Abstract
Background
Osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) is a distinctive modality commonly used by osteopathic physicians to complement their conventional treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. Previous reviews and meta-analyses of spinal manipulation for low back pain have not specifically addressed OMT and generally have focused on spinal manipulation as an alternative to conventional treatment. The purpose of this study was to assess the efficacy of OMT as a complementary treatment for low back pain.
Methods
Computerized bibliographic searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE, MANTIS, OSTMED, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were supplemented with additional database and manual searches of the literature.
Six trials, involving eight OMT vs control treatment comparisons, were included because they were randomized controlled trials of OMT that involved blinded assessment of low back pain in ambulatory settings. Data on trial methodology, OMT and control treatments, and low back pain outcomes were abstracted by two independent reviewers. Effect sizes were computed using Cohen's d statistic and meta-analysis results were weighted by the inverse variance of individual comparisons. In addition to the overall meta-analysis, stratified meta-analyses were performed according to control treatment, country where the trial was conducted, and duration of follow-up. Sensitivity analyses were performed for both the overall and stratified meta-analyses.
Results
Overall, OMT significantly reduced low back pain (effect size, -0.30; 95% confidence interval, -0.47 – -0.13; P = .001). Stratified analyses demonstrated significant pain reductions in trials of OMT vs active treatment or placebo control and OMT vs no treatment control. There were significant pain reductions with OMT regardless of whether trials were performed in the United Kingdom or the United States. Significant pain reductions were also observed during short-, intermediate-, and long-term follow-up.
Conclusion
OMT significantly reduces low back pain. The level of pain reduction is greater than expected from placebo effects alone and persists for at least three months. Additional research is warranted to elucidate mechanistically how OMT exerts its effects, to determine if OMT benefits are long lasting, and to assess the cost-effectiveness of OMT as a complementary treatment for low back pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Historically, low back pain has been the most common reason for visits to osteopathic physicians [1]. More recent data from the Osteopathic Survey of Health Care in America has confirmed that a majority of patients visiting osteopathic physicians continue to seek treatment for musculoskeletal conditions [2, 3]. A distinctive element of low back care provided by osteopathic physicians is osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT). A comprehensive evaluation of spinal manipulation for low back pain undertaken by the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research in the United States concluded that spinal manipulation can be helpful for patients with acute low back problems without radiculopathy when used within the first month of symptoms [4]. Nevertheless, because most studies of spinal manipulation involve chiropractic or physical therapy [5], it is unclear if such studies adequately reflect the efficacy of OMT for low back pain.
Although the professional associations that represent osteopaths, chiropractors, and physiotherapists in the United Kingdom developed a spinal manipulation package consisting of three common manual elements for use in the UK Back pain Exercise and Manipulation (UK BEAM) trial [6], there are no between-profession comparisons of clinical outcomes [7, 8]. It is well known that OMT comprises a diversity of techniques [9] that are not adequately represented by the UK BEAM trial package. Professional differences in spinal manipulation are more pronounced in research studies, where chiropractors have focused almost exclusively on high-velocity-low-amplitude techniques [10]. For example, a major trial of chiropractic manipulation as adjunctive treatment for childhood asthma used a high-velocity-low-amplitude thrust as the active treatment [11]. The simulated treatment provided in the sham manipulation arm of this chiropractic trial, which ostensibly was thought to have no therapeutic effect, had a marked similarity to OMT [10, 12]. Further, because differences in professional background and training lend themselves to diverse manipulation approaches, clinicians have been warned about generalizing the findings of systematic reviews to practice [13].
In addition to professional differences in the manual techniques themselves, osteopathic physicians in the United States, unlike allopathic physicians, chiropractors, or physical therapists, can treat low back pain simultaneously using both conventional primary care approaches and complementary spinal manipulation. This represents a unique philosophical approach in the treatment of low back pain. Consequently, there is a need for empirical data that specifically address the efficacy of OMT for such conditions as low back pain [14]. The present study was undertaken to address this need by conducting a systematic review of the literature on OMT and performing a meta-analysis of all randomized controlled trials for low back pain performed in ambulatory settings.
Methods
Search
A search of the English language literature was performed through August 2003 to identify reports of randomized controlled trials of OMT. We searched MEDLINE, OLDMEDLINE, EMBASE, MANTIS, OSTMED, Alt Health Watch, SciSearch, ClinicalTrials.gov, CRISP, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. A detailed description of the search strategy is provided in the Appendix [see Additional file 1]. Additionally, reports were sought from relevant reviews or meta-analyses of spinal manipulation [9, 15–32] and manual searches of reference citations in the reviewed literature sources.
Selection
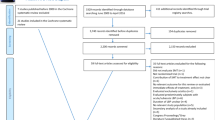
The search bibliographies and relevant reports were reviewed by the authors to identify randomized controlled trials involving OMT in human subjects. To assess the efficacy of OMT in primary care, eligibility was limited to randomized controlled trials of OMT performed by osteopaths, osteopathic physicians, or osteopathic trainees that included blinded assessment of low back pain in ambulatory settings. Trials that involved manipulation under anesthesia, industrial settings, or hospitalized patients were not included. Because there is potential confusion regarding the type of manipulation performed in some trials [33], the reported methods in each trial were carefully reviewed to assess eligibility for the meta-analysis. Overall, seven studies known or purported to involve OMT for low back pain were reviewed and excluded for not meeting all eligibility criteria [34–40]. A subsequent source [41] indicated that an osteopathic manipulation technique was used in the Irvine study [42]. Although several of the six included OMT trials were identified in multiple bibliographic databases, five [42–46] were indexed in MEDLINE. The Cleary [47] trial was identified exclusively through the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials.
Data extraction
Each eligible trial was independently reviewed by two of us to abstract data on methodological characteristics, OMT and control treatments, and low back pain outcomes. Conflicting data were resolved by consensus.
Trial characteristics
As shown in Table 1, the six OMT trials were conducted between 1973 and 2001 in the United Kingdom or the United States [42–47]. Two of the six trials each included two control treatments [43, 46], thus providing eight OMT vs control treatment comparisons. The trials generally were comparable in their methodology, with the possible exception of the Cleary [47] trial. Twenty contrasts were reported in the six trials (a contrast refers to a within-trial comparison between OMT and a control treatment with respect to a low back pain outcome at a given point in time). Following randomization, nine contrasts were reported within one month (short-term outcomes), another seven contrasts were reported within three months (intermediate-term outcomes), and the remaining four contrasts were reported within 12 months (long-term outcomes).
The methodological quality of four of the OMT trials [42–45] was independently confirmed in a recent systematic review that included a best evidence synthesis incorporating eight explicit quality criteria, including similarity of baseline characteristics of subjects or reporting of adjusted outcomes; concealment of treatment allocation; blinding of subjects; blinding of providers or other control for attention bias; blinded or unbiased outcomes assessment; subject dropouts reported and accounted for in the analysis; missing data reported and accounted for in the analysis; and intention-to-treat analysis or absence of differential co-interventions between groups in studies with full compliance [13]. The Cleary [47] trial was not eligible for this review because it did not include a sufficiently large number of subjects. Although the Licciardone [46] trial was not eligible for the review because it was published after the closing date of December 2002, it has been characterized as an innovative and important trial with many rigorous design features [48], and more recently has been identified as an evidence-based supplement relative to the previous review from the Cochrane Library [49].
Quantitative data synthesis
We used the effect size, computed as Cohen's d statistic, to report all trial results [50]. A negative effect size represented a greater decrease in pain among OMT subjects relative to control treatment subjects. Dichotomous pain measures were transformed to effect sizes by first computing the relevant P-value and then determining the effect size and 95% confidence interval (CI) that would obtain under the assumption of a two-tailed t-test for measuring the standardized mean difference between OMT and control treatments in the relevant number of subjects [50]. The meta-analysis results were weighted by the inverse variance for each OMT vs control treatment comparison. The Q statistic was used to test the homogeneity of trials included in each analysis [51].
The overall meta-analysis included the eight OMT vs control treatment comparisons. Four of the six trials, involving six of the eight OMT vs control treatment comparisons, each reported three contrasts [42, 43, 45, 46] (Table 1). The median contrast, as identified by the intermediate effect size among the three reported pain outcomes for a given OMT vs control treatment comparison, was used to represent the pain outcome for each of these six comparisons. These median contrasts were then combined with the lone contrasts reported in each of the two remaining OMT vs control treatment comparisons [44, 47]. Based on the similarity among trials (Table 1), a fixed-effects model initially was used to perform meta-analysis and the results were then compared with those of a random-effects model.
A series of sensitivity analyses were then performed. First, to address the possibility of bias by using the median contrasts method, analyses were repeated using the best-case and worst-case scenarios for the six relevant OMT vs control treatment comparisons [42, 43, 45, 46]. Second, to address the possibility of bias by including comparisons involving the same OMT group vs two different control treatment groups in two trials [43, 46], analyses were repeated using only one OMT vs control treatment comparison for each of these trials. Each of the four possible combinations of contrasts was analyzed. Third, the analysis was repeated after excluding the Cleary [47] trial. Finally, an analysis was performed using all 20 low back pain contrasts. Similar analyses were performed after stratifying trials according to control treatment, country where the trial was performed, and duration of follow-up.
As summarized in Table 2, there were 43 analyses performed, including the overall meta-analysis, seven stratified meta-analyses, and 35 sensitivity analyses. Meta-analysis was performed only when there were at least three contrasts available for data synthesis. Database management and analyses were performed using the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software package (Version 1.0.23, Biostat, Inc, Englewood, NJ 07631, USA).
Results
Overall analyses
The search for reports is summarized in Figure 1. A total of 525 subjects with low back pain were randomized in the eligible trials. The overall results are presented in Figure 2. There was a highly significant reduction in pain associated with OMT (effect size, -0.30; 95% CI, -0.47 – -0.13; P = .001). The Q statistic was non-significant, thus supporting the assumption of homogeneity among trials. The primary sensitivity analyses are presented in Table 3. Using a random-effects model, the results were virtually identical to those observed with a fixed-effects model. There were 729 (36 × 12) possible combinations of contrasts for analysis based on three contrasts for each of six OMT vs control treatment comparisons [42, 43, 45, 46] and one contrast for each of the two remaining OMT vs control treatment comparisons [44, 47]. The efficacy of OMT for low back pain was supported in both the best-case (effect size, -0.37; 95% CI, -0.55 – -0.20; P < .001) and worst-case (effect size, -0.18; 95% CI, -0.35 – 0.00; P = .046) scenarios. Similarly, when each trial was limited to one OMT vs control treatment comparison, OMT was found to be efficacious in each of the four analyses. OMT also demonstrated significantly greater low back pain reduction than control treatment in analyses with the Cleary [47] trial excluded and with all 20 contrasts included.
Stratified analyses
The results of stratified meta-analyses are presented in Table 4. There was a significant reduction in low back pain associated with OMT in trials vs active treatment or placebo control (effect size, -0.26; 95% CI, -0.48 – -0.05; P = .02), independent of fixed-effects or random-effects model specification. There were 243 (35 × 11) possible contrast combinations based on three contrasts for each of five OMT vs control treatment comparisons [42, 43, 45, 46] and one contrast for another remaining OMT vs control treatment comparison [47]. Both the best-case and worst-case scenarios demonstrated a greater reduction in pain with OMT than active treatment or placebo control, although the worst-case results did not achieve statistical significance. OMT was found to significantly reduce pain in the remaining analyses that limited OMT vs active treatment or placebo control comparisons to one per trial, excluded the Cleary [47] trial, and included all 16 contrasts. The OMT vs no treatment control comparisons were observed in trials in which all subjects received usual low back care in addition to their allocated treatment (ie, OMT and usual care vs only usual care) [44, 47]. For these trials, the all-contrasts model (ie, the only model with sufficient contrasts for data synthesis) demonstrated a highly significant reduction in pain with OMT.
Trials in both the United Kingdom (effect size, -0.29; 95% CI, -0.58 – 0.00; P = .050) and the United States (effect size, -0.31; 95% CI, -0.52 – -0.10; P = .004) demonstrated significant reductions in low back pain associated with OMT. In the sensitivity analyses, effect sizes were generally of comparable magnitude in both countries, although results in American trials consistently achieved statistical significance as a consequence of the larger sample sizes in these trials (Table 4).
There were significant reductions in low back pain associated with OMT during the short-term (effect size, -0.28; 95% CI, -0.51 – -0.06; P = .01), intermediate-term (effect size, -0.33; 95% CI, -0.51 – -0.15; P < .001), and long-term (effect size, -0.40; 95% CI, -0.74 – -0.05; P = .03) follow-up periods. Sensitivity analyses for temporal outcomes demonstrated that intermediate-term results consistently achieved statistical significance, generally because of the greater number of subjects in these analyses (Table 4). The results of the meta-analyses and sensitivity analyses are further summarized in Figure 3.
Summary of meta-analysis results. A denotes all-contrasts model; B, best-case scenario model; C, Cleary [47] trial excluded model; M, median contrasts model; NT, no treatment control; OMT, osteopathic manipulative treatment; W, worst-case scenario model. 1, 2, 3, and 4 indicate alternative models restricted to one OMT vs control treatment comparison per trial. A diamond indicates the inclusion of the relevant contrast or observation of the stated result. Sensitivity analyses are shaded in gray. Results are presented for each of the 43 analyses, including the overall meta-analysis, seven stratified meta-analyses, and 35 sensitivity analyses.
Discussion
Efficacy of osteopathic manipulative treatment
The overall results clearly demonstrate a statistically significant reduction in low back pain with OMT (Figure 2). Further, the meta-analysis results are quite robust as indicated by the comprehensive sensitivity analyses (Figure 3). Stratified meta-analyses to control for moderator variables demonstrated that OMT significantly reduced low back pain vs active treatment or placebo control and vs no treatment control. If it is assumed, as shown in a review [52], that the effect size is -0.27 for placebo control vs no treatment in trials involving continuous measures for pain, then the results of our study are highly congruent (ie, effect size for OMT vs no treatment [-0.53] = effect size for OMT vs active treatment or placebo control [-0.26] + effect size for placebo control vs no treatment [-0.27]).
It has been suggested that the therapeutic benefits of spinal manipulation are largely due to placebo effects [53]. A preponderance of results from our sensitivity analyses supports the efficacy of OMT vs active treatment or placebo control and therefore indicates that low back pain reduction with OMT is attributable to the manipulation techniques, not merely placebo effects. Also, as indicated above, OMT vs no treatment control demonstrated pain reductions twice as great as previously observed in clinical trials of placebo vs no treatment control [52]. Thus, OMT may eliminate or reduce the need for drugs that can have serious adverse effects [44].
Because osteopathic physicians provide OMT to complement conventional treatment for low back pain, they tend to avoid substantial additional costs that would otherwise be incurred by referring patients to chiropractors or other practitioners [54]. With respect to back pain, osteopathic physicians make fewer referrals to other physicians and admit a lower percentage of patients to hospitals than allopathic physicians [1], while also treating back pain episodes with substantially fewer visits than chiropractors [55]. Although osteopathic family physicians are less likely to order radiographs or prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, aspirin, muscle relaxants, sedatives, and narcotic analgesics for low back pain than their allopathic counterparts, osteopathic physicians have a substantially higher proportion of patients returning for follow-up back care than allopathic physicians [56]. In the United Kingdom, where general practitioners may refer patients with spinal pain to osteopaths for manipulation, it has been shown that OMT improved physical and psychological outcomes at little extra cost [57].
In our study, the effect sizes for OMT in the United Kingdom, where osteopaths are not licensed physicians, were generally comparable to those in the United States, where OMT is provided by licensed physicians. This consistency suggests that the results truly reflect the effects of OMT itself, and not other elements of low back care. It is not surprising that osteopaths in the United Kingdom achieved pain reduction with OMT similar to that of their physician counterparts in the United States. The training of osteopaths in the United Kingdom is highly focused on OMT, whereas osteopathic physicians undertake a medical curriculum that necessarily relegates OMT to one of many therapeutic approaches, albeit a fundamental one for osteopathic practitioners. Regardless of the career training path of the provider, it appears that OMT achieves clinically important reductions in low back pain.
Potential limitations
There are several potential limitations of this study that should be addressed. First, as with any meta-analysis, the individual trials varied somewhat with respect to methodology, including trial setting, subject characteristics, OMT and control treatment interventions, and pain measures (Table 1). Such heterogeneity has been commonly observed in previous meta-analyses of spinal manipulation, including a recent meta-analysis performed in collaboration with the Cochrane Back Review Group [31]. The latter study addressed potential heterogeneity by presenting stratified results according to chronicity of low back pain, type of control group, and duration of follow-up. This approach is analogous to the methods used in our study. Further, it should be noted that the assumption of homogeneity among trials was not rejected statistically in any of our eight overall or stratified median contrasts meta-analyses.
Second, because five trials each included repeated pain measures and two trials each included two control treatments, there was no unique set of independent outcomes for meta-analysis. Such interdependencies were noted to be a problem in an early meta-analysis of spinal manipulation [15]. We used the median contrasts method to address this problem because the median outcome represents an observed outcome that is easy to compute and is less vulnerable to extreme observations than other measures of central tendency. Further, sensitivity analysis was used to assess the range of possible combinations of outcomes. Thus, for the overall meta-analysis, there were 729 potential contrast combinations. Of these, both the best-case and worst-case scenarios demonstrated statistically significant results favoring OMT, thereby providing unequivocal evidence for the efficacy of OMT. Robust findings were also observed for trials performed in the United States and for intermediate-term outcomes.
Third, because there were a relatively small number of eligible trials, there were not sufficient contrasts for certain analyses and some results were imprecise. The latter phenomenon likely obviated the statistical significance of some results. Nevertheless, it is important to note that the direction of results favored OMT in each of the 43 meta-analyses and sensitivity analyses presented herein (Figure 3).
Fourth, there exists the possibility that the results of unpublished trials of OMT for low back pain may have altered significantly the conclusions of this study. To address this issue, we performed file drawer analysis by computing the fail-safe N [58]. This represents the number of unpublished trials of OMT for low back pain that would have met our inclusion criteria, and that also would have demonstrated an effect size averaging ≥ -0.10, which is assumed to reflect clinically insignificant levels of pain reduction. A total of 16 unpublished trials (assuming one control group per trial) with, in the aggregate, clinically insignificant pain reduction outcomes would have been needed to obviate the significance of our results. Only recently has government funding for research in the area of complementary and alternative medicine become more widely available, in response to the public's interest in such treatments. Historically, it is highly unlikely that 16 trials of OMT for low back pain would have been sponsored, conducted, and subsequently not published.
Finally, this study focused only on the efficacy of OMT with respect to pain outcomes. Generic health status, back-specific function, work disability, and back-specific patient satisfaction are other recommended outcome domains [59] that were not assessed because the included OMT trials did not consistently report these data.
Conclusion
The present study indicates that OMT is a distinctive modality that significantly reduces low back pain. The level of pain reduction is greater than expected from placebo effects alone and persists for at least three months. Additional research is warranted to elucidate mechanistically how OMT exerts its effects, to determine if OMT benefits are long lasting, and to assess the cost-effectiveness of OMT as a complementary treatment for low back pain.
References
Cypress BK: Characteristics of physician visits for back symptoms: a national perspective. Am J Public Health. 1983, 73: 389-395.
Licciardone JC, Herron KM: Characteristics, satisfaction, and perceptions of patients receiving ambulatory healthcare from osteopathic physicians: a comparative national survey. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2001, 101: 374-385.
Licciardone JC: Awareness and use of osteopathic physicians in the United States: results of the Second Osteopathic Survey of Health Care in America (OSTEOSURV-II). J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2003, 103: 281-289.
Agency for Health Care Policy and Research [AHCPR]: Acute low back problems in adults. Clinical Practice Guideline 14. 1994, Rockville, MD, US Department of Health and Human Services
Kuchera ML, DiGiovanna EL, Greenspan PE: Efficacy and complications. Foundations for Osteopathic Medicine. Edited by: Ward RC. 2003, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1143-1152. 2
Harvey E, Burton AK, Moffett JK, Breen A: Spinal manipulation for low-back pain: a treatment package agreed by the UK chiropractic, osteopathy and physiotherapy professional associations. Man Ther. 2003, 8: 46-51. 10.1054/math.2002.0472.
UK BEAM Trial Team: United Kingdom back pain exercise and manipulation (UK BEAM) randomised trial: effectiveness of physical treatments for back pain in primary care. BMJ. 2004, 329: 1377-10.1136/bmj.38282.669225.AE. doi:10.1136/bmj.38282.669225.AE.
UK BEAM Trial Team: United Kingdom back pain exercise and manipulation (UK BEAM) randomised trial: cost effectiveness of physical treatments for back pain in primary care. BMJ. 2004, 329: 1381-10.1136/bmj.38282.607859.AE. doi:10.1136/bmj.38282.607859.AE.
Lesho EP: An overview of osteopathic medicine. Arch Fam Med. 1999, 8: 477-484. 10.1001/archfami.8.6.477.
Mein EA, Greenman PE, McMillin DL, Richards DG, Nelson CD: Manual medicine diversity: research pitfalls and the emerging medical paradigm. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2001, 101: 441-444.
Balon J, Aker PD, Crowther ER, Danielson C, Cox PG, O'Shaughnessy D, Walker C, Goldsmith CH, Duku E, Sears MR: A comparison of active and simulated chiropractic manipulation as adjunctive treatment for childhood asthma. N Engl J Med. 1998, 339: 1013-20. 10.1056/NEJM199810083391501.
Nelson CD, McMillin DL, Richards DG, Mein EA, Redwood D: Manual healing diversity and other challenges to chiropractic integration. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2000, 23: 202-207. 10.1016/S0161-4754(00)90250-1.
Bronfort G, Haas M, Evans RL, Bouter LM: Efficacy of spinal manipulation and mobilization for low back pain and neck pain: a systematic review and best evidence synthesis. Spine J. 2004, 4: 335-356. 10.1016/j.spinee.2003.06.002.
Howell JD: The paradox of osteopathy. N Engl J Med. 1999, 341: 1465-1468. 10.1056/NEJM199911043411910.
Ottenbacher K, DiFabio RP: Efficacy of spinal manipulation/mobilization therapy: a meta-analysis. Spine. 1985, 10: 833-837.
Koes BW, Assendelft WJJ, van der Heijden GJMG, Bouter LM, Knipschild PG: Spinal manipulation and mobilisation for back and neck pain: a blinded review. BMJ. 1991, 303: 1298-1303.
Abenhaim L, Bergeron AM: Twenty years of randomized clinical trials of manipulative therapy for back pain: a review. Clin Invest Med. 1992, 15: 527-535.
Anderson R, Meeker WC, Wirick BE, Mootz RD, Kirk DH, Adams A: A meta-analysis of clinical trials of spinal manipulation. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1992, 15: 181-194.
DiFabio RP: Efficacy of manual therapy. Phys Ther. 1992, 72: 853-864.
Shekelle PG, Adams AH, Chassin MR, Hurwitz EL, Brook RH: Spinal manipulation for low-back pain. Ann Intern Med. 1992, 117: 590-598.
Scheer SJ, Radack KL, O'Brien DR: Randomized controlled trials in industrial low back pain relating to return to work. Part 1. Acute interventions. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995, 76: 966-973. 10.1016/S0003-9993(95)80076-X.
Koes BW, Assendelft WJJ, van der Heijden GJMG, Bouter LM: Spinal manipulation for low back pain: an updated systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Spine. 1996, 21: 2860-2873. 10.1097/00007632-199612150-00013.
Scheer SJ, Radack KL, O'Brien DR: Randomized controlled trials in industrial low back pain relating to return to work. Part 2. Discogenic low back pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996, 77: 1189-1197. 10.1016/S0003-9993(96)90147-1.
Scheer SJ, Watanabe TK, Radack KL: Randomized controlled trials in industrial low back pain. Part 3. Subacute/chronic pain interventions. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997, 78: 414-423. 10.1016/S0003-9993(97)90235-5.
van der Weide WE, Verbeek JHAM, van Tulder MW: Vocational outcome of intervention for low-back pain. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1997, 23: 165-178.
van Tulder MW, Koes BW, Bouter LM: Conservative treatment of acute and chronic nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials of the most common interventions. Spine. 1997, 22: 2128-2156. 10.1097/00007632-199709150-00012.
Bronfort G: Spinal manipulation: current state of research and its indications. Neurol Clin. 1999, 17: 91-111. 10.1016/S0733-8619(05)70116-X.
Ernst E, Harkness E: Spinal manipulation: a systematic review of sham-controlled, double-blind, randomized clinical trials. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2001, 22: 879-889. 10.1016/S0885-3924(01)00337-2.
Ferreira ML, Ferreira PH, Latimer J, Herbert R, Maher CG: Does spinal manipulative therapy help people with chronic low back pain?. Aust J Physiother. 2002, 48: 277-284.
Pengel HM, Maher CG, Refshauge KM: Systematic review of conservative interventions for subacute low back pain. Clin Rehabil. 2002, 16: 811-820. 10.1191/0269215502cr562oa.
Assendelft WJJ, Morton SC, Yu EI, Suttorp MJ, Shekelle PG: Spinal manipulative therapy for low back pain: a meta-analysis of effectiveness relative to other therapies. Ann Intern Med. 2003, 138: 871-881.
Cherkin DC, Sherman KJ, Deyo RA, Shekelle PG: A review of the evidence for the effectiveness, safety, and cost of acupuncture, massage therapy, and spinal manipulation for back pain. Ann Intern Med. 2003, 138: 898-906.
Haldeman S, Hooper PD, Phillips RB, Scaringe JG, Traina AD: Spinal manipulative therapy. The Adult Spine: Principles and Practice. Edited by: Frymoyer JW. 1997, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1837-1861. 2
Siehl D, Olson DR, Ross HE, Rockwood EE: Manipulation of the lumbar spine with the patient under general anesthesia: evaluation by electromyography and clinical-neurologic examination of its use for lumbar nerve root compression syndrome. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1971, 70: 433-440.
Doran DML, Newell DJ: Manipulation in treatment of low back pain: a multicentre study. Br Med J. 1975, 2: 161-164.
Hadler NM, Curtis P, Gillings DB, Stinnett S: A benefit of spinal manipulation as adjunctive therapy for acute low-back pain: a stratified controlled trial. Spine. 1987, 12: 703-706.
Ellestad SM, Nagle RV, Boesler DR, Kilmore MA: Electromyographic and skin resistance responses to osteopathic manipulative treatment for low-back pain. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1988, 88: 991-997.
MacDonald RS, Bell CMJ: An open controlled assessment of osteopathic manipulation in nonspecific low-back pain. Spine. 1990, 15: 364-370.
Boesler D, Warner M, Alpers A, Finnerty EP, Kilmore MA: Efficacy of high-velocity low-amplitude manipulative technique in subjects with low-back pain during menstrual cramping. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1993, 93: 203-214.
Hoffman KS, Hoffman LL: Effects of adding sacral base leveling to osteopathic manipulative treatment of back pain: a pilot study. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1994, 94: 217-226.
Patterson MM: Foundations for osteopathic medical research. Foundations for Osteopathic Medicine. Edited by: Ward RC. 2003, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1167-1187. 2
Hoehler FK, Tobis JS, Buerger AA: Spinal manipulation for low back pain. JAMA. 1981, 245: 1835-1838. 10.1001/jama.245.18.1835.
Gibson T, Grahame R, Harkness J, Woo P, Blagrave P, Hills R: Controlled comparison of short-wave diathermy treatment with osteopathic treatment in non-specific low back pain. Lancet. 1985, 1: 1258-1261. 10.1016/S0140-6736(85)92323-2.
Andersson GBJ, Lucente T, Davis AM, Kappler RE, Lipton JA, Leurgans S: A comparison of osteopathic spinal manipulation with standard care for patients with low back pain. N Engl J Med. 1999, 341: 1426-1431. 10.1056/NEJM199911043411903.
Burton AK, Tillotson KM, Cleary J: Single-blind randomised controlled trial of chemonucleolysis and manipulation in the treatment of symptomatic lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2000, 9: 202-207. 10.1007/s005869900113.
Licciardone JC, Stoll ST, Fulda KG, Russo DP, Siu J, Winn W, Swift J: Osteopathic manipulative treatment for chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2003, 28: 1355-1362. 10.1097/00007632-200307010-00002.
Cleary C, Fox JP: Menopausal symptoms: an osteopathic investigation. Complement Ther Med. 1994, 2: 181-186. 10.1016/0965-2299(94)90017-5.
Ernst E: Another negative trial of manipulative treatment for back pain. Focus Altern Complement Ther. 2004, 9: 43-44.
Margo K: Cochrane for clinicians: putting evidence into practice. Spinal manipulative therapy for low back pain. Am Fam Physician. 2005, 71: 464-465.
Rosenthal R: Parametric measures of effect size. The Handbook of Research Synthesis. Edited by: Cooper H, Hedges LV. 1994, New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation, 231-244.
Hedges LV, Olkin I: Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis. 1985, Boston, MA: Academic Press
Hróbjartsson A, Gøtzsche PC: Is the placebo powerless? An analysis of clinical trials comparing placebo with no treatment. N Engl J Med. 2001, 344: 1594-1602. 10.1056/NEJM200105243442106.
Ernst E: Does spinal manipulation have specific treatment effects?. Fam Pract. 2000, 17: 554-556. 10.1093/fampra/17.6.554.
Reilly BM, Hart A, Evans AT: Part II. Evidence-based medicine: a passing fancy or the future of primary care?. Dis Mon. 1998, 44: 370-399. 10.1016/S0011-5029(98)90006-2.
Shekelle PG, Markovich M, Louie R: Factors associated with choosing a chiropractor for episodes of back pain care. Med Care. 1995, 33: 842-850.
Hart LG, Deyo RA, Cherkin DC: Physician office visits for low back pain: frequency, clinical evaluation, and treatment patterns from a U.S. national survey. Spine. 1995, 20: 11-19.
Williams NH, Wilkinson C, Russell I, Edwards RT, Hibbs R, Linck P, Muntz R: Randomized osteopathic manipulation study (ROMANS): pragmatic trial for spinal pain in primary care. Fam Pract. 2003, 20: 662-669. 10.1093/fampra/cmg607.
Wolf FM: Meta-analysis: quantitative methods for research synthesis. Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences. Edited by: Lewis-Beck MS (Series). 1986, Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications, no. 07–059
Bombardier C: Outcome assessments in the evaluation of treatment of spinal disorders: summary and general recommendations. Spine. 2000, 25: 3100-3103. 10.1097/00007632-200012150-00003.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2474/6/43/prepub
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by a grant (No. D56HP00170) from the Health Resources and Services Administration, United States Department of Health and Human Services. The funding organization had no role in the design, conduct, and reporting of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
JCL, AKB, and LNK conceived and designed the study. LNK performed the literature searches. JCL and AKB extracted the data. JCL performed the statistical analyses. JCL, AKB, and LNK interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. JCL will act as guarantor for the paper. The guarantor accepts full responsibility for the conduct of the study, had access to the data, and controlled the decision to publish. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12891_2004_156_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Additional File 1: this file provides the timetable, databases, and search terms used to identify relevant studies for the meta-analysis. (DOC 32 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Licciardone, J.C., Brimhall, A.K. & King, L.N. Osteopathic manipulative treatment for low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 6, 43 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-6-43
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-6-43