Abstract
Background
Rotavirus affects 95% of children worldwide by age 5 years and is the leading cause of severe dehydrating diarrhea. The objective of this review was to estimate the burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE) in the Western European pediatric population.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search (1999-2010) was conducted in PubMed and other sources (CDC; WHO, others). Data on the epidemiology and burden of RVGE among children < 5 years-old in Western Europe --including hospital-acquired disease--were extracted.
Results
76 studies from 16 countries were identified. The mean percentage of acute gastroenteritis (AGE) cases caused by rotavirus ranged from 25.3%-63.5% in children < 5 years of age, peaking during winter. Incidence rates of RVGE ranged from 1.33-4.96 cases/100 person- years. Hospitalization rates for RVGE ranged from 7% to 81% among infected children, depending on the country. Nosocomial RVGE accounted for 47%-69% of all hospital-acquired AGE and prolonged hospital stays by 4-12 days. Each year, RVGE incurred $0.54- $53.6 million in direct medical costs and $1.7-$22.4 million in indirect costs in the 16 countries studied. Full serotyping data was available for 8 countries. G1P[8], G2P[4], G9P[8], and G3P[8] were the most prevalent serotypes (cumulative frequency: 57.2%- 98.7%). Serotype distribution in nosocomial RVGE was similar.
Conclusions
This review confirms that RVGE is a common disease associated with significant morbidity and costs across Western Europe. A vaccine protecting against multiple serotypes may decrease the epidemiological and cost burden of RVGE in Western Europe.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Rotavirus affects 95% of all non-vaccinated children worldwide by the age of five years, and is the leading cause of severe dehydrating diarrhea in that age group [1, 2]. Among the 23.6 million children under five years of age in the European Union, it is estimated that 3.6 million episodes of rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE) occur annually [3]. Transmitted by the fecal-oral route, most rotavirus infections are community-acquired, however nosocomial infections are a major component of hospital-acquired infections in children [4]. In a review from six countries in Europe in 2006, RVGE was reported as the major etiologic agent of pediatric nosocomial diarrhea, accounting for 31-87% of cases [4].
Rotavirus infection peaks in the winter months between November and February in temperate climates [1, 4, 5]. The predominance of a particular rotavirus genotype combination during an RVGE season may vary between geographical areas, and from one season to the next [6]. Of the seven sero-groups of rotavirus (groups A-G), three are capable of affecting humans (groups A-C). Group A rotavirus infections are the most common [5]; they are further classified into G- and P-types [7]. Rotavirus carrying either G1, G2, G3, G4, or G9 genotypes combined with P[4] or P[8] genotypes are currently the most common causes of RVGE in humans representing more than 90% of all RVGE cases observed in Europe, with G12 an emergent genotype [8].
Within the European Union, RVGE is estimated to occur at a rate of 1 symptomatic infection in every 7 children each year, accounting for 231 deaths, more than 87,000 hospitalizations and almost 700,000 outpatient visits [3]. Many episodes of RVGE are mild enough to be managed at home, however, within Europe, approximately 20% of children will see a medical practitioner during the illness, and an estimated 1 in 54 cases will result in hospitalization [3]. RVGE imposes a heavy economic burden by incurring not only direct (consultation, emergency, hospitalization, medication) costs, but also indirect costs (parent work days lost, childcare, etc....) [3, 9, 10].
Objectives of study
The objective of this study was to carry out a comprehensive scoping review of the recent literature on the burden of pediatric RVGE, both nosocomial and community-acquired, in Western Europe. We examined the epidemiology of RVGE, the distribution of rotavirus genotype combinations, morbidity and mortality due to RVGE, resources utilization and costs by country and according to healthcare setting.
Methods
Literature search strategy
A comprehensive literature search was conducted for studies pertaining to the burden of rotavirus infection on the pediatric population in Western Europe (< 5 years, unless otherwise specified). The searches, limited to articles published between 1st January 1999 and 1st May 2010, were carried out in the National Library of Medicine's Pubmed, the Center for Disease Control (CDC) rotavirus global surveillance http://www.cdc.gov/rotavirus/global_surveillance/surveillance.htm, and the World Health Organization (WHO) http://www.who.int/nuvi/rotavirus/en/. Studies were included if they were set in the following countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom (UK). The search terms used for this scoping review included: rotavirus, outcome, mortality, death, incidence, prevalence, nosocomial, home care, serotype, strain, cost, economic, burden, and resource use, where the asterisk represents a wildcard. English language articles were primarily reviewed along with promising articles in other languages. In addition, records were searched manually to identify the most relevant studies pertaining to the object of this document and bibliographies of retrieved articles were screened to identify additional sources of information.
Data extraction and analysis
For all studies, the dates reported refer to when studies were conducted, which was often several years before the publication date. Where data was available for an individual country within a multicountry study, both overall and data delineated by country were extracted. Where available, information was reported for both community-acquired and nosocomial RVGE, and from hospital, primary care or home care settings. An RVGE episode was considered to be nosocomial (hospital-acquired) if gastroenteritis symptoms occurred at least 48 h after children were admitted to hospital for a diagnosis other than diarrhea [4].
Epidemiology of RVGE
Incidence data was extracted as cases of RVGE per 100 patient-years for countries of interest. Information on incidence from studies conducted in a day-care setting and for nosocomial infection was captured separately. Where incidence data was reported as per child month, the original data were reported. In addition data was converted to person-years, for ease of comparison between settings. Likewise, incidence of nosocomial disease reported as cases per 1000 days of hospitalization was also provided as cases per 100 person-years in hospital.
The proportion of RVGE among cases of acute gastroenteritis was extracted. In the case where several surveillance studies were published for a single country, a pooled average of the proportion of RVGE among cases of acute gastroenteritis was calculated and reported, along with ranges across studies for each country. If available, the variation over time in the proportion of RVGE among cases of gastroenteritis was captured.
Data on infection seasonality was collected and reported.
Rotavirus genotype combinations
The proportion of each genotype combination among genotyped RVGE samples was extracted, where available. The most recently available studies from each country were used to gather information about the distribution of genotype combinations across the countries of interest. In addition, data concerning changes in the prevalence of genotype combinations over time was collected, as was any reference to emerging serotypes.
Morbidity and mortality
To assess disease severity, two types of data were extracted, where available. Firstly, the severity and proportion of patients suffering from dehydration due to RVGE was captured and secondly, disease severity as measured by the 20-point Vesikari scoring system [11]. The Vesikari scale is based on the duration and intensity of diarrhea and vomiting, intensity of fever and dehydration, and need for treatment and hospitalization [11]. A Vesikari score ≥ 11 is indicative of severe disease [11].
Mortality due to RVGE was captured as annual fatalities and mortality rates per 100,000 children less than five years of age.
Disease burden
For healthcare resource utilization, data on hospital admission rates, need for intravenous rehydration, and duration of hospital stay were collected. Hospitalization due to RVGE was defined as hospital admission of children presenting to hospital with severe acute community-acquired RVGE [12]. Cost-of-illness data captured included direct medical costs, out-of-pocket expenditures, and indirect costs attributed to lost productivity by parents of children suffering from RVGE. Costs are reported in 2009 US dollars (1 $US equals 0.721189 € [1st Jan 2009]) [13]. In addition, where a national cost estimate for the total cost of RVGE was available, we have presented the total cost of illness as a proportion of the gross national product of that country, to enable comparison between countries. The gross national product for each country for 2009 was obtained from the World Bank at http://data.worldbank.org/data-catalog [14].
Results
Literature review
Study selection
As shown in Figure 1, a total of 76 studies containing relevant data pertaining to RVGE in children under five years of age were captured. Studies were included on the following topics: incidence (n = 16 studies), proportion of RVGE among cases of acute gastroenteritis (n = 38 studies), seasonality of RVGE infection (n = 36 studies), serotype distribution (n = 25), disease severity (n = 20), mortality (n = 9), healthcare resource utilization (n = 36), and costs (n = 17). More than one type of data was available from a single study; hence the total number of studies is not the sum of those for each topic. A study was excluded if it was not carried out in humans, was a duplicate of what was already included, was not from a country of interest, did not include children under five years of age, if there were no original data (i.e. a review), or if data did not meet the criteria given above.
Overview of evidence available
An overview of the evidence available for each country is presented in Table 1, and detail about each study selected is given in the Additional file 1. Epidemiological data for RVGE in Western Europe was available from a total of 52 studies covering incidence, the proportion of RVGE among acute gastroenteritis cases, and seasonality of infection.
Epidemiology of RVGE
Incidence of community-acquired RVGE
The annual incidence of community-acquired RVGE among children under five years of age (per 100 person years) was reported in seven countries [15–19], ranging from 1.33 cases per 100 person-years (in Austria) to 4.96 cases per 100 person-years (in France) [15–19]. The incidence of RVGE was approximately 12-fold higher among children under three years of age in a daycare setting--between 2.2 and 2.5 cases per 100 child-months (26.4-30 cases per 100 person-years)--than for children in community-based studies [20, 21].
Home care setting
A high number of children with RVGE are not sick enough to be admitted to hospital and many patients receive no medical care [22]. Since rotavirus infection is not a notifiable disease and the exact diagnosis is not needed for individual patient management, the incidence rates given above may be an underestimate of the total disease incidence, and refer only to patients requiring medical attention. Examination of the literature showed that data concerning RVGE patients treated at home is sparse, most studies estimated the proportion of patients with RVGE receiving home care. For Europe, estimations of the proportion of RVGE patients receiving no medical care ranged from 25% to 51% of patients [3, 23, 24]. Two studies from a day care setting in France reported that 34.6% and 14.3% of RVGE cases, respectively, did not seek medical attention [20, 21].
Incidence of nosocomial RVGE
The incidence of nosocomial infection with RVGE reported among the hospitalized pediatric population was also higher than the incidence reported in community based studies [25]. A prospective study by Forster et al. that examined the incidence of RVGE among patients under five years old in hospitals from five countries (France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK) reported an overall incidence of nosocomial RVGE of 0.46 per 1000 days of hospitalization (16.8 per 100 person-years in hospital) [25]. The range across countries varied from 0 to 1.87 cases per 1000 days of hospitalization (0-68.2 per 100 person-years in hospital) [25]. Other studies from Austria, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Switzerland reported incidence rates for nosocomial RVGE within the range reported by the Forster study [15, 26–33].
Proportion of community-acquired RVGE
When limited to those studies that reported the proportion of community-acquired RVGE among reported gastroenteritis cases for children under five years of age, the mean percentage of cases caused by rotavirus infection ranged from 25.3% to 63.5%. Greece reported the lowest proportion (25.3%), while those with the highest proportion included Norway (63.5%) and Sweden (52.0%). The remainder of the countries reported a percentage of between 36% and 45% (Figure 2). These rates vary greatly depending on whether patients are seen in hospital, emergency room, or primary care physician clinic.
The REVEAL study, carried out in Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the UK, reported that RVGE in children under five years of age was responsible for between 53.0% and 68.9% of cases presenting to hospitals, 35.4% and 63.3% for those seen in emergency departments, and 7.7% and 41.3% of cases seeking primary care physicians [34]. A second prospective multicenter study of children under five years of age from France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK reported that the overall proportion of community-acquired rotavirus infections among reported hospitalized and ED acute gastroenteritis cases across the five countries was 43.4% [25]. Most of these cases (80.9%) occurred in children under 2 years of age [25]. In the REVEAL study, 86.1% of RVGE cases occurred in children aged between 3 months and 3 years of age while a larger study from EuroRotaNet reported that 81.5% of cases from 19 European countries were in patients under 2.5 years of age [35, 36].
Proportion of nosocomial RVGE
Only a few methodologically weak studies were identified relating to the prevalence of nosocomial RVGE among children hospitalized for other conditions, or the proportion of acute nosocomial gastroenteritis that was due to rotavirus. In the original reports, nosocomial RVGE was generally defined as disease occurring between 48 to 72 h after admission of the child to hospital, depending on the study [15, 26, 37]. The prevalence of nosocomial rotavirus infections among hospitalized children admitted for a diagnosis other than diarrhea ranged from 2.9% to 6.6% in four studies from France [26, 27, 37, 38]. Three studies from five countries (Austria, France, Germany, Spain and Switzerland) examined the proportion of nosocomial RVGE among cases of acute nosocomial gastroenteritis [15, 26, 30]. Nosocomial RVGE accounted for between 47% and 69% of all hospital-acquired acute gastroenteritis among hospitalized children in the studies covering Austria, Germany, Spain and Switzerland [15, 30]. In one French study conducted in 1999 during the peak of the rotavirus season, 97.8% of nosocomial diarrhea cases were due to rotavirus [26]. A comparison of community-acquired RVGE and nosocomial RVGE was carried out in a study from Austria, Germany and Switzerland [15]. Rotavirus was detected in 29.5%, 27% and 37.5% of children with community-acquired gastroenteritis, and in 57%, 69% and 49% of children with nosocomial gastroenteritis, in Austria, Germany and Switzerland, respectively [15]. The seasonality of nosocomial RVGE mirrored that of RVGE in the broader community, with most infections taking place in the winter months [15, 25–27, 29, 30, 39–42].
Patients with nosocomial disease were generally younger than those who acquired RVGE in the community [15, 26, 29, 42, 43]. Between 42.7% and 69.9% of children affected by nosocomial RVGE were under 6 months of age (mainly neonates) compared with 15.9% to 33.6% of patients with community-acquired disease [25, 42]. Across three studies covering five countries (Austria, France, Switzerland, Germany and Sweden), the median age of patients with nosocomial RVGE was between 2.8 and 9 months compared to a median age of between 12.5 and 16.7 months for patients with community-acquired RVGE [15, 39, 43]. Four risk factors were reported to be strongly associated with nosocomial RVGE in neonatal intensive care units including premature birth (Odds Ratio [OR]: 2.63; P < 0.001), infections other than rotavirus (OR: 2.35; P < 0.01), malformation (OR: 2.38; P < 0.01), and changes in glycemia and/or presence of jaundice (OR: 7.63; P < 0.001) [33].
Seasonality of RVGE
For most countries in Western Europe, RVGE was reported to occur most often during the winter and spring, from December to April or May. A slightly later rotavirus season was noted in Ireland (February to June), Greece (January to April), and Scandinavian countries (Denmark: January to June; Norway: March to May; Sweden: April) [23, 36, 44–48] No clear trend was found in relation to geographical or climatological parameters.
Rotavirus genotype combinations
Distribution of genotype combinations
Community-acquired RVGE
The predominant serotype of rotavirus causing RVGE varies from country to country and from year to year. The most recent serotype data from each country is presented here. Only one genotype combination (G1P[8]) was reported in all eight countries for which full serotyping data is available (Austria, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, Spain and the UK). G1P[8] was the most common genotype combination in Austria [15], Denmark [36]. France [36], Germany [25], Spain [25, 36], and the UK [36], accounting for between 48.6% and 84.7% of genotyped RVGE samples in those countries.
Nosocomial RVGE
The distribution of rotavirus genotype combinations among patients with nosocomial RVGE was reported in four studies covering seven countries (Austria, France, Germany, Italy, Spain Switzerland and the UK) [15, 25, 30, 49]. In general, the distribution of rotavirus genotype combinations among patients with nosocomial RVGE was very similar to the distribution among patients with community-acquired disease from the same study [15, 25, 30, 49]. For example, in a prospective multicenter study from France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK, G1P[8] accounted for 40.3% of genotyped samples among patients with community-acquired RVGE and 35% of nosocomial RVGE [25]. Similarly in the same study, G9P[8] accounted for 31.2% of community-acquired RVGE and 36.3% of nosocomial RVGE, and the proportions of other genotype combinations were similar [25].
Evolution over time of genotype combinations
Community-acquired RVGE
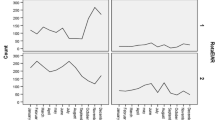
Information concerning serotype distribution over time for fully serotyped samples from children under five years of age was available for five countries (Denmark [36, 50], France [25, 36, 51], Italy [25, 52, 53], Spain [25, 30, 36, 54], and the UK [25, 36, 55, 56]) (Figure 3). However, on examination of the evolution of genotype distribution and predominance over time, we were not able to discern any overall trends in serotype distribution within the region. This is because serotype predominance appears to change on a season to season basis within each country, and may even differ from region to region within the same country.
Nosocomial RVGE
No studies examined the distribution of genotype combinations among patients with nosocomial RVGE over time.
Emerging rotavirus serotypes in Western Europe
Four studies, three from Italy and one from Spain described the emergence of new rotavirus serotypes in Western Europe [52, 54, 57, 58]. The emergence of the G9 serotype was documented in the winter season of 1999-2000 in Southern Italy (19% of all rotaviruses) [59], becoming then most prevalent in other European regions An earlier study from Barcelona, Spain, documented an increase in the levels of strains G1P[4] and G3P[4], which were considered uncommon at the time of the study (1998-1999). Additionally, two G5 strains were isolated in Barcelona; the origin of these G5 strains (porcine or human) was unclear [54]. G12P[8], an emerging potential human pathogen,[8] was documented in Denmark in 2002 (4.1% of all rotaviruses) and the UK (2.4%),[36] and was detected in very small proportions (< 1%) in France[36, 51] and Spain [36].
Morbidity and mortality
Disease severity
Community-acquired RVGE
Disease severity assessment using the 20-point Vesikari scale was reported by seven studies covering eight countries [15, 17, 20, 25, 31, 46]. In France and Greece, the proportion of children infected by rotavirus having moderate to severe gastroenteritis was significantly higher compared to children with non-rotavirus infection (82.8% vs 37.2% [P < .0001] in France; 65.4% vs 41.2% [P < .01] in Greece) [17, 46]. The proportion of patients presenting to hospitals with severe acute community-acquired RVGE (Vesikari score ≥ 11) was between 29% and 55% in a study covering Austria, Germany, and Switzerland; a study set in France, Italy, Spain and the UK reported an overall proportion of severe disease of 53.3% [15, 25].
Nosocomial RVGE
For patients with hospital-acquired infection, the overall proportion of patients with severe RVGE in France, Italy, Spain and the UK was 42.6%, while for Austria, Germany, and Switzerland severe infection affected 24.4%, 30.2% and 40%, respectively [15, 25].
Community-acquired versus nosocomial RVGE
In a study from Austria, Germany, and Switzerland, overall disease severity scores, by country, were similar in community-acquired (median score: 9-11) and nosocomial RVGE (median score: 8-9) [15]. When community-acquired RVGE and non-RVGE were compared, disease severity scores were significantly higher for rotavirus-positive gastroenteritis with a median score of 11 in Austria (vs 7 for non-rotavirus; P < .001) [31], and a mean score of 12.14 in France (vs 6.93 for non-rotavirus, P < .0001) [20].
Dehydration in community-acquired RVGE
The REVEAL study reported that the proportion of children with dehydration due to acute RVGE varied between 11.1% (Spain) and 71.4% (Sweden), and in most countries, was considerably higher than for those with rotavirus-negative disease [34]. In Belgium and the UK, the prevalence of dehydration was comparable among children with or without RVGE [34], whereas the dehydration prevalence ratio of rotavirus versus non-rotavirus disease was 1.82, 5.54, 3.27, 3.47, and 2.18, respectively, in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Sweden [34]. A second prospective multicenter study from France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK reported that dehydration was evident in 75.7% of patients with RVGE, and was severe in 11.3% of them [25]. In comparison, only 54.5% of children with non-RVGE were dehydrated, while 4.7% had severe dehydration [25]. Another study from France confirmed this trend, showing significant differences in dehydration between rotavirus-positive and negative gastroenteritis (26.8% vs.14.7%, P < .0001) as did a study from Greece [17, 46]. Further, one Italian community-based study showed that dehydration at initial presentation in primary care was associated with a higher likelihood of RVGE (OR: 1.8; 95% CI, 1.1-3; P = 0.02) [53].
Dehydration in community-acquired versus nosocomial RVGE
Only two studies compared the proportion of patients with dehydration for community-acquired RVGE with those for nosocomial infection; in both studies more patients with community-acquired disease experienced dehydration [43, 60]. In an Irish study, 80% of patients with community-acquired disease were dehydrated versus only 55% with nosocomial disease [60]. Likewise, in a study from Sweden, 10.8% of patients with community-acquired RVGE had either hypertonic dehydration, or severe dehydration needing intensive care treatment compared to only 0.8% of patients with nosocomial RVGE [43].
Mortality
Rotavirus fatalities were rare among young children in Western Europe with less than 10 deaths occurring per year in most countries [61], but appeared to pose a greater risk for children of younger age. For example, mortality due to nosocomial RVGE was highest among children less than 12 months of age compared to older ones (0.74 per 100,000 vs 0.16 per 100,000 children < 5 years per year), as suggested by a study from Spain [29].
Disease burden
Resource utilization
Community-acquired RVGE
In the REVEAL study, the proportions of hospital and emergency referrals among children presenting at primary care with acute RVGE ranged from 13.0% (relative risk [RR]: 3.37; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.77-6.43) to 57.1% (RR: 2.10; 95% CI: 0.92-4.75), and from 6.1% to 45.3% (RR: 2.80; 95% CI: 1.68-4.67), respectively, for all countries included in the study [34]. Additional country-specific studies reporting hospital admission rates for community-acquired disease due to acute RVGE were retrieved (France 81% [62]; Germany 7% [15]; Italy 11.2% [19]; Spain 9.2% [12]). In Greece, hospital admissions due to RVGE were significantly more frequent than non-RVGE (51.4% vs 22% non-rotavirus; P < 0.01) [46].
In the REVEAL study, hospital stay due to acute RVGE ranged from 2.5 days (Sweden) to 5.0 days in Germany [34]. In Denmark, 63% of young children hospitalised for rotavirus associated disease stayed for 3 days or less [45]. In France, hospitalization due to RVGE was longer than for other viral gastroenteritis cases [63].
Nosocomial RVGE
As reported in several studies, nosocomial rotavirus infection prolonged hospital stay, by 4.4 days in Belgium and Italy (national registry data) [64, 65], and between 9 and 12 days in Ireland [44, 60]. In France, nosocomial RVGE caused statistically significant prolongation of hospital stay, as reported in a prospective observational multicentre study (10 vs 3.9 days; P < .001) [26].
Costs
Cost of illness and productivity loss data due to RVGE was available from several studies in Western Europe (Table 2).
Hospital setting
In the REVEAL study, acute RVGE was associated with direct medical costs per patient ranging from $1,942 (UK) to $2,389 (Sweden) (Table 2) [68]. In the same setting, indirect costs including work days lost by parents of children hospitalized for RVGE as well as out-of-pocket expenses ranged between $260 (France) and $1,061 (UK) [68]. A portion of indirect costs was attributed to work days lost by parents per hospitalization episode, which varied between 2.3 days (France) and 6.4 days (Germany) [68].
Primary care setting
Indirect costs attributed to out-of-pocket expenses and work days lost by parents of children with RVGE ranged between $194 (Spain) and $623 (Belgium) (Table 2) [68]. In this setting, work days lost by parents per episode of RVGE varied between 3.4 days (France) and 7.5 days (UK) [68].
Home care setting
Cost data of RVGE management among children who do not seek medical care is limited (Table 2) [21, 24, 64, 67]. In France and Belgium, direct medical costs relating to the routine medical care of RVGE patients (over-the-counter medication) varied between $10 and $24 per patient [24, 64, 67]. A prospective study estimated the cost of care of children affected by RVGE while attending day care centers at $27; this estimate included the cost of over-the-counter medication, extra diapers, and parent work days lost [21]. Finally, in Belgium, an economic analysis estimated at $937,231 the annual burden of rotavirus disease among children less than 7 years of age in the home care setting [67].
National cost estimates
In Western Europe, rotavirus disease incurred direct medical costs of $543,775 (Italy) [65] to $53.6 million (Spain) [29] each year, and between $1.7 million (Italy) [65] and $22.4 million (Belgium) [64] in indirect costs (Table 2).
Discussion
Based on the currently available literature on rotavirus burden in Western Europe, this analysis revealed that incidence rates for RVGE in the under five year old population ranged between 1.33 and 4.96 cases per 100 person-years [15–19]. However, the incidence rate of RVGE is likely underestimated as many patients receive care at home. Estimation of the proportion of RVGE patients receiving no medical care ranged from 25% to 51% of patients [3, 23, 24]. Accurate estimates of total incidence rates accounting for all these RVGE cases were not possible due to the limited availability of epidemiological data from community-based cohort studies. The incidence of nosocomial infection due to RVGE reported among the hospitalized pediatric population is higher than the incidence reported in community-based studies ranging from 0 to 1.87 cases per 1000 days of hospitalization (0-68.2 per 100 person-years in hospital) depending on the country [25].
The prevalence of rotavirus infection varied from country to country. Among the pediatric population, community-acquired rotavirus infection accounts for between 25.3% (in Greece) to 63.5% (in Sweden) of acute gastroenteritis cases [77–79]. These variations may reflect actual differences in the proportion of RVGE and incidence of rotaviral disease, however, variations in the design of the studies captured in the review limits comparability across countries. Nosocomial RVGE accounted for between 47% and 69% of all hospital-acquired acute gastroenteritis among hospitalized children except in one study, conducted in France during the peak of the rotavirus season, where 97% of nosocomial diarrhea cases were due to rotavirus [15, 26, 30]. For most countries in Western Europe, the season for RVGE was reported to occur in the winter from December to April or May. A slightly later rotavirus season was noted in Ireland, Greece and Scandinavian countries. Nosocomial infection mirrored the seasonality of the community-acquired disease.
The most commonly isolated genotype combinations in the Western European region were G1P[8], G2P[4], and G9P[8] according to the most recent studies available for each country. G2P[8] and G3P[8] were also widespread in the region. Genotype combinations G1P[4], G4P[9], G9P[9], G9P[4], and G2P[10] were each reported in only one country. Non-typable and partially typed serotypes accounted for between 0.0% and 3.8% of all serotypes in studies where these were reported. In general, the distribution of rotavirus genotype combinations among patients with nosocomial RVGE was very similar to the distribution among patients with community-acquired disease from the same study [15, 25, 30, 49].
While several studies tracked the evolution of genotype distribution and predominance over time, we were not able to discern any overall trends in serotype distribution within the region. This is because serotype predominance appears to change on a season to season basis within each country, and may even differ from region to region within the same country. Emerging rotavirus serotypes were rarely reported in Italy and Spain.
Rotavirus fatalities were rare across the region with less than 10 deaths occurring per year in most countries among children under five years old; therefore, few studies included mortality data for RVGE. Mortality due to nosocomial RVGE was higher, reaching 0.74 per 100,000 children-year among children of less than 12 months of age compared to 0.16 per 100,000 children-year for those < 5 years) [29]. Comparison with a global literature review of mortality due to rotavirus shows that all of the countries in Western Europe have some of the lowest mortality rates globally [22]. A recent literature review of rotavirus burden of illness in the Middle East and North Africa reported annual mortality rates of between 0 and 112 per 100,000 children under five years of age depending on the country [80].
Resource utilization by rotavirus infected patients is generally higher than for non-RVGE related disease. Hospital admission for gastroenteritis is significantly more likely to happen in RV induced infections than for non-RV related disease [46] and, when compared to non-RVGE, RVGE is associated with significantly higher disease severity scores [20, 31]. Intravenous rehydration was more commonly administered to patients with acute RVGE in an emergency department or hospital setting, compared to patients with non-rotavirus disease, reflecting the higher level of dehydration in RVGE patients [25, 34]. In addition, hospitalization due to RVGE was longer than for other viral gastroenteritis causes [63].
Overall, the duration of hospital stay ranged between 2.5 days to 5.0 days for patients with community-acquired RVGE while nosocomial RVGE infection prolonged hospital stay by 4.4 days [68]. However, similar disease severity scores were reported for community-acquired and nosocomial RVGE. Little data is available concerning dehydration in nosocomial cases.
The cost of illness and productivity loss due to RVGE is large. Overall, at the country level, direct medical costs due to RVGE ranged between $543,775 and $53.6 million according to the size of the pediatric population and the type of health care provided, while indirect costs accounted for an additional $1.7 million to $22.4 million, annually [29, 64, 65]. Cost per patient varied by setting, with patients hospitalized for RVGE incurring the highest direct and indirect costs, and patients treated at home incurring the lowest costs; however, data pertaining to the cost of RVGE management among children who do not seek medical care is limited [21, 24, 64, 67, 68].
Limitations
Study limitations include the lack of available information on the burden of RVGE in terms of mortality, nosocomial diseases and home care; in addition, only few studies examining morbidity and economic burden were available, which restricted the evaluation of the global burden for the region. To describe and compare serotype distribution across countries, the most recent available data was considered, however, in some countries the only available data was not recent and thus did not cover the same time frame. Finally, the comparability of the data reported in this review depends on several methodological aspects such as study settings, period of observation, inclusion criteria for children, and the definition of nosocomial, which vary from study to study. Research is this area is ongoing [81–85] and reflects constant interest in assessing the RVGE burden in Western Europe in countries with limited access to vaccination due to low coverage rates or absence of country specific recommendations for vaccination.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RVGE is a common disease in Western Europe affecting the pediatric population. Data on the burden of RVGE in terms of mortality and home care is very limited for this region and while data on nosocomial infection is available variations in study setting and design may affect comparability of data. While 95% of cases are due to the main five genotypes, analysis of the evolution of different serotypes over time shows that the dominance of a certain serotype can change dramatically from year to year and from country to country. Vaccination programs may help to reduce the infection rates of this disease; a vaccine with broad and consistent serotype coverage would be important to help decrease the burden of RVGE in Western Europe.
References
Parashar UD, Bresee JS, Gentsch JR, Glass RI: Rotavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998, 4: 561-570. 10.3201/eid0404.980406.
Widdowson M-A, Steele D, Vojdani J, Wecker J, Parashar UD: Global rotavirus surveillance: preparing for the introduction of rotavirus vaccines. J Infect Dis. 2009, 200: S1-S8. 10.1086/605061.
Soriano-Gabarro M, Mrukowicz J, Vesikari T, Verstraeten T: Burden of rotavirus disease in European Union countries. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006, 25: S7-S11. 10.1097/01.inf.0000197622.98559.01.
Gleizes O, Desselberger U, Tatochenko V, Rodrigo C, Salman N, Mezner Z, Giaquinto C, Grimprel E: Nosocomial rotavirus infection in European countries: a review of the epidemiology, severity and economic burden of hospital-acquired rotavirus disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006, 25: S12-S21. 10.1097/01.inf.0000197563.03895.91.
Diggle L: Rotavirus diarrhoea and future prospects for prevention. Br J Nurs. 2007, 16: 970-974.
Iturriza-Gomara M, Green J, Brown DW, Ramsay M, Desselberger U, Gray JJ: Molecular epidemiology of human group A rotavirus infections in the United Kingdom between 1995 and 1998. J Clin Microbiol. 2000, 38: 4394-4401.
Iturriza-Gomara M, Kang G, Gray J: Rotavirus genotyping: keeping up with an evolving population of human rotaviruses. J Clin Virol. 2004, 31: 259-265. 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.04.009.
Matthijnssens J, Rahman M, Ciarlet M, Van Ranst M: Emerging Human Rotavirus Genotypes. Viruses in the Environment. Edited by: Palumbo E, Kirkwood C. 2009, Kerala, India: Research Signpost, 171-219.
Grimwood K, Lambert SB: Rotavirus vaccines: opportunities and challenges. Hum Vaccin. 2009, 5: 57-69. 10.4161/hv.5.2.6924.
External review of burden of disease attributable to rotavirus. [http://www.who.int/immunization_monitoring/burden/Rota_virus_Q5_mortality_esti-mates_external_review_report_2006_may.pdf]
Ruuska T, Vesikari T: Rotavirus disease in Finnish children: use of numerical scores for clinical severity of diarrhoeal episodes. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990, 22: 259-267. 10.3109/00365549009027046.
Cilla G, Gomariz M, Montes M, Mendiburu MI, Perez-Yarza EG, Perez-Trallero E: Incidence of hospitalization due to community-acquired rotavirus infection: a 12-year study (1996-2008). Epidemiol Infect. 2010, 1-7.
Historic exchange rates. [http://www.x-rates.com/cgi-bin/hlookup.cgi]
Gross domestic product 2009. [http://data.worldbank.org/data-catalog]
Fruhwirth M, Heininger U, Ehlken B, Petersen G, Laubereau B, Moll-Schuler I, Mutz I, Forster J: International variation in disease burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children with community- and nosocomially acquired infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001, 20: 784-791. 10.1097/00006454-200108000-00013.
Van Damme P, Giaquinto C, Huet F, Gothefors L, Maxwell M, Van der WM: Multicenter prospective study of the burden of rotavirus acute gastroenteritis in Europe, 2004-2005: the REVEAL study. J Infect Dis. 2007, 195 (Suppl 1): S4-S16.
Huet F, Chouchane M, Cremillieux C, Aubert M, Caulin E, Pothier P, Allaert FA: Prospective epidemiological study of rotavirus gastroenteritis in Europe (REVEAL study). Results in the French area of the study. Arch Pediatr. 2008, 15: 362-374. 10.1016/j.arcped.2008.01.021.
Karsten C, Baumgarte S, Friedrich AW, von Eiff C, Becker K, Wosniok W, Ammon A, Bockemuhl J, Karch H, Huppertz HI: Incidence and risk factors for community-acquired acute gastroenteritis in north-west Germany in 2004. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009, 28: 935-943. 10.1007/s10096-009-0729-1.
Giaquinto C, Callegaro S, Andreola B, Bernuzzi M, Cantarutti L, D'Elia R, Drago S, De Marchi A, Falconi P, Felice M, et al: Prospective study of the burden of acute gastroenteritis and rotavirus gastroenteritis in children less than 5 years of age, in Padova, Italy. Infection. 2008, 36: 351-357. 10.1007/s15010-008-7200-6.
Fau C, Billaud G, Pinchinat S, Lina B, Kaplon J, Pothier P, Derrough T, Marcelon L, Largeron N, Caulin E, et al: Epidemiology and burden of rotavirus diarrhea in day care centers in Lyon, France. Arch Pediatr. 2008, 15: 1183-1192. 10.1016/j.arcped.2008.02.016.
Floret D, Lina B, Pinchinat S, Billaud G, Ait-Belghiti F, Largeron N, Bellemin B, Trang CN, Fau C, Gaspard C, et al: Epidemiology and burden of rotavirus diarrhea in day care centers in Lyon, France. Eur J Pediatr. 2006, 165: 905-906. 10.1007/s00431-006-0187-z.
Parashar UD, Hummelman EG, Bresee JS, Miller MA, Glass RI: Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003, 9: 565-572. 10.3201/eid0905.020562.
Vesikari T, Rautanen T, Von Bonsdorff CH: Rotavirus gastroenteritis in Finland: burden of disease and epidemiological features. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999, 88: 24-30.
Melliez H, Levybruhl D, Boelle PY, Dervaux B, Baron S, Yazdanpanah Y: Cost and cost-effectiveness of childhood vaccination against rotavirus in France. Vaccine. 2008, 26: 706-715. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.11.064.
Forster J, Guarino A, Parez N, Moraga F, Roman E, Mory O, Tozzi AE, de Aguileta AL, Wahn U, Graham C, et al: Hospital-based surveillance to estimate the burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis among European children younger than 5 years of age. Pediatrics. 2009, 123: e393-e400. 10.1542/peds.2008-2088.
Thuret A, Patural H, Berthelot P, Benzait F, Martin I, Jusot JF, Teyssier G, Fabry J, Pozzetto B: Prospective follow-up of hospital-acquired diarrhoea in 28 paediatric wards of the south-east part of France during a winter season. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2004, 52: 131-137. 10.1016/j.patbio.2003.06.005.
Piednoir E, Bessaci K, Bureau-Chalot F, Sabouraud P, Brodard V, Andreoletti L, Bajolet O: Economic impact of healthcare-associated rotavirus infection in a paediatric hospital. J Hosp Infect. 2003, 55: 190-195. 10.1016/j.jhin.2003.07.002.
Marc E, Biscardi S, Soulier M, Lebon P, Gendrel D: Nosocomial rotavirus infections in a pediatric unit: surveillance during four successive winters. Med Mal Infect. 2007, 37: 61-66. 10.1016/j.medmal.2006.09.007.
Gil-Prieto R, San Martin M, Lopez dA, Alvaro-Meca A, Gonzalez A, Gil dM: Hospital-acquired rotavirus infections in Spain over a ten-year period (1998-2007). Hum Vaccin. 2009, 5:
Gutierrez-Gimeno MV, Martin-Moreno JM, Diez-Domingo J, Asensi-Botet F, Hernandez-Marco R, Correcher-Medina P, Sanchez-Fauquier A: Nosocomial Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Spain: A Multicentre Prospective Study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009
Fruhwirth M, Karmaus W, Moll-Schuler I, Brosl S, Mutz I: A prospective evaluation of community acquired gastroenteritis in paediatric practices: impact and disease burden of rotavirus infection. Arch Dis Child. 2001, 84: 393-397. 10.1136/adc.84.5.393.
Biermann KP, Neri S, Reali MF, De Martino M, Festini F: Incidence of nosocomial rotavirus infections in a pediatric hospital over a 3-year period. Minerva Pediatr. 2006, 58: 477-482.
Herruzo R, Omenaca F, Garcia S, Diez J, Sanchez-Fauquier A: Identification of risk factors associated with nosocomial infection by rotavirus P4G2, in a neonatal unit of a tertiary-care hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009, 15: 280-285. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02667.x.
Giaquinto C, Van Damme P, Huet F, Gothefors L, Maxwell M, Todd P, da Dalt L: Clinical consequences of rotavirus acute gastroenteritis in Europe, 2004-2005: the REVEAL study. J Infect Dis. 2007, 195 (Suppl 1): S26-S35.
Giaquinto C, Van Damme P: Age distribution of paediatric rotavirus gastroenteritis cases in Europe: the REVEAL study. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010, 42: 142-147. 10.3109/00365540903380495.
Iturriza-Gomara M, Dallman T, Banyai K, Bottiger B, Buesa J, Diedrich S, Fiore L, Johansen K, Korsun N, Kroneman A, et al: Rotavirus surveillance in europe, 2005-2008: web-enabled reporting and real-time analysis of genotyping and epidemiological data. J Infect Dis. 2009, 200 (Suppl 1): S215-S221.
Rouget F, Chomienne F, Laurens E, Radet C, Seguin G: Evaluation of a prevention program against nosocomial rotavirus infections in a pediatric ward. Arch Pediatr. 2000, 7: 948-954. 10.1016/S0929-693X(00)90008-3.
Pina P, Le Huidoux P, Lefflot S, Araujo E, Bellaiche M, Harzig M, Allouch PY, Foucaud P: Nosocomial rotavirus infections in a general pediatric ward: epidemiology, molecular typing and risk factors. Arch Pediatr. 2000, 7: 1050-1058. 10.1016/S0929-693X(00)00312-2.
Maille L, Beby-Defaux A, Bourgoin A, Koulmann L, Eucher V, Cardona J, Oriot D, Agius G: Nosocomial infections due to rotavirus and respiratory syncytial virus in pediatric wards: a 2-year study. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2000, 58: 601-606.
Armengaud JB, El Hajje MJ, Moulin F, Marc E, Chalumeau M, Lebon P, Gendrel D: Simultaneous outbreaks of rotavirus and respiratory syncytial virus in Paris: a 12-year survey. Med Mal Infect. 2007, 37: 262-265. 10.1016/j.medmal.2007.02.005.
Doit C, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Bourrillon A, Bingen E: Rotavirus infections in a paediatric hospital during 5 years. Arch Pediatr. 2007, 14: 1465-1467. 10.1016/j.arcped.2007.10.002.
Berner R, Schumacher RF, Hameister S, Forster J: Occurrence and impact of community-acquired and nosocomial rotavirus infections-a hospital-based study over 10 y. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999, 88: 48-52.
Johansen K, Hedlund KO, Zweygberg-Wirgart B, Bennet R: Complications attributable to rotavirus-induced diarrhoea in a Swedish paediatric population: report from an 11-year surveillance. Scand J Infect Dis. 2008, 40: 958-964. 10.1080/00365540802415509.
Lynch M, O'Halloran F, Whyte D, Fanning S, Cryan B, Glass RI: Rotavirus in Ireland: national estimates of disease burden, 1997 to 1998. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001, 20: 693-698. 10.1097/00006454-200107000-00010.
Fischer TK, Nielsen NM, Wohlfahrt J, Paerregaard A: Incidence and cost of rotavirus hospitalizations in Denmark. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007, 13: 855-859.
Kavaliotis I, Papaevangelou V, Aggelakou V, Mantagou L, Trimis G, Papadopoulou V, Vlachaki G, Nikolakopoulou N, Konstantopoulos A: ROTASCORE Study: epidemiological observational study of acute gastroenteritis with or without rotavirus in Greek children younger than 5 years old. Eur J Pediatr. 2008, 167: 707-708. 10.1007/s00431-007-0570-4.
Flem E, Vainio K, Dollner H, Midgaard C, Bosse FJ, Rognlien AG, Rojahn A, Nordbo SA, Storvold G, Njolstad G, et al: Rotavirus gastroenteritis in Norway: Analysis of prospective surveillance and hospital registry data. Scand J Infect Dis. 2009, 41: 753-759. 10.1080/00365540903161515.
Van Damme P, Giaquinto C, Maxwell M, Todd P, Van der WM: Distribution of rotavirus genotypes in Europe, 2004-2005: the REVEAL Study. J Infect Dis. 2007, 195 (Suppl 1): S17-S25.
Fruhwirth M, Brosl S, Ellemunter H, Moll-Schuler I, Rohwedder A, Mutz I: Distribution of rotavirus VP4 genotypes and VP7 serotypes among nonhospitalized and hospitalized patients with gastroenteritis and patients with nosocomially acquired gastroenteritis in Austria. J Clin Microbiol. 2000, 38: 1804-1806.
Fischer TK, Eugen-Olsen J, Pedersen AG, Molbak K, Bottiger B, Rostgaard K, Nielsen NM: Characterization of rotavirus strains in a Danish population: high frequency of mixed infections and diversity within the VP4 gene of P[8] strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2005, 43: 1099-1104. 10.1128/JCM.43.3.1099-1104.2005.
de Rougemont A, Kaplon J, Lebon P, Huet F, Denis F, Alain S, Fourcade L, Grosjean J, El Hajje MJ, Gendrel D, et al: Unexpected substitution of dominant rotavirus G genotypes in French hospitalized children over five consecutive seasons. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009, 28: 403-407. 10.1007/s10096-008-0640-1.
De Donno A, Grassi T, Bagordo F, Idolo A, Cavallaro A, Gabutti G: Emergence of unusual human rotavirus strains in Salento, Italy, during 2006-2007. BMC Infect Dis. 2009, 9: 43-10.1186/1471-2334-9-43.
Ansaldi F, Lai P, Valle L, Riente R, Durando P, Sticchi L, Tucci P, Biasci P, Crovari P, Gasparini R, et al: Burden of rotavirus-associated and non-rotavirus-associated diarrhea among nonhospitalized individuals in central Italy: a 1-year sentinel-based epidemiological and virological surveillance. Clin Infect Dis. 2008, 46: e51-e55. 10.1086/527449.
Villena C, El Senousy WM, Abad FX, Pinto RM, Bosch A: Group A rotavirus in sewage samples from Barcelona and Cairo: emergence of unusual genotypes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003, 69: 3919-3923. 10.1128/AEM.69.7.3919-3923.2003.
Iturriza-Gomara M, Elliot AJ, Dockery C, Fleming DM, Gray JJ: Structured surveillance of infectious intestinal disease in pre-school children in the community: 'The Nappy Study'. Epidemiol Infect. 2009, 137: 922-931. 10.1017/S0950268808001556.
Iturriza Gomara M, Simpson R, Perault AM, Redpath C, Lorgelly P, Joshi D, Mugford M, Hughes CA, Dalrymple J, Desselberger U, et al: Structured surveillance of infantile gastroenteritis in East Anglia, UK: incidence of infection with common viral gastroenteric pathogens. Epidemiol Infect. 2008, 136: 23-33.
Arista S, Giammanco GM, De Grazia S, Migliore MC, Martella V, Cascio A: Molecular characterization of the genotype G9 human rotavirus strains recovered in Palermo, Italy, during the winter of 1999-2000. Epidemiol Infect. 2004, 132: 343-349. 10.1017/S0950268803001602.
Martella V, Terio V, Del Gaudio G, Gentile M, Fiorente P, Barbuti S, Buonavoglia C: Detection of the emerging rotavirus G9 serotype at high frequency in Italy. J Clin Microbiol. 2003, 41: 3960-3963. 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3960-3963.2003.
Arista S, Giammanco GM, De Grazia S, Colomba C, Martella V: Genetic variability among serotype G4 Italian human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2005, 43: 1420-1425. 10.1128/JCM.43.3.1420-1425.2005.
Harrington M, Butler K, Cafferkey M: Rotavirus infection in hospitalised children: incidence and impact on healthcare resources. Ir J Med Sci. 2003, 172: 33-36. 10.1007/BF02914784.
Child rotavirus deaths. [http://www.who.int/immunization_monitoring/burden/rotavirus_estimates/en/index.html]
Martinot A, Hue V, Ego A, Dumonceaux A, Grandbastien B, Guillois B, Leclerc F: Rehydration modalities for acute diarrhea in hospitalized infants. Impact of a permanent short-stay pediatric observation unit. Arch Pediatr. 2001, 8: 1062-1070. 10.1016/S0929-693X(01)00584-X.
Fourquet F, Desenclos JC, Maurage C, Baron S: Acute gastro-enteritis in children in France: estimates of disease burden through national hospital discharge data. Arch Pediatr. 2003, 10: 861-868. 10.1016/S0929-693X(03)00459-7.
Bilcke J, Van Damme P, De Smet F, Hanquet G, Van Ranst M, Beutels P: The health and economic burden of rotavirus disease in Belgium. Eur J Pediatr. 2008, 167: 1409-1419. 10.1007/s00431-008-0684-3.
Panatto D, Amicizia D, Ansaldi F, Marocco A, Marchetti F, Bamfi F, Giacchino R, Tacchella A, Del Buono S, Gasparini R: Burden of rotavirus disease and cost-effectiveness of universal vaccination in the Province of Genoa (Northern Italy). Vaccine. 2009, 27: 3450-3453. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.054.
Fruhwirth M, Berger K, Ehlken B, Moll-Schuler I, Brosl S, Mutz I: Economic impact of community- and nosocomially acquired rotavirus gastroenteritis in Austria. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001, 20: 184-188. 10.1097/00006454-200102000-00013.
Bilcke J, Van Damme P, Beutels P: Cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination: exploring caregiver(s) and "no medical care"' disease impact in Belgium. Med Decis Making. 2009, 29: 33-50. 10.1177/0272989X08324955.
Giaquinto C, Van Damme P, Huet F, Gothefors L, Van der WM: Costs of community-acquired pediatric rotavirus gastroenteritis in 7 European countries: the REVEAL Study. J Infect Dis. 2007, 195 (Suppl 1): S36-S44.
Huet F, Largeron N, Trichard M, Miadi-Fargier H, Jasso-Mosqueda G: Burden of paediatric rotavirus gastroenteritis and potential benefits of a universal rotavirus vaccination programme with RotaTeq in France. Vaccine. 2007, 25: 6348-6358. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.06.015.
Melliez H, Boelle PY, Baron S, Mouton Y, Yazdanpanah Y: Morbidity and cost of rotavirus infections in France. Med Mal Infect. 2005, 35: 492-499. 10.1016/j.medmal.2005.08.007.
Sermet-Gaudelus I, de La RF, Salomon JL, Lachassine E, Leruez-Ville M, Baujat G, Trioche P, Valdes L, Parez N, Aujard Y: Rotavirus nosocomial infection in pediatric units. A multicentric observation study. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2004, 52: 4-10. 10.1016/j.patbio.2003.04.002.
Marsella M, Raimondi L, Bergamini M, Sprocati M, Bigi E, De Sanctis V, Borgna-Pignatti C, Gabutti G: Epidemiology of rotavirus-associated hospital admissions in the province of Ferrara, Italy. Eur J Pediatr. 2009, 168: 1423-1427. 10.1007/s00431-009-0942-z.
Lopez-de-Andres A, Jimenez-Garcia R, Carrasco-Garrido P, Alvaro-Meca A, Galarza PG, de Miguel AG: Hospitalizations associated with rotavirus gastroenteritis in Spain, 2001-2005. BMC Public Health. 2008, 8: 109-10.1186/1471-2458-8-109.
Luquero Alcalde FJ, Eiros Bouza JM, Rubio AP, Bachiller Luque MR, Castrodeza Sanz JJ, Ortiz de Lejarazu: Gastroenteritis by rotavirus in Spanish children. Analysis of the disease burden. Eur J Pediatr. 2008, 167: 549-555. 10.1007/s00431-007-0550-8.
Gil A, Carrasco P, Jimenez R, San Martin M, Oyaguez I, Gonzalez A: Burden of hospitalizations attributable to rotavirus infection in children in Spain, period 1999-2000. Vaccine. 2004, 22: 2221-2225. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.11.037.
Lorgelly PK, Joshi D, Iturriza GM, Gray J, Mugford M: Exploring the cost effectiveness of an immunization programme for rotavirus gastroenteritis in the United Kingdom. Epidemiol Infect. 2008, 136: 44-55.
Williams CJ, Lobanov A, Pebody RG: Estimated mortality and hospital admission due to rotavirus infection in the WHO European region. Epidemiol Infect. 2009, 137: 607-616. 10.1017/S0950268808001714.
Podkolzin AT, Fenske EB, Abramycheva NY, Shipulin GA, Sagalova OI, Mazepa VN, Ivanova GN: Hospital-based surveillance of rotavirus and other viral agents of diarrhea in children and adults in Russia, 2005-2007. J Infect Dis. 2009, 200: S228-S233. 10.1086/605054.
Phan TG, Yagyu F, Kozlov V, Kozlov A, Okitsu S, Muller WE, Ushijima H: Viral gastroenteritis and genetic characterization of recombinant norovirus circulating in Eastern Russia. Clin Lab. 2006, 52: 247-253.
Khoury H, Ogilvie I, El Khoury AC, Duan Y, Goetghebeur MM: Burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis in the Middle Eastern and North African pediatric population. BMC Infect Dis. 2011, 11: 9-10.1186/1471-2334-11-9.
Diez-Domingo J, Baldo JM, Patrzalek M, Pazdiora P, Forster J, Cantarutti L, Pircon JY, Soriano-Gabarro M, Meyer N: Primary care-based surveillance to estimate the burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis among children aged less than 5 years in six European countries. Eur J Pediatr. 2011, 170: 213-222. 10.1007/s00431-010-1289-1.
Diez-Domingo J, Surinach NL, Alcalde NM, Betegon L, Largeron N, Trichard M: Burden of paediatric Rotavirus Gastroenteritis (RVGE) and potential benefits of a universal Rotavirus vaccination programme with a pentavalent vaccine in Spain. BMC Public Health. 2010, 10: 469-10.1186/1471-2458-10-469.
Iturriza-Gomara M, Dallman T, Banyai K, Bottiger B, Buesa J, Diedrich S, Fiore L, Johansen K, Koopmans M, Korsun N, et al: Rotavirus genotypes co-circulating in Europe between 2006 and 2009 as determined by EuroRotaNet, a pan-European collaborative strain surveillance network. Epidemiol Infect. 2010, 1-15.
Jit M, Mangen MJ, Melliez H, Yazdanpanah Y, Bilcke J, Salo H, Edmunds WJ, Beutels P: An update to "The cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination: comparative analyses for five European countries and transferability in Europe". Vaccine. 2010, 28: 7457-7459. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.08.060.
Morgan C, Adlard N, Carroll S, Parvataneni L: Burden on UK secondary care of rotavirus disease and seasonal infections in children. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010, 26: 2449-2455. 10.1185/03007995.2010.518135.
Rotavirus epidemiology: EuroRotaNet strain surveillance. [http://sabin.org/files/jim_gray_ist.pdf]
Rahman M, Matthijnssens J, Goegebuer T, De Leener K, Vanderwegen L, Van Der Donck I, Van Hoovels L, De Vos S, Azim T, Van Ranst M: Predominance of rotavirus G9 genotype in children hospitalized for rotavirus gastroenteritis in Belgium during 1999-2003. J Clin Virol. 2005, 33: 1-6. 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.09.020.
Rosenfeldt V, Vesikari T, Pang XL, Zeng SQ, Tvede M, Paerregaard A: Viral etiology and incidence of acute gastroenteritis in young children attending day-care centers. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005, 24: 962-965. 10.1097/01.inf.0000183748.41027.a4.
Fischer TK: Incidence of hospitalizations due to rotavirus gastroenteritis in Denmark. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90: 1073-1075. 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2001.tb01366.x.
Branger B: 2001 national survey of nosocomial infection prevalence among newborns and under-eighteen children and adolescents in France. Arch Pediatr. 2005, 12: 1085-1093. 10.1016/j.arcped.2005.02.011.
Le Roux P, Marshall B, Toutain F, Mary JF, Pinon G, Briquet E, Le Luyer B: Nosocomial viral infections in a pediatric service: example of rotaviral gastroenteritis and respiratory syncytial viral bronchiolitis. Arch Pediatr. 2004, 11: 908-915. 10.1016/j.arcped.2004.04.022.
Forster J, Hammerschmidt T: Burden of acute rotavirus gastroenteritis (RV-AGE) in Germany: a comparison of federal statistics and epidemiological data. Gesundheitswesen. 2007, 69: 227-232. 10.1055/s-2007-973090.
Oh DY, Gaedicke G, Schreier E: Viral agents of acute gastroenteritis in German children: prevalence and molecular diversity. J Med Virol. 2003, 71: 82-93. 10.1002/jmv.10449.
Kafetzis DA, Maltezou HC, Zafeiropoulou A, Attilakos A, Stavrinadis C, Foustoukou M: Epidemiology, clinical course and impact on hospitalization costs of acute diarrhea among hospitalized children in Athens, Greece. Scand J Infect Dis. 2001, 33: 681-685. 10.1080/00365540110026935.
Palumbo E, Malorgio C, Siani A, Bonora G: Diarrhoea in children: aetiology and clinical aspects. Infez Med. 2009, 17: 95-99.
Grassi T, De Donno A, Guido M, Gabutti G: The epidemiology and disease burden of rotavirus infection in the Salento peninsula, Italy. Turk J Pediatr. 2008, 50: 132-136.
Gabutti G, Marsella M, Lazzara C, Fiumana E, Cavallaro A, Borgna-Pignatti C: Epidemiology and burden of rotavirus-associated hospitalizations in Ferrara, Italy. J Prev Med Hyg. 2007, 48: 5-9.
Koopmans M, Van Asperen I: Epidemiology of rotavirus infections in The Netherlands. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999, 88: 31-37.
Vainio K, Nordbo SA, Njolstad G, Storvold G, Dollner H, Midgaard C, Bosse FJ, Rognlien AG, Rojahn A, Wathne KO, et al: Detection and characterization of group A rotaviruses in children hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in Norway, 2006-2008. J Med Virol. 2009, 81: 1839-1844. 10.1002/jmv.21576.
Antunes H, Afonso A, Iturriza M, Martinho I, Ribeiro C, Rocha S, Magalhaes C, Carvalho L, Branca F, Gray J: G2P[4] the most prevalent rotavirus genotype in 2007 winter season in an European non-vaccinated population. J Clin Virol. 2009, 45: 76-78. 10.1016/j.jcv.2009.03.010.
Rodrigues F, Iturriza M, Gray J, Januario L, Lemos L: Epidemiology of rotavirus in Portugal: G9 as a major cause of diarrhoea in non-hospitalised children. J Clin Virol. 2007, 40: 214-217. 10.1016/j.jcv.2007.08.006.
Sanchez-Fauquier A, Montero V, Moreno S, Sole M, Colomina J, Iturriza-Gomara M, Revilla A, Wilhelmi I, Gray J: Human rotavirus G9 and G3 as major cause of diarrhea in hospitalized children, Spain. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006, 12: 1536-1541. 10.3201/eid1210.060384.
Gil de Miguel A, Carrasco GP, Esteban HJ, San Martin RM, Gonzalez LA: Burden of hospitalizations attributable to rotavirus infection in children in the Autonomous Region of Madrid, Spain, period 1999-2000. An Pediatr (Barc). 2006, 64: 530-535. 10.1157/13089917.
Visser LE, Cano PR, Gay NJ, Martinez Navarro JF: Impact of rotavirus disease in Spain: an estimate of hospital admissions due to rotavirus. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999, 88: 72-76.
Jit M, Pebody R, Chen M, Andrews N, Edmunds WJ: Estimating the number of deaths with rotavirus as a cause in England and wales. Hum Vaccin. 2007, 3: 23-26. 10.4161/hv.3.1.3748.
Riordan FA, Quigley T: Estimating hospital admissions due to rotavirus gastroenteritis from hospital episode statistics. J Infect. 2004, 49: 13-16. 10.1016/j.jinf.2004.02.006.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2334/12/62/prepub
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by Sanofi Pasteur MSD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
IO, HK, and MMG declare that they have no competing interests. AEK is an employee of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. and potentially owns stock and/or holds stock options in the Company. CG received consultancy honorarium and research grants from SPMSD, Merck and GSK-Bio.
Authors' contributions
IO & HK developed the search algorithm and drafted the manuscript. MMG, AEK, and CG participated in the design of the methodology and drafting of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Ogilvie, I., Khoury, H., Goetghebeur, M.M. et al. Burden of community-acquired and nosocomial rotavirus gastroenteritis in the pediatric population of Western Europe: a scoping review. BMC Infect Dis 12, 62 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-12-62
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-12-62