Abstract
Background
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and excessive salt intake are known as important risk factors for stomach cancer in humans. However, interactions of these two factors with gene expression profiles during gastric carcinogenesis remain unclear. In the present study, we investigated the global gene expression associated with stomach carcinogenesis and prognosis of human gastric cancer using a mouse model.
Methods
To find candidate genes involved in stomach carcinogenesis, we firstly constructed a carcinogen-induced mouse gastric tumor model combined with H. pylori infection and high-salt diet. C57BL/6J mice were given N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in their drinking water and sacrificed after 40 weeks. Animals of a combination group were inoculated with H. pylori and fed a high-salt diet. Gene expression profiles in glandular stomach of the mice were investigated by oligonucleotide microarray. Second, we examined an availability of the candidate gene as prognostic factor for human patients. Immunohistochemical analysis of CD177, one of the up-regulated genes, was performed in human advanced gastric cancer specimens to evaluate the association with prognosis.
Results
The multiplicity of gastric tumor in carcinogen-treated mice was significantly increased by combination of H. pylori infection and high-salt diet. In the microarray analysis, 35 and 31 more than two-fold up-regulated and down-regulated genes, respectively, were detected in the H. pylori-infection and high-salt diet combined group compared with the other groups. Quantitative RT-PCR confirmed significant over-expression of two candidate genes including Cd177 and Reg3g. On immunohistochemical analysis of CD177 in human advanced gastric cancer specimens, over-expression was evident in 33 (60.0%) of 55 cases, significantly correlating with a favorable prognosis (P = 0.0294). Multivariate analysis including clinicopathological factors as covariates revealed high expression of CD177 to be an independent prognostic factor for overall survival.
Conclusions
These results suggest that our mouse model combined with H. pylori infection and high-salt diet is useful for gene expression profiling in gastric carcinogenesis, providing evidence that CD177 is a novel prognostic factor for stomach cancer. This is the first report showing a prognostic correlation between CD177 expression and solid tumor behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Stomach cancer is the fourth most common cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide [1]. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is now recognized as a major risk factor for chronic gastritis and stomach cancer development [2]. In addition, environmental and host factors have also been shown to influence gastric carcinogenesis, and salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) and salty food are of particular importance, based on evidence from a number of epidemiological and experimental studies [3–6]. Thus, combined exposure to H. pylori infection and excessive salt intake appears to be very important for the development and progression of gastric tumors, although the detailed mechanisms, especially in terms of gene expression profiles, remain to be clarified.
High throughput microarray technology provides a powerful tool for comprehensive gene analysis, already applied to assess gene expression patterns in both human samples and animal models of gastric disorders [7–16]. Although many researchers have focused on gene expression in H. pylori-treated gastric cell lines [17–19], results in cell culture do not necessarily correlate with expression of specific genes in the in vivo microenvironment featuring host immune responses and stromal-epithelial interactions in cancers. Carcinogen-treated Mongolian gerbils have been used as a useful animal model of H. pylori-associated gastric carcinogenesis [20–24], and we previously reported that a synergistic interaction between H. pylori infection and high-salt intake accelerates chronic inflammation and tumor development in the stomachs of these animals [25, 26]. Unfortunately, there is little information available for the gerbil genome, hampering genetic and molecular analysis. Therefore, attention has focused on mouse models [12, 13], and establishment of a mouse model for stomach cancer featuring salt and H. pylori exposure is needed for investigations targeting genes involved in gastric carcinogenesis.
Previous microarray studies using rodent models did not distinguish and characterize expression profiles based on the interaction of H. pylori infection and salt intake. In the present study, we examined gene expression in the gastric mucosa in a H. pylori-infected and high-salt diet-treated mouse gastric tumor model by oligonucleotide microarray and found two candidate up-regulated genes including Cd177 and Reg3g. We also investigated the expression of CD177 in human advanced gastric cancers by immunohistochemistry, and obtained evidence as a potential prognostic factor for stomach carcinogenesis.
Methods
Inoculation with H. pylori
H. pylori was prepared by the same method as described previously [27, 28]. Briefly, H. pylori (Sydney strain 1) was inoculated on Brucella agar plates (Becton Dickinson, Cockeysville, MD, USA) containing 7% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) and incubated at 37°C under microaerophilic conditions at high humidity for 2 days. Then, bacteria grown on the plates were introduced into Brucella broth (Becton Dickinson) supplemented with 7% (v/v) FBS and incubated under the same conditions for 24-h. After 24-h fasting, animals were intra-gastrically inoculated H. pylori (1.0 × 108 colony-forming units). Before inoculation, the broth cultures of H. pylori were checked under a phase-contrast microscope for bacterial shape and mobility.
Animals and experimental protocol
Fifty-six specific pathogen-free male, 5- or 6-week-old C57BL/6J mice (CLEA Japan, Tokyo, Japan) were used in this study. All animals were housed in plastic cages on hardwood-chip bedding in an air-conditioned biohazard room with a 12-h light/12-h dark cycle, and allowed free access to food and water throughout. The experimental design was approved by the Animal Care Committee of the Aichi Cancer Center Research Institute, and the animals were cared for in accordance with institutional guidelines as well as the Guidelines for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiments (Science Council of Japan, June 1st, 2006).
The experimental design is illustrated in Figure 1A. The mice were divided into 4 groups (Groups A-D); 21, 5, 15, and 15 mice were assigned to A, B, C, and D groups, respectively, at the commencement of the experiment. Animals of Groups B and D were inoculated with H. pylori intra-gastrically on alternate weeks (total 7 times), while mice of the other groups were inoculated with Brucella broth alone. All mice were given N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU, Sigma Chemical, St Louis, MO, USA) in their drinking water at the concentration of 120 ppm on alternate weeks (total exposure was 5 weeks). For this purpose MNU was freshly dissolved in distilled water three times per week. Mice of Groups C and D received CE-2 diets (basal sodium content of 0.36%; CLEA Japan) containing 10% NaCl. During the exposure period, one animal of Group B, one of Group C and six of Group D died or became moribund and they were excluded from the experiment. At 40 weeks, the remained animals were subjected to deep anesthesia and laparotomy with excision of the stomach.
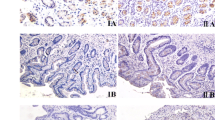
Experimental design and histopathological findings. A: Experimental design. Five- to six-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were inoculated with H. pylori SS1 strain (Groups B and D) or Brucella broth (Groups A and C). All animals were administered 120 ppm MNU in their drinking water on alternate weeks (total exposure, 5 weeks). Mice of Groups C and D were given basal diet (CE-2) containing 10% NaCl. B: Histopathological findings for MNU-induced mice gastric tumors. (a and b) Gastric adenoma in the pyloric region of an MNU-treated and H. pylori-infected mouse (Group B). (c and d) Gastric adenocarcinoma observed in Group B. Note the high cell density and cellular and structural atypia. Bar = 200 (a and c) or 100 μm (b and d).
Histological evaluation
For histological examination, the stomachs were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin for 24-h, sliced along the longitudinal axis into strips of equal width, and embedded in paraffin. Four-μm thick sections were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histological observation. Tumors were classified into adenoma and adenocarcinoma based on cellular and morphological atypia and invasive growth to submucosa as we reported previously [21].
RNA preparation and oligonucleotide microarray analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the whole gastric mucosa including both tumor and peripheral tissue using an RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and its quality checked with a microchip electrophoresis system (i-chip SV1210; Hitachi Chemical, Tokyo, Japan). High-quality samples were selected, and pooled for each group to avoid individual difference for oligonucleotide microarray assessment (Group A, n = 3; B, n = 4; C, n = 6; D, n = 7). The CodeLink Mouse Whole Genome Bioarray (Applied Microarrays, Tempe, AZ, USA) containing 35,587 probe sets per chip was used to analyze gene expression profiles. Hybridization, processing, and scanning were performed by Filgen, Inc. (Nagoya, Japan), scan data images being analyzed using a software package (Microarray Data Analysis Tool, Filgen). Complete-linkage hierarchical clustering was also examined on the four groups using a qualified probe subset (Filgen).
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR of expression profiles in mice stomach
Relative quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using a StepOne Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) with the mouse-specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) gene as an internal control. After DNase treatment, first strand cDNAs were synthesized from total RNA using a SuperScript VILO cDNA Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The PCR was accomplished basically following the manufacturer's instructions using a QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Kit (Qiagen). The primer sequences for each gene are listed in Table 1. Specificity of the PCR reactions was confirmed using a melt curve program provided with the StepOne software and electrophoresis of the PCR samples in 3% agarose gels. The expression levels of mRNAs were normalized to the mRNA level of Gapdh and compared with the control mice (Group A) by the ΔΔCT method.
Patients and tumor specimens
A total of 55 cases of primary advanced gastric cancer, surgically resected at Aichi Cancer Center Hospital (Nagoya, Japan) between 1995 and 2002, were investigated after obtaining informed consent. The study was approved by the ethics committee of Aichi Cancer Center. The patients were all male and the mean age and median follow-up period were 58.6 ± 10.2 years and 83 weeks, respectively. None had received preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Carcinomas with adjacent mucosa tissue were fixed and embedded in paraffin, and sectioned for staining with H&E. Classification of tumor staging and diagnosis of advanced cases were made according to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinomas [29]. The cancers had invaded the muscularis propria (T2 for TNM classification), the subserosa (T3), or the serosa and the peritoneal cavity (T4a), sometimes involving adjacent organs (T4b).
Immunohistochemistry using human gastric cancer tissue
We examined expression of CD177, for which a commercial primary antibody was available, in human gastric cancer tissues by immunohistochemistry. After inhibition of endogenous peroxidase activity by immersion in 3% hydrogen peroxide/methanol solution, antigen retrieval was carried out with 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 6.0) in a microwave oven for 10 min at 98°C. Then, sections were incubated with a mouse monoclonal anti-CD177 antibody (clone 4C4, diluted 1:100, Abnova, Taipei, Taiwan). Staining for CD177 was performed using a Vectastain Elite ABC Kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) and binding visualized with 0.05% 3,3′-diaminobenzidine. The results of CD177 immunostaining in neoplastic cells were classified into four degrees; grade 0 (none, 0-10% of positive cells), grade 1 (weak, 10-30%), grade 2 (moderate, 30-60%), and grade 3 (strong, over 60%) based on proportion of stained cells, and cases showing moderate to strong staining were considered as positive.
Statistical analysis
The Chi-square test with Bonferroni correction was used to assess incidences of gastric tumor. Quantitative values including multiplicity of tumor and relative expression of mRNA were represented as means ± SD or SE, and differences between means were statistically analyzed by ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Tukey test for multiple comparisons. Overall survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test for comparisons. Correlations between CD177 expression and clinicopathological factors were analyzed by ANOVA or Chi-square test. Multivariate analysis was performed to examine whether CD177 over-expression was an independent prognostic factor using the Cox proportional-hazards regression model. P values of < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Incidences and multiplicities of gastric tumors
The effective number of mice and the observed incidences and multiplicities of gastric tumors are summarized in Table 2. Tumors developed in the gastric mucosa of all MNU-treated groups (Groups A-D) (Figure 1B). In high-salt diet-treated groups (Groups C and D), the incidence of gastric tumor in Group D (H. pylori-infected; 100%) was significantly higher than that in Group C (non-infected; 50.0%) (P < 0.05). In basal diet groups (Groups A and B), the incidence was also increased by H. pylori-infection (Group A, 61.9% and Group B, 100%), albeit without statistical significance. The multiplicities of total tumors in both H. pylori-infected groups (Group B, 3.3 ± 1.0 tumors/mouse and Group D, 2.6 ± 1.1) were markedly higher than those in non-infected groups (Group A, 0.9 ± 0.8 and Group C, 1.0 ± 1.2) (P < 0.05). The multiplicity of gastric adenocarcinoma in Group D (2.1 ± 1.4) was slightly higher than that in Group B (1.8 ± 1.0) and significantly increased over the Group C value (0.8 ± 1.0) (P < 0.05). In contrast, the multiplicities of adenomas in Groups A and D (0.1 ± 0.4 and 0.4 ± 0.5, respectively) were significantly lower than in Group B (1.5 ± 0.6) (P < 0.05 and 0.01).
Gene expression profiling in the glandular stomachs by oligonucleotide microarray
With oligonucleotide microarrays, compared with the non-infected and basal diet-treated group (Group A), 34 genes were up-regulated and 169 were down-regulated more than two-fold in H. pylori-infected mice (Group B), 56 up-regulated and 129 down-regulated in high-salt diet-treated mice (Group C), and 69 up-regulated and 214 down-regulated in the combined group (Group D) (Figure 2A). Taken together, as shown in Table 3, we found that 35 genes were up-regulated and 31 genes were down-regulated more than two-fold only by the combination of H. pylori infection and high-salt diet. In addition, hierarchical clustering analysis was performed on the four groups with a total of 303 qualified probes using the complete-linkage clustering algorithm (Figure 3). Thirty-one probes including Cd177, Reg3g and Muc13 were confirmed to be within a cluster of probes up-regulated only in Group D. Subsequent analysis in the present study was focused on these genes, because it was considered that the genes in which expression was altered only in the combined group might be associated with gastric carcinogenesis and progression in humans.
Global gene analysis in the glandular stomach of MNU-treated mice using oligonucleotide microarray. A: Number of genes up- or down-regulated more than two-fold in the stomach of MNU-treated mice. In Venn’s diagram, the circles indicate up- (left) or down-regulated (right) genes in the stomach of MNU-treated mice with H. pylori infection, high-salt diet or their combination. The shaded area represents the up- or down-regulated genes more than two-fold only by the combination. B: Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of three selected up-regulated genes (Cd177, Reg3g, and Muc13) in the stomachs of MNU-treated mice. Expression levels of the genes in each sample were normalized by Gapdh as internal control using ΔΔCT method. Relative expression levels were represented as the X-fold change relative to Group A (fixed as 1.0). Statistical analysis was performed by the Kruskal-Wallis test for general analysis and Tukey test for multiple comparison. Bars, SE; *, P < 0.01 vs. Group A and < 0.05 vs. Group C; †, P < 0.01 vs. Group C.
Hierarchical clustering analysis of four experimental groups of MNU-treated mice. Expression data from 303 qualified probes (left). The four experimental groups were classified into two clusters (Groups A/C) and (Groups B/D) based on similarities in expression patterns. Each row represents a probe and each column represents a experimental group (Groups A-D). As shown in the color bar, green indicates up-regulation; red indicates down-regulation; and black indicates no change. Thirty-one probes constituted a cluster of probes up-regulated only in Group D (right).
The entire results of this microarray analysis have been submitted and are readily retrievable from the public database NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) with the accession number GSE29444 (sample number: GSM728857-60).
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of gene expression profiles in MNU-treated mouse stomachs
Relative quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of three selected up-regulated genes (Cd177, Reg3g, and Muc13) in H. pylori-infected and high-salt diet-treated mice confirmed increased expression of Cd177 and Reg3g, as shown in Figure 2B, with significant differences. Although expression level of Muc13 in Group D was higher than all other groups, there was no statistical significance among them (P = 0.0712 vs. Group C).
Immunohistochemical expression of CD177 in human advanced gastric cancers and correlation with clinicopathological factors
On immunohistochemical analysis of human gastric cancer tissues, CD177 was observed not only in the membranes and cytoplasms of infiltrated neutrophils, but also in gastric cancer cells of both well- and poorly-differentiated adenocarcinomas (Figure 4A). Cancer cells of signet-ring cell type (2 cases) were negative for CD177. Among 55 gastric cancer cases, moderate to strong expression of CD177 was observed in 33 (60.0%) (Table 4).
Immunohistochemistry for CD177 in human advanced gastric cancer and correlation with overall survival rate. A: Immunohistochemical analysis of CD177 expression in human gastric cancer tissue. (a and b) Negative staining (none to weak) for CD177 in a gastric adenocarcinoma. CD177 expression is present only in infiltrating neutrophils while neoplastic cells of well-differentiated (a) or poorly-differentiated (b) carcinoma are negative. Original magnification, ×100 (inset, ×400). (c and d) Note positive (moderate to strong) expression for CD177 in well-differentiated (c) or poorly-differentiated (d) gastric cancer cells. Original magnification, ×100 (inset, ×400). B: Comparison of Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival curves for CD177 negative and positive gastric cancer cases.
The follow-up period of the patients ranged from 9 to 606 weeks (median = 83 weeks). Five-year survival rates for CD177-positive and negative were 39.4% and 18.2%, respectively. From the Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis, CD177-positive expression was associated with better overall survival (P = 0.0294, log-rank test) (Figure 4B). There was no statistically significant correlation of CD177 expression with age, histological classification, depth of invasion, and lymph node metastasis (Table 4).
Multivariate analysis for overall survival of human gastric cancer cases
Using the Cox proportional hazards model, multivariate analysis of clinicopathological variables, including the patient age, tumor histological classification, invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, and CD177 expression (Table 5), revealed the last to be an independent factor for overall survival (P = 0.0323). Patient age and low differentiation of adenocarcinoma were also associated with poor overall survival (P = 0.0439 and 0.0017, respectively). Tumor invasion depth and lymph node metastasis were not independent factors of gastric cancer cases in the present study (P > 0.05).
Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrated that the mouse model combined with H. pylori infection and high-salt diet is a useful tool to investigate the detailed mechanisms both of development and progression of gastric neoplasms. A number of rodent models of gastric cancer have been developed under various conditions, including H. pylori or H. felis infection, exposure to chemical carcinogens, and genetic modification [21, 30]. Since H. pylori is known as a most closely-associated risk factor in man, animal models with infection of the bacterium, such as that utilizing Mongolian gerbils, are considered to be particularly important to mimic the background of human gastric carcinogenesis. On the other hand, there is a consensus that gastric cancer is a multifactorial disease [31]. Epidemiological studies and animal experiments have demonstrated that development of stomach cancer is also associated with many other factors including salt intake, alcohol drinking and cigarette, containing a wide variety of chemical carcinogen. In the present study, we attempted to mimic the gastric environment of human high-risk group exposed to combination of H. pylori infection, salt intake, and carcinogen.
As might be expected, there are both advantages and disadvantages of Helicobacter-infected mouse models. Instability of cag pathogenicity islands (PAI), a particularly important virulence factor of H. pylori, has been reported in the mouse model using SS1 strain [32]. Multiplicity of gastric tumors is difficult to examine in the gerbil model, because almost all of the stomach tumors in gerbils show invasive growth into the lamina propria or muscle layer. In the present study, our results demonstrated that H. pylori infection increased not only incidence but also multiplicity of gastric tumors in MNU-treated mice. Thus, the mouse model presented here has advantages in respect to investigate the multiplicity and tissue sampling for gene expression analysis.
In this study, we focused on the genes in which the expression was regulated only in H. pylori-infection and high-salt diet combined mice, which are expected to reflect the background of human high-risk group, to explore examples which might be associated with tumor progression. The two up-regulated genes selected, Cd177 and Reg3g could be confirmed to exhibit significant over-expression by relative quantitative RT-PCR. Expression level of Muc13 showed a tendency for increase with combination of H. pylori and salt, although this was not statistically significant. Muc13 is a recently identified gene encoding transmembrane mucin that is expressed in the stomach to large intestine [33]. Shimamura et al. have reported that overexpression of Muc13 is associated with differentiation towards the intestinal (differentiated) type of human gastric cancer [34]. In addition, the combined expression of MUC13 with other metaplasia biomarkers is shown to be a prognostic indicator in several types of gastric cancer [35]. In the present study, all gastric tumors observed in MNU-treated mice were histologically of differentiated type. The REG protein family is also known to be associated with gastric cancer development and Reg1α and Reg4 have been suggested as prognostic markers for advanced stomach cancers in man [36]. The present results indicate the possibility that Reg3g is also involved with progression of stomach tumor.
Immunohistochemical analysis of CD177 in advanced gastric cancer specimens showed expression to be significantly correlated with a good prognosis and survival rate after surgery. Importantly, multivariate analysis with clinicopathological factors as covariates further revealed high expression to be an independent prognostic factor for overall survival, as along with patient’s age and histological classification. To our knowledge, the present study is the first to provide evidence that high expression of CD177 is associated with favorable prognosis in advanced gastric cancer.
CD177 is a member of the leukocyte antigen 6 (Ly-6) gene superfamily, encoding two neutrophil-associated proteins, NB1 and PRV-1 [37, 38]. The NB1 glycoprotein is typically expressed on a subpopulation of neutrophils, located at plasma membranes and secondary granules. Recent studies have demonstrated that CD177 is over-expressed in neutrophils from 95% of patients with polycythemia vera and in half of patients with essential thrombocythemia [37]. Gonda et al. have reported a microarray analysis that Cd177 expression in whole gastric tissue of H. felis-infected mice with mucosal dysplasia is reduced by folic acid supplementation [39]. Because they compared stage-matched groups to detect up- or down-regulated genes only by treatment of folic acid, it is unclear if Cd177 expression is associated with gastritis or dysplasia. In our microarray results, there were no significant differences in expression of Ela2, which is a neutrophil-specific gene [40], and histological degrees of neutrophil infiltration were almost same among H. pylori-infected groups (data not shown). Therefore, the up-regulation of Cd177 observed in this study was considered to be caused not by increased infiltration of neutrophils into the gastric mucosa but by a change of gene expression in tumor cells. NB1 is similar in structure to urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), which is known to be associated with cell adhesion and migration [37]. Thus, there is a possibility that CD177 also acts as a regulator of adhesion and migration of neoplastic cells in gastric tumor. Further studies are needed to clarify the association between CD177 expression in gastric epithelial cells and tumor progression.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that the mouse model combined with H. pylori infection and high-salt diet is suitable for investigation of global gene expression associated with gastric tumor development and progression. Furthermore, our results suggest that CD177 expression might be associated with a favorable prognosis of gastric adenocarcinomas in man.
Abbreviations
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- Gapdh:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- H. pylori:
-
Helicobacter pylori
- Ly-6:
-
Leukocyte antigen 6
- MNU:
-
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea
- Muc13:
-
Mucin 13
- PAI:
-
Pathogenicity islands
- Reg3g:
-
Regenerating islet-derived 3 gamma
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- uPAR:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor.
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011, 61: 69-90. 10.3322/caac.20107.
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N, Schlemper RJ: Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001, 345: 784-789. 10.1056/NEJMoa001999.
Kono S, Hirohata T: Nutrition and stomach cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 1996, 7: 41-55. 10.1007/BF00115637.
Tsugane S: Salt, salted food intake, and risk of gastric cancer: epidemiologic evidence. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96: 1-6. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00006.x.
Joossens JV, Hill MJ, Elliott P, Stamler R, Lesaffre E, Dyer A, Nichols R, Kesteloot H: Dietary salt, nitrate and stomach cancer mortality in 24 countries. European cancer prevention (ECP) and the INTERSALT cooperative research group. Int J Epidemiol. 1996, 25: 494-504. 10.1093/ije/25.3.494.
Nozaki K, Shimizu N, Inada K, Tsukamoto T, Inoue M, Kumagai T, Sugiyama A, Mizoshita T, Kaminishi M, Tatematsu M: Synergistic promoting effects of Helicobacter pylori infection and high-salt diet on gastric carcinogenesis in Mongolian gerbils. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002, 93: 1083-1089. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01209.x.
Abe M, Yamashita S, Kuramoto T, Hirayama Y, Tsukamoto T, Ohta T, Tatematsu M, Ohki M, Takato T, Sugimura T, et al: Global expression analysis of N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced rat stomach carcinomas using oligonucleotide microarrays. Carcinogenesis. 2003, 24: 861-867. 10.1093/carcin/bgg030.
Hasegawa S, Furukawa Y, Li M, Satoh S, Kato T, Watanabe T, Katagiri T, Tsunoda T, Yamaoka Y, Nakamura Y: Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in intestinal-type gastric cancers using a complementary DNA microarray representing 23,040 genes. Cancer Res. 2002, 62: 7012-7017.
Boussioutas A, Li H, Liu J, Waring P, Lade S, Holloway AJ, Taupin D, Gorringe K, Haviv I, Desmond PV, et al: Distinctive patterns of gene expression in premalignant gastric mucosa and gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63: 2569-2577.
El-Rifai W, Frierson HF, Harper JC, Powell SM, Knuutila S: Expression profiling of gastric adenocarcinoma using cDNA array. Int J Cancer. 2001, 92: 832-838. 10.1002/ijc.1264.
Hofman VJ, Moreilhon C, Brest PD, Lassalle S, Le Brigand K, Sicard D, Raymond J, Lamarque D, Hebuterne XA, Mari B, et al: Gene expression profiling in human gastric mucosa infected with Helicobacter pylori. Mod Pathol. 2007, 20: 974-989. 10.1038/modpathol.3800930.
Kobayashi M, Lee H, Schaffer L, Gilmartin TJ, Head SR, Takaishi S, Wang TC, Nakayama J, Fukuda M: A distinctive set of genes is upregulated during the inflammation-carcinoma sequence in mouse stomach infected by Helicobacter felis. J Histochem Cytochem. 2007, 55: 263-274.
Takaishi S, Wang TC: Gene expression profiling in a mouse model of Helicobacter-induced gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98: 284-293. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00392.x.
Hippo Y, Taniguchi H, Tsutsumi S, Machida N, Chong JM, Fukayama M, Kodama T, Aburatani H: Global gene expression analysis of gastric cancer by oligonucleotide microarrays. Cancer Res. 2002, 62: 233-240.
Huff JL, Hansen LM, Solnick JV: Gastric transcription profile of Helicobacter pylori infection in the rhesus macaque. Infect Immun. 2004, 72: 5216-5226. 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5216-5226.2004.
Vivas JR, Regnault B, Michel V, Bussiere FI, Ave P, Huerre M, Labigne A, DE MM, Touati E: Interferon gamma-signature transcript profiling and IL-23 upregulation in response to Helicobacter pylori infection. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2008, 21: 515-526.
Maeda S, Otsuka M, Hirata Y, Mitsuno Y, Yoshida H, Shiratori Y, Masuho Y, Muramatsu M, Seki N, Omata M: cDNA microarray analysis of Helicobacter pylori-mediated alteration of gene expression in gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001, 284: 443-449. 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5006.
Marcos NT, Magalhaes A, Ferreira B, Oliveira MJ, Carvalho AS, Mendes N, Gilmartin T, Head SR, Figueiredo C, David L, et al: Helicobacter pylori induces beta3GnT5 in human gastric cell lines, modulating expression of the SabA ligand sialyl-Lewis x. J Clin Invest. 2008, 118: 2325-2336.
Mills JC, Syder AJ, Hong CV, Guruge JL, Raaii F, Gordon JI: A molecular profile of the mouse gastric parietal cell with and without exposure to Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001, 98: 13687-13692. 10.1073/pnas.231332398.
Tatematsu M, Nozaki K, Tsukamoto T: Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinogenesis in animal models. Gastric Cancer. 2003, 6: 1-7.
Tsukamoto T, Mizoshita T, Tatematsu M: Animal models of stomach carcinogenesis. Toxicol Pathol. 2007, 35: 636-648. 10.1080/01926230701420632.
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Takasu S, Hirano N, Ban H, Shi L, Kumagai T, Tanaka T, Tatematsu M: Pitavastatin fails to lower serum lipid levels or inhibit gastric carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori-infected rodent models. Cancer Prev Res. 2009, 2: 751-758. 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0082.
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Takasu S, Shi L, Hirano N, Ban H, Kumagai T, Tatematsu M: Anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, on Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis in Mongolian gerbils. Int J Cancer. 2009, 125: 1786-1795. 10.1002/ijc.24586.
Magari H, Shimizu Y, Inada K, Enomoto S, Tomeki T, Yanaoka K, Tamai H, Arii K, Nakata H, Oka M, et al: Inhibitory effect of etodolac, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on stomach carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005, 334: 606-612. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.06.132.
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Hirano N, Mizoshita T, Kato S, Takasu S, Ban H, Tatematsu M: Synergistic upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric mucosa of Mongolian gerbils by a high-salt diet and Helicobacter pylori infection. Histol Histopathol. 2008, 23: 593-599.
Kato S, Tsukamoto T, Mizoshita T, Tanaka H, Kumagai T, Ota H, Katsuyama T, Asaka M, Tatematsu M: High salt diets dose-dependently promote gastric chemical carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils associated with a shift in mucin production from glandular to surface mucous cells. Int J Cancer. 2006, 119: 1558-1566. 10.1002/ijc.21810.
Shimizu N, Inada KI, Tsukamoto T, Nakanishi H, Ikehara Y, Yoshikawa A, Kaminishi M, Kuramoto S, Tatematsu M: New animal model of glandular stomach carcinogenesis in Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori and treated with a chemical carcinogen. J Gastroenterol. 1999, 34 (Suppl. 11): 61-66.
Takasu S, Tsukamoto T, Cao XY, Toyoda T, Hirata A, Ban H, Yamamoto M, Sakai H, Yanai T, Masegi T, et al: Roles of cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 expression and beta-catenin activation in gastric carcinogenesis in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-treated K19-C2mE transgenic mice. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99: 2356-2364. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00983.x.
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association: Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma - 2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998, 1: 10-24.
Oshima H, Oguma K, Du YC, Oshima M: Prostaglandin E2, Wnt, and BMP in gastric tumor mouse models. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100: 1779-1785. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01258.x.
Fock KM, Talley N, Moayyedi P, Hunt R, Azuma T, Sugano K, Xiao SD, Lam SK, Goh KL, Chiba T, et al: Asia-Pacific consensus guidelines on gastric cancer prevention. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008, 23: 351-365. 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05314.x.
Thompson LJ, Danon SJ, Wilson JE, O’Rourke JL, Salama NR, Falkow S, Mitchell H, Lee A: Chronic Helicobacter pylori infection with Sydney strain 1 and a newly identified mouse-adapted strain (Sydney strain 2000) in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 2004, 72: 4668-4679. 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4668-4679.2004.
Williams SJ, Wreschner DH, Tran M, Eyre HJ, Sutherland GR, McGuckin MA: Muc13, a novel human cell surface mucin expressed by epithelial and hemopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276: 18327-18336. 10.1074/jbc.M008850200.
Shimamura T, Ito H, Shibahara J, Watanabe A, Hippo Y, Taniguchi H, Chen Y, Kashima T, Ohtomo T, Tanioka F, et al: Overexpression of MUC13 is associated with intestinal-type gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96: 265-273. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00043.x.
Suh YS, Lee HJ, Jung EJ, Kim MA, Nam KT, Goldenring JR, Yang HK, Kim WH: The combined expression of metaplasia biomarkers predicts the prognosis of gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012, 19: 1240-1249. 10.1245/s10434-011-2125-1.
Yamagishi H, Fukui H, Sekikawa A, Kono T, Fujii S, Ichikawa K, Tomita S, Imura J, Hiraishi H, Chiba T, et al: Expression profile of REG family proteins REG Ialpha and REG IV in advanced gastric cancer: comparison with mucin phenotype and prognostic markers. Mod Pathol. 2009, 22: 906-913. 10.1038/modpathol.2009.41.
Stroncek DF, Caruccio L, Bettinotti M: CD177: A member of the Ly-6 gene superfamily involved with neutrophil proliferation and polycythemia vera. J Transl Med. 2004, 2: 8-10.1186/1479-5876-2-8.
Kissel K, Santoso S, Hofmann C, Stroncek D, Bux J: Molecular basis of the neutrophil glycoprotein NB1 (CD177) involved in the pathogenesis of immune neutropenias and transfusion reactions. Eur J Immunol. 2001, 31: 1301-1309. 10.1002/1521-4141(200105)31:5<1301::AID-IMMU1301>3.0.CO;2-J.
Gonda TA, Kim YI, Salas MC, Gamble MV, Shibata W, Muthupalani S, Sohn KJ, Abrams JA, Fox JG, Wang TC, et al: Folic acid increases global DNA methylation and reduces inflammation to prevent Helicobacter-associated gastric cancer in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012, 142: 824-833. 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.058.
Sturrock A, Franklin KF, Wu S, Hoidal JR: Characterization and localization of the genes for mouse proteinase-3 (Prtn3) and neutrophil elastase (Ela2). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1998, 83: 104-108. 10.1159/000015144.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-230X/13/122/prepub
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant-in Aid for the Third-term Comprehensive 10-year Strategy for Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, Grant-in-Aid for the Cancer Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, and Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists B (20790318 and 22700935) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
TTo and TTs designed the study under the supervision of AN, KO, TTa and MT. MY, HB, NS, ST, LS and AS participated in the animal handling and procedures. Clinical sample collection and suggestions were provided by SI and YY. Sample analysis and evaluation were performed by TTo, TTs and MY. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Takeshi Toyoda, Tetsuya Tsukamoto contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Toyoda, T., Tsukamoto, T., Yamamoto, M. et al. Gene expression analysis of a Helicobacter pylori-infected and high-salt diet-treated mouse gastric tumor model: identification of CD177 as a novel prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol 13, 122 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-13-122
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-13-122