Abstract
Background
Sucrose is the primary photosynthesis product and the principal translocating form within higher plants. Sucrose transporters (SUC/SUT) play a critical role in phloem loading and unloading. Photoassimilate transport is a major limiting factor for seed yield. Our previous research demonstrated that SUT co-localizes with yield-related quantitative trait loci. This paper reports the isolation of BnA7.SUT1 alleles and their promoters and their association with yield-related traits.
Results
Two novel BnA7.SUT1 genes were isolated from B. napus lines 'Eagle' and 'S-1300' and designated as BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b, respectively. The BnA7.SUT1 protein exhibited typical SUT features and showed high amino acid homology with related species. Promoters of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b were also isolated and classified as pBnA7.SUT1.a and pBnA7.SUT1.b, respectively. Four dominant sequence-characterized amplified region markers were developed to distinguish BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b. The two genes were estimated as alleles with two segregating populations (F2 and BC1) obtained by crossing '3715'×'3769'. BnA7.SUT1 was mapped to the A7 linkage group of the TN doubled haploid population. In silico analysis of 55 segmental BnA7.SUT1 alleles resulted three BnA7.SUT1 clusters: pBnA7.SUT1.a- BnA7.SUT1.a (type I), pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.a (type II), and pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.b (type III). Association analysis with a diverse panel of 55 rapeseed lines identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in promoter and coding domain sequences of BnA7.SUT1 that were significantly associated with one of three yield-related traits: number of effective first branches (EFB), siliques per plant (SP), and seed weight (n = 1000) (TSW) across all four environments examined. SNPs at other BnA7.SUT1 sites were also significantly associated with at least one of six yield-related traits: EFB, SP, number of seeds per silique, seed yield per plant, block yield, and TSW. Expression levels varied over various tissue/organs at the seed-filling stage, and BnA7.SUT1 expression positively correlated with EFB and TSW.
Conclusions
Sequence, mapping, association, and expression analyses collectively showed significant diversity between the two BnA7.SUT1 alleles, which control some of the phenotypic variation for branch number and seed weight in B. napus consistent with expression levels. The associations between allelic variation and yield-related traits may facilitate selection of better genotypes in breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Sucrose is the principal transport form of photosynthetically assimilated carbohydrate in higher plants. It is synthesized in the source leaf or the pericarp of the pod and transported via the phloem to sink tissues and provides energy and carbon skeleton to the non-photosynthetic tissues. In sink tissues, sucrose may be used directly for metabolism or translocated to storage tissues (such as cotyledon and endosperm) for synthesis of three major storage products (oil, starch, and protein) through carbohydrate metabolism. On the basis of these storage products, crops are designated as oleaginous, farinose, or proteinacious crops [1–4].
Sucrose transporter (SUT) was first reported in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) (Amaranthaceae) [5]. In the last two decades, cDNA for SUTs has been isolated and cloned in higher plants (e.g., Solanaceae, Brassicaceae, Amaranthaceae, Poaceae) [6–8]. Immunolocalization analysis revealed that SUTs are located in plasma membranes of enucleate sieve and companion cells [9, 10]. SUTs have been reported to be expressed in various tissues of the transport pathway and sink cells in Arabidopsis, barley, potato, and rubber [9–13]. Mutation studies of SUTs have revealed that SUTs are responsible for restraining plant growth and pollen germination [14–16]. Antisense transformation experiments have clearly shown that SUTs also are responsible for retardation of sucrose translocation, fruit size reduction, and lowered fertility in tomato [17, 18]. Overexpression transformations showed lower sucrose concentration in leaves and increased growth rates of pea cotyledon [19, 20]. Early stages of seed development in Brassica exhibit a SUT association with starch and oil accumulation in the embryo; the further growth of the cotyledon leads to lipid synthesis and starch degradation [2, 21]. Results from another study have suggested that increased lipid synthesis is an effect of sucrose unloading [22]. However, detailed reports are lacking for SUT in Brassica napus (Brassicaceae).
B. napus is one of the major global oil crops. It is used for direct human consumption, as animal feed, and recently as a source of bio-fuel. High seed yield per unit is one of the most important challenges in B. napus breeding, while the harvest index (HI) is only about 0.2-0.3 [23, 24]. Generally, the HI of cereal crops can reach 0.5-0.6 in crop production under suitable conditions and management, with reserved assimilates in plants contributing 10-40% of the final yield at the grain filling stage [25]. The HI of soybean, one of the most important oil crops, also can reach 0.4-0.6 [26, 27] and has been successfully maximized during breeding [28]. Investigations have indicated that source and sink organs are not limiting, while assimilate translocation is the most critical limiting factor for seed yield in Brassica [29, 30]. SUT may be a key gene for increasing seed yield by translocating sucrose from source to sink.
In our previous investigation, a functional marker derived from SUT was co-localized with seed yield quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in B. napus [31]. We hypothesized that the SUT gene affects seed yield in B. napus. Here, a complete SUT (BnA7.SUT1) and promoters were isolated and characterized. A series of experiments and observations of the B. napus SUT made it possible to detect alleles located in the A7 linkage group, and allelic variation of BnA7.SUT1 was associated with seed yield-related traits. BnA7.SUT1.b and its promoter are linked to higher seed yield, while BnA7.SUT1.a is associated with increased seed weight.
Results
Isolation of BnA7.SUT1
Three Brassica fragments (two expressed sequence tagged and a bacterial artificial chromosome [BAC]; respective GenBank accession numbers AY190281, AY065839, and AC189334) were obtained from the large-scale sequence analysis results at The Arabidopsis Information Resource database and identified as having high sequence homology with the Arabidopsis AtSUC1 (At1G71880) sequence [6]. Primers (M1-M4) were designed based on conservative segments (see Additional file 1). With these primers, the main genomic segments of BnX.SUT1 were generated; the remnant fragments and promoter were obtained by thermal asymmetric interlaced (TAIL) PCR in the B. napus cultivar 'Eagle'. According to the contig, the complete open reading frame (ORF) was identified by using gene prediction programs (GENSCAN; FGENESH), and gene-specific primers were developed to generate BnX.SUT1 in line 'S-1300'. Of interest, the PT1 primer pair, which amplifies the 5'-end of BnX.SUT1, generated the expected band in 'Eagle' exclusively (Table 1). Thus, more than 2 kb of promoter and 5' untranslated region (UTR) were obtained by TAIL-PCR from 'S-1300', respectively. Based on the predicted 5' and 3' UTRs of the candidate SUT-like gene, common gene-specific primers were designed: sut-2L (5'-AGA ATG GGA GCT TTT GAA ACA G-3') and sut-2R (5'-GGC ATA GAG TAC ACT AAT GGA AG-3'). These primers were used to amplify the full-length cDNA and genomic sequences of BnX.SUT1. Forty-four cDNA sequences were isolated from various organs/tissues of 'Eagle' and 'S-1300' and were classified into four clusters (Additional file 2). Two clusters showed non-variation sequences and non-distinguished expression in six B. napus lines (data not shown) and were not included in further work in this investigation. The other two clusters were designated as BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b, obtained from 'Eagle' and 'S-1300', respectively.
Both putative ORFs of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b contain 1545 bp and encode a protein of 514 amino acids. The combination of the cDNA and genomic DNA sequences revealed that the BnA7.SUT1 gene is 2593 bp in length, containing four exons and three introns. The hydrophobicity profile analysis of BnA7.SUT1 revealed the presence of 12 transmembrane spanning domains, arranged in two sets of six putative transmembrane domains separated by a long central hydrophilic loop, with both terminal domains and a large central loop located on the intracellular side of the plasma membrane. BnA7.SUT1 belongs to the subgroup SUT1 (Additional file 3). The two predicted protein sequences are 98% identical, having seven amino acid differences between BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b (Figure 1), none of them in transmembrane domains. The cDNA of BnA7.SUT1 shared 76% sequence identity with a published BnSUT (GenBank accession no. EU570076), which has 508 amino acids. The BnA7.SUT1 sequence is very similar to the homologues from related species and showed more than 85% sequence similarity with AtSUC1 (AT1G71880) and BoSUC1 (AY065839) and 81% sequence similarity with AtSUC5 (NM_105847). Hence, the isolated BnA7.SUT1 alleles, homologous with Arabidopsis and B. oleracea, are novel SUT genes in B. napus.
Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b. The gray bars and black lines denote exons and introns in the CDS, while thick black lines indicate the promoter of BnA7.SUT1. The black rhombus and arrowhead with names distinguish amino acid sites and the locations of primers, respectively.
Nucleotide sequence analysis
Seventeen primer pairs were designed to generate fragments of about 400 bp to 1700 bp. Ten primer pairs were designed from the sequences of BnA7.SUT1.a and seven from the diverse domains of BnA7.SUT1.b. Four markers (Table 1 Figure 1) showed polymorphisms between 'Eagle' and 'S-1300'. ET3 and PT1, which were developed from BnA7.SUT1.a and its promoter, generated the expected fragments in 'Eagle' but not in 'S-1300'. By contrast, ET4 and PT5, amplifying BnA7.SUT1.b and its promoter, generated the expected bands in 'S-1300' exclusively (Figure 1). The four sequence-characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers were used to analyze the 55 cultivars/lines. And the panel lines were distinguished as three groups by these markers.
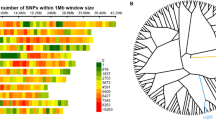
The 55 partial BnA7.SUT1 genomic fragments of ~1570 bp were amplified from the panel lines using primer pairs PT1-L/PT1-R and PT5-L/PT1-R (Figure 1), which are located 382 bp upstream and 1191 bp downstream from the start codon of BnA7.SUT1. In total, 142 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites were detected among the lines, including 120 SNPs in the promoter and 5'-UTR, 12 SNPs in exons, and 10 in introns. The genetic diversity between two regions was analyzed according to distinct different diversities in the 5'-end and gene regions. Nucleotide diversity was lower in gene regions (π = 0.00534) compared with 5'-end regions (π = 0.13502). Tajima's D of gene regions indicated non-significance, while the 5'-end of BnA7.SUT1 had a positive and significant Tajima's D value (Table 2). The results indicated that selection was present at the 5'-end and that the selection effect had not extended to the entire gene.
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) was estimated between 51 pairs of polymorphic sites (SNPs and indels) in the BnA7.SUT1 sequence; two LD blocks were observed at the 5'-end and gene regions, respectively (Figure 2). Abundant SNPs resulted in the same haplotypes among the lines, which could be classified into three clusters consistent with the results of the neighbor-joining distance tree (Additional file 4). Overall, we found interesting results indicating that the BnA7.SUT1.a promoter regulates only BnA7.SUT1.a and that the BnA7.SUT1.b promoter regulates both BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b, designated as pBnA7.SUT1.a- BnA7.SUT1.a (type I), pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.a (type II), and pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.b (type III). Nucleotide diversity was also separately evaluated for type I, type II, and type III based on 382-bp sequences of the 5'-end (Table 2). Type III and type I presented no polymorphisms and one indel (s330) among 18 and 16 lines, respectively. However, type II showed one SNP (s95) and three indels (s98, s229, and s330) among 21 lines (Figure 3).
Allelism analysis and genetic mapping
To identify the allelism of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b, '3715' (type III) and '3769' (type I) were used to develop F1, F2, and BC1 populations. With these populations, segregation ratios were analyzed using the markers PT1 and PT5. The segregation of heterozygous F1 plants to single-band plants in the F2 population showed the expected Mendelian ratio of 1:2:1 (number of plants was 45:119:61) (χ2 = 3.03, 0.10 < P < 0.25), and the expected ratio of 1:1 (number of plants was 46:49) in the BC1 population (χ2 = 0.074, 0.75 < P < 0.90). Therefore, BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b appeared to be alleles at a single locus.
BnA7.SUT1 showed high similarity with the BAC (AC189334) from B. rapa, and three simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers were developed according to the BAC sequence. Additionally, gene-specific primers were designed based on BnA7.SUT1.b. An SSR marker (sRsut1) and a gene-specific marker (lo-sut1) showed the same polymorphisms found in the 'Tapidor-NY7' (TN) doubled haploid (DH) population. Hence, BnA7.SUT1 was mapped to the A7 linkage group of the TN DH genetic map (Figure 4), consistent with result of Li et al. [31].
Association of BnA7.SUT1 with yield-related traits
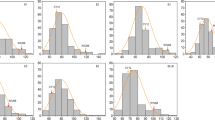
The mean phenotypic values for individual lines across four environments ranged from 4.1 to 9.8 for the number of effective first branches (EFB); 111.6 to 312.2 for the number of siliques per plant (SP); 11.5 to 32.5 for the number of seeds per siliques (SS); 5.0 to 19.5 g for seed yield per plant (PY); 174.0 to 842.1 g for block yield (BY); and 2.2 to 5.4 g for seed weight (TSW) (n = 1000), respectively. Analysis of variance showed significant (P = 0.01) phenotypic variation for all six yield-related traits among the 55 lines (Table 3), indicating that the assembled panel is suitable for association analysis. Heritabilities were 83.7%, 82.4%, 91.4%, 62.6%, 78.7.6%, and 95.1% for EFB, SP, SS, PY, BY, and TSW, respectively (Table 3). Significant positive phenotypic and genetic correlations between EFB and SP and between yield and silique traits (SP and SS) were observed (Table 3), indicating that an increase in any of the EFB, SP, or SS traits can increase seed yield.
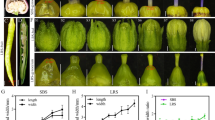
The panel lines evaluated for yield-related traits were mostly modern cultivars and breeding materials. There were considerable differences among the panel lines according to UPGMA cluster (Additional file 5). Population structure was observed among the 55 cultivars/lines based on the method by Hasan et al. [32].The slope of average likelihoods for the overall population was modeled at K = 4 (Figure 5); the most stable prediction (standard deviation = 1.99) was obtained with four groups. Each group consisted of 18, 16, 16, and 5 oilseed lines, respectively. Taking the LD (r2 > 0.8) level among sites into account and eliminating same-haplotype SNPs, five sites were significantly associated with at least one of the six yield-related traits (P < 0.05). Information including location, genotype, frequency, and probability value for each site is shown in Table 4. Of interest, the SNP sites (s60 and s222) from the promoter and s1448 from the exon of BnA7.SUT1 were associated with EFB and TSW and explained an average 12% and 11% of phenotypic variation throughout the four environments, respectively. The s222 SNP at the promoter in turn affected SP (Table 4). Phenotypic distributions of the previous four yield-related traits are illustrated in three genotypes by box-plots in Figure 6. Promoter BnA7.SUT1.b was associated with an increased EFB number and SP number. For TSW, no significant differences were observed between type I and type II with BnA7.SUT1.a. However, a significant difference was observed between type I and type III and between type II and type III with different BnA7.SUT1 alleles. Hence, polymorphisms at the promoter and coding domain sequence (CDS) of BnA7.SUT1 affect yield-related traits interactively.
Estimation of the most appropriate group K values, calculation SD over 10 independent runs. Mean L(K) over 10 runs for each K value. (B) Change rate of likelihood value calculated as L'(K) = L(K) -L(K-1). We followed the method of Evanno et al. [64].
Box-plots showing distributions of EFB, SP, BY, and TSW within types I, II, and III. (A) (B) (C) (D) are phenotypic details for EFB, SP, BY, and TSW, respectively. 08WH, year 2008 Wuhan; 09WH, year 2009 Wuhan; 09YC, year 2009 Yichang; 09HG, year 2009 Huanggang. aa represents genotype pBnA7.SUT1.a- BnA7.SUT1.a; ba represents genotype pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.a; and bb represents genotype pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.b. * t-test between ba genotype and aa genotype, between bb genotype and aa genotype significant at P = 0.05, ** significant at P = 0.01; ※ t-test between bb genotype and ba genotype significant at P = 0.05, ※ ※ significant at P = 0.01.
Expression pattern analysis by real-time PCR
Spatial and developmental expression profiling of BnA7.SUT1 was performed using real-time PCR on all three genotypes, type I, type II, and type III, to extract RNA from different organs/tissues at the seed-filling stage. BnA7.SUT1 mRNA showed a higher expression level in vegetative organs, reaching its highest level in stems and leaf blades (Figure 7A). Greater abundance was detected in stems of type II and type III genotypes, indicating that the effect of the BnA7.SUT1.b promoter was stronger than BnA7.SUT1.a promoter in stems. On the other hand, BnA7.SUT1 showed lower expression levels in reproductive organs. In flower buds, BnA7.SUT1 showed similar transcript levels in all three genotypes.
Real-time PCR analysis of BnA7.SUT1 expression. (A) Expression of BnA7.SUT1 in different organs, including source leaf and stem, bud, pod 25 DAF, pericarp of pod, and young seeds among diverse genotypes. (B) Expression in leaf including various developmental stages. 70 DAS is the reproductive stage of winter B. napus. (C) Expression in the pod during the developmental period. Pistil was dissected from the bud.
When pods reached 25 days after flowing (DAF), transcription of BnA7.SUT1 showed variations in pods, pericarp, and young seeds in different genotypes. Higher abundance was detected in pods and pericarp of type III genotypes and in developing seeds of type I genotypes. The expression level of BnA7.SUT1.b was 3-fold higher than that of BnA7.SUT1.a in pods, and 10-fold higher in pericarp. However, the expression of BnA7.SUT1.b decreased by three times in developing seeds as compared to BnA7.SUT1.a, which showed that BnA7.SUT1.b accumulated at higher levels in pods and pericarp, while BnA7.SUT1.a produced higher expression levels when regulated by the promoter of BnA7.SUT1.a (Figure 7A). Different alleles of BnA7.SUT1 also exhibited diverse expression levels when regulated by the same promoter of BnA7.SUT1.b, indicating that alleles of BnA7.SUT1 also present different gene expression patterns.
In different developmental phases, source leaves were sampled 100 days after sowing (DAS) initially, then at monthly intervals. The abundance of the BnA7.SUT1 transcript declined to a low level at flowering. As pods matured, the expression of BnA7.SUT1 again showed increased expression levels (Figure 7B). In the developing pods, BnA7.SUT1 was highly expressed in the pistil when pods were rapidly elongating and remained at a relatively high level at 3 DAF and 12 DAF. However, expression decreased to a low level at 25 DAF, when the dry weight of pods reached the maximum (Figure 7C).
Discussion
Isolation and genetic variations of BnA7.SUT1
Our current research describes the isolation of a novel SUT gene BnA7.SUT1 and its two alleles BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b in B. napus. The cDNAs of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b showed 18 polymorphic sites and variations in seven amino acids, none of which are located in the SUT transmembrane. The predicted proteins showed similarity with all the other SUTs in amino acid sequence and protein secondary structures with histidine residue position 65 [6, 33]. A higher similarity of BnA7.SUT1 with other functional SUTs indicated that BnA7.SUT1 proteins may play an important role in sucrose transport.
We observed frequent sequence exchanges in BnA7.SUT1 that resulted in generation of two alleles of BnA7.SUT1. Gene conversion and unequal crossing-over are important in generating variation at gene sequences, and recombination events produce novel genotypes [34]. Sequence analysis of 55 B. napus lines showed that the BnA7.SUT1 gene could be classified into three genotypes. The type III genotype showed 98% genomic sequence similarity with the type II genotype. The polymorphisms were located in the 5'UTR, and there was a 3-bp indel polymorphism at position 229-231 between the type I and type III genotypes; the type II genotype contained either polymorphism. Upstream of the indel, type II and type III genotypes showed the same polymorphisms among the three genotypes; in contrast, downstream of the indel, type I and type II presented the same polymorphisms. Hence, we hypothesized that type II is the result of rearrangements between type I and type III, although this hypothesis requires further molecular evidence. Newly generated chimeras were selected and maintained in a population; however, the BnA7.SUT1.a- BnA7.SUT1.b genotype could not be found in association with the promoter of BnA7.SUT1.a and may have been selected against during the breeding process. Similar recombination of HvFT1 (barley) has generated various alleles [35], which support our findings. The Zep allele was generated as a result of recombination with different promoters and regulated the expression level of Zep [36].
Association between BnA7.SUT1 and yield-related traits
SUTs drive translocation of sucrose and in turn affect seed yield and fruit size [18, 37]. In another study carried out in our laboratory, identification of yield-related QTLs in a B. napus functional map [38] indicated that a functional marker from SUT in the A7 linkage group was related to EFB, SP, and TSW in the A7 linkage group [31, 39]. Here, we report likely polymorphisms in BnA7.SUT1 associated with yield-related traits, and allelic variation at the promoter and CDS of BnA7.SUT1 correlated with expression pattern and phenotype. Polymorphisms at the promoter and CDS regions with an effect on expression abundance are likely candidates for causative QTPs [40, 41]. Similarly, allelic polymorphism at the promoter and intron of HvFT1 in barley contribute to variation in flowering time [35].
SUTs have three types of clades designated as protype SUT1 (clade I), SUT2 (clade II), and SUT4 (clade III) [38, 42–44], and BnA7.SUT1 falls into the protype SUT1 (clade I). Generally, SUT1 mRNA and protein, notably OsSUT1, AtSUC2, and StSUT1, are present in mature phloem and primarily involved in phloem loading. The rice SUT, OsSUT1, plays a significant role in sucrose transport in developing shoots and roots, which is a decisive factor for seed germination and early seedling growth [42]. AtSUC1 also has a role in vegetative growth and for normal gametophyte functioning [16]. In higher plants, sugars and hormones interact and form an intricate regulatory sensing and signaling network [45], and altered sucrose levels can change the quantity of sucrose-derived metabolites and sucrose-specific signaling [46]. In the current work, BnA7.SUT1 showed higher expression levels in the stem of type II and type III genotypes, consistent with increased EFB. These results indicated that blocking translocation of sucrose at the stem influences either carbon abundance for metabolism or signals.
Oilseed plants with lush branches and leaves, in contrast, produce many empty pods and shrunken seeds at maturity, resulting from insufficient import to the developing seeds [47]. Breeding experiences indicated that translocation of carbohydrate assimilate from source to sink is a major constraint on seed yield [29, 48]. The lower expression of BnA7.SUT1 in type I genotypes resulted in the lowest yield in the three genotype lines, suggested that retardation of photoassimilate translocation leads to decreased yield. At the pod-filling stage, most leaves abscise and the pod remains primarily a photosynthetic organ [49]. The volume of the pod is estimated at 20 DAF, and the dry weight of the pod reaches a maximum at 25 DAF when sucrose is stored in the pericarp for the later period of seed development [48]. The lower expression observed here of BnA7.SUT1 in the pod and developing seed suggests an effective role in the photoassimilate unloading process. BnA7.SUT1 showed a reduced expression trend as the pod reached maximum weight (25 DAF). The low expression level of BnA7.SUT1 in the pod may be the result of the failure of transportation of sucrose in the developing seed. In our investigation, seed weight was negatively correlated with seed yield. Plants with fewer branches and siliques could distribute more storage substance into each seed with a resulting larger seed weight, indicating that 'sink' is sufficient in general oilseed plants. 'Source' is also not the limitation for seed yield in oilseed [29, 30]. Therefore, 'flow' is the most important factor and controls seed yield. Our results support this reasoning. The promoter BnA7.SUT1.b correlation with increasing EFB number may be a potential resource for breeding.
Some key genes are closely correlated with yield-related traits. Of great interest, application of dwarfing genes caused a green revolution in the 1960s and doubled grain production only in 40 years [50–52]. On the other hand, most phenotypic variation of agronomic traits is continuous and remarkably influenced by different alleles. In tomato, alleles of fw2.2 result in fruit size variation up to 30% and appear to have been responsible for a key transition during domestication [53]. Plant architecture is very important for improving yield traits; tb1 acts as a major contributor to apical dominance in maize and regulates lateral branching in rice [54, 55]. Moreover, GS3 and Ghd7 show significant effects on grain size and multiple yield-related traits in rice, respectively [56, 57]. Thus, characterization and application of crucial genes/alleles may be an effective means of improving yield. Our investigation indicated that SUT may play an important role in sucrose translocation and affect seed yield in B. napus. Investigations with larger and/or natural sets of B. napus are necessary to validate the association. Furthermore, alteration of sucrose concentration will provide convincing evidence. However, the current characterization of allelic variation and association with yield may be a potential basis for breeding.
Conclusions
Previous QTL analysis of seed yield-related trait associations with functional markers showed that SUT was located in the QTL interval associated with branch number and seed weight. In this study, we isolated different alleles of BnA7.SUT1 and identified three genotypes. Lines with the BnA7.SUT1.b promoter exhibited better seed yield-related traits. At the pod development phase, BnA7.SUT1 showed an increased expression level and a decreasing trend with increasing seed weight. These results indicate reduced transport of photoassimilate from source to sink. BnA7.SUT1 may play an important role in photoassimilate accumulation and storage, in turn affecting seed yield.
Methods
Plant materials
Two B. napus lines 'S-1300' and 'Eagle', showing variation in vegetative and reproductive traits, were grown under field conditions and used to isolate BnX.SUT1. 'S-1300' is a Chinese semi-winter self-incompatible line, and 'Eagle' is a Swedish spring line. A panel of 55 semi-winter B. napus cultivars/lines maintained at Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, PRC, were used for association in this study. F1, F2, and BC1 populations, resulting from the cross '3715'×'3769', were employed for allelism analysis. The TN DH population, resulting from a cross between 'Tapidor' and 'NY7' [58], served for mapping BnA7.SUT1. Marker-differentiated cultivars/lines were planted during 2008-2010 at Huazhong Agricultural University. Their leaves, shoots, flower buds, pods, pericarps of pods, and young seeds at the filling stage (20 DAF), leaves, and pods at different developmental stages were used for expression analysis by real-time PCR.
Field experiments and trait measurements
The experiments were conducted in three locations (Wuhan, Huanggang, Yichang) in Hubei Province, China. Fifty-five B. napus cultivars/lines were grown for two consecutive growing seasons during 2007/08 and 2008/09 at Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China; they were also grown at the local Academy of Agricultural Science sites in Yichang and Huanggang during 2008/09. Rapeseed plots were subsequently followed by rice crops in all experimental fields. All trials were designed as randomized blocks with three replications in each environment. Each plot consisted of three rows, 3.5 m length with 0.25 m distance between rows. Seeds were sown between the last 5 days of September and the first 5 days of October with the distance between plants in each row reduced to 0.15 cm at 40 days post-emergence. All trials were managed following normal, standard agricultural practices.
At maturity, 12 plants in the middle row were randomly harvested from each plot for evaluation of the following quantitative traits: number of EFB, number of SP, number of SS, TSW, and seed YP. Residual plants of each block were harvested and used to determine BY (Additional file 6).
DNA extraction and genetic mapping of BnA7.SUT1
Genomic DNA of the planted materials, including parents, segregating population, and the panel of 55 cultivars/lines, was extracted from young leaves according to CTAB methodology [59], and DNA from three individuals in each variety/line was mixed for PCR analysis. Based on sequences of the BAC (AC189334) and BnA7.SUT1, the SSR marker and gene-specific primers were designed and used to map the gene in the TN DH population using JoinMap 3.0 http://www.kyazma.nl/index.php/mc.JoinMap.
Sequencing and analysis
Promoter and partial CDS regions of BnA7.SUT1 were generated using primer pairs as follows: PT1-L/PT1-R and PT5-L/PT1-R. PCR was performed in reaction volumes of 20 μL containing the following: 50 ng genomic DNA, 1 unit Taq polymerase (MBI Fermentas, Lithuania), 2 μL 10× Taq buffer with (NH4)2SO4, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dNTP mix (Sangon, China), and 0.5 μM of each primer. PCR conditions were initial denaturation for 4 min at 94°C, 30 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, annealing at 60°C for 45 s, and extension for 60 s at 72°C, followed by an extension of 10 min at 72°C. PCR products were separated by 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis and detected by staining with ethidium bromide. The PCR products were purified using the Gel Purification Kit (Sago, Shanghai, China) and ligated into the pMD18-T vector (TaKaRa, Japan). Positive transformed clones were selected for sequencing. The fragments were analyzed using the SEQMAN application of the DNASTAR software suite (Windows version 5.0.2; DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA) and aligned in MEGA 4.0 [60]. Singletons, which occurred only once as polymorphisms among the sequenced materials, were analyzed until they were confirmed as correct. The LD level between sites and Tajima's D statistic were calculated using TASSEL 2.1 [61].
Population structure and statistical analyses
The AFLP technique, following the protocol of Vos et al. [62] with minor modifications by Lu et al. [63], was employed to genotype the 55 breeding lines. AFLP primers amplify different marker alleles at multiple loci in the allotetraploid B. napus genome. It is difficult or impossible to assign the different marker alleles to individual loci in genotypes with high allelic diversity. All AFLP alleles were scored as present or absent in each genotype. In total, 139 polymorphisms were obtained with restriction enzymes PstI/MseI. Subsequently, the data were used to infer the population structure (Q) with the model-based Bayesian clustering approach in the software STRUCTURE 2.2 [64]. The membership coefficients were calculated as 10 independent runs for each k (set from 1 to 10) with a burn-in of 50, 000 iterations followed by 50, 000 interactions. A summary of the average of data likelihoods (LnP(D)) is shown in Additional file 7.
Mean values, variance components of each yield-related trait, heritability, and correlation coefficients were calculated, respectively. Variance components were computed for lines, environments, interaction between lines and environments, and error. Broad-sense heritability was estimated according to the formula , where is the genotypic variance, is the interactional variance of genotype and environment, is the error variance, r is the number of replicates of each environment, and n is the number of environments [65].
Associations between polymorphism sites and yield-related traits were implemented using general linear model analysis in the software package TASSEL 2.1 [61]. The Q matrix was used as the covariate in the analysis to control the population structure. All polymorphisms were tested, and P values for individual polymorphisms were estimated based on 10, 000 permutations. The rescaled P value accounts for the proportion of the random marker with a permuted P value less than or equal to 0.05. Data from each test environment were calculated independently.
RNA extraction and real-time PCR
Total RNAs were extracted from respective tissues using Tripure reagent (Bioteke, http://www.bioteke.com/chn/). Subsequently, the cDNAs were synthesized with M-MLV reverse transcriptase and an oligo (dT) primer (Fermentas, USA) in a 20 μL volume according to the manufacturer's instructions. The resultant first strand cDNA mixture was diluted with sterile distilled water and used as a template for PCR and for real-time PCR. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed using the SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). The PCR reactions contained 400 nM of both forward and reverse gene-specific primers and 8.4 μL of the 50-fold diluted reverse transcriptase (RT) reaction in a final volume of 20 μL. The thermal cycling protocol was followed by DNA polymerase activation at 95°C for 3 min. The PCR amplification was carried out with 45 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, primer annealing at 60°C for 15 s, and extension at 72°C for 30 s. Optical data were acquired following the extension step, and the PCR reactions were subject to melting curve analysis beginning at 65°C through 95°C, at 0.1°C s-1. The amplified products were sequenced to ensure that each primer pair amplified one specific gene. The data are presented as an average ± SD of three independently produced RT preparations used for PCR runs, each having four replicates. The relative expression levels were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCT method [66].
References
Weselake RJ: Storage Product Metabolism in Microspore-Derived Cultures of Brassicaceae. Biotech Agric For. 2005, 56: 97-122.
Rawsthorne S: Carbon flux and fatty acid synthesis in plants. Prog Lipid Res. 2002, 41 (2): 182-196. 10.1016/S0163-7827(01)00023-6.
Hill LM, Morley-Smith ER, Rawsthorne S: Metabolism of sugars in the endosperm of developing seeds of oilseed rape. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131 (1): 228-236. 10.1104/pp.010868.
Rae AL, Perroux JM, Grof CP: Sucrose partitioning between vascular bundles and storage parenchyma in the sugarcane stem: a potential role for the ShSUT1 sucrose transporter. Planta. 2005, 220 (6): 817-825. 10.1007/s00425-004-1399-y.
Riesmeier JW, Willmitzer L, Frommer WB: Isolation and characterization of a sucrose carrier cDNA from spinach by functional expression in yeast. EMBO J. 1992, 11 (13): 4705-4713.
Sauer N, Stolz J: SUC1 and SUC2: two sucrose transporters from Arabidopsis thaliana; expression and characterization in baker's yeast and identification of the histidine-tagged protein. Plant J. 1994, 6 (1): 67-77. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6010067.x.
Barker L, Kühn C, Weise A, Schulz A, Gebhardt C, Hirner B, Hellmann H, Schulze W, Ward JM, Frommer WB: SUT2, a putative sucrose sensor in sieve elements. Plant Cell. 2000, 12 (7): 1153-1164.
Aoki N, Whitfeld P, Hoeren F, Scofield G, Newell K, Patrick J, Offler CE, Clarke B, Rahman S, Furbank RT: Three sucrose transporter genes are expressed in the developing grain of hexaploid wheat. Plant Mol Biol. 2002, 50: 453-462. 10.1023/A:1019846832163.
Sauer N, Ludwig A, Knoblauch A, Rothe P, Gahrtz M, Klebl F: AtSUC8 and AtSUC9 encode functional sucrose transporters, but the closely related AtSUC6 and AtSUC7 genes encode aberrant proteins in different Arabidopsis ecotypes. Plant J. 2004, 40 (1): 120-130. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02196.x.
Sivitz AB, Reinders A, Ward JM: Analysis of the Transport Activity of Barley Sucrose Transporter HvSUT1. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46: 1666-1673. 10.1093/pcp/pci182.
Liesche J, Schulz A, Krugel U, Grimm B, Kühn C: Dimerization and endocytosis of the sucrose transporter StSUT1 in mature sieve elements. Plant Signal Behav. 2008, 3 (12): 1136-1137. 10.4161/psb.3.12.7096.
Tang CR, Huang DB, Yang JH, Liu SJ, Sakr S, Li HP, Zhou YH, Qin YX: The sucrose transporter HbSUT3 plays an active role in sucrose loading to laticifer and rubber productivity in exploited trees of Hevea brasiliensis (para rubber tree). Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33 (10): 1708-1720. 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02175.x.
Aoki N, Scofield GN, Wang XD, Patrick JW, Offler CE, Furbank RT: Expression and localisation analysis of the wheat sucrose transporter TaSUT1 in vegetative tissues. Planta. 2004, 219 (1): 176-184. 10.1007/s00425-004-1232-7.
Gottwald JR, Krysan PJ, Young JC, Evert RF, Sussman MR: Genetic evidence for the in planta role of phloem-specific plasma membrane sucrose transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000, 97 (25): 13979-13984. 10.1073/pnas.250473797.
Srivastava AC, Dasgupta K, Ajieren E, Costilla G, McGarry RC, Ayre BG: Arabidopsis plants harbouring a mutation in AtSUC2, encoding the predominant sucrose/proton symporter necessary for efficient phloem transport, are able to complete their life cycle and produce viable seed. Ann Bot. 2009, 104 (6): 1121-1128. 10.1093/aob/mcp215.
Sivitz AB, Reinders A, Ward JM: Arabidopsis sucrose transporter AtSUC1 is important for pollen germination and sucrose-induced anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147 (1): 92-100. 10.1104/pp.108.118992.
Riesmeier JW, Willmitzer L, Frommer WB: Evidence for an essential role of the sucrose transporter in phloem loading and assimilate partitioning. EMBO J. 1994, 13 (1): 1-7.
Hackel A, Schauer N, Carrari F, Fernie AR, Grimm B, Kühn C: Sucrose transporter LeSUT1 and LeSUT2 inhibition affects tomato fruit development in different ways. Plant J. 2006, 45 (2): 180-192. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02572.x.
Leggewie G, Kolbe A, Lemoine R, Roessner U, Lytovchenko A, Zuther E, Kehr J, Frommer WB, Riesmeier JW, Willmitzer L, et al: Overexpression of the sucrose transporter SoSUT1 in potato results in alterations in leaf carbon partitioning and in tuber metabolism but has little impact on tuber morphology. Planta. 2003, 217 (1): 158-167.
Rosche E, Blackmore D, Tegeder M, Richardson T, Schroeder H, Higgins TJ, Frommer WB, Offler CE, Patrick JW: Seed-specific overexpression of a potato sucrose transporter increases sucrose uptake and growth rates of developing pea cotyledons. Plant J. 2002, 30 (2): 165-175. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01282.x.
Eastmond PJ, Rawsthorne S: Coordinate changes in carbon partitioning and plastidial metabolism during the development of oilseed rape embryos. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122 (3): 767-774. 10.1104/pp.122.3.767.
Weber H, Borisjuk L, Wobus U: Molecular physiology of legume seed development. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2005, 56: 253-279. 10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144201.
Yuan WZ, Guan CY: Harvest index in rapeseed affected by a few physiogical factoes. Acta Agronomic Sinica. 1997, 23 (5): 580-586.
Yuan WZ, Guan CY, Liao AL: Contribution of Harvest Index to Seed Yield of Rapeseed. Journal of Natural of Hunan Normal University. 1999, 22 (1): 65-69.
Yang JC, Zhang JH: Crop management techniques to enhance harvest index in rice. J Exp Bot. 2010, 61 (12): 3177-3189. 10.1093/jxb/erq112.
Board JE, Modali H: Dry matter accumulation predictors for optimal yield in soybean. Crop Science. 2005, 45 (5): 1790-1799. 10.2135/cropsci2004.0602.
Yazdani F, Allahdadi I, Akbari GA: Impact of superabsorbent polymer on yield and growth analysis of soybean (Glycine max L.) under drought stress condition. Pak J Biol Sci. 2007, 10 (23): 4190-4196.
Zhu XG, Long SP, Ort DR: Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010, 61: 235-261. 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112206.
Chhabra ML: Translocation pattern of assimilates in India mustard. Proc 7th Int Rapeseed Cong, May 11-14, 1987, Poznan, Poland. 1987, 3: 804-812.
Shen JX, Fu TD, Yang GS, Ma CZ, Tu JX: Genetic analysis of rapeseed self-incompatibility lines reveals significant heterosis of different patterns for yield and oil content traits. Plant Breed. 2005, 124 (2): 111-116. 10.1111/j.1439-0523.2004.01069.x.
Li YY, Shen JX, Wang TH, Chen QF, Zhang XG, Fu TD, Meng JL, Tu JX, Ma CZ: QTL analysis of yield-related traits and their association with functional markers in Brassica napus L. Aust J Agr Res. 2007, 58 (8): 759-766. 10.1071/AR06350.
Hasan M, Friedt W, Pons-Kuhnemann J, Freitag NM, Link K, Snowdon RJ: Association of gene-linked SSR markers to seed glucosinolate content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus ssp. napus). Theor Appl Genet. 2008, 116 (8): 1035-1049. 10.1007/s00122-008-0733-3.
Lu JM, Bush DR: His-65 in the proton-sucrose symporter is an essential amino acid whose modification with site-directed mutagenesis increases transport activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998, 95 (15): 9025-9030. 10.1073/pnas.95.15.9025.
Kuang H, Woo SS, Meyers BC, Nevo E, Michelmore RW: Multiple genetic processes result in heterogeneous rates of evolution within the major cluster disease resistance genes in lettuce. Plant Cell. 2004, 16 (11): 2870-2894. 10.1105/tpc.104.025502.
Casas AM, Djemel A, Ciudad FJ, Yahiaoui S, Ponce LJ, Contreras-Moreira B, Gracia MP, Lasa JM, Igartua E: HvFT1 (VrnH3) drives latitudinal adaptation in Spanish barleys. Theor Appl Genet. 2011, 122 (7): 1293-12304. 10.1007/s00122-011-1531-x.
Wolters AM, Uitdewilligen JG, Kloosterman BA, Hutten RC, Visser RG, van Eck HJ: Identification of alleles of carotenoid pathway genes important for zeaxanthin accumulation in potato tubers. Plant Mol Biol. 2010, 73 (6): 659-671. 10.1007/s11103-010-9647-y.
Baud S, Wuillème S, Lemoine R, Kronenberger J, Caboche M, Lepiniec L, Rochat C: The AtSUC5 sucrose transporter specifically expressed in the endosperm is involved in early seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 43 (6): 824-836. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02496.x.
Sauer N: Molecular physiology of higher plant sucrose transporters. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581 (12): 2309-2317. 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.048.
Shi JQ, Li RY, Qiu D, Jiang CC, Long Y, Morgan C, Bancroft I, Zhao JY, Meng JL: Unraveling the Complex Trait of Crop Yield With Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping in Brassica napus. Genetics. 2009, 182 (3): 851-861. 10.1534/genetics.109.101642.
Takahashi Y, Teshima KM, Yokoi S, Innan H, Shimamoto K: Variations in Hd1 proteins, Hd3a promoters, and Ehd1 expression levels contribute to diversity of flowering time in cultivated rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009, 106 (11): 4555-4560. 10.1073/pnas.0812092106.
Rebbeck TR, Spitz M, Wu X: Assessing the function of genetic variants in candidate gene association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2004, 5 (8): 589-597. 10.1038/nrg1403.
Scofield GN, Hirose T, Aoki N, Furbank RT: Involvement of the sucrose transporter, OsSUT1, in the long-distance pathway for assimilate transport in rice. J Exp Bot. 2007, 58 (12): 3155-3169. 10.1093/jxb/erm153.
Srivastava AC, Ganesan S, Ismail IO, Ayre BG: Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis AtSUC2 Sucrose/H+ symporter by tissue-specific complementation reveals an essential role in phloem loading but not in long-distance transport. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148 (1): 200-211. 10.1104/pp.108.124776.
Kühn C, Hajirezaei MR, Fernie AR, Roessner-Tunali U, Czechowski T, Hirner B, Frommer WB: The sucrose transporter StSUT1 localizes to sieve elements in potato tuber phloem and influences tuber physiology and development. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131 (1): 102-113. 10.1104/pp.011676.
Rolland F, Baena-Gonzalez E, Sheen J: Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: Conserved and novel mechanisms. Annual Review of Plant Biology. 2006, 57: 675-709. 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105441.
Wind J, Smeekens S, Hanson J: Sucrose: metabolite and signaling molecule. Phytochemistry. 2010, 71 (14-15): 1610-1614. 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.07.007.
Jullien A, Mathieu A, Allirand JM, Pinet A, de Reffye P, Cournède PH, Ney B: Characterization of the interactions between architecture and source-sink relationships in winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus) using the GreenLab model. Ann Bot. 2011, 107 (5): 765-779. 10.1093/aob/mcq205.
Pu HM, Qi CK, Fu SZ: Growth characteristic of pod and source-sink response in oilseed. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences. 1993, 3: 22-25.
Malagoli P, Laine P, Rossato L, Ourry A: Dynamics of nitrogen uptake and mobilization in field-grown winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus) from stem extension to harvest - I. Global N flows between vegetative and reproductive tissues in relation to leaf fall and their residual N. Ann Bot. 2005, 95 (5): 853-861. 10.1093/aob/mci091.
Khush GS: Green revolution: the way forward. Nat Rev Genet. 2001, 2 (10): 815-822. 10.1038/35093585.
Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M: Generating high-yielding varieties by genetic manipulation of plant architecture. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2004, 15 (2): 144-147. 10.1016/j.copbio.2004.02.003.
Hedden P: The genes of the Green Revolution. Trends in Genetics. 2003, 19 (1): 5-9. 10.1016/S0168-9525(02)00009-4.
Frary A, Nesbitt TC, Grandillo S, Knaap E, Cong B, Liu J, Meller J, Elber R, Alpert KB, Tanksley SD: fw2.2: a quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science. 2000, 289 (5476): 85-88. 10.1126/science.289.5476.85.
Doebley J, Stec A, Hubbard L: The evolution of apical dominance in maize. Nature. 1997, 386 (6624): 485-488. 10.1038/386485a0.
Takeda T, Suwa Y, Suzuki M, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M, Ueguchi C: The OsTB1 gene negatively regulates lateral branching in rice. Plant J. 2003, 33 (3): 513-520. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01648.x.
Fan CC, Xing YZ, Mao HL, Lu TT, Han B, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF: GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet. 2006, 112 (6): 1164-1171. 10.1007/s00122-006-0218-1.
Xue WY, Xing YZ, Weng XY, Zhao Y, Tang WJ, Wang L, Zhou HJ, Yu SB, Xu CG, Li XH, et al: Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet. 2008, 40 (6): 761-767. 10.1038/ng.143.
Qiu D, Morgan C, Shi JQ, Long Y, Liu J, Li RY, Zhuang X, Wang Y, Tan X, Dietrich E, et al: A comparative linkage map of oilseed rape and its use for QTL analysis of seed oil and erucic acid content. Theor Appl Genet. 2006, 114 (1): 67-80. 10.1007/s00122-006-0411-2.
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL: Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus. 1990, 12: 13-15.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S: MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007, 24 (8): 1596-1599. 10.1093/molbev/msm092.
Andersen JR, Schrag T, Melchinger AE, Zein I, Lubberstedt T: Validation of Dwarf8 polymorphisms associated with flowering time in elite European inbred lines of maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet. 2005, 111 (2): 206-217. 10.1007/s00122-005-1996-6.
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, et al: AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23 (21): 4407-4414. 10.1093/nar/23.21.4407.
Lu GY, Yang GS, Fu TD: Linkage map construction and mapping of a dominant genic male sterility gene (Ms) in Brassica napus. J Genet Genomics. 2004, 31 (11): 1309-1315.
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J: Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol. 2005, 14 (8): 2611-2620. 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x.
Gao ZR: Quantitative genetics. Sichang University, Chongqing, China; 1986.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001, 25 (4): 402-408. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to several anonymous reviewers for helpful suggestions in revising the manuscript. We thank Professor Jinling Meng (National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China) for providing the TN DH population derived from the cross Tapidor×Ningyou7. We gratefully acknowledge the efforts of Associate Professor Duane Falk of the University of Guelph and Gautam Mayank for reading and editing the English version of the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the State Key Basic Research and Development Plan of China (2007CB109001) and Hi-Tech Research and Development Programs of China (2011AA10A104) and by the National Science Foundation of China (30971802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors' contributions
FL designed and carried out the linkage, association, and expression analyses and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. CM conceived of and supervised the overall research. XW participated in the sequence amplification and alignment. CG, JZ, YW, and NC participated in field experimentation. XL implemented field management. JW, BY, JS, JT, and TF helped draft the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12870_2011_952_MOESM1_ESM.XLS
Additional file 1: Sequence of primers used to isolate BnA7.SUT1 and analyze the expression pattern of BnA7.SUT1. M1-M4 were used to generate the main genomic segments of BnA7.SUT1; STAs and STBs were used to generate promoter sequences of BnA7.SUT1.a and BnA7.SUT1.b with degenerate primers for TAD1-6, respectively; RT-A and RT-B were used to analyze the BnA7.SUT1 expression pattern, with AC (derived from B. napus Actin, GeneBank accession number: AF111812) as an endogenous control. (XLS 14 KB)
12870_2011_952_MOESM3_ESM.BMP
Additional file 3: An un-rooted tree was developed using the ClustalX program based on available amino acid sequences of SUTs. Sucrose transporters (SUTs) are from Asarina barclaiana: AbSUT1 (AAF04294); Apium graveolens: AgSUT3 (ABB89051); Alonsoa meridionalis: AmSUT1 (AAF04295); Arabidopsis thaliana: AtSUC1 (CAA53147), AtSUC2 (CAA53150), AtSUC3 (AAC32907), AtSUC4 (NP_172467), AtSUC5 (AAG52226), AtSUC6 (NP_199174), AtSUC7 (NP_176830), AtSUC8 (NP_179074), AtSUC9 (NP_196235), Brssica napus: BnSUTx (ACB47398); Brassica oleracea: BoSUC1 (AAL58071), BoSUC2 (AAL58072); Bambusa oldhamii: BoSUT1 (AAY43226); Citrus sinensis: CsSUT2 (AAM29153); Datisca glomerata: DgSUT4 (CAG70682); Daucus carota: DcSUT1 (BAA89458); Euphorbia esula: EeSUCx (AAF65765); Eucommia ulmoides: EuSUT2 (AAX49396); Hevea brasiliensis: HbSUT2a (ABJ51934), HbSUT2b (ABJ51932), HbSUT5 (ABK60189); Hordeum vulgare: HvSUT1 (CAB75882), HvSUT2 (CAB75881); Juglans regia: JrSUT1 (AAU11810); Lycopersicum esculentum: LeSUT2 (AAG12987), LeSUT4 (AAG09270); Lotus japonicus: LjSUT4 (CAD61275); Malus domestica: MdSUT1 (AAR17700); Manihot esculenta: MeSUT2 (ABA08445), MeSUT4 (ABA08443); Nicotiana tabacum: NtSUT1 (X82276), NtSUT3 (AAD34610); Oryza sativa: OsSUT1 (AAF90181), OsSUT2 (AAN15219), OsSUT3 (BAB68368), OsSUT4 (BAC67164), OsSUT5 (BAC67165); Plantago major: PmSUC1 (CAI59556), PmSUC2 (X75764), PmSUC3 (CAD58887); Populus tremula×Populus tremuloides: Pt×PtSUT1-1 (CAJ33718); Pisum sativum: PsSUT1 (AAD41024); Ricinus communis: RcSCR1 (CAA83436); Solanum demissum: SdSUT2 (AAT40489); Saccharum hybridum: ShSUT1 (AAV41028); Spinacea oleracea: SoSUT1 (Q03411); Solanum tuberosum: StSUT1 (CAA48915), StSUT4 (AAG25923); Triticum aestivum: TaSUT1A (AAM13408), TaSUT1B (AAM13409), TaSUT1D (AAM13410); Vicia faba: VfSUCx (CAB07811); Vitis vinifera: VvSUCy (AAL32020), VvSUC11 (AAF08329), VvSUC12 (AAF08330), VvSUC27 (AAF08331); Zea mays: ZmSUT1 (BAA83501), ZmSUT2 (AAS91375), ZmSUT4 (AAT51689). The BnA7.SUT1 is classified into SUT1 clade. (BMP 1 MB)
12870_2011_952_MOESM4_ESM.EMF
Additional file 4: A neighbor-joining distance tree for BnA7.SUT1 from different genotype lines. The numbers on nodes are bootstrap values, and values lower than 60 are not shown. The sequences from pBnA7.SUT1.a- BnA7.SUT1.a, pBnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.a, and p BnA7.SUT1.b- BnA7.SUT1.b form exclusive clades, respectively. (EMF 13 KB)
12870_2011_952_MOESM6_ESM.XLS
Additional file 6: Phenotypic means for six yield-related traits across four environments. a breeding country. (XLS 20 KB)
12870_2011_952_MOESM7_ESM.XLS
Additional file 7: Summary of the average of the probability of data likelihoods (LnP(D)) for the set of Brassica napus genotypes. Likelihoods were averaged over 10 independent runs with a burn-in of 50, 000 iterations. The set of 55 Brassica napus genotypes was tested for K = 1-10 subpopulations. (XLS 14 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Ma, C., Wang, X. et al. Characterization of Sucrose transporter alleles and their association with seed yield-related traits in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol 11, 168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-168
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-168