Abstract
Background
Echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF) has been identified as a common ultrasound finding in association with fetal aneuploidy. Little is known about the association of this soft marker aneuploidy in various ethnic groups. Although it is commonly thought Asians in general have a higher incidence of EIF, it is unknown whether this also applies to Japanese as a subpopulation. The purpose of this study is to determine the antenatal incidence and postnatal significance of EIF observed during sonography in Japanese patients.
Methods
A cohort of Japanese patients who underwent ultrasound screening from 1997 to 1999 in the ultrasound unit at the New York University School of Medicine was identified. Variables included age, gestational age, serum markers, and the presence or absence of aneuploidy. Patients with first degree paternal or maternal Japanese ancestry were included for analysis. Examinations were performed between 14 and 24 weeks gestation. The prevalence of EIF was calculated. The control group was based on previously published data in the U.S (7.3% prevalence).
Results
A total of 154 subjects were identified, 148 were available for final analysis. Twenty-two fetuses had an EIF, 19 (86.4%) left-sided, 3 (13.6%) right-sided. Seventeen patients had other sonographic markers associated with aneuploidy. The mean maternal age at diagnosis was 30.7 ± 3.9 years and the mean gestational age was 19.8 ± 1.6 weeks. The prevalence of EIF was 14.8%. Compared to published population prevalence, there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.005). No abnormal karyotypes were found.
Conclusion
Asians of Japanese origin may have a higher prevalence of echogenic intracardiac foci, thus affecting the positive predictive value of this sonographic marker for aneuploidy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The population frequency of chromosomal anomalies at birth is 1 in 165 [1]. Hook in 1981 established the relationship between advanced maternal age and fetal aneuploidy [2]. Using advanced maternal age (i.e. >35 years old) as the only screening method, 80% of fetal aneuploidy will be missed [1].
Technological advances in ultrasonography have allowed an increase in the prenatal detection of structural findings associated with aneuploidy. Recently, subtle ultrasound findings have been adopted as potential genetic markers for aneuploidy thus adjusting the overall maternal age related risk. The most common of such markers for aneuploidy include: echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF), echogenic bowel (EB), choroid plexus cyst (CPC), shortened long bones (femur and humerus), and renal pyelectasis (RP). The majority of these "soft markers" are associated with an increased risk of trisomy 21, with the exception of the CPC, which is more specific for trisomy 18 [3], and EIF for trisomy 21 and 13 [4].
There is conflicting evidence in the literature regarding not only the management of isolated ultrasound "soft markers" in low risk populations, but also their potential association with aneuploidy, particularly EIF [5, 6]. There is a paucity of information in the literature regarding the prevalence of these markers in different racial or ethnic groups, as well as other possible confounders of this tool [7].
The current study was performed to determine the rate of echogenic intracardiac foci in patients of Japanese ancestry and the difference between Japanese patients and a racially mixed general population.
Methods
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the New York University School of Medicine. A cohort of patients who presented for midtrimester ultrasound evaluation to the New York University School of Medicine was analyzed over a 3-year period from 1997 – 1999. Data was abstracted from the patient's prenatal records and our ultrasound database.
Inclusion criteria included patients of first degree Japanese ancestry, estimated gestational age between 14 and 24 weeks, and a finding of EIF regardless of presence or absence of other "soft markers". Exclusion criteria included the presence of major anomalies and unavailability of karyotypic analysis.
The variables analyzed included age, gestational age at ultrasound screening, biochemical serum markers, the presence or absence of aneuploidy, the presence or absence of EIF. Per protocol in our ultrasound unit, presence or absence of markers for aneuploidy is routinely noted on ultrasound reports. The total number of fetal anatomy ultrasounds performed during this time period and the number of amniocenteses were also assessed.
Sonographic examination for the detection of congenital anomalies was performed between 14 and 24 weeks gestation using Acuson 128XP (Acuson, Mountain View CA). All sonographic evaluations were performed by two operators for each patient: the first was a sonographer certified in obstetrical ultrasound (SM), the second was a maternal fetal medicine attending (AR). The patient's ethnic background was determined by self-reporting on the prenatal patient record. The patients were presented with a list of choices including: African, Asian, Indian, Hispanic, Caucasian, or other. Patients with first degree relationship of either paternal or maternal Japanese ancestry were identified among self-reported Asian patients at the time of ultrasound. At our institution, sub-ethnicity identification is routine at the time of ultrasound in patients with sonographic abnormalities.
Echogenic intracardiac foci were defined as echogenic foci found in either or both ventricles on either an apical or lateral four-chamber view. Per protocol, to qualify as an echogenic focus, the dot had to be as bright as bone [8]. Other markers for aneuploidy were defined as follows: pyelectasis – renal pelvis ≥5 mm; short femur and short humerus – ≥10 day lag in growth.
The prevalence of EIF was calculated for our study cohort. The control group EIF prevalence of 7.33% was based on previously published data in the U.S. In a meta-analysis by Smith-Bindman in 2001 [9], a total of five studies [8, 10–13] were examined that included evaluations of EIF. The total number of subjects was 5,948 with a total number of 436 subjects or 7.33% (95% CI 6.64, 7.96) having the finding of EIF.
Karyotypes were determined by the cytogenetics laboratory at NYU School of Medicine. Infants at birth were assessed by attending pediatricians for stigmata of Down syndrome and selective genetic analysis in the postnatal period was performed at the physician's discretion. Chi-square analysis was performed using a personal computer and statistical software (SPSS, Chicago, IL).
Results
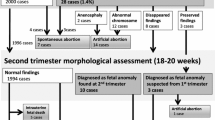
A total of 154 patients of Japanese ancestry underwent targeted ultrasound screening during the study period. Five patients were excluded from final analysis due to limited follow up secondary to transfer of care (1/5) or moving out of the country (4/5). There were 149 patients available for analysis which included 148 singleton pregnancies and 1 twin gestation. The mean maternal age at diagnosis was 30.7 ± 3.9 years and the mean gestational age at diagnosis was 19.8 weeks. Twenty-two fetuses were identified with an EIF, 19 (86.4%) were left-sided, 3 (13.6%) were right-sided. Two fetuses had multiple foci, one had three calcifications and the other one had two calcifications. One patient had a spontaneous preterm delivery at 21 weeks gestation. Seventeen patients (89.4%) were identified with other sonographic markers associated with aneuploidy, in addition to EIF (Table 1). There were no abnormal karyotypes among the study population. There were no patients in the study group with abnormal results of maternal serum screening.
The prevalence of EIF in our study cohort was 14.8%. When compared to a previously published prevalence of 7.3%, there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.005).
Discussion
Schechter, in 1987, was the first author to note a hyperechoic focus within the left ventricular chamber that was associated with the chordae tendinae [4]. In a 1994 review of three fetuses with sonographic and pathologic correlation, Brown et. al. [15] found that EIF represents papillary muscle mineralization within the fetal heart.
Bromley et. al. in 1995 reported a 4.9% incidence of EIF among 1334 patients studied. They also found that 18% of fetuses with trisomy 21 had an EIF and that sonographic identification of an EIF had a fourfold increase risk of trisomy 21 [8]. Petrikovsky et. al. in 1995 reported a 3.6% incidence of EIF in 1139 patients, all of whom had a normal karyotype. The subjects in this study were not stratified by ethnic origin. Interestingly, the echogenic focus was present in all infants who underwent echocardiographic examination within the first three months of life [16]. In 1996, the same author failed to find any correlation between unusually appearing echogenic foci and adverse perinatal outcome [17].
Bromley et. al., in 1997, incorporated maternal age and the presence of EIF in the sonographic scoring index for the detection of trisomy 21 [13]. The same group in 1998 reported a 4.8% incidence of aneuploidy in 290 fetuses that had an EIF. In that study the incidence of aneuploidy in patients less than 35 years old was 3.6%. Only one of the 14 aneuploid fetuses had an echogenic intracardiac focus as the only sonographic marker, and this occurred in a woman older than 35 years [18]. Bromley, in 2002, reported similar findings focusing on the likelihood ratios (LR). With an isolated finding of EIF, there was a non-significant LR of 1.4 (95%CI 0.6 – 4.3) as compared to controls [19].
Smith-Bindman et. al., in a 2001 meta-analysis (a total of 56 studies describing 1930 fetuses with Down syndrome and 130,365 unaffected fetuses were included) of second trimester ultrasound to detect Down syndrome determined that when ultrasonographic markers were observed without associated fetal structural malformations, sensitivity for each one was low (range, 1%–16%), and most fetuses with such markers had normal outcomes [9]. Of the 5 studies in the meta-analysis that specifically looked at EIF there were a total of 5948 patients, 7.3% of whom had EIF.
In 2000, Shipp et. al. [7] reported on EIF and its correlation to maternal race. They reported a 30.4% prevalence of EIF in Asian patients. There, however, were only 46 (489 total patients) patients in the Asian cohort of their study. Additionally, there was no stratification of Asian patients into various geographic origins. So, it is not known whether they were mainly Japanese or mainly composed of patients of other Asian origin. The current study focuses on Japanese patients only and with a larger sample (148 vs. 49).
A recent meta-analysis by Sotiriadis, et. al [20], evaluated all comers races with eleven studies for a total of 51,831 pregnancies. Positive and negative likelihood ratios for an isolated finding of EIF were 5.4 and 0.81, respectively. Specificity was approximately 96%. However, a weakness of this meta-analysis is that many of the studies selected were of high risk subjects. In 2001, Nyberg [21] evaluated the ultrasound findings in 186 fetuses with trisomy 21 and 8728 controls. EIF was the most common marker found among affected fetuses after exclusion of major anomalies (7.1%). The positive LR for an isolated finding if EIF was 1.8. It is not clear why this is significantly lower than that found in the meta-analysis by Sotiriadis as it appears they both evaluated subjects of similar risk. The most likely explanation is the data from the meta-analysis more likely represents the true population given the larger numbers.
Limitations of the current study include a small sample size, the retrospective nature of the review, and the use of a meta-analysis sample that may not be truly representative of the general population. In general, studies of EIF are limited by factors such as technique, experience, and equipment. Our preliminary results revealed no increase in the incidence of aneuploidy despite an increased incidence of EIF. As there is not conclusive evidence in the literature that links isolated EIF to an increased risk of aneuploidy in low risk populations. Caution should be exerted when counseling these patients regarding these findings until there is general expert consensus or conclusive scientific evidence regarding this issue.
Conclusions
We report a 14.8% prevalence of EIF in patients of Japanese ancestry. When compared to a previously reported incidence of 7.3% in other low risk groups [9], there is a statistically significant difference. We identified a homogeneous ethnic group which may allow for a more conclusive analysis of this sub-population rather than broader groups based on racial dispositions. We conclude that there is an increased prevalence of EIF in patients of Japanese ancestry. Additionally, the positive predictive value for detecting aneuploidy in Japanese patients is likely even lower than other populations based on its higher prevalence. It is important to consider the LR of EIF both as an isolated and combined finding when counseling patients for invasive genetic diagnosis. Based on these results, invasive prenatal diagnosis for an isolated EIF in Japanese patients may not be warranted.
References
Drugan A, Johnson MP, Evans MI: Ultrasound screening for fetal chromosome anomalies. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 2000, 90: 98-107. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(20000117)90:2<98::AID-AJMG2>3.0.CO;2-H.
Hook EB: Chromosome-Abnormalities in Older Women by Maternal Age - Evaluation of Regression-Derived Rates in Chorionic Villus Biopsy Specimens. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1990, 35: 184-187.
Snijders RJM, Shawa L, Nicolaides KH: Fetal Choroid-Plexus Cysts and Trisomy-18 - Assessment of Risk-Based on Ultrasound Findings and Maternal Age. Prenatal Diagnosis. 1994, 14: 1119-1127.
Lehman CD, Nyberg DA, Winter TC, Kapur RP, Resta RG, Luthy DA: Trisomy-13-Syndrome - Prenatal Us Findings in A Review of 33 Cases. Radiology. 1995, 194: 217-222.
Winter TC, Anderson AM, Cheng EY, Komarniski CA, Souter VL, Uhrich SB, Nyberg DA: Echogenic intracardiac focus in 2nd-trimester fetuses with trisomy 21: Usefulness as a US marker. Radiology. 2000, 216: 450-456.
Bettelheim D, Deutinger J, Bernaschek G: The value of echogenic foci ('golfballs') in the fetal heart as a marker of chromosomal abnormalities. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1999, 14: 98-100. 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1999.14020098.x.
Shipp TD, Bromley B, Lieberman E, Benacerraf BR: The frequency of the detection of fetal echogenic intracardiac foci with respect to maternal race. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2000, 15: 460-462. 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2000.00138.x.
Bromley B, Lieberman E, Laboda L, Benacerraf BR: Echogenic Intracardiac Focus - A Sonographic Sign for Fetal Down-Syndrome. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1995, 86: 998-1001. 10.1016/0029-7844(95)00323-J.
Smith-Bindman R, Hosmer W, Feldstein VA, Deeks JJ, Goldberg JD: Second-trimester ultrasound to detect fetuses with Down syndrome - A meta-analysis. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2001, 285: 1044-1055. 10.1001/jama.285.8.1044.
Vibhakar NI, Budorick NE, Scioscia AL, Harby LD, Mullen ML, Sklansky MS: Prevalence of aneuploidy with a cardiac intraventricular echogenic focus in an at-risk patient population. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 1999, 18: 265-268.
Nyberg DA, Luthy DA, Resta RG, Nyberg BC, Williams MA: Age-adjusted ultrasound risk assessment for fetal Down's syndrome during the second trimester: description of the method and analysis of 142 cases. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1998, 12: 8-14. 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1998.12010008.x.
Manning JE, Ragavendra N, Sayre J, Laifer-Narin SL, Melany ML, Grant EG, Crandall BF: Significance of fetal intracardiac echogenic foci in relation to trisomy 21: A prospective sonographic study of high-risk pregnant women. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1998, 170: 1083-1084.
Bromley B, Lieberman E, Benacerraf BR: The incorporation of maternal age into the sonographic scoring index for the detection at 14-20 weeks of fetuses with Down's syndrome. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1997, 10: 321-324. 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1997.10050321.x.
Schechter AG, Fakhry J, Shapiro LR, Gewitz MH: In utero thickening of the chordae tendinae. A cause of intracardiac echogenic foci. J Ultrasound Med. 1987, 6: 691-695.
Brown DL, Roberts DJ, Miller WA: Left-Ventricular Echogenic Focus in the Fetal Heart - Pathological Correlation. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 1994, 13: 613-616.
Petrikovsky BM, Challenger M, Wyse LJ: Natural-History of Echogenic Foci Within Ventricles of the Fetal Heart. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1995, 5: 92-94. 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1995.05020092.x.
Petrikovsky B, Challenger M, Gross B: Unusual appearances of echogenic foci within the fetal heart: Are they benign?. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1996, 8: 229-231. 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1996.08040229.x.
Bromley B, Lieberman E, Shipp TD, Richardson M, Benacerraf BR: Significance of an echogenic intracardiac focus in fetuses at high and low risk for aneuploidy. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 1998, 17: 127-131.
Bromley B, Lieberman E, Shipp TD, Benacerraf BR: The genetic sonogram - A method of risk assessment for Down syndrome in the second trimester. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2002, 21: 1087-1096.
Sotiriadis A, Makrydimas G, Ioannidis JP: Diagnostic performance of intracardiac echogenic foci for Down syndrome: a meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2003, 101: 1009-1016. 10.1016/S0029-7844(03)00168-6.
Nyberg DA, Souter VL, El Bastawissi A, Young S, Luthhardt F, Luthy DA: Isolated sonographic markers for detection of fetal Down syndrome in the second trimester of pregnancy. J Ultrasound Med. 2001, 20: 1053-1063.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2393/4/12/prepub
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
None declared.
Authors' contributions
AR designed the protocol, supervised the project, and collected the data; KL prepared and revised the manuscript; EF supervised the analysis and revised the manuscript SM performed the ultrasounds and assisted in data collection; MP designed the protocol and supervised the project
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Rebarber, A., Levey, K.A., Funai, E. et al. An ethnic predilection for fetal echogenic intracardiac focus identified during targeted midtrimester ultrasound examination: A retrospective review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 4, 12 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-4-12
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-4-12