Abstract
Background
The flowering process in plants proceeds through the induction of an inflorescence meristem triggered by several pathways. Many of the genes associated with both the flowering process and floral architecture encode transcription factors of the MADS domain family. Gerbera, a member of the sunflower family, Asteraceae, bears compressed inflorescence heads (capitula) with three different flower types characterized by differences in both sexuality and floral symmetry. To understand how such a complex inflorescence structure is achieved at the molecular level, we have characterized the array of Gerbera MADS box genes. The high number of SQUAMOSA-like genes in Gerbera compared to other model species raised the question as to whether they may relate to Gerbera's complex inflorescence structure and whether or not a homeotic A function is present.
Results
In this paper we describe six Gerbera genes related to the SQUAMOSA/APETALA1/FRUITFULL genes of snapdragon and Arabidopsis. Based on phylogenetic analysis of the entire gene lineage, our data indicates that GSQUA1 and GSQUA3 are members of the SQUA/AP1 clade, while GSQUA2, GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 are co-orthologs of the Arabidopsis FUL gene. GSQUA1/GSQUA3 and GSQUA4/GSQUA5/GSQUA6, respectively, represent several gene duplication events unknown in the model systems that may be specific to either Gerbera or Asteraceae. GSQUA genes showed specific expression profiles. GSQUA1, GSQUA2, and GSQUA5 were inflorescence abundant, while GSQUA3, GSQUA4, and GSQUA6 expression was also detected in vegetative organs. Overexpression of GSQUA2 in Gerbera led to accelerated flowering, dwarfism and vegetative abnormalities, all new and specific phenomena observed in transgenic Gerbera plants with modified MADS box gene expression.
Conclusions
Based on expression patterns, none of the Gerbera SQUA-like genes are likely to control flower organ identity in the sense of the floral A function. However, our data shows that the FUL-like gene GSQUA2 plays a vital role in meristem transition. The roles of other GSQUA-genes in Gerbera floral development are intriguing, but require still further study.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Arabidopsis thaliana has been the principal model plant for molecular developmental studies of flowers for two decades. Several traits of Arabidopsis contribute to its attractiveness as a model system. However, not all phenomena in angiosperm flower development are present in Arabidopsis, and some processes are in fact specific to Arabidopsis or its close relatives (reviewed in [1]). Thus, extrapolating floral developmental paradigms from Arabidopsis to other flowering plants is not always straightforward [1–3]. To obtain a broader understanding of floral development, studies on species representing a broad taxonomic distribution are necessary. Our research interest has focused on floral development in Gerbera hybrida, a model species of the sunflower family (Asteraceae). Gerbera inflorescences consist of hundreds of flowers, which can be divided into three different types based on their size, sex, and position in the inflorescence. We have previously shown that many basic principles of floral development apply to Gerbera [4], but that in addition, Gerbera has special features of its own [5, 6]. For example, the B and C functions of the ABC model of flower development [7] are applicable to Gerbera, but the A function has remained elusive.
Based on the ABC model, A function genes are involved in determining sepal and petal identity by repressing C function in whorls one and two [7]. Arabidopsis has two A class genes APETALA1 and APETALA2 (AP1, AP2) [8–12]. AP1 is a MADS box gene, as are the majority of the ABC function genes [12], while AP2 is a member of the AP2/ERF ethylene response family. Both AP1 and AP2 act as A function genes, but they also have several other functions (reviewed in [1]). AP1 has been shown to fulfil a dual function in specifying Arabidopsis sepal and petal identity as well as affecting floral meristem development [9, 13]. AP1 acts closely together and partially redundantly with other inflorescence architecture genes, CAULIFLOWER (CAL) and FRUITFULL (FUL) [14]. Despite attempts to establish similar functions for related genes in other plant species, success has been limited. For example, the Antirrhinum SQUAMOSA (SQUA) gene plays a role in inflorescence meristem development but does not affect floral organ identity [15]. A similar function has been shown for the related gene Antirrhinum DEFH28, which is not involved in determination of sepal and petal identity [16]. Several plant species appear to have genes closely related to AP1, but apparently none have similar functions in specifying sepal and petal identity [17–22]. The pea (Pisum sativum) gene PEAM4 seems to be the closest to AP1 in function and has been suggested to be a functional homologue of AP1 [23] based on similar expression pattern and floral phenotype. However, several authors [1, 24–26] have been inclined to suggest that the entire concept of an A function might be specific to Arabidopsis and perhaps other Brassicaceae.
In addition to previously characterized Gerbera MADS box genes [4–6], we have recently identified several Gerbera genes similar to AP1, FUL [9, 11] and SQUA [15]. AP1 and SQUA are often described as A function genes, but only AP1 has characteristics of a homeotic selector gene. AP1 and SQUA do, however, play strong roles in defining floral meristem identity, together with the genes LEAFY in Arabidopsis and FLORICAULA in snapdragon [27, 28].
Here, we analyze the expression and phylogenetic position of six Gerbera genes, G erbera SQUA MOSA-LIKE1-6 (GSQUA1-6), which are closely related to AP1, SQUA, and FUL. Our data indicate that none of the GSQUA genes are, by themselves, likely to play a role in defining floral organ identity in the sense of the A function of the floral ABC model [7]. However, GSQUA2 does function as a strong positive regulator of meristem transition in Gerbera. Overexpression of GSQUA2 in transgenic Gerbera results in an early flowering dwarf phenotype, which displays abnormal vegetative architecture.
Results
Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of the Gerbera hybrida GSQUAgenes
GSQUA1 was isolated earlier by low stringency screening of an inflorescence cDNA library using a spruce MADS box gene probe, and was so named based of its sequence similarity to SQUA of Antirrhinum [4, 15]. PCR amplification using a degenerate MADS-box specific primer yielded three additional partial sequences of Gerbera SQUA-like genes: GQUA2, GSQUA3, and GSQUA4. Two more SQUA-like genes, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6, were identified from a Gerbera EST collection [29]. Full length cDNA sequences were recovered using 5' and 3' RACE for all GSQUA genes except for GSQUA4.
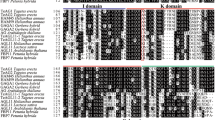
In Arabidopsis, the A function/meristem-identity gene AP1 and the fruit function/meristem-identity gene FUL share a high degree of sequence similarity despite their partially different functions [9, 11, 14]. The C termini of plant MADS domain proteins are variable, but within closely related groups, conserved protein motifs can be recognized. Both AP1- and FUL-like proteins are characterized by such motifs, the euAP1-motif for the former, and the paleoAP1- or FUL-motif for the latter [2, 30]. Alignment of the predicted amino acid sequence of GSQUA2 with similar sequences from other plant species showed that GSQUA2 contains a protein motif similar but not identical to the paleoAP1/FUL-motif. The same motif was also recognizable in GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6. In contrast, GSQUA3 possessed a euAP1-motif (CFPS) that is divergent from the consensus motif (CaaX) [2, 30], while still containing several conserved amino acids (Figure 1). In the previously isolated GSQUA1 protein [4] a euAP1-motif was not evident, but phylogenetic analysis (Additional files 1 and 2) nevertheless suggested a close relationship between GSQUA1 and GSQUA3. The deduced Gerbera GSQUA amino acid sequence alignments and the corresponding protein motifs are shown in Figure 1.
Alignment of C-terminal ends of AP1-like proteins. Gerbera GSQUA proteins were aligned with closely related proteins from Arabidopsis (AP1, P35631; FUL, Q38876; CAL, Q39081), snapdragon (SQUA, Q38742; DEFH28, Q941M9, AmFUL, Q7XBN7), chrysanthemum (CDM111, Q84LD6), and sunflower (HAM75, Q8RVR0; HAM92, Q84LC0). The paleoAP1/FUL protein motif is shown in blue [2, 30]. EuAP1-like proteins contain both an acidic domain (shown in dark red), which has been shown to have transcriptional activity in yeast [86], and a farnesylation motif (shown in red italics) at their C termini [35]. The whole domain marked red represents the euAP1 motif according to [30].
Phylogenetic analysis suggested that GSQUA1 and GSQUA3 are close paralogs, together co-orthologous to AP1 (and SQUA). Similarly, GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 are co-orthologs of FUL, and GSQUA2 is phylogenetically close to the snapdragon gene DEFH28. Although interrationships among the AP1/SQUA, DEFH28, and FUL clades are not well supported in the phylogenetic analysis, the conserved C terminal motifs suggest that GSQUA2/DEFH28/AmFUL are FUL-like. The full maximum likelihood tree, based on our sequences added to the alignment of [2], is shown in Additional file 2. An alignment of GSQUA DNA sequences is shown in Additional file 1.
RNA gel blots and in situ hybridization of GSQUAgenes
Figure 2 summarizes the expression patterns of GSQUA2-6 at RNA gel blot level. Based on previous studies, GSQUA1 expression was in the young inflorescence, scape and bracts [4]. In addition to GSQUA1, the expression of GSQUA2, and GSQUA5 was restricted to floral tissues and no expression was detected in vegetative organs. Interestingly, GSQUA3, GSQUA4 and GSQUA6 also showed expression in leaves, in addition to expression in floral and inflorescence-derived organs. None of the studied GSQUA genes were expressed in Gerbera roots. At the level of single (ray) flowers at relatively late developmental stages, GSQUA2 and GSQUA3 transcripts were most abundant in whorls one and two, while GSQUA4, GSQUA5, and GSQUA6 were expressed in all floral whorls (Figure 2). Different developmental stages of Gerbera ray flower petals (see [31]) were screened by RNA gel blot hybridization to ascertain whether expression levels of GSQUA genes varied over time. The expression levels of GSQUA3 and GSQUA5 did not vary during ray flower petal development, whereas the expression of GSQUA4 was barely detected during ray flower petal development, and both GSQUA2 and GSQUA6 showed differential expression. GSQUA2 expression was stronger during early stages (1,2,3) and faded noticeably toward later developmental stages (4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11). GSQUA6 expression displayed a pattern opposite to that of GSQUA2; its expression grew stronger toward later developmental stages (8,9,10,11) (Additional file 3).
To localize GSQUA expression during the early stages of inflorescence development, a more detailed RNA in situ hybridization analysis of young, developing Gerbera inflorescences (diameter 6-17 mm) was performed (Figure 3). In general, GSQUA genes studied here showed a wide range of expression patterns. In fact, the vasculature of the capitulum receptacle was the only common location where all of the GSQUA genes were expressed. In contrast to other GSQUA genes, GSQUA1 was entirely restricted to the vasculature of the capitulum receptacle and petals [4].While GSQUA2 and GSQUA5 were found to be expressed in all parts of the inflorescence, GSQUA3 and GSQUA6 displayed a slightly narrower expression pattern at the inflorescence level. GSQUA4 was expressed only in the reproductive organs in addition to the vasculature (Figure 3a, b, ). Figure 3b shows examples of developing individual ray flowers, while the summary in Figure 3a is based on larger number of in situ hybridizations. GSQUA2 expression was also seen in the receptacle between the emerging individual flowers (inflorescence size 6 mm, visible also in inflorescence size 14 mm) and petal expression was localized to the adaxial surfaces (Figure 3b). The location of emerging flowers in the developing inflorescence was marked by strong GSQUA2 expression even before clear anatomical differentiation was visible at the center of the capitulum (inflorescence diameter 6 mm) (Figure 3c).
RNA in situ expression analysis of GSQUA genes. (a, b) Developing Gerbera inflorescence (diameter 9-17 mm). Results for GSQUA1 were previously published in [4]. Generally, many GSQUA genes are widely expressed during inflorescence development. Expression in vasculature of the receptacle in addition to floral organs is a common feature. Both GSQUA2 and GSQUA5 are expressed in all floral organs while especially GSQUA4 has more specific expression pattern. (c) The expression of GSQUA2 starts early and marks the location of emerging individual flowers in the developing young inflorescence (diameter 6 mm).
Phenotypic changes in GSQUA2overexpression lines
For functional analysis, we were only able to obtain clear and consistent phenotypes by overexpressing GSQUA2. Transformation of Gerbera with GSQUA2 under the 35S promoter yielded five lines strongly overexpressing GSQUA2 and one line with weaker overexpression, which correlated with milder phenotypic changes (Additional file 4). Compared to the non-transformed Gerbera cultivar 'Terra Regina', all strong overexpression lines showed altered vegetative growth very early in development. The posture of the plants was upright, with leaves curving adaxially. The normal growth habit that leads to a tight rosette-like arrangement of leaves in Gerbera [32] was loosened, with the segments/vegetative axis of the stem strongly elongated. Inflorescences started to form after only two months in the greenhouse whereas the wild type cultivar 'Terra Regina' typically reaches the flowering stage after 6 months (Figure 4). Root formation of the overexpression plants was poor. The plants were susceptible to molds in greenhouse conditions and they typically died after forming only a few inflorescences. Transformants grown in more controlled and contamination-free growth chamber conditions survived for longer periods of time. The general appearance of overexpression lines of GSQUA2 was unstable due to their aberrant architecture, and they required support to remain upright. One milder phenotype was also observed (TR3). This line was not as dramatically dwarfed, but was clearly smaller and more delicate in structure, both vegetatively and inflorescence-wise, as compared to non-transgenic plants. RNA gel blot analysis showed strong expression for GSQUA2 in the inflorescence, but overexpression in leaves was weaker compared to overexpression lines showing the dwarfed phenotype (Additional file 4).
Transgenic Gerbera overexpressing GSQUA2. (a) Gerbera overexpressing GSQUA2 displays dwarf phenotype and flowers early. Wild type cultivar 'Terra Regina' on the left side. Scale bar, 20 cm. (b) Normal Gerbera growth habit is sympodial, the leaves forming a rosette-like structure consisting of tightly packed sympodial units. (c) In plants overexpressing GSQUA2, vegetative axes between sympodial units are strongly elongated compared to the wild type plant. Examples of sympodial units are framed in yellow squares.
The number of flowers in the inflorescence of GSQUA2 overexpression lines was reduced compared to wild type. Non-transformed Gerbera 'Terra Regina' inflorescences, grown side by side with the transformants in the greenhouse, contained on average about 900 individual flowers. The GSQUA2 overexpression lines produced on average only 420 flowers in their inflorescences (Table 1).
Inspection of GSQUA2 overexpression lines with stereomicroscopy or scanning electron microscopy showed no homeotic changes in floral organs of any flower type (data not shown). However, petals of all flower types were shorter compared to the wild type petals, which is congruent with dwarfism and the overall smaller size of the inflorescence. Additionally, inflorescence color differed from wild type in being paler. Despite three transgenic lines producing antisense RNA for GSQUA2, no silencing of the endogenous GSQUA2 was observed.
Discussion
The GSQUAsubfamily of MADS box genes contains at least six members in Gerbera
In addition to the previously published Gerbera SQUA-like genes, GSQUA1 [4], GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 [29], we isolated three new sequences, GSQUA2, GSQUA3 and GSQUA4. The number of GSQUA genes is large compared to most other plant species and it is tempting to relate this diversity to the complex structure of the Gerbera inflorescence [33]. Arabidopsis AP1 and FUL, which function in sepal and petal, fruit, and meristem development [9, 11, 14], are closely related to GSQUAs at the sequence level. The relationship of the two Arabidopsis proteins has been further analyzed by [2] and [30], and they described conserved C-terminal protein motifs (euAP and paleoAP/FUL) in a number of AP1- and FUL like sequences. Identification of these motifs facilitates the classification of related proteins, since phylogenetic analysis of AP1- and FUL-like sequences is not always unambiguous. The paleoAP1/FUL-like protein sequences have a hydrophobic motif (L/MPPWML), which is not found in euAP1-like sequences. EuAP1-like sequences in turn have two conserved motifs, a transcription activation domain RRNaLaLT/NLa (where 'a' stands for an acidic amino acid [2]) and a farnesylation signal CaaX (where C is Cys, 'a' is an aliphatic amino acid, and X is Cys, Met, Ser, Ala, or Glu [34]) that terminates the protein. A farnesylation motif generally directs proteins to a membrane [34], but the role of farnesylation in plant proteins might be more diverse [35–37]. In the case of transcription factors, this function could be part of post-transcriptional regulation, or necessary for protein complex formation [36]. AP1 has been shown to be farnesylated in planta, but membrane localization was not observed [36]. Not all euAP1-like proteins possess this farnesylation signal, however, and thus it may not be an essential part of the protein function [1, 23].
Based on the presence of conserved C terminal protein motifs, GSQUA3 can be classified as belonging to the euAP1-like proteins, while GSQUA2, GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 harbor a paleoAP1/FUL-like protein motif at the C terminus of their amino acid sequence (Figure 1). GSQUA1 does not possess a recognizable protein motif of either type at its C terminal end, but phylogenetic analysis places it close to GSQUA3 (Figure 2). In fact, the GSQUA1 sequence terminates 16 amino acids before the expected euAP1 protein motif. Furthermore, the GSQUA3 protein sequence contains the transcriptional activation domain RSNELDLSL, but no strong transcriptional activation was seen in yeast assays [38]. The motif differs slightly from the consensus motif RRNaLaLT/NLa [2], the second arginine being replaced by serine in GSQUA3 and threonine or asparagine being substituted for serine. The functional relevance of these changes is not clear. Despite the close sequence similarity in the C terminal domain of GSQUA3 to related proteins such as AP1 and SQUA [9, 11, 15], the farnesylation domain of GSQUA3 (CFPS) differs from the most common version of the motif, CFAA/T [35], which is found in many plant SQUA-like proteins [2]. EuAP1-protein motifs similar to Gerbera GSQUA3 are also present in related protein sequences of other species in Asteraceae, including sunflower (Helianthus annuus) and Chrysanthemum (Dendrathema grandiflorum) (HAM75, HAM92, CDM111) [21, 39]. Still, these Asteraceae specific variants are within the definition of the farnesylation motif CaaX [35]. The current definition of the consensus motif is possibly too narrow, and as more plant species are studied in detail, the farnesylation consensus motif may require redefinition.
A detailed phylogenetic analysis of GSQUA2, GSQUA3, GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 produced results in line with the relationships suggested by analysis of C terminal protein motifs. The maximum likelihood tree suggests that GSQUA2 may be orthologous to the snapdragon gene DEFH28, which is involved in the regulation of floral meristem identity and fruit development [16]. Both of these DEFH28 functions are similar to FUL of Arabidopsis, and the authors concluded that DEFH28 most likely represents the ortholog of FUL. However, this interpretation was later challenged by [2] based on the discovery of AmFUL, which, according to phylogenetic and protein motif analysis more likely represents the snapdragon gene orthologous to FUL. Unfortunately, AmFUL has not been further characterized. GSQUA2 does share the early flowering function of DEFH28, however. A potential role of GSQUA2 in fruit development was not studied in this work.
Previous and recent studies on FUL-like genes further distinguish two groups [1, 2, 40]. FUL and AmFUL belong to the euFUL group [41, 2], while AGL79 and DEFH28 belong to euFULII group [16, 40]. Based on the phylogenetic analysis GSQUA4, GSQUA5, and GSQUA6 genes are closer to the euFUL group, while GSQUA2 belongs to the euFULII group.
GSQUA1 [4] and GSQUA3 appear to be recent paralogs and are co-orthologous to SQUA of snapdragon [15]. Similarly, GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 are coorthologous to FUL of Arabidopsis [14, 41].
The expression patterns for GSQUAgenes do not support a homeotic A function
All GSQUA genes, despite being closely related, exhibit different expression patterns at the vegetative and floral organ levels. However, none of the GSQUA genes investigated share the expression pattern of Arabidopsis AP1 or snapdragon SQUA in the sense that they would be particularly abundant in floral whorls 1 and 2 (sepals and petals) in early stages of development. In general, at earlier developmental stages, expression domains of GSQUAs are widespread at the inflorescence level, with the exception of GSQUA4, which is expressed in reproductive organs and in the vasculature of the capitulum receptacle (Figure 3a, b). Only later in floral development GSQUA2 and GSQUA3 are weakly expressed in sepals and petals (Figure 2). The expression in vasculature is common among all GSQUA genes studied here. Expression in vasculature is also known for FUL [41] and AmFUL [2], but vascular expression is not a uniform trait for euAP1-, euFUL- or euFULII-like genes. This expression pattern may reflect a function in developing vascular bundles, but the phenomenon has not been extensively discussed previously and its functional significance for GSQUA genes remains unclear.
The broad expression pattern of GSQUA2 during early stages of ray flower development resembles what has been previously reported for FUL and other FUL-like genes, and contrasts with the expression of AP1, which is confined to the first two whorls [10]. FUL-like genes are commonly expressed in the carpel [21, 42–45], meristems [13, 41] and vegetative tissues, including bracts [18, 21, 43, 46]. Expression has also been observed in the inflorescence [18, 19, 21, 47, 48], floral meristems [19, 49], stamens [17, 45], and perianth organs [17, 42, 43, 45]. For some species, expression has been visible in all floral whorls [45, 50]. The expression pattern for Arabidopsis FUL is biphasic, which is in accordance with its early (floral meristem identity) and late (silique development) functions in reproductive development [14, 41].
The functional role of FUL in fruit development was first detected in Arabidopsis mutant lines lacking FUL expression. Gerbera does not bear a fruit similar to Arabidopsis; its ovary position is inferior as opposed to superior in Arabidopsis and the fruits (achenes) are indehiscent. Thus the late function for GSQUA2 might be entirely different (like DEFH28 in snapdragon; [16]) or lacking completely. The most dramatic phenotypic effects in 35S::FUL lines are cell type changes in valve margins and the outer replum, which lead to developmental failure of the dehiscence zone and eventually to indehiscent fruit [14]. Interestingly, GSQUA2 expresses strongly in ovary inner walls and the ovule (Figure 3), so despite the fact that no homeotic changes in GSQUA2 overexpression lines were visible in ovaries and ovules at the relatively late developmental stage 8, a role for GSQUA2 in Gerbera fruit development, possibly at the level of cell differentiation, cannot be ruled out.
GSQUA2is involved in meristem transition
Among the several related GSQUA genes of Gerbera, only GSQUA2 lent itself to further functional characterization based on transgenic Gerbera lines overexpressing the gene. Several transgenic lines both for GSQUA3 and GSQUA5 were generated and analyzed for overexpression and downregulation, but no consistent floral phenotypes were observed. Both genes, GSQUA2 and FUL, seem to share the same function of meristem identity determination in early floral development, but the inflorescence abundance of GSQUA2 expression distinguishes it from FUL, as FUL is expressed also in vegetative parts of Arabidopsis [13]. However, when GSQUA2 is ectopically expressed throughout Gerbera tissues, dramatic vegetative changes such as dwarfism and vegetative axis elongation appear. Gerbera growth habit is sympodial with very short, leafy lateral shoots forming the sympodia. Typically, the sympodial rhizome forms 7-24 leaves before the first inflorescence is formed by the apical meristem. Two inflorescences are formed per one vegetative shoot, the second inflorescence being formed in the axil of the uppermost leaf primordium. The vegetative axis continues to develop in the axil of the second leaf primordium. The fully-formed axis grows 2-8 leaves before forming a terminal inflorescence, a lateral inflorescence, and again a vegetative shoot, the growth cycle being iterative [32]. The vegetative axis between lateral shoots is very short and the lateral shoots form a tightly packed entity. However, in plants overexpressing GSQUA2, the vegetative axis between lateral shoots is strongly elongated compared to wild type Gerberas (Figure 4). The poor root formation of the overexpression lines may be to ectopic expression of GSQUA2 under the 35S promoter, which interferes with the normal root development and is thus not necessarily informative of the gene's normal function.
Overexpression lines of GSQUA2 flower substantially earlier than wild type plants, which suggests this gene to be involved in floral meristem transition. The strong localized expression of GSQUA2 in emerging flower primordia at the early stages of flower development also supports this hypothesis (Figure 3c). Despite of the strong expression in overexpression lines, only minor morphological changes, such as reduced petal size and color, were detected at the level of individual flowers. At the inflorescence level, however, a considerably reduced number of flowers was observed, since the overexpression lines for GSQUA2 contained only half the number of flowers in their inflorescences as non-transgenic Gerbera. A similar phenomenon was reported with birch BpMADS4 overexpression lines [51], and may relate to accelerated development, including accelerated consumption of the inflorescence meristem.
In wheat and ryegrass, the AP1-like MADS-box gene VRN1 is expressed in vegetative tissues and has been suggested to control the transition to flowering [52, 53]. Based on the vegetative expression pattern, GSQUA3, GSQUA4 and GSQUA6 are Gerbera candidates for this kind of function, but at least for GSQUA3 we have data that its ectopic expression does not cause early flowering.
In Arabidopsis, accelerated flowering is regularly observed when different MADS-box genes are overexpressed, including those not directly related to flowering time [54–63]. In Gerbera, all overexpression lines with MADS box genes other than GSQUA2 have retained their normal vegetative size and flowering time, although many have displayed homeotic or meristem identity changes in the inflorescences [4–6].
GSQUA proteins interact with other Gerbera MADS domain proteins
AP1/SQUA-like MADS domain proteins have been suggested to function as mediators of higher order complex formation, acting as 'bridge proteins' and facilitating the formation of protein quartets [64, 65]. However, based on pairwise assays [38], GSQUA proteins seem unlikely to function as interaction mediators in Gerbera, since their interaction capacity appears to be limited [38]. This feature distinguishes all GSQUA proteins from the closely related Petunia protein FBP29. FBP29 is capable of interacting with several MADS domain proteins of different functional classes [43]. Moreover, other FUL-like proteins from Petunia, PFG and FBP26, show more extensive interaction capacity than the studied GSQUA proteins [42, 43]. Also Arabidopsis FUL was shown to be active in multiple protein-protein interactions [66]. GSQUA2 was found to interact with three other Gerbera MADS domain proteins in a screen of fourteen proteins, whereas GSQUA1 and GSQUA3 proteins interacted with only two other proteins, all partners being members of the SEP-like GRCD family of Gerbera proteins. GSQUA5 remained inactive in pairwise assay showing no interaction with any tested Gerbera proteins. The most interesting GSQUA2 specific partner is GRCD2, a pleiotropically active Gerbera SEP-like protein with functions in carpel identity, meristem identity and inflorescence determinacy [6]. Interestingly, when GSQUA2 and GRCD2 were combined in yeast, a strong autoactivation function emerged - separately, neither of the proteins show transcriptional activation. This function of the GSQUA2/GRCD2 dimer could reflect its importance in Gerbera floral development. Both GSQUA2 and GRCD2 are co-expressed in young inflorescences and their expression patterns are overlapping [6], rendering the interaction feasible also in planta.
When assaying for higher order complex formation, GSQUA proteins showed greater activity. Together with the Gerbera B function dimer GGLO1/GDEF2, and when combined with a Gerbera SEP-like GRCD protein and with a C function GAGA protein, all GSQUA proteins showed activity [38]. While GSQUA proteins did not interact with each other in the pairwise assays, addition of a GRCD protein made some complexes with two GSQUA proteins stable in yeast.
Even as interaction of GSQUAs with E function proteins (GRCD4 and GRCD5, pairwise) or with B function proteins (GGLO1/GDEF2, threesome) can be seen as consistent with a homeotic A function for GSQUAs, interaction with C function proteins (GAGA1 and GAGA2, threesome with GRCDs) is not. In Arabidopsis, expression of AP1 (with homeotic A function) is excluded in cells where the C-function gene AGAMOUS (AG) is expressed [67]. AP1 alone does not repress the C function in whorls one and two, but rather acts together with the non-MADS proteins LEUNIG and SEUSS [68, 69] in a complex including other MADS domain proteins, AGL24 and SVP [68]. However the AG gene has functions beyond the floral homeotic one in Arabidopsis. AG is known to control the meristematic state of flower primordia and to downregulate the meristem organizing gene WUSCHEL together with unknown factors [70, 71] which in Petunia are MADS domain proteins [72].
It is tempting to relate the large number of SQUA-like genes in Gerbera to the complex structure of the inflorescence in Asteraceae. At least some interactions for homologous Chrysanthemum MADS domain proteins are similar to the Gerbera proteins. CDM41, which is closely related to GSQUA proteins, interacts with Chrysanthemum CDM44, which is homologous to SEP3 of Arabidopsis [21]. This interaction is similar to GSQUAs' interaction with GRCD4 and GRCD5. In yeast three-hybrid assay, CDM41 combined with the Chrysanthemum B protein heterodimer (CDM86 and CDM115), and the complex was active, as are Gerbera complexes with a GSQUA protein and the B protein dimer. Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) also contains several genes closely related to AP1 and FUL [39]. Obviously duplication of this lineage of genes has also taken place in sunflower. Perhaps gene duplication and divergence in the SQUA/AP1/FUL gene lineage has participated, together with the unique diversity in TCP family transcription factors [73] to help shape the complex Asteraceae inflorescence.
Conclusions
Gerbera has an array of SQUA-like genes, which can be classified either as euAP1-like, or as FUL-like [2, 30]. However, none of these genes appear to act as an A function gene in the sense of the classical ABC model [7]. Based on these results, Gerbera can be added to the growing list of plant species that lack the A function comparable to Arabidopsis. GSQUA2 is intimately involved in the regulation of meristem transition in Gerbera as overexpression of GSQUA2 led to accelerated flowering. The role of GSQUA1, GSQUA3, GSQUA4, GSQUA5, and GSQUA6 in the floral development of Gerbera requires further study. The complex inflorescence structure and the high number of Gerbera GSQUA-like genes lead to a temptation to associate these two phenomena, but verifying this hypothesis requires more research.
Methods
Identification of Gerbera GSQUAgenes
GSQUA2, GSQUA3 and GSQUA4 were identified using reverse transcription PCR with inflorescence mRNA as a template. The 5' primer E0364 (GCG GAG CTC GAG TTA AGA GRA TAG ARA ACA , where R = A/G) was designed based on previously published alignment of the MADS domain from several plant species, including Gerbera [4, 74]. The 5' end of the primer contained two restriction enzyme recognition sites (for SacI and XhoI) to aid cloning. For the 3' end, an anchored oligo-d(T) primer (G ACC ACG CGT ATC GAT GTC GAC TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TV, V = G/C/A) (Boehringer Mannheim 5'/3' RACE kit 1734792) was used. This primer contained three restriction enzyme cut sites (MluI, ClaI, SalI) at its 5' end. The cDNA was synthesized from Gerbera inflorescence mRNA (pooled RNA sample, inflorescence sizes 10-13 mm in diameter) (Boehringer Mannheim kit 1483188). Taq DNA polymerase (Promega), 50 pmols of both primers and Gerbera inflorescence cDNA were used in a standard PCR reaction with 30 cycles. In an agarose gel, the result of the PCR showed several clear-cut bands of DNA. Four bands (estimated sizes 820 bp, 780 bp, 700 bp, and 550 bp) were isolated from the gel, ligated into the pBluescriptII SK + vector and sequenced. The largest fragment contained nearly full length sequences for GSQUA2, GSQUA3 and GSQUA4. GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 were identified in the Gerbera EST collection previously described [29]. GSQUA5 was recovered as a full-length cDNA from the EST collection, but GSQUA6 was about 100 nucleotides short at the 5' end of the gene.
Isolation of full length sequences
Amplification with the E0364 primer left MADS box genes short of sequences encoding the amino acids in the N terminus of the protein. The missing sequences were amplified by the 5' RACE method [75] (5'/3' RACE kit, Boehringer Mannheim, cat. no. 1734792). Gene specific 5' RACE primers were designed from the intervening region between the MADS and the K boxes to ensure sufficient specificity. New cDNA was synthesized from Gerbera inflorescence mRNA (pooled RNA sample, inflorescence sizes 10-13 mm) (Boehringer Mannheim kit cat. no. 1483188). For each reaction, a band of approximate size of 500 bp was isolated from an agarose gel and ligated into the pGEM-T Easy vector (Promega). The missing 3' sequences of GSQUA3 and GSQUA4 were amplified using the same RACE kit. Finally, each full-length cDNA sequence was reamplified using gene specific 5' and 3' primers, ligated into the vector pBluescriptII SK + and verified by sequencing. Full-length sequences were obtained by 5' and 3' RACE methods for all GSQUA genes, except for GSQUA4, which lacks nucleotides encoding presumably about eight N terminal amino acids.
Phylogeny reconstruction
For phylogenetic positioning of the GSQUA nucleotide sequences, we added them to the large data set used in [2]. The original data was kindly transmitted by A. Litt, and sequence abbreviations used by [2] apply to the present tree as well. The new alignment including Gerbera SQUA-like genes was made by hand, using the inferred amino acid sequences as a guide. The original GSQUA1 sequence in the [2] data matrix was deleted to avoid double representation. Phylogenetic analysis on the nucleotide data was performed using the maximum likelihood method, via the PHYML program [76], web interface [77]. 100 bootstrap resampling replicates were done to estimate support for the clades [78]. The options used with the PHYML web interface were the HKY molecular evolutionary model [79], transition/transversion ratio preset to 4, estimated proportion of invariant sites = 0.065, empirical nucleotide frequencies [f(A) = 0.32198, f(C) = 0.21318, f(G) = 0.24109, f(T) = 0.22375], 4 substitution rate categories, estimated gamma distribution parameter = 1.095, starting tree constructed using BIONJ [80], tree topology optimization using NNI and SPR tree rearrangement algorithms to search tree space, and branch length and rate parameter optimization.
RNA gel blots
RNAs from different plant organs and from different stages of petal development (stages 1-11, see [31]) were isolated using Trizol (Invitrogen, cat. no. 11596-018) and quantified by spectrophotometer. Equal amounts (10 μg) of RNA were run in a 0.8% agarose gel as described by [31]. The rRNA bands were visualized by EtBr staining to record even loading of the gel. The RNA was blotted on Hybond-N membrane (Amersham Biosciences) and hybridized in the UltraHyb hybridization buffer (Ambion). For GSQUA2, a gene specific probe (260 or 320 bp) from the 3' UTR was used. The probe was labeled with [ 32P] dCTP and hybridized at + 42°C for 16 h. The membranes were washed with 1 x SSC, 0.1% SDS at + 42°C for 20 minutes. Subsequent washes were performed at + 65°C in the same buffer for 15 minutes, 1-2 times depending on the desired level of final activity. Films were exposed at -80°C. For GSQUA3, GSQUA5, and GSQUA6, full length probes (889 bp, 948 bp, and 812 bp) were used in hybridization due to unspecific hybridization patterns produced with shorter 3' probes. For GSQUA4, a longer probe of 450 bp was used due to problems with specificity. For RNA blots hybridized with longer probes, more stringent washing conditions with 0.2 x SSC, 0.1% SDS at + 65°C were applied, leading to increased specificity judged by simpler band patterns.
In situhybridization
In situ hybridization analysis was performed as described in [81] and [82]. GSQUA2, GSQUA3, GSQUA4, GSQUA5 and GSQUA6 gene specific antisense probes (250 bp, 385 bp, 300 bp, 187 bp and 235 bp from the 3' UTR) were prepared and quantitated using the DIG RNA labeling kit (Boehringer Mannheim cat. no. 11175025910) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Paraffin sections (10 μm thick) were mounted in 50% glycerol after hybridization. A 217 bp fragment of Gerbera GGLO1 from the 3' UTR [4] was used as a sense control in in situ hybridization.
Plant material and transformation
Gerbera hybrida var. 'Terra Regina' was obtained from the commercial producer Terra Nigra, De Kwakel, the Netherlands. In the greenhouse, day length followed the natural day length during the summer season and was set to ten hours during the winter - day length is, however, not critical for Gerbera growth and flowering. The temperature was +16... + 18°C during nighttime and + 18... + 20°C during daytime. The plants were drip-irrigated and fertilized with NPK fertilizer (Kukka-Superex NPK 11-3-26, Kekkilä, Finland). The relative humidity was set for 65%. In growth chambers, temperatures were + 18°C at night and + 20°C during day, and the day length was set to 10 hours. For functional analysis, the full length GSQUA sequences were cloned under the CaMV 35S promoter in both sense and antisense orientation as described in [83]. Gerbera transformation was performed using an Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer method as previously described [84, 85].
References
Litt A: An evaluation of A-function: Evidence from the APETALA1 and APETALA2 gene lineages. Int J Plant Sci. 2007, 168: 73-91. 10.1086/509662.
Litt A, Irish VF: Duplication and diversification in the APETALA1/FRUITFULL floral homeotic gene lineage: implications for the evolution of floral development. Genetics. 2003, 165: 821-833.
Kuhlemeier C, Sinha N: Growth and development The diversity of plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007, 10: 1-3. 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.11.012.
Yu DY, Kotilainen M, Pöllänen E, Mehto M, Elomaa P, Helariutta Y, Albert VA, Teeri TH: Organ identity genes and modified patterns of flower development in Gerbera hybrida (Asteraceae). Plant J. 1999, 17: 51-62. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00351.x.
Kotilainen M, Elomaa P, Uimari A, Albert VA, Yu D, Teeri TH: GRCD1, an AGL2 like MADS box gene participates in the C function during stamen development in Gerbera hybrida. Plant Cell. 2000, 12: 1893-1902. 10.1105/tpc.12.10.1893.
Uimari A, Kotilainen M, Elomaa P, Yu D, Albert VA, Teeri TH: Integration of reproductive meristem fates by a SEPALLATA-like MADS-box gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004, 101: 15817-15822. 10.1073/pnas.0406844101.
Coen ES, Meyerowitz EM: The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature. 1991, 353: 31-37. 10.1038/353031a0.
Kunst L, Klenz JE, Martinez-Zapater J, Haughn GW: AP2 Gene Determines the Identity of Perianth Organs in Flowers of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 1989, 1: 1195-1208. 10.1105/tpc.1.12.1195.
Irish VF, Sussex IM: Function of the apetala-1 gene during Arabidopsis floral development. Plant Cell. 1990, 2: 741-753. 10.1105/tpc.2.8.741.
Mandel MA, Gustafson-Brown C, Savidge B, Yanofsky MF: Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene APETALA1. Nature. 1992, 360: 273-277. 10.1038/360273a0.
Bowman JL, Alvarez J, Weigel D, Meyerowitz EM, Smyth DR: Control of flower development in Arabidopsis thaliana by APETALA 1 and interacting genes. Development. 1993, 119: 721-743.
Jofuku KD, den Boer BG, Van Montagu M, Okamuro JK: Control of Arabidopsis flower and seed development by the homeotic gene APETALA2. Plant Cell. 1994, 6: 1211-1225. 10.1105/tpc.6.9.1211.
Mandel MA, Yanofsky MF: The Arabidopsis AGL8 MADS box gene is expressed in inflorescence meristems and is negatively regulated by APETALA1. Plant Cell. 1995, 7: 1763-1771. 10.1105/tpc.7.11.1763.
Ferrándiz C, Gu Q, Martienssen R, Yanofsky MF: Redundant regulation of meristem identity and plant architecture by FRUITFULL, APETALA1 and CAULIFLOWER. Development. 2000, 127: 725-734.
Huijser P, Klein J, Lonnig WE, Meijer H, Saedler H, Sommer H: Bracteomania, an inflorescence anomaly, is caused by the loss of function of the MADS-box gene squamosa in Antirrhinum majus. EMBO J. 1992, 11: 1239-1249.
Müller BM, Saedler H, Zachgo S: The MADS-box gene DEFH28 from Antirrhinum is involved in the regulation of floral meristem identity and fruit development. Plant J. 2001, 28: 169-179. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01139.x.
Kyozuka J, Harcourt R, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES: Eucalyptus has functional equivalents of the Arabidopsis AP1 gene. Plant Mol Biol. 1997, 35: 573-584. 10.1023/A:1005885808652.
Elo A, Lemmetyinen J, Turunen ML, Tikka L, Sopanen T: Three MADS-box genes similar to APETALA1 and FRUITFULL from silver birch (Betula pendula). Physiol Plant. 2001, 112: 95-103. 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1120113.x.
Hart JK, Hannapel DJ: In situ hybridization of the MADS-box gene POTM1 during potato floral development. J Exp Bot. 2002, 53: 465-471. 10.1093/jexbot/53.368.465.
Fornara F, Parenicova L, Falasca G, Pelucch N, Masiero S, Ciannamea S, Lopez-Dee Z, Altamura MM, Colombo L, Kater MM: Functional characterization of OsMADS18, a member of the AP1/SQUA subfamily of MADS box genes. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135: 2207-2219. 10.1104/pp.104.045039.
Shchennikova AV, Shulga OA, Immink R, Skryabin KG, Angenent GC: Identification and characterization of four chrysanthemum MADS-box genes, belonging to the APETALA1/FRUITFULL and SEPALLATA3 subfamilies. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134: 1632-1641. 10.1104/pp.103.036665.
Fernando DD, Zhang S: Constitutive expression of the SAP1 gene from willow (Salix discolor) causes early flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev Genes Evol. 2006, 216: 19-28. 10.1007/s00427-005-0026-7.
Berbel A, Navarro C, Ferrándiz C, Canas LA, Madueno F, Beltran J: Analysis of PEAM4, the pea AP1 functional homologue supports a model for AP1-like genes controlling both floral meristem and floral organ identity in different plant species. Plant J. 2001, 25: 441-451. 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00974.x.
Theissen G, Kim JT, Saedler H: Classification and phylogeny of the MADS-box multigene family suggest defined roles of MADS-box gene subfamilies in the morphological evolution of eukaryotes. J Mol Evol. 1996, 43: 484-516. 10.1007/BF02337521.
Theissen G, Becker A, di Rosa A, Kanno A, Kim JT, Munster T, Winter KU, Saedler H: A short history of MADS-box genes in plants. Plant Mol Biol. 2000, 42: 115-149. 10.1023/A:1006332105728.
Smyth DR: Morphogenesis of flowers - Our evolving view. Plant Cell. 2005, 17: 330-341. 10.1105/tpc.104.030353.
Weigel D, Alvarez J, Smyth DR, Yanofsky MF, Meyerowitz EM: LEAFY controls floral meristem identity in Arabidopsis. Cell. 1992, 69: 843-859. 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90295-N.
Coen ES, Romero JM, Doyle S, Elliott R, Murphy G, Carpenter R: Floricaula: a Homeotic Gene Required for Flower Development in Antirrhinum Majus. Cell. 1990, 63: 1311-1322. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90426-F.
Laitinen RA, Immanen J, Auvinen P, Rudd S, Alatalo E, Paulin L, Ainasoja M, Kotilainen M, Koskela S, Teeri TH, Elomaa P: Analysis of the floral transcriptome uncovers new regulators of organ determination and gene families related to flower organ differentiation in Gerbera hybrida (Asteraceae). Genome Res. 2005, 15: 475-486. 10.1101/gr.3043705.
Vandenbussche M, Theissen G, Van de Peer Y, Gerats T: Structural diversification and neo-functionalization during floral MADS-box gene evolution by C-terminal frameshift mutations. Nucl Acids Res. 2003, 31: 4401-4409. 10.1093/nar/gkg642.
Helariutta Y, Elomaa P, Kotilainen M, Seppänen P, Teeri TH: Cloning of cDNA coding for dihydroflavonol-4-reductase (DFR) and characterization of dfr expression in the corollas of Gerbera hybrida var Regina (Compositae). Plant Mol Biol. 1993, 22: 183-193. 10.1007/BF00014927.
Leffring L: De bloemproduktie van Gerbera (Flower production of Gerbera). PhD thesis 834. Agricultural University, Wageningen,The Netherlands; 1981.
Teeri TH, Kotilainen M, Uimari A, Ruokolainen S, Ng YP, Malm U, Pöllänen E, Broholm S, Laitinen R, Elomaa P, Albert VA: Floral developmental genetics of Gerbera (Asteraceae). Adv Bot Res. 2006, 44: 323-351. 10.1016/S0065-2296(06)44008-8.
Galichet A, Gruissem W: Protein farnesylation in plants--conserved mechanisms but different targets. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003, 6: 530-535. 10.1016/j.pbi.2003.09.005.
Hancock JF, Cadwallader K, Paterson H, Marshall CJ: A CAAX or a CAAL motif and a second signal are sufficient for plasma membrane targeting of ras proteins. EMBO J. 1991, 10: 4033-4039.
Yalovsky S, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Bracha K, Toledo-Ortiz G, Gruissem W: Prenylation of the floral transcription factor APETALA1 modulates its function. Plant Cell. 2000, 12: 1257-1266. 10.1105/tpc.12.8.1257.
Suzuki N, Yamaguchi Y, Koizumi N, Sano H: Functional characterization of a heavy metal binding protein CdI19 from Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2002, 32: 165-173. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01412.x.
Ruokolainen S, Ng YP, Albert VA, Elomaa P, Teeri TH: Large scale interaction analysis predicts that the Gerbera hybrida floral E function is provided both by general and specialized proteins. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10: 129-10.1186/1471-2229-10-129.
Shulga OA, Shchennikova AV, Angenent GC, Skryabin KG: MADS-box genes controlling inflorescence morphogenesis in sunflower. Russ J Dev Bio. 2008, 39: 2-5.
Litt A, Kramer EM: The ACB model and the diversification of floral organ identity. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009, doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.11.019
Gu Q, Ferrándiz C, Yanofsky MF, Martienssen R: The FRUITFULL MADS-box gene mediates cell differentiation during Arabidopsis fruit development. Development. 1998, 125: 1509-1517.
Immink RGH, Hannapel DJ, Ferrario S, Busscher M, Franken J, Lookeren Campagne MM, Angenent GC: A petunia MADS box gene involved in the transition from vegetative to reproductive development. Development. 1999, 126: 5117-5126.
Immink RGH, Ferrario S, Busscher-Lange J, Kooiker M, Busscher M, Angenent GC: Analysis of the petunia MADS-box transcription factor family. Molecular genetics and genomics: MGG. 2003, 268: 598-606.
Busi MV, Bustamante C, D'Angelo C, Hidalgo-Cuevas M, Boggio SB, Valle EM, Zabaleta E: MADS-box genes expressed during tomato seed and fruit development. Plant Mol Biol. 2003, 52: 801-815. 10.1023/A:1025001402838.
Hileman LC, Sundström JF, Litt A, Chen M, Shumba T, Irish VF: Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the MADS-box gene family in tomato. Mol Biol Evol. 2006, 23: 2245-2258. 10.1093/molbev/msl095.
Sreekantan L, Clemens J, McKenzie MJ, Lenton JR, Croker SJ, Jameson PE: Flowering genes in Metrosideros fit a broad herbaceous model encompassing Arabidopsis and Antirrhinum. Physiol Plant. 2004, 121: 163-173. 10.1111/j.0031-9317.2004.00304.x.
Calonje M, Cubas P, Martinez-Zapater JM, Carmona MJ: Floral meristem identity genes are expressed during tendril development in grapevine. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135: 1491-1501. 10.1104/pp.104.040832.
Skipper M, Pedersen KB, Johansen LB, Frederiksen S, Irish VF, Johansen BB: Identification and quantification of expression levels of three FRUITFULL-like MADS-box genes from the orchid Dendrobium thyrsiflorum (Reichb.f.). Plant Science. 2005, 169: 579-586. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.04.011.
Pnueli L, Abu-Abeid M, Zamir D, Nacken W, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Lifschitz E: The MADS box gene family in tomato: temporal expression during floral development, conserved secondary structures and homology with homeotic genes from Antirrhinum and Arabidopsis. Plant J. 1991, 1: 255-266. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.1991.00255.x.
Wu YH, Zhang JS, Zheng Z, Xue S, Li Y: Molecular cloning and characterization of two tobacco MADS-box genes. Sexual plant reproduction. 2000, 13: 163-169. 10.1007/s004970000054.
Elo A, Lemmetyinen J, Novak A, Keinonen K, Porali I, Hassinen M, Sopanen T: BpMADS4 has a central role in inflorescence initiation in silver birch (Betula pendula). Physiol Plant. 2007, 131: 149-158. 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.00947.x.
Jensen LB, Andersen JR, Frei U, Xing Y, Taylor C, Holm PB, Lübberstedt T: QTL mapping of vernalization response in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) reveals co-location with an orthologue of wheat VRN1. Theor Appl Genet. 2005, 110: 527-536. 10.1007/s00122-004-1865-8.
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J: Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 100: 6263-6268. 10.1073/pnas.0937399100.
Mizukami Y, Ma H: Ectopic expression of the floral homeotic gene AGAMOUS in transgenic Arabidopsis plants alters floral organ identity. Cell. 1992, 71: 119-131. 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90271-D.
Mizukami Y, Ma H: Determination of Arabidopsis Floral Meristem Identity by AGAMOUS. Plant Cell. 1997, 9: 393-408. 10.1105/tpc.9.3.393.
Michaels SD, Amasino RM: FLOWERING LOCUS C encodes a novel MADS domain protein that acts as a repressor of flowering. Plant Cell. 1999, 11: 949-956. 10.1105/tpc.11.5.949.
Sheldon CC, Burn JE, Perez PP, Metzger J, Edwards JA, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES: The FLF MADS box gene: a repressor of flowering in Arabidopsis regulated by vernalization and methylation. Plant Cell. 1999, 11: 445-458. 10.1105/tpc.11.3.445.
Borner R, Kampmann G, Chandler J, Gleissner R, Wisman E, Apel K, Melzer S: A MADS domain gene involved in the transition to flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2000, 24: 591-599. 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00906.x.
Hartmann U, Hohmann S, Nettesheim K, Wisman E, Saedler H, Huijser P: Molecular cloning of SVP: a negative regulator of the floral transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2000, 21: 351-360. 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00682.x. 70
Ratcliffe OJ, Nadzan GC, Reuber TL, Riechmann JL: Regulation of flowering in Arabidopsis by an FLC homologue. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126: 122-132. 10.1104/pp.126.1.122.
Favaro R, Pinyopich A, Battaglia R, Kooiker M, Borghi L, Ditta G, Yanofsky MF, Kater MM, Colombo L: MADS-box protein complexes control carpel and ovule development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2003, 15: 2603-2611. 10.1105/tpc.015123.
Michaels SD, He Y, Scortecci KC, Amasino RM: Attenuation of FLOWERING LOCUS C activity as a mechanism for the evolution of summer-annual flowering behavior in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003, 100: 10102-10107. 10.1073/pnas.1531467100.
Castillejo C, Romera-Branchat M, Pelaz S: A new role of the Arabidopsis SEPALLATA3 gene revealed by its constitutive expression. Plant J. 2005, 43: 586-596. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02476.x.
Kaufmann K, Melzer R, Theissen G: MIKC-type MADS-domain proteins: structural modularity, protein interactions and network evolution in land plants. Gene. 2005, 347: 183-198. 10.1016/j.gene.2004.12.014.
Theissen G, Melzer R: Molecular mechanisms underlying origin and diversification of the angiosperm flower. Ann Bot. 2007, 100: 603-619. 10.1093/aob/mcm143.
de Folter S, Immink RGH, Kieffer M, Pařenicová L, Henz SR, Weigel D, Busscher M, Kooiker M, Colombo L, Kater MM, Davies B, Angenent GC: Comprehensive interaction map of the Arabidopsis MADS box transcription factors. Plant Cell. 2005, 17: 1424-1433. 10.1105/tpc.105.031831.
Gustafson-Brown C, Savidge B, Yanofsky MF: Regulation of the arabidopsis floral homeotic gene APETALA1. Cell. 1994, 76: 131-143. 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90178-3.
Gregis V, Sessa A, Colombo L, Kater MM: AGL24, SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE, and APETALA1 redundantly control AGAMOUS during early stages of flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2006, 18: 1373-1382. 10.1105/tpc.106.041798.
Sridhar VV, Surendrarao A, Liu Z: APETALA1 and SEPALLATA3 interact with SEUSS to mediate transcription repression during flower development. Development. 2006, 133: 3159-3166. 10.1242/dev.02498.
Lohmann JU, Hong RL, Hobe M, Busch MA, Parcy F, Simon R, Weigel D: A molecular link between stem cell regulation and floral patterning in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2001, 105: 793-803. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00384-1.
Lenhard M, Bohnert A, Jurgens G, Laux T: Termination of stem cell maintenance in Arabidopsis floral meristems by interactions between WUSCHEL and AGAMOUS. Cell. 2001, 105: 805-814. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00390-7.
Ferrario S, Shchennikova AV, Franken J, Immink RGH, Angenent GC: Control of floral meristem determinacy in petunia by MADS-box transcription factors. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140: 890-898. 10.1104/pp.105.072660.
Broholm SK, Tähtiharju S, Laitinen RAE, Albert VA, Teeri TH, Elomaa P: A TCP domain transcription factor controls flower type specification along the radial axis of the Gerbera (Asteraceae) inflorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 9117-9122. 10.1073/pnas.0801359105.
Purugganan MD, Rounsley SD, Schmidt RJ, Yanofsky MF: Molecular evolution of flower development: diversification of the plant MADS-box regulatory gene family. Genetics. 1995, 140: 345-356.
Frohman MA, Dush MK, Martin GR: Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988, 85: 8998-9002. 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998.
Guindon S, Gascuel O: A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol. 2003, 52: 696-704. 10.1080/10635150390235520.
Guindon S, Lethiec F, Duroux P, Gascuel O: PHYML online-Aweb server for fast maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic inference. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33: W557-W559. 10.1093/nar/gki352.
Felsenstein J: Confidence-limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 1985, 39: 783-791. 10.2307/2408678.
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T: Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol. 1985, 22: 160-174. 10.1007/BF02101694.
Gascuel O: BIONJ: An improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data. Mol Biol Evol. 1997, 14: 685-695.
Di Laurenzio L, Wysocka-Diller J, Malamy JE, Pysh L, Helariutta Y, Freshour G, Hahn MG, Feldmann KA, Benfey PN: The SCARECROW Gene Regulates an Asymmetric Cell Division That Is Essential for Generating the Radial Organization of the Arabidopsis Root. Cell. 1996, 86: 423-433. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80115-4.
Mähönen AP, Bonke M, Kauppinen L, Riikonen M, Benfey PN, Helariutta Y: A novel two-component hybrid molecule regulates vascular morphogenesis of the Arabidopsis root. Genes Dev. 2000, 14: 2938-2943. 10.1101/gad.189200.
Elomaa P, Uimari A, Mehto M, Albert VA, Laitinen RAE, Teeri TH: Activation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Gerbera hybrida (Asteraceae) suggests conserved protein-protein and protein-promoter interactions between the anciently diverged monocots and eudicots. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133: 1831-1842. 10.1104/pp.103.026039.
Elomaa P, Honkanen J, Puska R, Seppänen P, Helariutta Y, Mehto M, Kotilainen M, Nevalainen L, Teeri TH: Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of antisense chalcone synthase cDNA to Gerbera hybrida inhibits flower pigmentation. Bio/technology. 1993, 11: 508-511. 10.1038/nbt0493-508.
Elomaa P, Mehto M, Kotilainen M, Helariutta Y, Nevalainen L, Teeri TH: A bHLH transcription factor mediates organ, region and flower type specific signals on dihydroflavonol-4-reductase (dfr) gene expression in the inflorescence of Gerbera hybrida (Asteraceae). Plant J. 1998, 16: 93-99. 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00273.x.
Cho S, Jang S, Chae S, Kyung MC, Moon YH, An G, Sung KJ: Analysis of the C-terminal region of Arabidopsis thaliana APETALA1 as a transcription activation domain. Plant Mol Biol. 1999, 40: 419-429. 10.1023/A:1006273127067.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Richard Immink of Wageningen Plant Research International, the Netherlands for generously sharing material, advice and inspiring discussions, Dr. Amy Litt for transmitting her original AP1/FUL-like data matrix, M.Sc. Katriina Mouhu for helpful discussions on gibberellin, Ph.D. Ursula J. Malm for the PCR of full length GSQUA2, Eija Takala for excellent technical assistance and gardener Sanna Peltola for taking good care of the transgenic Gerbera lines used in this study. The plant breeding company Terra Nigra B.V., the Netherlands, is thanked for providing plant material and the Academy of Finland for funding (grant no 207410 and the Programme for Centres of Excellence in Research).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors' contributions
SR designed the experiments, carried out the experiments, analyzed the results and drafted the manuscript. YPN performed the RNA gel blot and in situ analyses for GSQUA5 and GSQUA6. SKB carried out the light microscopic and SEM analysis of the transformant lines for GSQUA2. VAA did the phylogenetic analysis, participated in the interpretation of the results and helped to draft the manuscript. PE participated in the design of the experiments, analysis of the results and helped to draft the manuscript. THT supervised the study, contributed to the design of the experiment, analysis of the results and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12870_2009_622_MOESM1_ESM.TXT
Additional file 1: GSQUA nucleotide sequence alignment. Nucleotide sequence alignment of the Gerbera GSQUA genes with other APETALA1 and FRUITFULL like genes. (TXT 158 KB)
12870_2009_622_MOESM2_ESM.DOC
Additional file 2: Phylogenetic tree of SQUA-like genes. Phylogenetic analysis on the nucleotide data was performed using the maximum likelihood method. (DOC 130 KB)
12870_2009_622_MOESM3_ESM.PPT
Additional file 3: Expression of GSQUAs during ray flower petal development. RNA gel blots showing the expression of GSQUA2, GSQUA3, GSQUA4, GSQUA5, and GSQUA6 at different stages of Gerbera ray flower development. (PPT 237 KB)
12870_2009_622_MOESM4_ESM.PPT
Additional file 4: Transgenic lines overexpressing GSQUA2. RNA gel blots showing GSQUA2 overexpression in transgenic lines. (PPT 151 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruokolainen, S., Ng, Y.P., Broholm, S.K. et al. Characterization of SQUAMOSA-like genes in Gerbera hybrida, including one involved in reproductive transition. BMC Plant Biol 10, 128 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-128
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-128