Abstract
Background
Boron (B)-deficiency is a widespread problem in many crops, including Citrus. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in nutrient deficiencies. However, little is known on B-deficiency-responsive miRNAs in plants. In this study, we first identified miRNAs and their expression pattern in B-deficient Citrus sinensis roots by Illumina sequencing in order to identify miRNAs that might be involved in the tolerance of plants to B-deficiency.
Results
We isolated 52 (40 known and 12 novel) up-regulated and 82 (72 known and 10 novel) down-regulated miRNAs from B-deficient roots, demonstrating remarkable metabolic flexibility of roots, which might contribute to the tolerance of plants to B-deficiency. A model for the possible roles of miRNAs in the tolerance of roots to B-deficiency was proposed. miRNAs might regulate the adaptations of roots to B-deficiency through following several aspects: (a) inactivating reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling and scavenging through up-regulating miR474 and down-regulating miR782 and miR843; (b) increasing lateral root number by lowering miR5023 expression and maintaining a certain phenotype favorable for B-deficiency-tolerance by increasing miR394 expression; (c) enhancing cell transport by decreasing the transcripts of miR830, miR5266 and miR3465; (d) improving osmoprotection (miR474) and regulating other metabolic reactions (miR5023 and miR821). Other miRNAs such as miR472 and miR2118 in roots increased in response to B-deficiency, thus decreasing the expression of their target genes, which are involved in disease resistance, and hence, the disease resistance of roots.
Conclusions
Our work demonstrates the possible roles of miRNAs and related mechanisms in the response of plant roots to B-deficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Boron (B)-deficiency is a widespread problem in many agricultural crops, including Citrus. Over 132 crops are susceptible to B-deficiency, and low B availability in soils inhibits vegetative and reproductive growth in a large number of crops [1]. To cope with B-deficiency, plants have evolved a considerable degree of developmental plasticity, including adaptations via cascades of molecular networks. One of the most obvious features of the adaptations to B-deficiency is the changes in expression profiles of genes involved in a broad spectrum of biochemical, cellular and physiological processes, including B uptake and translocation, carbohydrate and energy metabolism, stress response, signaling and regulation, cell wall, protein process, nucleic acid metabolism, amino acid and fatty acid metabolism [2–5].
Small RNAs (sRNAs) have been identified as important post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression in plants. Based on the differences of biogenesis and function, endogenous sRNAs in plants can been divided into two classes, microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). miRNAs, which are approx. 21-nucleotide (nt) in length and are generated from non-coding transcripts capable of forming imperfectly complementary hairpin structures by the RNase DICER-LIKE1 (DCL1) or DCL4, have been known to negatively regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level by specific binding and cleavage of their target mRNAs, or by repression of target mRNA translation [6]. Since the first identification of plant miRNAs in 2002 [7], increasing evidence shows that plant miRNAs play crucial roles in almost all biological and metabolic processes [8]. Therefore, miRNA-related research has become one of the hottest topics in plant biology.
In addition to their involvement in plant normal growth and development, miRNAs also regulate the adaptations of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses [8, 9]. Evidence in Arabidopsis thaliana, tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), rapeseed (Brassica napus), rice (Oryza sativa), and common bean (Phaselus vulgaris) has demonstrated the important roles of miRNAs in phosphorus (P), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S) and cupper (Cu) deficiencies [10–13].
In A. thaliana, miR399 has been predicted to target three genes, which encode a phosphate transporter (PHT1;7), a ubiquitin-conjugating E2 enzyme, and a DEAD box helicase; however, only the E2 enzyme encoded by UBC24 has been experimentally validated [14]. miR399 is up-regulated in P-deficient roots and suppressed in P-sufficient roots and is negatively correlated with that of its target gene UBC24[15, 16]. The inverse relationship of expression patterns between UBC24 homologs and miR399 under P-deficiency has been confirmed in common bean [17] and rice [18]. Transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing miR399 also had decreased level of UBC24 transcripts [15]. In accordance with being inhibited by miR399s, UBC24 down-regulates P uptake and root-to-shoot allocation. Phenotypes of both the Arabidopsis T-DNA knockout ucb24 mutants and the miR399-overexpressing transgenic Arabidopsis plants resemble those of a previously reported pho2 mutant, a P overaccumulator [19]. Therefore, miR399 plays important roles in maintaining P homeostasis by regulating UBC24 transcript levels [20]. Following the first identification, more and more P-deficiency-responsive miRNAs are being identified in various plant species, including Arabidopsis[11, 15, 16, 21], rapeseed [16], soybean (Glycine max) [21], white lupin (Lupinus albus) [22], Medicago truncatula[23], rice [15], switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) [24], common bean [13, 17] and tomato [10]. So far, the majority of validated P-deficiency-responsive miRNA target genes are transcription factors, and other target genes mainly encode for abiotic/biotic stress-responsive proteins and enzymes related to protein modification/degradation [25]. The diverse functions of these target genes mean that a broad range of biological processes are coordinated in response to P-deficiency.
In A. thaliana, miR395 is enhanced during sulfate-limitation, and its induction is controlled by a key transcription factor (SLIM1) in the S assimilation pathway [26]. Each plant miRNA regulates several genes, but usually the targets belong to the same gene family. However, miR395 targets members of the ATP sulfurylase (APS) gene family [14] and the sulfate transporter SULTR2;1 [26]. miR395 has been shown to mediate regulation of sulfate accumulation and allocation by targeting APS and SULTR2;1, respectively [12].
Recent work showed that in Arabidopsis, the expression of miR397, miR398, miR408, and miR857 was induced by Cu-deficiency and negatively correlated with the accumulation of transcripts for Cu:zinc (Zn) superoxide dismutase (CSD1 and CSD2), COX5b-1 (a subunit of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase), plantacyanin and laccases. It has been suggested that miRNA-mediated down-regulation is a general mechanism to regulate non-essential Cu proteins, thus allowing plants to save Cu for the most essential functions during Cu-starvation [27]. Also, miRNAs have been demonstrated to play important roles in response to N and iron (Fe) deficiencies [13, 16, 28]. Therefore, miRNAs may be involved in the adaptive responses of plant to B-deficiency. Recently, Ozhuner et al. [29] investigated B-toxicity-responsive miRNAs in barley roots and leaves and concluded that the signal transduction mechanism in leaves regulated by miR408 played an important role in barley B-tolerance. In addition, the expression level of miR399 in barley roots and leaves was differentially regulated by B-toxicity. However, little information about B-deficiency-responsive plant miRNAs is available.
Identification of miRNAs is a key step for understanding their regulatory functions in plants. Plant miRNAs were discovered by both experimental and computational approaches. However, both the computational approach by searching for homologous sequences using EST or genomic sequences and the small-scale traditional sequencing approach are mostly limited to the identification of conserved miRNAs [30]. Recently developed high-throughput sequencing techniques (e.g. 454 technology and Illumina platform) have become powerful tools to uncover the large list of sRNA species in plants. These deep sequencing strategies may identify both known and novel miRNAs at unprecedented sensitivities and provide quantitative profiling of miRNA expression [11].
Citrus belong to evergreen subtropical fruit trees and are commercially grown in many countries. In 1936, Morris first described B-deficiency in field grown Citrus in South Africa [31]. In China, B-deficiency is frequently observed in Citrus orchards and is responsible for loss of productivity and poor fruit quality [32]. Although the effects of B-deficiency on Citrus growth, mineral nutrients, B uptake and distribution, CO2 assimilation, photosystem II photochemistry, photosynthetic enzymes, respiration, carbohydrate metabolism, antioxidant system and proteomics have been examined in some details [32–37], no data are available on B-deficiency-responsive miRNAs in Citrus. In this study, we reported the high-throughput sequencing (Illumina) analysis of sRNAs from roots of Citrus sinensis seedlings grown in B-sufficient (control) and -deficient nutrient solution with the objectives of identifying miRNAs that might be involved in the tolerance of plants to B-deficiency.
Results
Plant growth and B concentration in roots and leaves
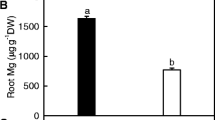
As shown in Table 1, 0 μM B treatment decreased shoot and whole plant dry weight (DW), and B concentration in roots and leaves, increased the ratio of root DW to shoot DW, but did not affect root DW. B concentration in 0 μM B-treated leaves was much lower than the sufficiency range of 30 to 100 μg g−1 DW [38]. Based on these results, plants treated with 0 μM B are considered B-deficient, and those treated with 10 μM B are considered B-sufficient.
High-throughput sequencing and annotation of miRNAs in roots
Two libraries were constructed from C. sinensis roots subjected to 0 or 10 μM B for 15 weeks, respectively. These libraries were sequenced by Illumina sequencing, leading to the generation of 22,998,100 and 22,576,217 raw reads from libraries of control and B-deficiency, respectively (Table 2). After removal of adaptors, low quality tags and contaminants, the length distribution of clean reads was summarized in Additional file 1. Reads with length of 24 nt were at the most abundant, followed by the reads with length of 22 nt and 21 nt. B-deficiency resulted in fewer 22 nt and 24 nt reads and more 20 nt and 23 nt reads. Generally speaking, the length distribution of sRNAs was similar to previous reports in higher plants such as sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) [30], Medicago truncatula[39], Arabidopsis[40] and trifoliate orange (Citrus trifoliata) [41]. This suggests that the Illumina sequencing data of sRNA libraries is reliable.
As shown in Table 2, 16,586,059 clean reads (2,343,700 unique reads) from control and 16,889,709 clean reads (2,669,645 unique reads) from B-deficient roots were mapped to C. clementina genome using SOAP. Exon, intron, miRNA, rRNA, snRNA, snoRNA and tRNA reads were annotated, respectively. Reads used for prediction of novel miRNAs for control and B-deficient roots were 3,776,597 and 4,030,300, respectively.
Identification of known miRNAs in roots
To identify the known miRNAs in the two libraries constructed from control and B-deficient roots, clear reads were aligned with known plant miRNAs from miRBase 18 (http://www.mirbase.org/). Only the perfectly matched sequences were considered. A total of 538 known miRNAs was identified in the two libraries (Additional file 2). To compare the abundance of miRNAs in different libraries, the count of reads was normalized to TPM. In control library, the most abundant miRNA identified was miR3954 (83,883.0865 TPM), followed by miR156 (32,511.4115 TPM) and miR166 (22,220.8316 TPM). However, miR156 abundance (22,980.3671 TPM) in B-deficient library ranked third after miR3954 (122,762.6342 TPM) and miR166 (42,066.0747 TPM) (Additional file 2). The known miRNAs with normalized read-count less that ten in the two libraries were not used for further analysis, because the use of low expressed miRNAs is apt to cause false results [39]. After removing these miRNAs, a total of 238 miRNAs were further analyzed (Additional file 3).
Identification of novel miRNAs in roots
After removal of the rRNAs, snRNAs, snoRNAs, tRNAs and known miRNAs, the remained sequences that were not annotated were used to predict novel miRNAs using the Mireap (http://sourceforge.net/projects/mireap/). Based on the criteria for annotation of plant miRNAs [6, 42], we identified a total of 108 novel miRNAs from control and B-deficient roots (Additional file 4). Similar to the known miRNAs, novel miRNAs with very low expression were excluded from the expression analysis [39], thus leading to 60 miRNAs that were used for further analysis (Additional file 5).
Differentially expressed miRNAs between control and B-deficient roots
A miRNA was considered differentially expressed when the miRNA had both a fold-change of more that 1.5 and a P-value of less than 0.01. Based on the two criteria, 40 known and 12 novel miRNAs were up-regulated, and 72 known and 10 novel miRNAs were down-regulated in response to B-deficiency (Additional files 3 and 5).
Validation of high-throughput sequencing results by real time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
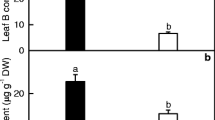
As only one mixed sample of B-deficient and control RNA was sequenced, it was necessary to measure the expression of a selection of miRNAs to validate that the changes observed were biologically consistent. qRT-PCR analysis showed that 23 of the 26 miRNAs tested were comparable in magnitude to the expression profiles obtained by the high-throughput sequencing (Figure 1). This technique was thus validated in 88.5% of cases.
Relative abundances of selected known miRNAs in B-deficient and control roots revealed by qRT-PCR. Bars represent mean ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences were tested between control and B-deficient roots for the same miRNA. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05. All the values were expressed relative to the control roots.
Prediction of targets for differentially expressed miRNAs
A total of 1228 (103) genes were predicted based on the 112 (22) differentially expressed known (novel) miRNAs in C. sinensis roots (Additional files 6 and 7). GO categories were assigned to all the predicted targets according to the cellular component, molecular function and biological process. Categories based on the cellular component showed that the potential targets for the 112 and 22 differentially expressed known and novel miRNAs were associated with 15 and 8 components, respectively, with the highest percentage of membrane (Figure 2A). Based on the molecular function, the targets for the known and novel miRNAs were classified into 17 and 11 categories, respectively, the highest percentage of two categories were nucleic acid binding and metal ion binding (Figure 2B). As shown in Figure 2C, the known and novel miRNAs targets were involved in 18 and 11 biological processes, respectively, the most two GO terms are developmental process and response to stress for known miRNAs and developmental process and nucleic acid metabolism process for novel miRNAs, respectively.
qRT-PCR relative expression analysis of target genes
In plants, genes targeted by miRNAs are believed to be regulated mainly via endonucleolytic cleavage of mRNAs due to their near-perfect complementarity to their target genes, although evidence indicates the existence of widespread translational inhibition [43]. Twenty-nine genes targeted by 10 down-regulated and two up-regulated miRNAs were assayed by qRT-PCR (Table 3). Seventeen of the 29 target genes had the expected changes in mRNA levels, suggesting that miRNAs play a role in regulating gene expression under B-deficiency by cleaving mRNAs. However, the expression changes of 11 target genes displayed a positive correlation with their corresponding miRNAs. The remaining one target gene was not detected in control and B-deficient roots. Overall, there was no obvious pattern in the expression profiles of target genes in response to B-deficiency. For example, the relative expression levels of nine genes targeted by down-regulated miR157 were validated by qRT-PCR. Four genes displayed decreased expression, while five had increased expression. The results were consistent with those reported in Arabidopsis[40].
Root metabolites and enzymes
B-deficient roots displayed decreased concentration of anthocyanin and increased levels of flavonoids (Figure 3). B-deficiency increased root proline concentration, and decreased its proline dehydrogenase (PDH) activity (Figure 4). As shown in Figure 5, B-deficient roots had increased glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)-NAD (deaminative) activity, but decreased GDH-NADH (aminative) activity.
Discussion
As important post-transcriptional regulators, the expressions of many plant miRNAs are regulated by various biotic and abiotic stresses, including nutrient (S, Cu, P, Fe and N) deficiencies, which may contribute to the development of adaptive responses to deal with unfavorable growth conditions [8, 9, 11, 13, 16, 26, 44]. Although the genes responsible for tolerance of plants to B-deficiency has been examined in some detail [4, 5], little information is available on the roles of miRNAs under B-deficiency. In this study, we identified 538 known miRNAs (Additional file 2) and 108 novel miRNAs (Additional file 4) from control and B-deficient roots. A 1.5-fold cut-off was set to determine up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs in addition to a P-value of less than 0.01. Based on the two criteria, 52 (40 known and 10 novel) up-regulated miRNAs and 82 (70 known and 10 novel) down-regulated miRNAs were identified in B-deficient roots (Additional files 3 and 5), demonstrating that the expression profiles of miRNAs in B-deficient roots were greatly affected.
Our finding that root miR474 was up-regulated under B-deficiency (Additional file 3) agrees with the previous results obtained on drought-stressed rice and maize (Zea mays) leaves [45] and salt-stressed maize roots [46]. Wei et al. [45] showed that under drought stress, the transcript of miR474 and the concentration of proline were increased in maize, whereas its target gene PDH was down-regulated. They concluded that drought-induced increase in miR474 expression might down-regulate PDH, thus increasing the accumulation of proline, an osmoprotectant. In addition to improving osmoprotection responses to drought stress, proline acts as a free radical scavenger to protect plants from oxidative damage. Hajiboland and Bastani [47] observed that proline concentration in tea roots and leaves increased under B-deficiency and drought stress, especially in roots, suggesting that the B-deficiency-induced accumulation of proline may be a strategy for tea plants to counteract the oxidative stress. Therefore, proline level in B-deficient roots might be enhanced due to decreased PDH activity resulting from enhanced expression level of miR474, thus improving the adaptation of plants to B-deficiency. As expected, B-deficient roots displayed decreased PDH activity and increased proline concentration (Figure 4).
We found that miR157 in roots was down-regulated by B-deficiency (Additional file 3), as previously obtained on N- and P- deficient common bean roots. However, common bean root miR157 was up-regulated by Fe-deficiency and manganese (Mn)-toxicity [13]. In plants, miR156 and miR157 have been grouped in one miRNA family because of their high degree of sequence similarity and their conserved targets, the squamosa promoter binding protein-like (SPL) proteins [48]. Gou et al. [49] observed a positive relationship of anthocyanin concentration and miR156 activity and an inverse relationship of flavonol (a subclasse of flavonoid) concentration and miR156 activity. As expected, B-deficient roots had lower anthocyanin concentration and higher flavonoid concentration (Figure 4) due to decreased expression of miR157. Gou et al. [49] suggested that at one of the miR156 targets, SPL9, negatively regulates anthocyanin accumulation by directly inhibiting expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes through disruption of the MYB-bHLH-WD40. However, SPL9 in C. sinensis roots was down-regulated by B-deficiency (Table 3).
Our observation that root miR158 was decreased under B-deficiency (Additional file 3) agrees with the previous report that miR158 was down-regulated in P-deficient tomato roots [10] and N-deficient Arabidopsis seedlings [28]. However, Buhtz et al. [50] observed that miR158 was up-regulated in the phloem of B. napus under Fe-deficiency. In Arabidopsis seedlings, miR158 were up-regulated in response to salt stress [51]. Expression of miR158a in Arabidopsis roots increased under hypoxia [40]. miR158 is predicted to target three genes encoding a pentatricopeptide repeat containing protein of unknown function, fucosyltransferases (xyloglucan fucosyltransferases) and a lipase [52]. However, root expression levels of fucosyltransferase 2 and lipase class 3 family protein decreased in response to B-deficiency (Table 3).
Root transcript of miR5023 decreased in response to B-deficiency (Additional file 3). This means that its target genes: FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein and root hair defective 3 GTP-binding protein (RHD3) (Additional file 6), might be up-regulated under B-deficiency. This is validated by our qRT-PCR data that the expression of the two genes in roots increased in response to B-deficiency (Table 3). FK506-binding proteins (FKBP), cyclosporins (CyPs) and parvulin (Pvn) are the three major classes of peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerases (PPIases), which are considered to assist chaperones by accelerating the slow rate-limiting isomerization steps. Among these, the best-studied class of PPIases is that of FKBPs by far. Increasing evidence shows that in addition to their role in protein folding, plant FKBPs are involved in abiotic stress response [53]. Nigam et al. [54] showed that yeast cells overexpressing FKBP20 displayed enhanced tolerance to high temperatures. The up-regulation of RHD3 in B-deficient roots agrees with the previous results obtained by Yang et al. [37] in B-deficient C. sinensis roots and by Redondo-Nieto et al. [4] in B-deficient M. truncatula root nodules. In Arabidopsis, RHD3 has been suggested to be required for cell wall biosynthesis and actin organization [55]. Xu et al. [56] observed that transgenic poplar plants overexpressing PeRHD3 had less adventitious roots, more lateral roots, and longer and more root hairs. Thus, the number of lateral roots in B-deficient C. sinensis seedlings might increase due to increased expression level of RHD3. This agrees with the previous reports data that B-deficiency increased lateral root formation of plants [57]. These results imply that RHD3 may be involved in the tolerance of plants to B-deficiency.
Zhou et al. [58] reported that overexpression of miR165 resulted in a drastic reduction in the transcript levels of its target genes [all five class III homeodomain leucine-zipper (HD-ZIP III) genes] in Arabidopsis seedlings. Hawker and Bowman [59] showed that HD-ZIP III genes played a role in promoting Arabidopsis lateral root formation. Therefore, B-deficient roots might have increased expression level of HD-ZIP III due to decreased abundance of miR165 (Additional file 3), thus enhancing lateral root formation. Indeed, qRT-PCR analysis showed that the expression levels of three HD-ZIP III transcription factors (ILF1/REV, ATHB-8 and ATHB-15) increased in B-deficient roots (Table 3). This is also supported by the previous reports that B-deficiency increased the lateral root formation [57].
Recently, Xu et al. [30] observed an inverse relationship between the abundance of miR1857 in the red-flesh mutant of sweet orange and the expression level of its target gene encoding lycopene β-cyclase, a key enzyme of the carotenoid biosynthesis pathway. In our study, root miR1857 was was up-regulated under-B deficiency (Additional file 3), implying that carotenoid biosynthesis might be impaired in B-deficient roots due to decreased expression of lycopene β-cyclase gene.
Our finding that root miR2118 was induced by B-deficiency (Additional file 3) agrees with the previous reported that the transcript of miR2118 was enhanced in salt-stressed roots of Vigna unguiculata[60], NaCl, drought and ABA treated P. vulgaris seedlings [61], Fe-deficient common bean leaves [13], and drought-stressed M. truncatula shoots [62], and with our qRT-PCR data that the expression of one target gene encoding LRR and NB-ARC domains-containing disease resistance protein decreased in B-deficient roots (Table 3). However, P-deficiency and Mn-toxicity down-regulated the transcript of miR2118 in common bean leaves [13]. Wong et al. [63] reported that the abundance of disease resistance protein (TIR-NBS-LRR class, a target gene of miR2118) mRNA in Thellungiella salsuginea leaves was down-regulated in response to drought and short-term salinity stress. However, the abundance of TIR-NBS-LRR class disease resistance protein in Thellungiella halophila leaves increased under long-term salinity stress [64]. Therefore, miR2118 might be involved in abiotic stresses as well as biotic stresses.
Evidence shows that the target genes of miR472 are involved in disease resistance [65]. We found that miR472 was enhanced in B-deficient roots (Additional file 3), meaning that disease resistance protein gene might be down-regulated, thus decreasing the disease resistance of roots. As expected, the expression of three genes encoding disease resistance protein (TIR-NBS-LRR class) family, LRR and NB-ARC domains-containing disease resistance protein, and disease resistance protein (CC-NBS-LRR class) family decreased in B-deficient roots (Table 3). This agrees with the fact that B increases the disease resistance in plants [66].
We found that root miR394 was up-regulated by B-deficiency (Additional file 3), as previously reported on P-starved tomato roots [10], NaCl-treated Arabidopsis seedlings [51], Fe-deficient Malus xiaojinensis roots [67], and N-deficient maize shoots (miR394s) [44]. Ni et al. [68] showed that overexpression of miR394a in Arabidopsis reduced the transcript of an F-box gene (At1g27340, also known as LEAF CURLING RESPONSIVENESS, LCR) containing a miR394 complementary target site. In Arabidopsis, a null mutation in DOR gene, which encodes a putative F-box protein, led to a substantial increase in drought tolerance as well as a hypersensitive ABA response of stomatal closing; conversely, the transgenic plants overexpressing DOR gene showed decreased drought tolerance [69]. Song et al. [70] reported that both miR394 and LCR transcripts were regulated by salt and drought stresses and ABA treatment, concluding that the silencing of LCR mRNA by miR394 is essential to maintain a certain phenotype favorable for the adaptive response to abiotic stresses. Therefore, B-deficiency might down-regulate the accumulation of LCR mRNA in C. sinensis roots due to increased transcript of miR394 (Additional file 3), thus improving the tolerance of plants to B-deficiency. However, Li et al. [71] observed that miR394a was up-regulated in response to drought stress but down-regulated in response to salinity stress in soybean roots. miR394a,b,c were up-regulated in roots, stems and leaves of B. napus by sulfate-deficiency and Cd stress except for the down-regulation of miR394 in sulfate-deficient leaves [72]. In Arabidopsis, root miR394b and shoot miR394a and miR394b were initially up-regulated and then down-regulated under Fe-deficiency [73].
miR782 is predicted to target genes encoding maize protein disulfide isomerase (PDIL5-1) [74] and MYB transcription factor (MYBML2) [75]. Our result showed that root expression of miR782 decreased in response to B-deficiency (Additional file 3), implying that the expression of PDI and MYBML2 might be up-regulated in B-deficient roots. Protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs) are molecular chaperones that contain thioredoxin (TRX) domains and aid in the formation of proper disulfide bonds during protein folding. Chen et al. [76] showed that transgenic rice seedlings overexpressing a protein disulfide isomerase-like protein (PDIL) gene displayed enhanced tolerance to mercury (Hg), accompanied by lower levels of superoxide anion radicals, H2O2 and malondialdehyde (MDA), higher activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), and increased concentrations of non-protein thiols and reduced glutathione (GSH). Plant MYB proteins are characterized by a highly conserved MYB DNA-binding domain. Plant MYB transcription factors are involved in regulatory networks controlling development, metabolism and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Rubio et al. [77] showed that a conserved MYB transcription factor was involved in phosphate starvation signaling in both vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Thus, the down-regulation of miR782 in B-deficient roots might provide an adaptive strategy of plants to B-deficiency.
B-deficiency decreased the transcript of root miR830 (Additional file 3). This agrees with the previous report that miR830a in Arabidopsis seedlings was down-regulated at low temperature (16°C) [78]. However, miR830 was up-regulated in P-deficient roots and down-regulated in P-deficient stems and leaves of white lupin [22]. miR830 is predicted to target two genes encoding RanBP1 domain-containing protein and kinesin motor-related [79]. qRT-PCR analysis showed that B-deficient roots had increased expression of kinesin motor-related, but decreased expression of RanBP1 domain-containing protein (Table 3). Kinesins, a superfamily of microtubule motor proteins ubiquitous in all eukaryotic organisms, function in the unidirectional transport of vesicles and organelles, cytokinesis, signal transduction, and morphogenesis [80]. Therefore, the down-regulation of miR830 in B-deficient roots might be advantageous to normal growth and development of plants under B-deficiency.
We found that the transcript of miR843 decreased in B-deficient roots (Additional file 3), implying that its target genes: leucine rich repeat protein (LRP), plant homedomain (PHD)-finger, oligomeric golgi complex 7-like[81] and sulfate transporter[82], might be up-regulated under B-deficiency. qRT-PCR analysis showed that B-deficient roots had enhanced expression of LRP, but decreased expression of sulfate transporter (Table 3). Park et al. [83] observed that heterologous expression of rice LRP (OsLRP) resulted in the activation of defense response and enhanced resistance to bacterial soft rot in Chinese cabbage. Thus, the higher expression of LRP might partially compensate for the decreased disease resistance in B-deficient plants [66]. Wei et al. [84] reported that transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing the GmPHD2 from soybean displayed enhanced salt tolerance through control of ROS signaling and scavenging. Liu et al. [85] observed that overexpression of OsPHD1 enhanced the tolerance of transgenic rice plants to drought, high salt and cold stresses. Therefore, the down-regulation of miR843 in B-deficient roots might be an adaptive response. Our observation that B-deficiency decreased the transcript of root sulfate transporter (Table 3) disagrees with the previous reports that B-deficiency increased the abundances of phosphate transporter 3;1 [37] in C. sinensis roots and of K+ channel in B. napus roots [86].
We observed that B-deficiency increased the transcript of miR821 in roots (Additional file 3), which agrees with the previous data that miR821 was expressed in roots of salt-stressed plants, and not expressed in healthy, non-stressed plants [87]. Down-regulation of its target gene, putative enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase by miR821 is indicative of the impact of the β-oxidation pathway of unsaturated fatty acids, which might lead to decrease in carbon flux in the form of acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA can eventually enter the TCA cycle [88]. This agrees with our report that B-deficient C. sinensis roots displayed decreased root respiration [37]. In this study, the transcript of GDH1, a target gene of miR821 [89], might be down-regulated in B-deficient roots, thus decreasing the activity of root GDH. As expected, GDH-NADH (aminative) activity was down-regulated in B-deficient C. sinensis roots (Figure 5B). However, GDH-NAD (deaminative) activity in roots increased in response to B-deficiency (Figure 5A). Robinson et al. [90] reported that the primary role of GDH was the oxidation of glutamate under conditions where carbon is limited. Thus, B-deficiency-induced increase in GDH-NAD activity agrees with the previous study showing that B-deficiency decreased or did not affect root concentrations of non-structural carbohydrates [37]. Beato et al. [91] showed that GDH genes, Ntgdh-NAD;A1 and Ntgdh-NAD;B2, were up-regulated in N-deficient tobacco roots, accompanied by decreased concentrations of glucose and fructose.
B-deficiency decreased the expression level of root miR5266 (Additional file 3). As expected, the transcript of ammonium transporter 1;1 targeted by miR5266 (Additional file 6) was enhanced in B-deficient roots (Table 3), hence facilitating the uptake of ammonium from external environments as well as the translocation of ammonium from roots to shoots [92]. This agrees with the previous reports that B-deficient tobacco roots had higher concentration of ammonium [2]. The higher uptake of ammonium might compensate for the reduced nitrate uptake by repressing root plasmalemma H+-ATPase (PMA2) gene expression [2]. However, the expression of ammonium transporter 2 targeted by miR5562 (Additional file 6) decreased in B-deficient roots (Table 3).
The expression of autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPase 11 gene (a target gene of miR3465, Additional file 6), might be up-regulated in B-deficient roots due to decreased transcript of miR3465 (Additional file 3). This agrees with our finding that B-deficiency increased the abundances of autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPase 11 in C. sinensis roots [37].
Conclusions
We first identified miRNAs and their expression pattern in B-deficient C. sinensis roots by Illumina sequencing. A total of 538 known miRNAs and of 108 novel miRNAs was identified from control and B-deficient roots. In B-deficient roots, 52 (40 known and 12 novel) up-regulated and 82 (72 known and 10 novel) down-regulated miRNAs were isolated. This demonstrates remarkable metabolic flexibility of C. sinensis roots, which might contribute to the tolerance of roots to B-deficiency. A model for the possible roles of miRNAs in the tolerance of roots to B-deficiency was proposed through the integration of the present results and available data in the literature (Figure 6). miRNAs might regulate the adaptations of C. sinensis roots to B-deficiency through following several aspects: (a) activation of the defense response, ROS signaling and scavenging due to increased expression of miR474 and decreased expression of miR782 and miR843; (b) increasing the number of lateral roots (miR5023) and maintaining a certain phenotype favorable for the adaptive response to B-deficiency (miR394); (c) enhancing cell transport by decreasing the accumulation of miR830, miR5266 and miR3465; (c) improving osmoprotection (miR474) and regulating other metabolic reactions (miR5023 and miR821). In addition, both miR472 and miR2118 expression increased in B-deficient C. sinensis roots, thus decreasing the expression of their target genes, which are involved in disease resistance, and hence, the disease resistance of roots. Therefore, the discovery and characterization of these B-deficiency-responsive miRNAs will help us to elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in the tolerance of plants to B-deficiency. Although the absolute conditions without B created under pot conditions do not exist in field, because there is always certain level of B supply in field conditions even under highly B-deficient conditions, pot results should stand ture under field conditions, because typical B-deficient symptoms: corky split veins of Citrus leaves usually occur in the sand culture and in field conditions [33, 38, 93].
Methods
Plant culture and B treatments
Plant culture and B treatments were performed according to Yang et al. [37]. Briefly, 5-week-old seedlings of ‘Xuegan’ [Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck] were transplanted into 6 L pots containing fine river sand. Ten weeks after transplanting, each pot was supplied every other day with B-deficient (0 μM H3BO3) or -sufficient (10 μM H3BO3, control) nutrient solution for 15 weeks. There were 10 replications per B treatment with 2 pots in a completely randomized design. Plants grown in the absence of B first developed in the apex and in the actively growing leaves because B is phloem immobile in Citrus. B-deficient symptoms in mature leaves were characterized by enlargement, splitting and corking of leaf veins [33, 34]. At the end of the experiment, approx. 5-mm-long root apices were frozen immediately in liquid N2 after being excised from the seedlings. Root samples were stored at −80°C until extraction.
Plant DW, root and leaf B
At the end of the experiment, seven plants per treatment from different replications were harvested. The plants were divided into their separate parts (roots and shoots). The plant material was then dried at 80°C for 48 h and the DW measured. B concentration in roots and leaves was assayed by ICP emission spectrometry after microwave digestion with HNO3[37].
Root flavonoids, anthocyanin, proline, proline dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase
Flavonoid and anthocyanin were assayed as described by Krizek et al. [94] and Wagner [95], respectively. Free proline and proline dehydrogenase (PDH) were assayed according to Bates et al. [96] and Veeranjaneyulu and Kumari [97], respectively. The amination (NADH) and deamination (NAD) reactions of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) were assayed according to Loyola-Vargas and de Jimenez [98].
Isolation of sRNAs, library construction and high-throughput sequencing
About 0.1 g mixed frozen B-sufficient and -deficient roots from five replictations were used to extract RNA. Total RNA was extracted from frozen roots using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) following manufacturer’s instructions. Two sRNA libraries were constructed according to Wang et al. [62]. Briefly, sRNAs were isolated from the total RNA by size fractionation with 15% Tris-borate-EDTA urea polyacrylamide gel (TBU). Then the sRNAs were ligated with 5' and 3' adaptor by T4 RNA ligase after being dephosphorylated by alkaline phosphatase. The adaptor-ligated sRNAs were transcribed to single-stranded cDNA using Superscript II reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen). Thereafter, the single-stranded cDNA was used as templates for double-stranded synthesis by PCR amplification using the primer designed according to the adapter sequence. The obtained PCR products were sequenced on a Solexa sequencer (Illumina) at the Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI), Shenzhen, China.
sRNA annotation and miRNA identification
The raw reads obtained from the Solexa sequencing were cleaned by removing adaptors, low quality tags as well as contaminant reads including those reads with 5´-primer contaminants, reads without 3´-primer, reads with poly A, reads without the insert tag, and reads with length less than 18 nt. We use software developed by the BGI to deal with the data from the Solexa sequencing. The clean reads were then used to analyze length distribution and common/specific sequences. Thereafter, the clear reads were mapped to Citrus clementina genome (JGI version 0.9, http://www.phytozome.org/clementine.php, 35976 sequences) using SOAP, only perfectly mapped sequences were retained and analyzed further. rRNAs, tRNAs, snRNAs and snoRNAs were removed from the sRNAs sequences through BLASTn search using NCBI Genebank database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi/) and Rfam (10.1) database (http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/databases/rfam.html) (e = 0.01). The remaining sequences were aligned with known plant miRNAs from miRBase 18 (http://www.mirbase.org/). Only the perfectly matched sequences were considered to be conserved miRNAs. Reads that were not annotated were used to predict novel miRNAs using a prediction software Mireap (http://sourceforge.net/projects/mireap/), which was developed by the BGI, by exploring the secondary structure, the Dicer cleavage site and the minimum free energy of the unannotated small RNA tags which could be mapped to genome. Parameters were set as follows: minimal miRNA sequence length (18), maximal miRNA sequence length (25), minimal miRNA reference sequence length (20), maximal miRNA reference sequence length (23), maximal copy number of miRNAs on reference (20), maximal free energy allowed for a miRNA precursor (−18 kcal/mol), maximal space between miRNA and miRNA* (300), minimal base pairs of miRNA and miRNA* (16), maximal bulge of miRNA and miRNA* (4), maximal asymmetry of miRNA/miRNA* duplex (4) and flank sequence length of miRNA precursor (20).
Differential expression analysis of miRNAs under B-deficiency
Both the fold change between B-deficiency and -sufficiency (control) and the P-value were calculated from the normalized expression of transcript per million (TPM) [62]. Normalized expression was calculated by the following formula: Normalized expression = Actual miRNA count/Total count of clean reads*1,000,000. The fold change between B-deficiency and control was calculated as: Fold-change = log2 (B-deficiency/Control). The p-value was calculated by the following formula:
A 1.5-fold cut-off was set to determine up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs in addition to a P-value of less than 0.01.
Target prediction of miRNAs
Target prediction of miRNAs was performed by RNAhybrid based on rules suggested by Allen et al. [14] and Schwab et al. [52].
Functions of the potential targets of the differentially expressed miRNAs
To reveal the functions of the predicted target genes of the differentially expressed miRNAs, all targets were mapped to GO terms in the database (http://www.geneontology.org/), and calculated gene numbers for each term. The GO results were expressed as three categories: cellular component, molecular function, biological process [99].
Validation of miRNA expression by real time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from B-sufficient and -deficient roots as described above. About 2.0 μg total RNA was polyadenylated with ATP by poly(A) polymerase and reverse-transcribed with poly(T) adapter primer by PrimeScript® RTase at 42°C according to manufacturer’s instruction (Takara, Japan). Add enough RNA-free dH2O to bring to a final volume of each tube to 100 μL and pipet 1 μL aliquot to the next qRT-PCR. Twenty-six miRNAs were selected to perform qRT-PCR to validate the miRNA expression obtained from the high-throughput sequencing. miRNA special (forward) primers were designed according to the miRNA sequence but excluded the last two to five nucleotides at 3' end of the miRNA. A 5' extension of three to five nucleotides, which was chosen randomly and relatively GC-rich, was added to each forward primer to increase the melting temperature [100]. All the primers were assigned to Primer Software Version 5.0 (PREMIER Biosoft International, USA) to assess their quality. All the primers used were listed in Additional file 8. For qRT-PCR, 20 μL reaction solution contained 10 μL ready-to-use SYBR® Premix Ex TaqTM II (Takara, Japan), 0.8 μL 10 μM miRNA forward primer, 0.8 μL 10 μM Uni-miR qPCR primer, 2 μL cDNA template and 6.4 μL dH2O. qRT-PCR was performed with a Mastercycler Ep Realplex System (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) using actin (AEK97331.1) as internal control. The cycling conditions were 60 s at 95°C, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 10 s, 60°C for 30 s. Samples for qRT-PCR were run in at least three biological replicates with three technical replicates. Relative miRNA expression was calculated using ddCt algorithm. For the normalization of miRNA expression, actin gene was used as an internal standard and the roots from control plants were used as reference sample, which was set to 1.
qRT-PCR analysis of miRNA target gene expression
Total RNA was extracted from frozen B-sufficient and -deficient roots using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) following manufacturer’s instructions. The sequences of the F and R primers used were given in Additional file 9. qRT-PCR analysis of miRNA target gene expression was performed using a Mastercycler Ep Realplex System (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) as previously described by Yang et al. [37].
Experimental design and statistical analysis
There were 20 pot seedlings per treatment in a completely randomized design. Experiments were performed with 4–7 replicates. Differences among treatments were separated by the least significant difference (LSD) test at P < 0.05 level.
Availability of supporting data
“The data set supporting the results of this article are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus repository under accession no GSE57016 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE57016)”. The mature miRNA and precursor sequences will be submitted to miRBase registry and assigned final names after final acceptance of the manuscript.
References
Shorrocks VM: The occurrence and correction of boron deficiency. Plant Soil. 1997, 193: 121-148. 10.1023/A:1004216126069.
Camacho-Cristóbal JJ, González-Fontes A: Boron deficiency decreases plasmalemma H+-ATPase expression and nitrate uptake, and promotes ammonium assimilation into asparagine in tobacco roots. Planta. 2007, 226: 443-451. 10.1007/s00425-007-0494-2.
Camacho-Cristóbal JJ, Rexach J, Herrera-Rodríguez MB, Navarro-Gochicoa MT, González-Fontes A: Boron deficiency and transcript level changes. Plant Sci. 2011, 181: 85-89. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.05.001.
Redondo-Nieto M, Maunoury N, Mergaert P, Kondorosi E, Bonilla I, Bolaños L: Boron and calcium induce major changes in gene expression during legume nodule organogenesis. Does boron have a role in signalling?. New Phytol. 2012, 195: 14-19. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04176.x.
Xu FS, Zeng CY, Peng LS, Shi L: Analysis of gene expression profile in response to low boron stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Acta Agri Univ Jiangxiensis. 2010, 32: 1004-1009.
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B: MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2006, 57: 19-53. 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105218.
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP: MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev. 2002, 16: 1616-1626. 10.1101/gad.1004402.
Sun G: MicroRNAs and their diverse functions in plants. Plant Mol Biol. 2012, 80: 17-36. 10.1007/s11103-011-9817-6.
Eldem V, Okay S, Ünver T: Plant microRNAs: new players in functional genomics. Turk J Agric For. 2013, 37: 1-21.
Gu M, Xu K, Chen AQ, Zhu YY, Tang GL, Xu GH: Expression analysis suggests potential roles of microRNAs for phosphate and arbuscular mycorrhizal signaling in Solanum lycopersicum. Physiol Plant. 2010, 138: 226-237. 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2009.01320.x.
Hsieh LC, Lin SI, Shih ACC, Chen JW, Lin WY, Tseng CY, Li WH, Chiou TJ: Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151: 2120-2132. 10.1104/pp.109.147280.
Liang G, Yang F, Yu D: MicroRNA395 mediates regulation of sulfate accumulation and allocation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2010, 62: 1046-1057.
Valdés-López O, Yang SS, Aparicio-Fabre R, Graham PH, Reyes JL, Vance CP, Hernández G: MicroRNA expression profile in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under nutrient deficiency stresses and manganese toxicity. New Phytol. 2010, 187: 805-818. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03320.x.
Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC: MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell. 2005, 121: 207-221. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.004.
Bari R, Pant BD, Stitt M, Scheible WR: PHO2, microRNA399, and PHR1 define a phosphate-signaling pathway in plants. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141: 988-999. 10.1104/pp.106.079707.
Pant BD, Musialak-Lange M, Nuc P, May P, Buhtz A, Kehr J, Walther D, Scheible WR: Identification of nutrient-responsive Arabidopsis and rapeseed microRNAs by comprehensive real-time polymerase chain reaction profiling and small RNA sequencing. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150: 1541-1555. 10.1104/pp.109.139139.
Liu JQ, Allan DL, Vance CP: Systemic signaling and local sensing of phosphate in common bean: cross-talk between photosynthate and microRNA399. Mol Plant. 2010, 3: 428-437. 10.1093/mp/ssq008.
Hu B, Zhu C, Li F, Tang J, Wang Y, Lin A, Liu L, Che R, Chu C: LEAF TIP NECROSIS1 plays a pivotal role in regulation of multiple phosphate starvation responses in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156: 1101-1115. 10.1104/pp.110.170209.
Dong B, Rengel Z, Delhaize E: Uptake and translocation of phosphate by pho2 mutant and wild-type seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta. 1998, 205: 251-256. 10.1007/s004250050318.
Shukla LI, Chinnusamy V, Sunkar R: The role of microRNAs and other endogenous small RNAs in plant stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008, 1779: 743-748. 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.04.004.
Zeng HQ, Zhu YY, Huang SQ, Yang ZM: Analysis of phosphorus-deficient responsive miRNAs and cis-elements from soybean (Glycine max L.). J Plant Physiol. 2010, 167: 1289-1297. 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.04.017.
Zhu YY, Zeng HQ, Dong CX, Yin XM, Shen QR, Yang ZM: MicroRNA expression profiles associated with phosphorus deficiency in white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Sci. 2010, 178: 23-29. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.09.011.
Branscheid A, Sieh D, Pant BD, May P, Devers EA, Elkrog A, Schauser L, Scheible WR, Krajinski F: Expression pattern suggests a role of miR399 in the regulation of the cellular response to local Pi increase during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2010, 23: 915-926. 10.1094/MPMI-23-7-0915.
Matts J, Jagadeeswaran G, Roe BA, Sunkar R: Identification of microRNAs and their targets in switchgrass, a model biofuel plant species. J Plant Physiol. 2010, 167: 896-904. 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.02.001.
Kuo HF, Chiou TJ: The role of microRNAs in phosphorus deficiency signaling. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156: 1016-1024. 10.1104/pp.111.175265.
Kawashima CG, Yoshimoto N, Maruyama-Nakashita A, Tsuchiya YN, Saito K, Takahashi H, Dalmay T: Sulphur starvation induces the expression of microRNA-395 and one of its target genes but in different cell types. Plant J. 2009, 57: 313-321. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03690.x.
Abdel-Ghany SE, Pilon M: MicroRNA-mediated systemic down-regulation of cooper protein expression in response to low copper availability in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283: 15932-15945. 10.1074/jbc.M801406200.
Liang G, He H, Yu D: Identification of nitrogen starvation-responsive microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One. 2012, 7: e48951-10.1371/journal.pone.0048951.
Ozhuner E, Eldem V, Ipel A, Okay S, Sakcali S, Zhang B, Boke H, Unver T: Boron stress responsive microRNAs and their targets in barley. PLoS One. 2013, 8: e59543-10.1371/journal.pone.0059543.
Xu Q, Liu Y, Zhu A, Wu X, Ye J, Yu K, Guo W, Deng X: Discovery and comparative and comparative profiling of microRNAs in a sweet orange red-flesh mutant and its wild type. BMC Genomics. 2010, 11: 246-10.1186/1471-2164-11-246.
Morris AA: Progress report on ‘hard fruit’. British S Africa Co Mazoe Citrus Exp Sta (S Rhodesia) Ann Rept. 1936, 15: 60-61.
Chen LS, Han S, Qi YP, Yang LT: Boron stresses and tolerance in Citrus. Afr J Biotech. 2012, 11: 5961-5969.
Han S, Chen LS, Jiang HX, Smith BR, Yang LT, Xie CY: Boron deficiency decreases growth and photosynthesis, and increases starch and hexoses in leaves of Citrus seedlings. J Plant Physiol. 2008, 165: 1331-1341. 10.1016/j.jplph.2007.11.002.
Han S, Tang N, Jiang HX, Yang LT, Li Y, Chen LS: CO2 assimilation, photosystem II photochemistry, carbohydrate metabolism and antioxidant system of Citrus leaves in response to boron stress. Plant Sci. 2009, 176: 143-153. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.10.004.
Liu GD, Jiang CC, Wang YH: Distribution of boron and its forms in young ‘Newhall’ navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osb.) plants grafted on two rootstocks in response to deficient and excessive boron. Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2011, 57: 93-104. 10.1080/00380768.2010.551299.
Sheng O, Song SW, Peng SA, Deng XX: The effects of low boron on growth, gas exchange, boron concentration and distribution of ‘Newhall’ navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osb.) plants grafted on two rootstocks. Sci Hort. 2009, 121: 278-283. 10.1016/j.scienta.2009.02.009.
Yang LT, Qi YP, Lu YB, Gu P, Sang W, Feng H, Zhang HX, Chen LS: iTRAQ protein profile analysis of Citrus sinensis roots in response to long-term boron deficiency. J Proteomics. 2013, 93: 179-206.
Chapman HD: The mineral nutrition of Citrus. The Citrus Industry, Volume 2. Edited by: Reuther W, Webber HJ, Batchelor LD. 1968, CA: Division of Agricultural Sciences, University of California, 127-189.
Chen L, Wang T, Zhao M, Tian Q, Zhang WH: Identification of aluminum-responsive microRNAs in Medicago truncatula by genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. Planta. 2010, 235: 375-386.
Moldovan D, Spriggs A, Yang J, Pogson BJ, Dennis ES, Wilson IW: Hypoxia-responsive microRNAs and trans-acting small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2010, 61: 165-177. 10.1093/jxb/erp296.
Song C, Wang C, Zhang C, Korir NK, Yu H, Ma Z, Fang J: Deep sequencing discovery of novel and conserved microRNAs in trifoliate orange (Citrus trifoliata). BMC Genomics. 2010, 11: 431-10.1186/1471-2164-11-431.
Meyers BC, Axtell MJ, Bartel B, Bartel DP, Baulcombe D, Bowman JL, Cao X, Carrington JC, Chen X, Green PJ, Griffiths-Jones S, Jacobsen SE, Mallory AC, Martienssen RA, Poethig RS, Qi Y, Vaucheret H, Voinnet O, Watanabe Y, Weigel D, Zhu JK: Criteria for annotation of plant MicroRNAs. Plant Cell. 2008, 20: 3186-3190. 10.1105/tpc.108.064311.
Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto YY, Sieburth L, Voinnet O: Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science. 2008, 320: 1185-1190. 10.1126/science.1159151.
Zhao M, Tai H, Sun S, Zhang F, Xu Y, Li WX: Cloning and characterization of maize miRNAs involved in responses to nitrogen deficiency. PLoS One. 2012, 7: e29669-10.1371/journal.pone.0029669.
Wei LY, Zhang DF, Xiang F, Zhang ZX: Differentially expressed miRNAs potentially involved in the regulation of defense mechanism to drought stress in maize seedlings. Inter J Plant Sci. 2009, 170: 979-989. 10.1086/605122.
Ding D, Zhang L, Wang H, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zheng Y: Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann Bot. 2009, 103: 29-38.
Hajiboland R, Bastani S: Tolerance to water stress in boron-deficient tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Folia Hort. 2012, 24: 41-51.
Martin RC, Asahina M, Liu PP, Kristof JR, Coppersmith JL, Pluskota WE, Bassel GW, Goloviznina NA, Nguyen TT, Martínez-Andújar C, Kumar MBA, Pupel P, Nonogaki H: The microRNA156 and microRNA172 gene regulation cascades at post-germinative stages in Arabidopsis. Seed Sci Res. 2010, 20: 79-87. 10.1017/S0960258510000085.
Gou JY, Felippes FF, Liu CJ, Weigel D, Wang JW: Negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by a miR156-targeted SPL transcription factor. Plant Cell. 2011, 23: 1512-1522. 10.1105/tpc.111.084525.
Buhtz A, Pieritz J, Springer F, Kehr J: Phloem small RNAs, nutrient stress responses, and systemic mobility. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10: 64-10.1186/1471-2229-10-64.
Liu HH, Tian X, Li YJ, Wu CA, Zheng CC: Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA. 2008, 14: 836-843. 10.1261/rna.895308.
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D: Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell. 2005, 8: 517-527. 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.018.
Gollan PJ, Bhave M, Aro EM: The FKBP families of higher plants: exploring the structures and functions of protein interaction specialists. FEBS Let. 2012, 586: 3539-3547. 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.09.002.
Nigam N, Singh A, Sahi C, Chandramouli A, Grover A: SUMO-conjugating enzyme (Sce) and FK506-binding protein (FKBP) encoding rice (Oryza sativa L.) genes: genome-wide analysis, expression studies and evidence for their involvement in abiotic stress response. Mol Genet Genomics. 2008, 279: 371-383. 10.1007/s00438-008-0318-5.
Hu Y, Zhong R, Morrison WH, Ye ZH: The Arabidopsis RHD3 gene is required for cell wall biosynthesis and actin organization. Planta. 2003, 217: 912-921. 10.1007/s00425-003-1067-7.
Xu M, Xie W, Huang M: Overexpression of PeRHD3 alters the root architecture in Populus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012, 424: 239-244. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.083.
Hajiboland R, Farhanghi F, Aliasgharpour M: Morphological and anatomical modifications in leaf, stem and roots of four plant species under boron deficiency conditions. Anal Biol. 2012, 34: 13-27.
Zhou GK, Kubo M, Zhong R, Demura T, Ye ZH: Overexpression of miR165 affects apical meristem formation, organ polarity establishment and vascular development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48: 391-404. 10.1093/pcp/pcm008.
Hawker NP, Bowman JL: Roles for class III HD-Zip and KANADI genes in Arabidopsis root development. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135: 2261-2270. 10.1104/pp.104.040196.
Paul S, Kundu A, Pal A: Identification and validation of conserved microRNAs along with their differential expression in roots of Vigna unguiculata grown under salt stress. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Culture. 2011, 105: 233-242. 10.1007/s11240-010-9857-7.
Arenas-Huertero C, Pérez B, Rabanal F, Blanco-Melo D, De la Rosa C, Estrada-Navarrete G, Sanchez F, Covarrubias AA, Reyes JL: Conserved and novel miRNAs in the legume Phaseolus vulgaris in response to stress. Plant Mol Biol. 2009, 70: 385-401. 10.1007/s11103-009-9480-3.
Wang T, Chen L, Zhao M, Tian Q, Zhang WH: Identification of drought-responsive microRNAs in Medicago truncatula by genome-wide high throughout sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2011, 12: 367-378. 10.1186/1471-2164-12-367.
Wong CE, Li Y, Labbe A, Guevara D, Nuin P, Whitty B, Diaz C, Golding GB, Gray GR, Weretilnyk EA, Griffith M, Moffatt BA: Transcriptional profiling implicates novel interactions between abiotic stress and hormonal responses in Thellungiella, a close relative of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140: 1437-1450. 10.1104/pp.105.070508.
Gao F, Zhou YJ, Huang LY, He DC, Zhang GF: Proteomic analysis of long-term salinity stress-responsive proteins in Thellungiella halophila leaves. Chin Sci Bull. 2008, 53: 3530-3537. 10.1007/s11434-008-0455-6.
Lu S, Sun YH, Chiang VL: Stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus. Plant J. 2008, 55: 131-151. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03497.x.
Frenkel O, Yermiyahu U, Forbes GA, Fry WE, Shtienberg D: Restriction of potato and tomato late blight development by sub-phytotoxic concentrations of boron. Plant Pathol. 2010, 2010 (59): 626-633.
Yu C, Sun R, Wang Y, Zhang X, Han Z: Cloning and expression analysis of miR394a under iron deficiency in Malus xiaojinensis. Chin Agri Sci Bull. 2012, 28 (28): 158-162.
Ni Z, Hu Z, Jiang Q, Zhang H: Overexpression of gma-MIR394a confers tolerance to drought in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012, 427: 330-335. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.055.
Zhang Y, Xu W, Li Z, Deng XW, Wu W, Xue Y: F-box protein dor functions as a novel inhibitory factor for abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure under drought stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148: 2121-2133. 10.1104/pp.108.126912.
Song JB, Gao S, Sun D, Li H, Shu XX, Yang ZM: miR394 and LCR are involved in Arabidopsis salt and drought stress responses in an abscisic acid-dependent manner. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13: 210-10.1186/1471-2229-13-210.
Li H, Dong Y, Yin H, Wang N, Yang J, Liu X, Wang Y, Wu J, Li X: Characterization of the stress associated microRNAs in Glycine max by deep sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11: 170-10.1186/1471-2229-11-170.
Huang SQ, Xiang AL, Che LL, Chen S, Li H, Song JB, Yang ZM: A set of miRNAs from Brassica napus in response to sulphate deficiency and cadmium stress. Plant Biotechnol J. 2010, 8: 887-899. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00517.x.
Kong WW, Yang ZM: Identification of iron-deficiency responsive microRNA genes and cis-elements in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010, 48: 153-159. 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.12.008.
Xu C, Yang RF, Li WC, Fu FL: Identification of 21 microRNAs in maize and their differential expression under drought stress. Afr J Biotech. 2010, 9: 4741-4753.
Barozai MYK, Din M, Baloch IA: Identification of microRNAs in ecological model plant Mimulus. J Biophys Chem. 2011, 2: 322-331. 10.4236/jbpc.2011.23037.
Chen Z, Pan Y, Wang S, Ding Y, Yang W, Zhu C: Overexpression of a protein disulfide isomerase-like protein from Methanothermobacter thermoautotrophicum enhances mercury tolerance in transgenic rice. Plant Sci. 2012, 197: 10-20.
Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martín AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J: A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev. 2001, 15: 2122-2133. 10.1101/gad.204401.
Lee H, Yoo SJ, Lee JH, Kim W, Yoo SK, Fitzgerald H, Carrington JC, Ahn JH: Genetic framework for flowering-time regulation by ambient temperature-responsive miRNAs in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38: 3081-3093. 10.1093/nar/gkp1240.
Fahlgren N, Howell MD, Kasschau KD, Chapman EJ, Sullivan CM, Cumbie JS, Scott A, Givan SA, Law TF, Grant SR, Dangl JL, Carrington JC: High-throughput sequencing of Arabidopsis microRNAs: evidence for frequent birth and death of miRNA genes. PLoS One. 2007, 2: e219-10.1371/journal.pone.0000219.
Li Y, Xu Y, Chong K: The novel functions of kinesin motor proteins in plants. Protoplasma. 2012, 249 (Suppl 2): S95-S100.
Zhang ZM, Song R, Peng H, Luo M, Shen YO, Liu L, Zhao MJ, Pan GT: Bioinformatic prediction of microRNAs and their target genes in maize. Acta Agronom Sin. 2010, 36: 1324-1335. 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.01324.
Jay F, Wang Y, Yu A, Taconnat L, Pelletier S, Colot V, Renou JP, Voinnet O: Misregulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 8 underlies the developmental abnormalities caused by three distinct viral silencing suppressors in Arabidopsis. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7: e1002035-10.1371/journal.ppat.1002035.
Park YH, Choi C, Park EM, Kim HS, Park HJ, Bae SC, Ahn I, Kim MG, Park SR, Hwang DJ: Over-expression of rice leucine-rich repeat protein results in activation of defense response, thereby enhancing resistance to bacterial soft rot in Chinese cabbage. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 2012 (31): 1845-1850.
Wei W, Huang J, Hao YJ, Zou HF, Wang HW, Zhao JY, Liu XY, Zhang WK, Ma B, Zhang JS, Chen SY: Soybean GmPHD-type transcription regulators improve stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. PLoS One. 2009, 4: e7209-10.1371/journal.pone.0007209.
Liu Y, Liu C, Li Z, Xia M, Jiang H, Cheng B, Zhou J, Zhu S: Overexpression of a plant homedomain (PHD) finger transcription factor, OsPHD1, can enhance stress tolerance in rice. J Agri Biotech. 2011, 19: 462-469.
Wang ZF, Wang ZH, Shi L, Wang LJ, Xu FS: Proteomic alterations of Brassica napus root in response to boron deficiency. Plant Mol Biol. 2010, 74: 265-278. 10.1007/s11103-010-9671-y.
Sanan-Mishra N, Kumar V, Sopory SK, Mukherjee SK: Cloning and validation of novel miRNA from basmati rice indicates cross talk between abiotic and biotic stresses. Mol Genet Genomics. 2009, 282: 463-474. 10.1007/s00438-009-0478-y.
Misra P, Pandey A, Tiwari M, Chandrashekar K, Sidhu OP, Asif MH, Chakrabarty D, Singh PK, Trivedi PK, Nath P, Tuli R: Modulation of transcriptome and metabolome of tobacco by Arabidopsis transcription factor, AtMYB12, leads to insect resistance. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152: 2258-2268. 10.1104/pp.109.150979.
Colaiacovo M, Subacchi A, Bagnaresi P, Lamontanara A, Cattivelli L, Faccioli P: A computational-based update on microRNAs and their targets in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Genomics. 2010, 11: 595-10.1186/1471-2164-11-595.
Robinson SA, Slade AP, Fox GG, Phillips R, Ratcliffe RG, Stewart GR: The role of glutamate dehydrogenase in plant nitrogen metabolism. Plant Physiol. 1991, 1991 (95): 509-516.
Beato VM, Navarro-Gochicoa MT, Rexach J, Herrera-Rodríguez MB, Camacho-Cristóbal JJ, Kempa S, Weckwerth W, González-Fontes A: Expression of root glutamate dehydrogenase genes in tobacco plants subjected to boron deprivation. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011, 49: 1350-1354. 10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.06.001.
Li BZ, Mike M, Li SM, Li HY, Zhu SW, Shi WM, Su YH: Molecular basis and regulation of ammonium transporter in rice. Rice Sci. 2009, 16: 314-322. 10.1016/S1672-6308(08)60096-7.
Yang CQ, Liu YZ, An JC, Li S, Jin LF, Zhou GF, Wei QJ, Yan HQ, Wang NN, Fu LN, Liu X, Hu XM, Yan TS, Peng SA: Digital gene expression analysis of corky split vein caused by boron deficiency in ‘Newhall’ navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) for selecting differentially expressed genes related to vascular hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2013, 8: e65737-10.1371/journal.pone.0065737.
Krizek DT, Britz SJ, Mirecki RM: Inhibitory effects of ambient levels of solar UV-A and UV-B radiation and growth on Cv. New Red Fire lettuce Physiol Plant. 1988, 103: 1-7.
Wagner G: Content and vacuole/extravacuole distribution of neutral sugar, free amino acids and anthocyanin in protoplast. Plant Physiol. 1979, 64: 88-93. 10.1104/pp.64.1.88.
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID: Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil. 1973, 39: 205-208. 10.1007/BF00018060.
Veeranjaneyulu K, Kumari BDR: Proline metabolism during water stress in mulberry. J Exp Bot. 1989, 214: 581-583.
Loyola-Vargas V, de Jimenez ES: Differential role of glutamate dehydrogenase in nitrogen metabolism of maize tissues. Plant Physiol. 1984, 76: 536-540. 10.1104/pp.76.2.536.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G: Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genetics. 2000, 25: 25-29. 10.1038/75556.
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, Lao KQ, Livak KJ, Guegler KJ: Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33: e179-10.1093/nar/gni178.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171947) and the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
YBL carried out most of the experiments and drafted the manuscript. LTY participated in the design of the study and coordination. YPQ participated in the design of the study. YL directed the study. ZL and YBC carried out the cultivation of seedlings. ZRH performed the statistical analysis. LSC designed and directed the study and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12870_2014_1542_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Additional file 1: Length distribution of small RNAs from control and B-deficient roots of Citrus sinensis seedlings.(DOC 49 KB)
12870_2014_1542_MOESM3_ESM.xls
Additional file 3: List of known miRNAs in Citrus sinensis roots after removing these miRNAs with normalized read-count less than 10 TPM in two miRNA libraries constructed from control and B-deficient roots.(XLS 47 KB)
12870_2014_1542_MOESM5_ESM.xls
Additional file 5: List of novel miRNAs in Citrus sinensis roots after removing these miRNAs with normalized read-count less than 10 TPM in two miRNA libraries constructed from control and B-deficient roots.(XLS 22 KB)
12870_2014_1542_MOESM9_ESM.doc
Additional file 9: Specific primer pairs used for qRT-PCR expression analysis of selected miRNA target genes.(DOC 74 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, YB., Yang, LT., Qi, YP. et al. Identification of boron-deficiency-responsive microRNAs in Citrus sinensis roots by Illumina sequencing. BMC Plant Biol 14, 123 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-123
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-123