. Only 41% of those studies reported outcomes on activity and participation.
Aspects such as the impact of CTS on functioning and health-related quality of life was included in only a few trials and limited to measures of days taken to return to work. A number of region-specific, patient-based outcome instruments which include questions about appearance, use of hand in self-care, work and leisure have been developed in the last 10 years. Examples of these are the Patient Evaluation Measure (PEM)[43] and the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (DASH)[44]. They are not disease-specific measures but region-specific and their validity has been tested in patient populations with a range of upper extremity musculoskeletal disorders, including CTS. Questions such as those from the DASH optional work module 'did you have difficulty using your usual technique at work?' or 'did you have difficulty in doing your work as well as you would like?' evaluate participation in work and provide useful additional information beyond the simple quantification of sick days. There are also a number of generic measures of health-related quality of life, such as the SF-36 [45] which capture participation and the psychosocial impact of the disease or disorder and which can be used in CTS patients. Of the RCTs reviewed, none used generic measures of participation or other health-related quality of life or health status measures.
Whilst it is important to obtain a comprehensive assessment of the impact of CTS on body function and structure as well as activity and participation, the use of a large battery of instruments also increases the burden on the patient and the tester. There was some overlap between the concepts assessed in trial outcomes. For example, in the domains body functioning, the functions of muscles were assessed by manual muscle testing of the abductor pollicis brevis muscle, dynamometry for pinch and power grip strength and degree of thenar wasting. In several trials two or more of these measures were used concurrently. A review of the evidence is needed on which of these methods and instruments is most valid, reliable and responsive which, in turn, reduces assessment burden and redundancy of similar outcome measures.
The use of the disease-specific measure, the BCTQ is becoming more established in recent trials. A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the BCTQ indicated that it is valid for the population, has good reliability and is responsive [46] and should replace any other non-standardised methods for assessing self-reported symptom resolution and functional status. The two subscales together encompass the two domains of the ICF – body function and activities. The use of clinician-derived measures of motor and sensory function was high yet the lack of detail on instruments, methods of testing and reference to published protocols or literature on psychometric properties of these tests raises questions over whether these were employed in the same way, thus hindering comparability of results. There are several advantages to using standardised outcome measures: if data about the reproducibility and population-specific validity of an instrument are known the use of it as a primary outcome measure is justified; knowledge of the responsiveness of an outcome measures can inform sample size calculations which are important to ensure that studies are adequately powered; and finally, the results from several studies can be compared and pooled if the same outcomes have been assessed using the same standardised methods and instruments.
This review has some limitations: we considered RCTs only in this review, based on the assumption that in well-designed trials careful attention would be paid to the selection of outcome measures. There are however a number of large follow-up and cohort studies which also report outcomes from surgical decompression and inclusion of these studies may have highlighted additional outcome domains and instruments.
Conclusion
The ICF provides a useful framework for identifying the concepts contained in outcome measures employed to date in trials of surgical intervention for CTS. It can help in the selection of the most appropriate domains to be assessed, especially where studies are designed to capture the impact of the intervention at individual and societal level. The findings of this review on surgical outcomes indicate that studies to date have focused primarily on assessment of impairment and less on the activity limitations and participation restrictions. It is important that consensus is achieved on which outcome measures should be used for which domains and on the standardisation of methods. A minimum set of outcome measures should include patient-reported scales of symptom severity and functional status such as the BCTQ, clinical measures of motor and sensory function and everyday performance in self-care, work and leisure as well as health-related quality of life. Further work is needed to review the psychometric properties of existing instruments in CTS populations and to develop consensus on a core set of outcome measures to be used in future clinical trials for CTS which crosses all three domains of the ICF.
References
Lundborg G: Nerve injury and repair, regeneration, reconstruction and cortical remodelling. 2004, Philadelphia: Elsevier, Churchill Livingstone, 2
Mueller M, Tsui D, Schnurr R, Biddulph-Deisroth L, Hard J, MacDermid JC: Effectiveness of hand therapy interventions in primary management of carpal tunnel syndrome: a systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy. 2004, 17 (2): 210-228.
Burke FD: Carpal tunnel syndrome: reconciling 'demand management' with clinical need. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2000, 25B (2): 121-127.
Gerritsen AA, de Vet HC, Scholten RJ, van Tulder MW, Bouter LM: Enabling meta-analysis in systematic reviews on carpal tunnel syndrome. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2002, 27A (5): 828-832.
Scholten RJ, Gerritsen AA, Uitdehaag BM, van Geldere D, de Vet HC, Bouter LM: Surgical treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2004, Art. No.: CD003905., 1
O'Connor D, Marshall S, Massy-Westropp N: Non-surgical treatment (other than steroid injection) for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003, Art. No.: CD003219., 1
WHO: International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. 2002, Geneva: World Health Organisation
Cieza A, Brockow T, Ewert T, Amman E, Kollerits B, Chaterji S, Ustun B, Stucki G: Linking health-status measurements to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2002, 34: 205-210. 10.1080/165019702760279189.
Brockow T, Cieza A, Kuhlow H, Sigl T, Franke T, Harder M, Stucki G: Identifying the concepts contained in outcome measures of clinical trials on musculoskeletal disorders and chronic widespread pain using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health as a Reference. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2004, 30-36. 10.1080/16501960410015371. Suppl 44
Szilvia G, Brockow T, Cieza A, Ewert T, Omar Z, Resch KL: Identifying the concepts contained in outcome measures of clinical trials on stroke using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health as a reference. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2002, 36 (suppl 44): 56-62.
Thoma A, Veltri K, Haines T, Duku E: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing endoscopic and open carpal tunnel decompression. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 2004, 114 (5): 1137-1146.
Thoma A, Veltri K, Haines T, Duku E: A systematic review of reviews comparing the effectiveness of endoscopic and open carpal tunnel decompression. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 2004, 113 (4): 1184-1191.
Holmgren-Larsson H, Leszniewski W, Linden U, Rabow L, Thorling J: Internal neurolysis or ligament division only in carpal tunnel syndrome – results of a randomized study. Acta Neurochirurgica. 1985, 74 (3–4): 118-121. 10.1007/BF01418799.
Lowry WE, Follender AB: Interfascicular neurolysis in the severe carpal tunnel syndrome. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research. 1988, 227: 251-254.
Mackinnon SE, McCabe S, Murray JF, Szalai JP, Kelly L, Novak C, Kin B, Burke GM: Internal neurolysis fails to improve the results of primary carpal tunnel decompression. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1991, 16A (2): 211-218.
Agee JM, McCarroll HR, Tortosa RD, Berry DA, Szabo RM, Peimer CA: Endoscopic release of the carpal tunnel: a randomized prospective multicenter study. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1992, 17A (6): 987-995.
Brown RA, Gelberman RH, Seiler JG, Abrahamsson SO, Weiland AJ, Urbaniak JR, Schoenfeld DA, Furcolo D: Carpal tunnel release: a prospective, randomized assessment of open and endoscopic methods. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 1993, 75-A (9): 1265-1275.
Erdmann MWH: Endoscopic carpal tunnel decompression. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1994, 19B (1): 5-13.
Foulkes GD, Atkinson RE, Beuchel C, Doyle JR, Singer DI: Outcome following epineurotomy in carpal tunnel syndrome: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1994, 19A (4): 539-547.
Sennwald GR, Benedetti R: The value of one-portal endoscopic carpal tunnel release: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 1995, 3 (2): 113-116. 10.1007/BF01552386.
Dumontier C, Sokolow C, Leclercq C, Chauvin P: Early results of conventional versus two-portal endoscopic carpal tunnel release. A prospective study. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1995, 20B (5): 658-662.
Jacobsen MB, Rahme H: A prospective, randomized study with an independent observer comparing open carpal tunnel release with endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1996, 21B (2): 202-204.
Leinberry CF, Hammond NL, Siegfried JW: The role of epineurotomy in the operative treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 1997, 79A (4): 555-557.
Citron ND, Bendall SP: Local symptoms after open carpal tunnel release. A randomized prospective trial of two incisions. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1997, 22B (3): 317-321.
Nakamichi K, Tachibana S: Ultrasonographically assisted carpal tunnel release. Journal of Hand Surgery. 1997, 22A (5): 853-862.
Bruser P, Richter M, Larkin G, Lefering R: The operative treatment of CTS and its relevance to endoscopic release. European Journal of Plastic Surgery. 1999, 22: 80-84. 10.1007/s002380050153.
Mackenzie DJ, Hainer R, Wheatley MJ: Early recovery after endoscopic vs. short-incision open carpal tunnel release. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2000, 44 (6): 601-604.
Trumble TE, Diao E, Abrams RA, Gilbert-Anderson MM: Single-portal endoscopic carpal tunnel release compared with open release. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2002, 84A (7): 1107-1115.
Jugovac I, Burgic N, Micovic V, Radolovic-Prenc L, Uravic M, Golubovic V, Stancic MF: Carpal tunnel release by limited palmar incision vs traditional open technique: randomized controlled trial. Croatian Medical Journal. 2002, 43 (1): 33-36.
Shum C, Parisien M, Strauch RJ, Rosenwasser MP: The role of flexor tenosynovectomy in the operative treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2002, 84A (2): 221-225.
Ferdinand RD, MacLean JGB: Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release in bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome: a prospective, randomised, blinded assessment. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2002, 84B (3): 375-9. 10.1302/0301-620X.84B3.12224.
Borisch N, Haussmann P: Neurophysiological recovery after open carpal tunnel decompression: comparison of simple decompression and decompression with epineurotomy. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2003, 28B (5): 450-454.
Macdermid JC, Richards RS, Roth JH, Ross DC, King GJ: Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release: a randomized trial. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2003, 28A (3): 475-480.
Saw NL, Jones S, Shepstone L, Meyer M, Chapman PG, Logan AM: Early outcome and cost-effectiveness of endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release: a randomized prospective trial. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2003, 28B (5): 444-449.
Helm RH, Vaziri S: Evaluation of carpal tunnel release using the Knifelight instrument. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2003, 28B (3): 251-254.
Wong KC, Hung LK, Ho PC, Wong JM: Carpal tunnel release. A prospective, randomised study of endoscopic versus limited-open methods. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 2003, 85B (6): 863-868.
Bhattacharya R, Birdsall PD, Finn P, Stothard J: A randomized controlled trial of knifelight and open carpal tunnel release. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2004, 29B (2): 113-115.
Dias JJ, Bhowal B, Wildin CJ, Thompson JR: Carpal tunnel decompression. Is lengthening of the flexor retinaculum better than simple division?. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2004, 29B (3): 271-276.
Kharwadkar N, Naique S, Molitor PJ: Prospective randomized trial comparing absorbable and non-absorbable sutures in open carpal tunnel release. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2005, 30B (1): 92-95.
Lorgelly PK, Dias JJ, Bradley MJ, Burke FD: Carpal tunnel syndrome, the search for a cost-effective surgical intervention: a randomised controlled trial. Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 2005, 87 (1): 36-40. 10.1308/1478708051469.
Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ, Daltroy LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH, Katz JN: A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 1993, 75A (11): 1585-1592.
Gummesson C, Atroshi I, Ekdahl C: The quality of reporting and outcome measures in randomized clinical trials related to upper-extremity disorders. Journal of Hand Surgery. 2004, 29A: 727-734.
Dias J, Bhowal B, Wildin C, Thompson J: Assessing the outcome of disorders of the hand: is the patient evaluation measure reliable, valid, responsive and without bias?. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2001, 83-B (2): 235-240. 10.1302/0301-620X.83B2.10838.
Hudak P, Amadio P, Bombardier C, (UECG) TUECG: Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: The DASH (Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand). American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 1996, 29: 602-608. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199606)29:6<602::AID-AJIM4>3.0.CO;2-L.
Ware J, Snow K, Kosinki M, Gandek B: The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). 1993, Boston: The Health Institute, New England Medical Center
de Carvalho Leite JC, Jerosch-Herold C, Song F: A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2006, 7: 78-10.1186/1471-2474-7-78.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2474/7/96/prepub
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the British Association of Hand Therapists Ltd through a research bursary award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
CJH conceived of the original idea, obtained funding and participated in the search, review and drafting of the manuscript. JCCL carried out the searching and reviewing of studies and helped draft the manuscript. FS provided expert advice on systematic reviewing and contributed to the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jerosch-Herold, C., Leite, J.C.d.C. & Song, F. A systematic review of outcomes assessed in randomized controlled trials of surgical interventions for carpal tunnel syndrome using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) as a reference tool. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 7, 96 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-7-96
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-7-96