Abstract
Background
Saprophytic filamentous fungi are ubiquitous micro-organisms that play an essential role in photosynthetic carbon recycling. The wood-decayer Pycnoporus cinnabarinus is a model fungus for the study of plant cell wall decomposition and is used for a number of applications in green and white biotechnology.
Results
The 33.6 megabase genome of P. cinnabarinus was sequenced and assembled, and the 10,442 predicted genes were functionally annotated using a phylogenomic procedure. In-depth analyses were carried out for the numerous enzyme families involved in lignocellulosic biomass breakdown, for protein secretion and glycosylation pathways, and for mating type. The P. cinnabarinus genome sequence revealed a consistent repertoire of genes shared with wood-decaying basidiomycetes. P. cinnabarinus is thus fully equipped with the classical families involved in cellulose and hemicellulose degradation, whereas its pectinolytic repertoire appears relatively limited. In addition, P. cinnabarinus possesses a complete versatile enzymatic arsenal for lignin breakdown. We identified several genes encoding members of the three ligninolytic peroxidase types, namely lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and versatile peroxidase. Comparative genome analyses were performed in fungi displaying different nutritional strategies (white-rot and brown-rot modes of decay). P. cinnabarinus presents a typical distribution of all the specific families found in the white-rot life style. Growth profiling of P. cinnabarinus was performed on 35 carbon sources including simple and complex substrates to study substrate utilization and preferences. P. cinnabarinus grew faster on crude plant substrates than on pure, mono- or polysaccharide substrates. Finally, proteomic analyses were conducted from liquid and solid-state fermentation to analyze the composition of the secretomes corresponding to growth on different substrates. The distribution of lignocellulolytic enzymes in the secretomes was strongly dependent on growth conditions, especially for lytic polysaccharide mono-oxygenases.
Conclusions
With its available genome sequence, P. cinnabarinus is now an outstanding model system for the study of the enzyme machinery involved in the degradation or transformation of lignocellulosic biomass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Filamentous fungi are a source of powerful enzymes for plant biomass breakdown and/or hydrolysis in green and white biotechnology, especially biorefining [1]. The enzymatic modification of lignin-derived aromatic compounds is of strategic importance both for biomass valorization of the other plant-cell-wall compounds in the green chemistry sector and for the biotransformation of these aromatic compounds into high-value products (foods, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals) or industrial compounds (surfactants, adhesives and biomaterials).
The proportions of the constituent polymers of plant cell walls, i.e. cellulose, hemicelluloses, pectin and lignins, fluctuates with botanical origin, tissue, and age of the plant. In response to the structural complexity and heterogeneity of the different plant cell wall polymers, saprophytic fungi produce a complex arsenal of enzymes to gain access to the carbon source. Lignocellulolytic fungi have traditionally been classified into three main fungal groups according to the appearance of the plant material remaining after decomposition [2]. Soft-rot fungi partially degrade plant polysaccharides by mobilizing cellulases and hemicellulases, and cause wood softening [3]. In contrast, brown-rot fungi such as Postia placenta produce enzymes involved in extracellular generation of Fenton’s reagent, where hydroxyl radicals resulting from the reaction between Fe(II) and hydrogen peroxide may ultimately cause cellulose depolymerization [4]. Lignin is apparently only slightly modified in this process, and remains as a crumbly, brownish material. Unlike the above two groups, white-rot fungi are the only organisms able to effectively degrade lignin, in a process called enzymatic combustion [5] where peroxidases cooperate with other oxidoreductases [6]. The decayed wood resulting from attack by white-rot fungi becomes white and stringy. For selective white-rot fungi, the white color is caused by rapid hemicellulose and lignin breakdown of the cell-wall constituents, followed later by cellulose degradation [7].
The white-rot fungus Pycnoporus is very efficient at completely degrading lignin [8]. The Pycnoporus genus belongs to the phylum Basidiomycota, class Agaricomycetes, order Polyporales, family Polyporaceae. The genus Pycnoporus is divided into four species with different geographic origins: P. cinnabarinus is widely distributed especially in the Northern hemisphere, P. coccineus in countries bordering the Indian and Pacific Oceans, P. sanguineus in the tropics and subtropics of both hemispheres, and P. puniceus, a rare species found in Africa, India, Malaysia and New Caledonia. Pycnoporus mycelia and fruiting bodies are characterized by red-to-orange pigmentation due to phenoxazinone pigments including cinnabarin, tramesanguin and cinnabarinic acid [9]. P. cinnabarinus is a heterothallic homobasidiomycete with a tetrapolar mating system. Its life cycle includes a short monokaryotic stage after spore germination, followed after mating by an indefinite dikaryotic stage where karyogamy and meiosis can take place. The fungus is able to produce fruiting body structures and to generate stable monokaryotic cell-lines amenable to genetic improvement by formal genetics and genetic engineering, e.g. development of expression systems for high- level ligninase production [10].
P. cinnabarinus has a large array of copper- and iron-containing metalloenzymes involved in transforming plant-cell-wall aromatics [11, 12] and harbors original metabolic pathways involved in functionalizing these cell-wall aromatics to yield high-added-value compounds such as aromas and antioxidants [13, 14]. P. cinnabarinus is listed as a food- and cosmetic-grade microorganism [15]. Among enzymes involved in lignin degradation, P. cinnabarinus is known to produce high-redox-potential laccase as the predominant enzyme at very high levels of up to 1 g per liter [16, 17]. The potential of Pycnoporus fungi lies in their laccases which find a variety of applications, such as bioconversion of agricultural by-products and raw plant materials into valuable products, biopulping and biobleaching paper pulp [18–22], dye bleaching in the textile and dye industries [23–25], wastewater treatment [26–28], removal of phenolic compounds in beverages [29], biosensor and biofuel cell construction [30], and producing substances of pharmaceutical importance [31].
All studies performed over the last decade support the Pycnoporus genus as a strong contender for green and white biotechnology applications. Here, we describe the sequencing and annotation of the P. cinnabarinus monokaryotic cell-line BRFM137 genome, its growth profiling and its secretome analyses under different culture conditions. Lignocellulolytic repertoires of P. cinnabarinus are highlighted and compared with other fungal counterparts. P. cinnabarinus emerges as a versatile white-rot fungus for biotechnological applications.
Methods
Strain, DNA preparation and culture conditions
Monokaryotic strain P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 [9] was obtained from the International Centre of Microbial Resources dedicated to Filamentous Fungi (CIRM-CF, Marseille, France, http://cirm.esil.univ-mrs.fr/crbmarseille/pages/index_mizenpage.php). Genomic DNA was isolated from ground mycelia powder as described in Lomascolo et al.[32], and a roughly 180 μg sample was sent to GATC Biotech AG (Constanz, Germany) for genome sequencing.
For construction of the cDNA library, P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 was grown as described in Lomascolo et al.[17] with five types of substrate: (i) 20 g/L maltose, (ii) 20 g/l maltose and 0.1 g/l ferulic acid, (iii) 5 g/l maltose and 15 g/l oat spelt xylan (Sigma), (iv) 5 g/l maltose and 15 g/l autoclaved maize bran (ARD, Pomacle, France) and (v) 5 g/l maltose and 15 g/l Avicel cellulose (Sigma). The other constituents of the medium were: diammonium tartrate (1.84 g/l); disodium tartrate (2.3 g/l); KH2PO4 (1.33 g/l); CaCl2 · 2H2O (0.1 g/l); MgSO4 · 7H2O (0.5 g/l); FeSO4 · 7H2O (0.07 g/l); ZnSO4 · 7H2O (0.046 g/l); MnSO4 · H2O (0.035 g/l); CuSO4 · 5H2O (0.007 g/l); yeast extract (1 g/l). After 4–5 days of cultivation, the fungal mycelia from each of the five culture conditions were homogenized in liquid nitrogen, and total RNA was extracted following a standard phenol/chloroform method [33]. RNA from all the culture conditions was pooled and sent to GATC Biotech AG for reverse transcription and sequencing via Illumina technology.
For proteomic analysis, liquid cultures (LC) with non-immobilized or immobilized mycelia on 2 × 2 × 1 cm polyurethane cubes (10 per vial) were run in 250 ml baffled flasks containing 100 ml medium according to Lomascolo et al.[17]. Three LC conditions were used: (i) 20 g/l maltose (LC-M), (ii) 5 g/l maltose, 15 g/l Avicel cellulose (Sigma) and 15 g/l autoclaved maize bran (ARD) (LC-M-MB-A), and (iii) 5 g/l maltose and 15 g/l micronized birchwood (LC-B). Solid-state fermentation (SSF) cultures were also performed with five different substrates: sugarcane bagasse (Orizaba, Mexico), banana skins, wood shavings (Farmer Litter, Weldom, France), hemp (Zolux Litter, Weldom, France) and micronized birchwood. Each substrate was homogenized in water to obtain a moisture content of 70% (w/w). Five grams of substrate (wet weight) was placed in a 250 ml flask and inoculated with 1.2 ml of mycelial suspension (50 ml of nutrient medium and two mycelial mats from precultures) according to a protocol adapted from Meza et al.[34, 35]. For each growth condition, culture supernatants were harvested after 3, 7 and 10 days of cultivation and then pooled.
For growth profiling on 35 carbon sources, P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 was grown on agar plates according to Espagne et al.[36], using either 10 g/l simple carbohydrates or 30 g/l complex carbohydrates. The kraft-lignin was purchased from Sigma (reference: 370959).
Genome sequencing and data assembly
The P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 genome was sequenced by a combination of methods: (i) sequencing of genomic DNA and two normalized cDNA libraries obtained from cultures grown on different substrates (maltose, oat spelt xylan, cellulose and autoclaved maize bran) using 454/GS Roche FLX Titanium technology, (ii) sequencing of genomic DNA with Illumina/Solexa Genome Analyzer II technology, and (iii) sequencing of a 3 kbp paired-end genomic library using Illumina/Solexa Genome Analyzer II technology. The genomic Roche 454 read sets were uploaded to the ng6 storage environment [37]. Reads were cleaned using pyrocleaner [38], which applied a low-complexity filter followed by a read-size filter (over 100 bp) and a duplication-removal filter. The 454 reads were then assembled using wgs-assembler version 6.0. The Illumina mate pair reads were filtered out using the contig alignment information. All short aligned read pairs and long reads were then reassembled to produce contigs and scaffolds using the same assembly software versions. The 454 transcriptome reads of P. cinnabarinus were also cleaned using pyrocleaner, but this time the duplicated sequences were not filtered out. The reads were de novo assembled using tgicl (TIGR Gene Indices clustering tools) and annotated using various databases. The reads and contigs were aligned on the genome using Exonerate to produce gff files. These gff files were uploaded to gbrowse (http://genome-browser.toulouse.inra.fr:9090/cgi-bin/gb2/gbrowse/). Gene prediction was performed using Augustus [39] with the fungal gene model: Phanerochaete chrysosporium. The corresponding gff outputs were also uploaded to the gbrowse environment. Ensembl fungal transcripts of Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus terreus, Aspergillus nidulans, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Aspergillus clavatus, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus oryzae were also aligned on the genome and the results uploaded to gbrowse. For P. cinnabarinus, a biomart environment was set up to link de novo contigs to their genomic alignment location (http://genomebrowser.toulouse.inra.fr:9090/biomart/martview).
All the data are available at the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), EMBL-EBI, Accession number: [EMBL: PRJEB5237].
Gene prediction and functional annotation
Orthologous groups construction
Orthologous groups (OGs) were built by running OrthoMCL [40] software on the best protein models from: 1) P. cinnabarinus BRFM137, 2) Trametes versicolor, (TaxID: 717944) 3) Postia placenta (TaxID: 561896), 4) Phanerochaete chrysosporium RP-78 (TaxID: 273507), 5) Schizophyllum commune H4-8 (TaxID: 578458), 6) Coprinopsis cinerea okayama7#130 (TaxID: 240176), 7) Laccaria bicolor S238N-H82 (TaxID: 486041), 8) Agaricus bisporus (TaxID: 936046), 9) Gloeophyllum trabeum (TaxID: 670483), 10) Ustilago maydis (TaxID: 5270), 11) Saccharomyces cerevisiae RM11-1a (TaxID: 285006), 12) Schizosaccharomyces pombe (TaxID: 4896), 13) Aspergillus niger (TaxID: 380704), 225 14) Trichoderma reesei QM6a (TaxId: 431241), 15) Nectria haematococca (TaxID: 140110), 16) Neurospora crassa (TaxID: 367110), 17) Myceliophthora thermophila (TaxID: 573729), 18) Chaetomium globosum (TaxID: 306901), 19) Mucor circinelloides (TaxID: 747725), 20) Homo sapiens (TaxID: 9606) and 21) Arabidopsis thaliana (TaxID: 3702). Each OG is a set of proteins across one or more species in the 21 listed genomes that represents putative orthologs and in-paralogs. All-versus-all BLASTP was set a 10−8 cutoff.
Global functional annotation
Global functional annotation was based on the analysis of each OG. All 15788 OGs were used as a seed for the functional annotation process based on the bioinformatics initiative Gene Ontology [41]. OGs containing at least one sequence from P. cinnabarinus were selected (7002 OGs). All sequences included in OG were ordered following the species list above. Sequences from each OG were queried using BLAST against the NCBI non-redundant (NR) protein database. A strict E-value threshold of 10−120 was applied to select homologous sequences retrieved by BlastP. These homologs were mapped to the global Gene Ontology annotation files (ftp://ftp.pir.georgetown.edu/databases/idmapping/idmapping.tb.gz).
If GO information was retrieved for the first sequence, the process was ended; if no information was retrieved for the first sequence in the OG list, the second sequence was used for mapping. In the particular case where several sequences were present in the same species, sequences were ordered by length. All the coding sequences (CDS) not included in OGs were directly BLASTed as described above.
Identification of repeated sequences
RepeatScout [42] was used to identify de novo DNA repeats in the P. cinnarinus genome. Default parameters (with l = 15) were used. The RepeatScout library was then filtered as follows: i) all the sequences less than 100 bp in size were discarded; ii) repeats counting less than ten copies in the genome were removed (as they may correspond to protein-coding gene families) and iii) repeats having significant hits to known proteins in UNIPROT (The UNIPROT Consortium, 2008) other than proteins known to belong to transposable elements (TEs) were removed. The remaining consensus sequences were annotated manually by a TBLASTX search [43] against RepBase [44] to classify them into known TE families. To identify full-length long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons, a second de novo search was performed with LTR_STRUC [45]. The TBLASTX algorithm was to check the full-length candidate LTR retrotransposon sequences for homology against the sequences from the RepBase database. The number of repeat element occurrences and the percent of genome coverage were assessed using RepeatMasker [46] by masking the genome assembly with the consensus sequences coming from the RepeatScout and LTR_STRUC pipelines. MISA (http://pgrc.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa/download/misa.pl) was used with default parameters to identify mono- to hexanucleotide simple sequence repeat (SSR) motifs. Mini-satellites (motif of 7 to 100 bp) and satellites (motif >100 bp) were searched for in the P. cinnabarinus genome using Tandem Repeats Finder software [47] with the following parameters: 2; 7; 7; 80; 10; 50; 500.
Carbohydrate-active enzyme and lignin degradation enzyme annotation
All putative proteins were compared to the entries in the CAZy database [48, 49] using BLASTP. The proteins with E-values smaller than 0.1 were further screened by a combination of BLAST searches against individual protein modules belonging to the AA (Auxiliary Activities), GH (Glycosyl Hydrolases), GT (GlycosylTransferases), PL (Polysaccharide Lyases), CE (Carbohydrate Esterases) and CBM (Carbohydrate-Binding Modules) classes (http://www.cazy.org/). HMMer 3 [50] was used to query against a collection of custom-made hidden Markov model (HMM) profiles constructed for each CAZy family. All identified proteins were then manually curated. Within families, subfamilies were manually defined according to their homology relationships between members of the focal family. Protein sequences obtained from automatic prediction by Augustus software were annotated via this procedure, and all identified proteins were then manually curated.
Structural annotation of the corresponding oxidative encoding genes (number, size and position of introns) was checked manually. To do this, each AA sequence detected was BLASTP-searched against the NCBI non-redundant database. The results with the most satisfactory E-values and coverage were retained.
Then, first the target protein sequence was aligned with the sequence previously selected by BLASTP using ClustalW (http://www.genome.jp/tools/clustalw/); second, the target nucleic acid sequence was translated in three reading frames (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/st/emboss_sixpack/). Gene intron splice sites were determined based on consensus sequences fitting the GT-AG rule as described in Breathnach et al.[51].
Identification of proteins in secretomes by LC-MS/MS analysis
Proteins from the diafiltered supernatants of P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 cultures were separated by 1D SDS-PAGE electrophoresis according to the protocol of Couturier et al.[52]. After protein trypsinolysis, peptide analysis was performed by LC-MS/MS as described in Arfi et al.[53] using the PAPPSO platform facilities (Jouy-en-Josas, France; http://pappso.inra.fr). Based on the list of peptides, proteins were identified by querying the MS/MS data against the predicted proteins obtained from the P. cinnabarinus genome de novo sequencing data.
Annotation of protein secretion and glycosylation pathways
A. niger proteins related to protein secretion and glycosylation according to Pel et al.[54] and extended with additional proteins were used in a BLASTP search towards the P. cinnabarinus fasta file. The first hits were compared to the A. niger proteins to identify bi-directional BLAST best hits. An E-value cut-off of 10−10 was used. The description of the gene products was taken from the Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD) after identifying the S. cerevisiae orthologs.
Results and discussion
Characteristics of the P. cinnabarinusgenome
The genome of the monokaryotic strain P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 was sequenced by 454 pyrosequencing and Illumina sequencing runs to reach a final 31-fold coverage. The genome was ultimately assembled into 784 scaffolds with N50 of 165118 bp. Table 1 reports the features of the assembled genome sequences. The G + C content of the P. cinnabarinus genome was 52.55%. Genome size was 33.67 Mb and a total of 10,442 ORFs were identified in the structural annotation procedure. The number of ORFs in P. cinnabarinus is close to the average number among the order Polyporales. For instance, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Postia placenta, Wolfiporia cocos and Ceriporiopsis subvermispora count 10048, 12541, 12747 and 12125 detected ORFs in their genomes, respectively [4, 6, 55, 56]. P. cinnabarinus genome size is slightly lower than in P. placenta (42.5 Mb), C. subvermispora (39 Mb) and W. cocos (50.5 Mb).
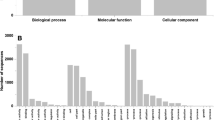
In general, functional annotation hinges on the propagation of existing functional information via single homology searches. The resolution of functional inference could be improved by differentiating homologs into orthologs (homologous genes resulting from a speciation event) and paralogs (homologous genes resulting from a duplication event) [57]. Orthologs are assumed to have more chance of sharing the same function than paralogs. Gene duplication is an essential contributing factor for evolving novel functions, and one of the duplicates could undergo evolutionary events such as sub-functionalization, neofunctionalization, etc. (see [58, 59] for review). We therefore based our annotation strategy on the searches for OGs within 21 selected genomes followed by similarity searches from each OG. An outline flow of the functional annotation procedure based on this phylogenomic approach is shown in Figure 1. 15,788 OGs were retrieved using a best reciprocal hit approach. The OGs included 8,647 putative CDS from P. cinnabarinus, totaling ~83% of total CDS. Based on a sequence homology searches within each OG against the NR database using a strict E-value cutoff of 10−120, 5,018 genes were annotated across the GO categories. In addition, 399 orphan genes were annotated using the standard Blast2GO procedure. The annotation procedure enabled us to annotate 5,417 CDS corresponding to ~52% of total CDS (Additional file 1: Table S1). To compare with the classical method, fewer than 30% of total CDS were annotated using the Blast2GO procedure. Our approach based on ortholog clustering enables us to infer functional information directly from OGs using a subsequent drastic threshold for similarity searches and offers a conceptual framework for inferring information from various genomes. The 5,417 annotated genes were grouped into functional groups (Figure 2). Finally, a GO tree depth was calculated to assess amount and quality of GO annotations (Figure 3).
Annotation strategy for P. cinnabarinus based on a phylogenomic approach. Orthologous groups (OGs) were formed from 21 genomes by running the OrthoMCL software using a BLASTP cutoff E- value of 1e−8. OGs containing at least one sequence from P. cinnabarinus were selected (7002 OGs) and used as a seed for the functional annotation process based on the bioinformatics initiative Gene Ontology. Sequences from each OG were BLAST-queried against a NCBI non-redundant (NR) protein database using a cutoff E-value of 10−120. The mapping procedure was carried out with the global Gene Ontology annotation files. The process was ended once GO information was retrieved. For orphan genes, the coding sequences were directly annotated using B2Go procedures.
Repeated sequences were identified in the genome of P. cinnabarinus and a library of 1,118 consensus sequences was generated using RepeatScout [41]. After the different filtering steps, we were left with 190 consensus sequences: 13, 9, 5 and 5 consensus sequences showed homologies with Class 1 gypsy, copia, DIRS and Long Interspersed Element (LINE) retrotransposons, respectively, and 8 with Class 2 transposons (Table 2). The remaining 150 consensus sequences were uncategorized. Of the 9 putative full-length LTRs identified using LTR_STRUC, three were attributed to Gypsy/Ty3-like elements and two to Copia/Ty1-like elements. The remaining four sequences are excluded from further analyses. RepeatMasker masked 8.21% of the genome assembly: 2.91% by repeated elements belonging to unknown/uncategorized families, 2.5% by Class 1 Gypsy retrotransposons, 0.95 by Class 1 Copia retrotransposons, 0.2 by Class 1 DIRS retrotransposons, 0.7 by Class 1 LINE retrotransposons and 0.95 by Class 2 DNA transposons (Table 2).
The number of full-length LTR was lower in P. cinnabarinus than in other white-rots [6], although the TE genome coverage was in the range of other white-rot fungi. A total of 1,707 SSRs were identified in the P. cinnabarinus genome corresponding to 350 mono-, 380 di-, 820 tri-, 91 tetra-, 25 penta- and 41 hexanucleotide motifs. A total of 2368 mini-satellites and 10 satellites were identified for a genome coverage of 0.42% and 0.01%, respectively. The number of microsatellites was in the range of those found in other white-rot and Polyporaceae genomes, although the genome of P. cinnabarinus was less rich in mini-satellite and satellite sequences [60].
Carbohydrate metabolism, lignin-degrading oxidoreductases and wood decay
Carbohydrates and lignin are intimately interconnected in all land-plant cell-walls. The accessibility of all cell-wall components i.e. cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin and lignin, is strongly limited by the covalent cross-linkages of the constituents which create an intricate network and a physical barrier that resists microbial breakdown. Among the predicted lignin-degrading activities, a total of five laccases (AA1_1), one ferroxidase (AA1_2), one multicopper oxidase (AA1), nine ligninolytic peroxidases (AA2) including lignin peroxidases (LiP), manganese peroxidases (MnP) and versatile peroxidases (VP), one cellobiose dehydrogenase containing an iron reductase domain (AA8-AA3_1), three aryl-alcohol oxidases and one glucose oxidase (AA3_2), two alcohol oxidases (AA3_3), two pyranose oxidases (AA3_4), seven copper radical oxidases (AA5_1), one benzoquinone reductase (AA6), and one iron reductase domain (AA8) linked to a CBM1 were identified (Table 3 and Additional file 2: Table S2). P. cinnabarinus was initially considered to lack class-II peroxidases based on extracellular activities in the culture medium [16]. Remarkably, nine class II peroxidases were annotated and divided into at least four LiP, three MnP, one VP and one atypical VP. On average, white-rot fungi have 12 members of the AA2 family (Table 4). The only exception is S. commune in which the AA2 family is absent [61], although it is considered as a white-rot fungus despite limited lignin-degrading ability. Members of family AA2 can be considered as one of the most important family markers to differentiate white-rot and brown-rot fungi, since brown-rot (BR) fungi contain no AA2 members [6, 49]. In addition to class II peroxidases, P. cinnabarinus contains several laccases (AA1_1) and one cellobiose dehydrogenase (AA8-AA3_1), meaning that this fungus contains a complete, versatile ligninolytic enzymatic spectrum. A number of enzymes are proposed to supply the hydrogen peroxide required for oxidase activity. Among these, the best established candidate is glyoxal oxidase of family AA5_1, and P. cinnabarinus has seven candidate gene models in this family. Interestingly, P. cinnabarinus also possesses several other hydrogen peroxide providers, such as GMC oxidoreductases from family AA3_2 which includes at least three aryl-alcohol oxidases. In summary, the white-rot fungus P. cinnabarinus possesses a complete enzymatic arsenal for lignin breakdown. The full set of ligninolytic enzymes identified suggests that this fungus may exploit different strategies for ligninolysis, including oxidation mediated by class II peroxidases requiring hydrogen peroxide or by laccases in the presence of redox mediators, or via Fenton chemistry [49, 62, 63].
P. cinnabarinus is fully equipped with putative enzymes from families classically involved in cellulose degradation (GH1, GH3, GH5, GH6, GH7, GH12, GH45) and can grow on pure cellulose. However, P. cinnabarinus possesses the smallest number of GH members among the white-rot fungi. The P. cinnabarinus genome encodes 15 lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) of family AA9, a number similar to that encoded by other white-rot fungal genomes (Table 4). The P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 genome contains a gene encoding a CDH (ORF scf185013.g1). This gene codes for the CDH already described by Moukha et al.[11], Sigoillot et al.[64] and Bey et al.[65]. Concerning xylan degradation, only two GH10 and two GH43 enzymes were identified in P. cinnabarinus, which is less than the average number of representatives in the white-rot group (respectively of 5.2 and 9). No members of family GH51 could be found in the P. cinnabarinus genome. The GH51 family includes α-L-arabinofuranosidases acting on terminal non-reducing α-L-arabinofuranose residues in arabinose-containing compounds [66]. Terminal arabinose residues are found in the rhamnogalacturonan I from dicot primary cell walls, and glucuronoarabinoxylan from grass primary cell walls, so the absence of GH51 could partly constrain the complete degradation of hemicelluloses and pectic polysaccharides in P. cinnabarinus and is consistent with the lack of such cell wall components in wood. The number of other P. cinnabarinus genes encoding pectinolytic enzymes also seems to be limited. The members of family GH28 are fewer than the average number found in other fungi, and no representative of family GH54 including α-L-arabinofuranosidase was found. Also, P. cinnabarinus contains no candidate gene of the pectinolytic families PL1 (pectin/pectate lyase), PL3 (pectate lyase), PL9 (pectate lyase), CE12 (rhamnogalacturonan acetyl esterase) or GH53 (endo-β-1,4-galactanase). P. cinnabarinus is the only fungus lacking a family GH53 member among the selected white- and brown-rots. Family GH53 enzymes degrade galactans and arabinogalactans in the pectic component of plant cell walls. This genomic repertoire is consistent with the very poor growth of P. cinnabarinus observed on apple pectin and citrus pectin as substrates (Figure 4).
In conclusion, white-rot fungi possess more representatives of lignocellulolytic enzymes than the brown-rot group, especially in the families AA2 (12 vs. 0) AA3_2 (6.3 vs. 1.4), AA5_1 (6.8 vs. 3.4), AA9 (15.2 vs. 3.8) and CBM1 (18.8 vs. 1.7) (Table 4). Based on these results, P. cinnabarinus clearly belongs to the classical white-rot fungi, with a distribution typical of all the specific families found for this nutritional strategy.
To study the growth ability of P. cinnabarinus, growth profiling was performed on 35 carbon sources, including mono-, oligo- or polysaccharides, crude plant biomass, casein and lignin, and the profiles were compared with the CAZy gene content of the P. cinnabarinus genome. On average, growth was better on crude plant biomass substrates than on pure mono- oligo- or polysaccharides (Figures 4 and 5). Interestingly, growth on cotton seed hulls was poor, not only compared with the other plant biomass substrates but also compared with several pure substrates. Previous studies suggest that this is probably due to the high lignin content of cotton seed hulls (about 20–25%). The other plant biomass substrates are poorer in lignin (2–4%), suggesting that high lignin content inhibits growth of P. cinnabarinus in the culture conditions tested. This correlates with very poor growth on kraft lignin as sole substrate. As lignin may not be sole carbon source, the poor growth could be related to the possible impurities from lignocellulose introduced during lignin preparation. Growth is better on galactomannan (guar gum) than on xylan, suggesting a better mannan degrading system. Endomannanases are found in GH5 and GH26, but there are no family GH26 members in the P. cinnabarinus genome, suggesting that the good growth is mainly due to the GH5_7 endomannanase, together with the three GH2 β-mannosidases and one GH27 α-galactosidase. Inulin- and sucrose-degrading enzymes are found in GH32, but only one member of family GH32 is found in the P. cinnabarinus genome. Considering that growth on sucrose is significantly better than growth on inulin, this gene probably encodes an invertase rather than an inulinase. These growth profiling studies estimated growth speed by measuring the diameter of the on-plate fungal mycelium on plates. However, growth is also related to density of mycelium with dense, medium and thin mycelia on the plates. The fast growth on poor media, especially when no carbon source is added, could also be due to thin mycelial expansion to avoid starvation.
Gene structure and localization of the ligninolytic repertoire in P. cinnabarinus
Descriptions of the P. cinnabarinus laccases (AA1_1)
Five laccases stricto sensu (AA1_1), one multicopper oxidase (Mco, AA1) and one ferroxidase (AA1_2) sequence were identified in the genome and in the cDNA library, even partially (Additional file 3: Table S3). Structural annotation of the genes (designated lac1 to lac5) was performed, and the gene lcc3-1 15 (or lac1) coding for LacI protein was identified [17, 67]. In 2000, Otterbein et al.[68] demonstrated the presence of a second laccase isoenzyme, called Lac2, in the culture medium of P. cinnabarinus BRFM137.
Lac2 was purified and its N-terminal sequence was determined [68]. However, the corresponding gene has never been identified and cloned, and the biochemical properties of the Lac2 protein have never been determined. Based on the N-terminal sequence, we were able to determine the corresponding gene sequence, named lac2, from the strain BRFM137 genome sequencing data (Additional file 4: Table S4). The five laccase-encoding genes have a size of about 2.1–2.3 kb interrupted by 10 to 12 introns. Based on the intron and exon positions of each gene, we were able to classify the various laccase genes into three groups (Additional file 5: Figure S1). Lac2/lac5 (12 introns) and lac1/lac3 (10 introns) pairs have a similar structural organization with homologous intron positions, whereas the lac4 gene is organized slightly differently (length of exons and introns). The lac4 gene comprised 11 exons but showed a slightly different structure from lac1 and lac3, and an experimentally-found stop codon was confirmed in exon 6 (Additional file 5: Figure S1). In contrast to other laccase-encoding genes, the full-length lac4 mRNA could not be found. The multiplicity of laccase genes and their groupings are common features in fungi and are discussed in Additional file 6: Data S1 [69–80]. In the P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 genome, several laccase-encoding genes were identified on the same scaffold. For instance, the lac1 and lac3 genes were separated by approximately 23 kb in the same reading frame on scaffold 185007.
Descriptions of the P. cinnabarinus ligninolytic peroxidases (AA2)
We have shown that the P. cinnabarinus genome encodes a large set of ligninolytic peroxidases of family AA2. Nine full-length AA2 sequences were detected from the genomic DNA of P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 (Table 3). After an initial automatic classification as LiPs and MnPs, they were manually reclassified following the strategy described by Ruiz-Dueñas et al.[81] for manual annotation of the complete inventory of heme peroxidases of Pleurotus ostreatus. This protocol was based on a combined analysis of the deduced amino acid sequences and structural homology models obtained using the crystal structures of related enzymes as templates. The identified members of family AA2 share common structural features, including four disulfide bridges and residues coordinating two calcium ions, a proximal histidine (acting as fifth heme iron ligand), and distal histidine and arginine residues (involved in enzyme activation by hydrogen peroxide), as shown in Figure 6. The presence of specific catalytic residues [82] allowed us to classify the nine members of family AA2. Firstly, three short MnPs (Figure 6A-C) characterized both by the presence of a manganese oxidation site formed by two glutamates and one aspartate at the internal heme propionate region, and by a shorter C-terminal tail than that of long and extralong MnPs [6]. Secondly, four LiPs (Figure 6D-G) containing a 174-Trp residue exposed to the solvent responsible for oxidation of high-redox-potential aromatic compounds. Thirdly, one VP (Figure 6H) including both a catalytic Trp residue exposed to the solvent and a manganese oxidation site; fourth, one atypical VP (Figure 6I) differing from VPs in one of the three acidic residues of the manganese oxidation site. A partial sequence for the first 138 amino acids of the N-terminal end of an additional putative class II peroxidase was also identified and could be hypothetically annotated as a LiP6. The above set of AA2 peroxidases identified in P. cinnabarinus is close to that identified in Trametes versicolor (in both cases consisting of MnP, LiP, VP and atypical-VP) [84], although the total number of sequences is lower in Pycnoporus. Two genes encoding heme peroxidases of a recently discovered superfamily of heme-thiolate peroxidases (HTP) [85] were also identified in P. cinnabarinus.
Molecular models for the nine class-II heme peroxidases (AA2) found in the P. cinnabarinus genome. MnP models (A-C) present a Mn2+ oxidation site characteristic of typical MnPs, formed by two glutamates and one aspartate at the internal heme propionate region; LiP models (D-G) exhibit a Trp residue exposed to the solvent, which has been involved in high-redox-potential aromatic compound oxidation by typical LiPs; the VP model (H) obtained for the only peroxidase of this family identified in the genome analysis evidences both the Mn2+ oxidation site and the Trp residue exposed to the solvent, characteristic of members of this class-II family; the atypical VP (I) contains an aspartate residue (Asp36) in a position occupied by a glutamate in VPs and MnPs. Two axial histidines, one acting as heme iron ligand (proximal histidine) and the second (distal histidine) contributing to the heme reaction with peroxide, together with an arginine residue characterizing class-II peroxidases are also shown in the nine molecular homology models. Four disulfide bridges are depicted as green sticks. These homology models were obtained at the Swiss-Model protein-homology server [83] using P. eryngii VPL (PDB entries 4FCS, 2VKA and 3FJW) and P. chrysosporium LiPH2 and LiPH8 (PDB entries 1LLP, 1B80 and 1B82) crystal structures as templates.
These peroxidases are widely distributed in fungal genomes, including those from soft-rot, brown-rot and white-rot fungi [6, 84, 86, 87]. However, only a few of them have so far been studied, with those from Leptoxyphium fumago and Agrocybe aegerita being the best characterized. They are known to catalyze halogenation reactions and to possess catalase, peroxidase and peroxygenase activities [88]. Consequently, similar reactions are expected to be catalyzed by the HTPs identified in the P. cinnabarinus genome sequence.
All lip and mnp genes except MnP2 and LiP6 were also found in the cDNA library (Additional file 3: Table S3). The mnp genes present lengths of 1.4–1.5 kb, (Additional file 7: Table S5) and and count 4–6 introns according to gene. The two genes encoding VP and the four LiPs showed relatively similar sizes (about 1.45 kb) and were interrupted by six introns, for coding sequences of similar length (about 1.1 kb).
Considering the analysis of the intron/exon structure, a division of family AA2 into several subgroups could be proposed. vp and lip genes share a similar structural organization and form one group (Additional file 8: Figure S2 A), whereas mnp genes are a more heterogeneous group in terms of gene structure, i.e. exons 2 and 3 of the mnp2/mnp3 pair merge into a single exon in mnp1 while exons 3, 4 and 5 of the mnp1/mnp2 pair correspond to a single exon in mnp3. Finally, atypical-vp gene was totally different in length (1728 bp), number and structure of exons/introns compared with the other class II peroxidase genes analyzed (Additional file 8: Figure S2 A).
In the genome of P. cinnabarinus, we noted that some class II peroxidase genes were grouped on the same scaffold, forming a cluster of peroxidases. This was the case for mnp3, lip1, lip2 and lip3 genes, each separated by about 2 kb and oriented in the same transcriptional direction on the 184983 scaffold. Johansson and Nyman [89] had already described in T. versicolor, a similar cluster of three genes encoding two LiPs (LPGIII, LPGIV) and one MnP (MPG1) in a genomic region of 10 kb, oriented in the same transcriptional direction and separated by approximately 2.4 kb. In addition, the intron/exon organization of these T. versicolor genes pointed to a similar structure for the two LPGIII and LPGIV (about 1470 bp in length, including six introns), whereas the MPG1 gene was slightly different (1400 bp interrupted by five introns).
After analyzing the recently-sequenced T. versicolor genome sequence [6], we identified an additional lip gene (1441 bp in length, including six introns) 6.8 kb upstream of the above sequences, completing the same cluster of three lip and one mnp genes as that observed in P. cinnabarinus. Compared with other class II peroxidases (see the dendrogram in Figure 7), these sequences appear closely related to those located at the same positions in the cluster identified in P. cinnabarinus (mnp3/mnp2, lip1/lip12, lip2/lip2 and lip3/lip1 in P. cinnabarinus/T. versicolor). The co-localization of these genes in both genomes suggests they may occupy a large orthologous genomic region that has been preserved in these two closely-related species sharing a common ancestor [84]. htp1, htp2 and lip6 genes also clustered on scaffold 184962 at 7.9 kb (htp1 and htp2) and 34.1 kb (htp2 and lip6) apart (Additional file 8: Figure S2 B). Similarly, two of the three htp genes identified in T. versicolor, only 1.2 kb apart, form a cluster on scaffold 12 but are arranged in the same transcriptional direction, whereas those from P. cinnabarinus are found in a transcriptionally convergent orientation, and the nearest class II gene is located 64 kb away. This suggests that unlike what is observed for mnp3, lip1, lip2 and lip3 genes, the organization of htp genes does not appear to be conserved between these two species of the core polyporoid clade. Almost all of these peroxidase genes were transcribed, as they were recovered in the P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 cDNA library (Additional file 3: Table S3). The cloning of partial lip-like genes is described in Additional file 9: Data S2 [90–93].
Figure 7 provides a dendrogram showing sequence relationships between 223 protein sequences of basidiomycete class II peroxidases [6], including those identified in the genome of P. cinnabarinus. Five peroxidase groups can be distinguished. Cluster A consists of 39 short MnPs where the three P. cinnabarinus MnPs appear closely related to seven of the 12 short MnPs identified in the T. versicolor genome sequence [84], and relatively distant from the 11 VPs from P. eryngii, P. ostreatus, P. pulmonarius, P. sapidus, B. adusta and Spongipellis sp. also included in this cluster. A well-defined cluster B contains all the LiP (45) sequences, including the 4 LiPs from P. cinnabarinus closely related to the 10 LiPs identified in T. versicolor, as well as the only P. cinnabarinus VP grouped together with the two other VPs (from T. versicolor and Ganoderma sp.) contained in this cluster. Cluster C consists of 16 short MnPs, four VPs and seven atypical VPs, plus the only atypical VP identified in P. cinnabarinus which is grouped together with VPs and atypical VPs from other species (T. versicolor, D. squalens and different Ganoderma species), all of them clustered together with P. cinnabarinus within the core polyporoid clade. The clearly-differentiated cluster D is composed of intermixed long and extralong MnPs absent in P. cinnabarinus and characterized by the presence of 10–20 and 20–30 extra amino acid residues at the C-terminal end, respectively (compared with short MnPs), and by containing one more disulfide bridge than LiPs, short MnPs and VPs (and their atypical variants). Different groups of generic peroxidases (GP) and atypical MnPs (not identified in P. cinnabarinus) are located next to the root of the dendrogram in the cluster D.
Dendrogram of 223 sequences of class-II basidiomycete heme peroxidases (AA2) showing the position of nine sequences from the P. cinnabarinus genome (orange background). Evolutionary analysis was performed with MEGA5 using Poisson distances and an unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean clustering. The cytochrome c peroxidase from P. ostreatus, monokaryon PC9, was used to root the tree (http://phylobench.vital-it.ch/raxml-bb/). The dendogram was used to illustrate the clustering of sequences (clusters A to E). Clusters with no P. cinnabarinus sequences included were collapsed. Most of the sequences were obtained from the analysis of fungal genome sequences deposited at the US Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (JGI), with the rest collected from GenBank [86]. Fungal abbreviations are as follows: BJEAD, Bjerkandera adusta (JGI); DICSQ, Dichomitus squalens (JGI); FOMME, Fomitiporia mediterranea (JGI); GANSP, Ganoderma sp. (JGI); HETAN, Heterobasidion annosum (JGI); PHLBR, Phlebia brevispora (JGI); PYCCI, Pycnoporus cinnabarinus; STEHI, Stereum hirsutum (JGI); TRACE, Trametopsis cervina; and TRAVE, Trametes versicolor (JGI). Other fungal species with peroxidase sequences included in the collapsed clusters are: Agaricus bisporus (JGI), Auricularia delicata (JGI), Bjerkandera sp (JGI), Ceriporiopsis rivulosa, Coprinellus disseminatus, Coprinopsis cinerea (JGI), Fomitopsis pinicola (JGI), Ganoderma applanatum, Ganoderma australe, Ganoderma formosanum, Ganoderma lucidum, Gelatoporia subvermispora (JGI), basidiomycete IZU-154, Laccaria bicolor (JGI), Lentinula edodes, Phanerochaete chrysosporium (JGI), Phanerochaete sordida, Phlebia radiata, Pleurotus eryngii, Pleurotus ostreatus (JGI), Pleurotus pulmonarius, Pleurotus sapidus, Punctularia strigosozonata (JGI), Rhodonia placenta (JGI), Spongipellis sp., Taiwanofungus camphoratus, Wolfiporia cocos (JGI).
Descriptions of other AA proteins involved in ligninolysis
Other putative AA proteins produce the hydrogen peroxide necessary for the catalytic cycle of hydrogen peroxide-dependent fungal peroxidases (LiP, MnP, VP). The ability of hydrogen peroxide to generate hydroxyl radicals (OH•) also points to another role of hydrogen peroxide in the biodegradation of wood, where these hydroxyl radicals (OH•) could initiate the attack of lignocellulose [94]. For these reasons, research into hydrogen peroxide-producing enzymes – especially AA3_2 (aryl alcohol oxidases) and AA5_1 (glyoxal oxidases) – has surged. The subfamily AA5_1 contains glyoxal oxidases (called Glox) and copper radical oxidases (called Cro), which are enzymes related to glyoxal oxidases containing conserved active site residues but that diverge in terms of other structural features [95]. In P. cinnabarinus, seven AA5_1 enzymes have been identified in P. cinnabarinus BRFM137, including three glyoxal oxidases stricto sensu and four “radical copper oxidases” (Additional file 10: Table S6). Furthermore, these three glox and four cro were also expressed in the cDNA library.
Glox and Cro encoding genes (AA5_1) have diverse characteristics in P. cinnabarinus. The gene sizes ranged from 1.85 to 4.45 kb and were interrupted by one to 22 introns, corresponding to coding sequences ranging from 1.6 to 3 kb (Additional file 11: Table S7). The structure of the gene called cro2 stands out 19 from the others, with a large number (22) of introns. In contrast, the sequences identified as glox sensu stricto share comparable size (1.85 kb) and structure (three introns) and form a homogeneous group. Based on the analysis of the intron/exon structure of each Pycnoporus AA5_1 encoding gene (Additional file 12: Figure S3 A), we could propose dividing AA5_1 into three subgroups corresponding to: (i) the glox sequences, which had strong intron position homology, (ii) the cro1, cro3 and cro4 sequences, and (iii) the very different cro4 sequence. Moreover, the three glox genes formed a cluster oriented in the same transcriptional direction and grouped on the same scaffold, with glox2 and glox3 separated by only 1.1 kb (Additional file 12: Figure S3 B). This type of organization has also been found for the genes named cro3, cro4 and cro5 in P. chrysosporium ([95]; Additional file 13: Data S3 [95–97]). Additional file 14: Figure S4 and Additional file 15: Data S4 report the structural comparison between the Glox1 protein sequence from P. cinnabarinus and that of Gaox (PDB reference 1GOG) [97].
Secretome analyses and lignocellulosic degradation
Several recent studies have shown that the diversity (number and type) of hemicellulolytic and ligninolytic enzymes or isoenzymes produced by basidiomycetes depends on substrate used and mode of cultivation (liquid culture (LC) or solid-state fermentation (SSF)) [98–102]. Agro-residues such as fruit peels (banana, mandarin, melon, peach and apple peels) are rich in cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, soluble sugars and aromatic compounds, and were found to be substrates favoring the production of glycoside hydrolases and laccases in white-rot basidiomycetes [99]. Lignocellulosic residues such as straw, bran and wood chips favor the peroxidase production by most basidiomycetes [99]. LC promotes the production of laccases and hydrolases while SSF promotes the production of peroxidases, including MnPs [101, 102]. We thus ran several P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 cultures via both LC and SSF in presence of simple or complex “natural” substrates to compositionally analyze the corresponding secretomes (Additional file 16: Table S8).
Analysis of the P. cinnabarinus secretomes detected 184 proteins in LC-M (maltose), 166 proteins in LC-B (maltose and micronized birchwood), 121 proteins in LC-M-MB-A (maltose, maize bran, Avicel), and 139 proteins in SSF cultures. Most of the secreted proteins in our culture conditions consisted of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes), which represented 55% and 52% of the total proteins detected in LC-M-MB-A and SSF, respectively, and 41% and 47% in LC-M and LC-B, respectively (Additional file 16: Table S8). CAZyme distributions were compared according to the different cultures conditions (Figure 8). Interestingly, the LPMOs of family AA9 were only identified in the conditions including complex substrates, and no AA9 protein was found in the control condition with maltose. Moreover, different AA9 proteins were produced in response to different growth conditions. For instance, three AA9 proteins were produced only with birchwood, whereas two different AA9 proteins were identified in cultures with maize bran and Avicel. This result indicates that there is a differential regulation of the LPMO genes that is dependent on growth substrates and/or on temporal scale. Indeed, the AA9-encoding genes may also be constrained by strict short expression during substrate-supported fungal growth. In recent studies, a preponderance of AA9 was produced exclusively in sugar beet pulp conditions [103]. The detailed distribution of the (hemi)cellulolytic and ligninolytic proteins detected in secretomes is described in Additional file 16: Table S8. Interestingly, all the representatives of the ligninolytic AA families were identified in these conditions, although with different distribution patterns depending on growth conditions (Additional file 17: Table S9). Three AA1_1 laccases (scf184817_g29; scf185007_g100; scf185007_g107) were identified in all conditions studied here, demonstrating that these enzymes are widely and constitutively produced by the fungus. Contrary to laccases, members belonging to the class II peroxidases (AA2) were only identified in the secretomes from SSF cultures (one Lip and one MnP) and in LC-M (atypical-VP). Despite the major role of family peroxidases AA2 in lignin degradation, no AA2 protein was detected in the conditions using the hardwood substrate (birchwood). The class II peroxidases could be constrained by a fine-tuned regulation or, alternatively, be not produced in our growth conditions. The expression and regulation of class II peroxidase-encoding genes depend on environmental signals such as concentration of carbon and nitrogen, exposure to metal ions and xenobiotics, temperature shock, and daylight [104].
A number of cellulolytic enzymes were produced in all conditions studied. For instance, secretomes contained members of the families GH3, GH6, GH7 and GH12, which are principally involved in cellulose breakdown. However, the endo-β-1,4-glucanases of the subfamily GH5_5 were only produced when birchwood was used in the culture medium. We also identified a number of xylan-degrading enzymes produced only in the LC-M-MB-A (maltose, maize bran, Avicel), including members of families CE1, CE15, GH3, GH5, GH10. Moreover, family CE1 members were only found when maize bran was used in the cultures. Among the known activities in the CE1 family, feruloyl esterase activity mobilizes key enzymes acting on ferulic and diferulic acid bridges embedded in the hemicellulose from plant cell walls [105]. Maize fiber xylan features among the most complex heteroxylans and is highly substituted by feruloylated branches yielding a large in ferulic acid content of up to 3% of the dry mass [106]. Thus, the breakdown of this substrate required varied enzymes, as suggested by the diversity of xylanolytic enzymes produced by P. cinnabarinus in presence of maize bran.
Protein secretion and glycosylation pathways
The main lignocellulolytic enzymes of P. cinnabarinus are extracellular, and the proteins are secreted and processed during secretion by the secretion and glycosylation systems of the fungus. Analysis of the genes involved in protein secretion and glycosylation shows that P. cinnabarinus contains the entire machinery needed for protein secretion via the classical secretory pathway (Additional file 18: Table S10 and Additional file 19: Table S11, respectively). Transport of secretory proteins is expected to take place both via a pathway dependent on a signal recognition particle (SRP) and via an SRP-independent pathway, as genes for both pathways were identified. Protein transport from one compartment to the next in the secretory pathway is carried out by various protein complexes, such as the COPI/COPII complexes, Transport Protein Particule (TRAPP) complex and the exocyst complex (Additional file 18: Table S10).
The genome contains homologs of subunits in these complexes and indicates that the complexes are highly conserved in P. cinnabarinus. We also screened for V- and T-SNAREs (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein Receptors) in the genome and for secretion-related GTPases. Both the SNARE proteins and secretion-related GTPases are expected to function at discrete steps in the secretory pathway, and for most proteins we were able to identify a bi-directional best hit, indicating conservation of these functions, probably at the same step along the secretory pathway.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an important organelle that harbors the enzymes required for proper folding of secretory proteins. P. cinnabarinus is fully equipped with the enzymes needed for protein folding and disulfide bridge formation (Additional file 18: Table S10). The machinery to deal with misfolded or unfolded proteins (the Unfolded Response Pathway (UPR)) is also conserved, although we were unable to identify a clear ortholog of the Hac1/XBP1 transcription factor in the P. cinnabarinus genome. Hac1/HacA (in fungi) or Xbp1 (mammalian cells) is a bZIP transcription factor that is uniquely activated by an unconventional splicing event mediated by Ire1p (acting as sensor and endonuclease) and Trl1p (acting as ligase) [107]. The presence of proteins involved in Hac1 activation, such as the sensor (Ire1p) and the tRNA ligase (Trl1p), in the P. cinnabarinus genome suggests that this same UPR mechanism via HacA activation is also present in P. cinnabarinus. The removal of misfolded protein via the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) system, which targets misfolded proteins for degradation in the proteasome, is conserved, since we identified orthologous proteins to the ERAD and proteasome (Additional file 18: Table S10).
We also analyzed the presence of genes related to post-translational modifications in the secretory system including protein N- and O-glycosylation as well as glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis, (Additional file 19: Table S11). The biosynthetic genes required for the formation of nucleotide sugar GDP-mannose, UDP-glucose, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine and UDP-galactose together with transporter to localize the nucleotide sugars in the ER or Golgi lumen were identified. The genes encoding the proteins for stepwise synthesis of the dolicholphosphate-linked oligosaccharide (ALG genes; asparagine (N)-linked- glycosylation) as well as the transfer of the oligosaccharide to asparagine residues (OST-complex) are conserved and found in the genome of P. cinnabarinus. Similarly, genes homologous to the attachment of the mannose residue to serine or threonine residues (O-linked glycosylation), which are carried out by protein mannosyl transferase (PMT), are also conserved. Like in other fungi, P. cinnabarinus has a genome that contains multiple PMT homologs. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis and transfer of the pre-assembled GPI anchor also takes place in the ER. Most of the genes involved in GPI-anchor biosynthesis were identified. The genes encoding Golgi-localized proteins that are involved in outer chain elongation (Och1p/Mnn9p mannosyltransferase complexes) are not present in the P. cinnabarinus genome.
The genes encoding proteins that are expected to add the second and third mannosyltransferase to O-chains are present, but genes homologous to α-1-3-mannosyltransferase that add the fourth or fifth mannose to O-chains were not identified. Thus the post-transcriptional glycosylation events in the Golgi appear to be severely curtailed in P. cinnabarinus to much the same extent as previously reported for the basidiomycete S. commune[61, 108]. Galactofuranosylation is a type of modification found on glycoproteins in Aspergillus species [109], but the genes involved in this process are absent in P. cinnabarinus. This raises prospects for using P. cinnabarinus to produce pharmaceutical proteins, as the glycostructures (N- and O-chains) have a mammalian-like structure and are devoid of the highly antigenic galactofuranose residues found in expression hosts such as A. niger see [109] for review.
Mating-type loci and their genes in P. cinnabarinus
In the past, the fungal lifecycle of P. cinnabarinnus was studied in order to select monokaryotic lines with characteristics specifically tied to lignocellulose degradation [17]. Pycnoporus species are heterothallic Agaricomycetes with two mating type loci controlling the fungal lifecycle [8, 110]. One mating type locus (A locus) in the tetrapolar Agaricomycetes encodes two types of homeodomain transcription factors (HD1 and HD2) in divergently-transcribed gene pairs, whereas the other (B locus) contains genes for pheromones and pheromone precursors, respectively [111, 112].
The A mating type locus
HD1 and HD2 mating type proteins from P. chrysosporium (ADN97192.1, ADN97171.1) were successfully used to screen the Pycnoporus EST contigs. Pycnoporus, like other basidiomycetes [110], has at least one HD1 and one HD2 gene for homeodomain transcription factors. The HD1 protein a1-1 deduced from contig > GCTO4WP02F0TDF.f.pc.1 dna:contig contig::GCTO4WP02F0TDF.f.pc.1:1:2252:1 is 495 aa long. Its N-terminal domain is related to the N-terminal of mating type proteins from other species (Additional file 20: Figure S5 A) and is expected to act in heterodimerization with compatible HD2 proteins while discriminating HD2 proteins from the same mating type [111]. The two classes of homeodomain proteins encoded in basidiomycete mating type loci are defined by their distinct homeodomain sequences [113]. HD1 proteins have a TALE-class homeodomain with three extra amino acids in-between Helix I and Helix II of the three-helical DNA-binding domain. Some amino acid exchanges in the conserved DNA-recognition motif (WFxNxR) in Helix III are tolerated [112]. In the Pycnoporus a1-1 protein, the position of the HD1 homeodomain is only recognized by sequence alignment with related HD1 proteins from other species (Additional file 20: Figure S5 A). The DNA-recognition sequence in Helix III is degenerated and Helix II has undergone a deletion. Previous research failed to find the expected conserved HD1 motif in respective proteins of Postia placenta[4]. We note from other species that a defective HD1 homeodomain does not inevitably cause loss-of-function in mating type regulation provided that the HD2 homeodomain in a HD1-HD2 heterodimer continues to function [114].
A HD2 gene for the 569 aa-long protein a2-1 was found on > GCTO4WP02F01PN.f.pc.1 dna:contig contig::GCTO4WP02F01PN.f.pc.1:1:2027:1. The protein has a classical 60 amino acid-long homeodomain with all invariant residues in the DNA-binding motif which is highly sequence-conserved with HD2 mating type proteins from other Agaricomycetes (Additional file 20: Figure S5 B).
Interestingly, contig GCTO4WP02F0TDF.f.pc.1 contains not only the full-length coding sequence of protein a1-1 (>scf185007.g8) but also, downstream on the opposite strand, the 3-terminal half of gene β-fg for an unknown fungal protein (>scf185007.g7), which in most Agaricomycetes flanks one side of the homeodomain transcript factor locus [115]. At the other side of the loci, a mip gene for a mitochondrial intermediate peptidase is usually present [116]. P. chrysosporium and P. placenta differ from other analyzed Agaricomycetes in the relative order of their single HD1 gene to mip and β-fg. These are the two species where HD1 gene neighbors β-fg and not mip and is transcribed in the same direction as mip, suggesting that there has been an inversion of the mating type locus [115, 117]. Contig GCTO4WP02F0TDF.f.pc.1 indicates that Pycnoporus is another species with this same inverted arrangement. P. chrysosporium (Phanerochaetaceae) and P. placenta (Fomitopsidaceae), like Pycnoporus (Coriolaceae), belong to the Polyporales, and an inversion event early in evolution is likely [118].
The B mating type locus
The bipolar P. chrysosporium contains five genes for pheromone receptors, three of which cluster together in a locus orthologous to the B mating type locus of tetrapolar species, whereas two others belong to the still-unexplored non-mating-type G protein-coupled transmembrane receptors of the Agaricales [115, 117]. The five P. chrysosporium proteins were used to screen the Pycnoporus EST contigs, and five hits were found. Three models contained full-length (PciSTE3.2, PciSTE3.3) or nearly complete (PciSTE3.4) ORFs for G protein-coupled transmembrane receptors (Additional file 21: Figure S6). The other two contained a 5′ half of a gene (PciSTE3N) and a 3′ half of a gene (PciSTE3C), respectively, and it is possible that these two EST contigs present the same gene (Additional file 21: Figure S6). Sequence analysis of the nearly- complete proteins using ClustalW for alignment (http://www.clustal.org/clustal2/), GeneDoc (http://www.psc.edu/biomed/genedoc/) for manual corrections, and the neighbor-joining function in MEGA4 software [119] indicates that PciSTE3.4 groups with the two non-mating-type G protein-coupled transmembrane receptors of P. chrysosporium (Additional file 22: Figure S7 A), whereas PciSTE3.2 and PciSTE3.3 cluster with the B-mating-type-orthologous receptors, respectively (Additional file 22: Figure S7 B,C). This finding suggests that P. cinnabarinus, like other tetrapolar Agaricales, has B-mating-type-specific and non-mating-type genes for pheromone receptors [112, 115]. We also analyzed the N-terminal ends and the C-terminal ends of the proteins separately and together with the protein halves deduced from the incomplete EST contigs GCTO4WP02FNFO2.f.pc.1 and GCTO4WP02F7KNS.f.pc.1, respectively. In both phylogenetic trees, the partial pheromone receptors group with PciSTE3.2 and with the B orthologous PchSTE3.2 of P. chrysosporium, which is evidence that the sequences may come from the same gene. As in several other species [112, 115], there are thus at least three expressed paralogous candidate genes for B-mating-type function in P. cinnabarinus.
Pheromone precursors are short peptide chains of up to about 100 aa and the mature pheromones are 9 to 14 aa-long peptides, which are difficult to find in BLAST searches even at lowest stringency due to strongly divergent sequences [112, 120]. Searches starting with the five identified P. chrysosporium pheromone precursor sequences [112, 117] were unsuccessful, but sequences from Serpula lacrymans (http://genome.jgi-psf.org/SerlaS7_3_2/SerlaS7_3_2.home.html) and cross-searches with the detected P. cinnabarinus pheromone precursors identified a total of seven potential 39-to-65-aa-long pheromone precursors. All possess the typical CAAX (cysteine-aliphatic-aliphatic-any amino acid) motif at the C-terminus and a MDA/DF-motif at the N-terminus (Additional file 23: Figure S8). Three are very distinct in sequence, as is typical for B-mating-type pheromone precursors, whereas four others share more similarity, resembling the precursors of presumed non-mating-type pheromone-like peptides [112, 115].
Conclusions
The P. cinnabarinus genome contains the genes encoding the full enzymatic portfolio for lignin degradation, notably peroxidases and numerous auxiliary enzymes for the generation of hydrogen peroxide. Several laccase-encoding gene models and AA2 peroxidases (MnP, LiP or VP) were identified in P. cinnabarinus. A large number of these genes are expressed as they have been detected as transcripts in the cDNA library. Furthermore, secretome analysis showed effective and differential secretion of several peroxidases, copper radical oxidases, and aryl alcohol, glucose and pyranose oxidases under our culture conditions. These genes structurally organize into a set of clusters and intron/exon position homologies. The physical proximity of these genes (lac, lip, mnp, glox) suggests that this organization may result from chromosomal rearrangements such as local duplications. Furthermore, the different isoenzymes annotated in P. cinnabarinus evidenced high diversity in terms of primary sequence and predicted biochemical characteristics. In P. cinnabarinus, post-transcriptional glycosylation capabilities appear reduced to the strict minimum, making it a promising candidate for heterologous protein production in biotechnological applications. In conclusion, P. cinnabarinus is shown to be an outstanding and representative model white-rot fungi for studying the enzyme machinery involved in the degradation and/or transformation of lignocellulosic materials.
References
Kubicek CP: Lignocellulose Biorefinery. Fungi and Lignocellulosic Biomass. 2012, Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell
Sánchez C: Lignocellulosic residues: biodegradation and bioconversion by fungi. Biotechnol Adv. 2009, 27: 185-194.
Martinez D, Berka RM, Henrissat B, Saloheimo M, Arvas M, Baker SE, Chapman J, Chertkov O, Coutinho PM, Cullen D, Danchin EG, Grigoriev IV, Harris P, Jackson M, Kubicek CP, Han CS, Ho I, Larrondo LF, de Leon AL, Magnuson JK, Merino S, Misra M, Nelson B, Putnam N, Robbertse B, Salamov AA, Schmoll M, Terry A, Thayer N, Westerholm-Parvinen A, et al: Genome sequencing and analysis of the biomass-degrading fungus Trichoderma reesei (syn. Hypocrea jecorina). Nat Biotechnol. 2008, 26: 553-560.
Martinez D, Challacombe J, Morgenstern I, Hibbett D, Schmoll M, Kubicek CP, Ferreira P, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Martínez AT, Kersten P, Hammel KE, Vanden Wymelenberg A, Gaskell J, Lindquist E, Sabat G, Bondurant SS, Larrondo LF, Canessa P, Vicuna R, Yadav J, Doddapaneni H, Subramanian V, Pisabarro AG, Lavín JL, Oguiza JA, Master E, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Harris P, Magnuson JK, et al: Genome, transcriptome, and secretome analysis of wood decay fungus Postia placenta supports unique mechanisms of lignocellulose conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009, 106: 1954-1959.
Kirk TK, Farrell RL: Enzymatic “combustion”: the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987, 41: 465-505.
Floudas D, Binder M, Riley R, Barry K, Blanchette RA, Henrissat B, Martínez AT, Otillar R, Spatafora JW, Yadav JS, Aerts A, Benoit I, Boyd A, Carlson A, Copeland A, Coutinho PM, de Vries RP, Ferreira P, Findley K, Foster B, Gaskell J, Glotzer D, Górecki P, Heitman J, Hesse C, Hori C, Igarashi K, Jurgens JA, Kallen N, Kersten P, et al: The Paleozoic origin of enzymatic lignin decomposition reconstructed from 31 fungal genomes. Science. 2012, 336: 1715-1719.
Martínez AT, Speranza M, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Ferreira P, Camarero S, Guillén F, Martínez MJ, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC: Biodegradation of lignocellulosics: microbial, chemical, and enzymatic aspects of the fungal attack of lignin. Int Microbiol. 2005, 8: 195-204.
Lomascolo A, Uzan-Boukhris E, Herpoël-Gimbert I, Sigoillot J-G, Lesage-Meessen L: Peculiarities of Pycnoporus species for applications in biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011, 92: 1129-1149.
Herpoël I, Moukha S, Lesage-Meessen L, Sigoillot JC, Asther M: Selection of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus strains for laccase production. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000, 183: 301-306.
Alves AM, Record E, Lomascolo A, Scholtmeijer K, Asther M, Wessels JG, Wösten HA: Highly efficient production of laccase by the basidiomycete Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004, 70: 6379-6384.
Moukha SM, Dumonceaux TJ, Record E, Archibald FS: Cloning and analysis of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus cellobiose dehydrogenase. Gene. 1999, 234: 23-33.
Halaouli S, Asther M, Kruus K, Guo L, Hamdi M, Sigoillot J-C, Asther M, Lomascolo A: Characterization of a new tyrosinase from Pycnoporus species with high potential for food technological applications. J Appl Microbiol. 2005, 98: 332-343.
Lesage-Meessen L, Haon M, Delattre M, Thibault J-F, Colonna-Ceccaldi B, Asther M: An attempt to channel the transformation of vanillic acid into vanillin by controlling methoxyhydroquinone formation in Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1997, 47: 393-397.
Estrada Alvarado I, Navarro D, Record E, Asther M, Asther M: Fungal biotransformation of p-coumaric acid into caffeic acid by Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: an alternative for producing a strong natural antioxidant. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003, 19: 157-160.
Lesage-Meessen L, Delattre M, Haon M, Thibault JF, Ceccaldi BC, Brunerie P, Asther M: A two-step bioconversion process for vanillin production from ferulic acid combining Aspergillus niger and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. J Biotechnol. 1996, 50: 107-113.
Eggert C, Temp U, Eriksson KEL: The lignolytic system of the white-rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: purification and characterization of the laccase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996, 62: 1151-1158.
Lomascolo A, Record E, Herpoël-Gimbert I, Delattre M, Robert JL, Georis J, Dauvrin T, Sigoillot JC, Asther M: Overproduction of laccase by a monokaryotic strain of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus using ethanol as inducer. J Appl Microbiol. 2003, 94: 618-624.
Herpoël I, Jeller H, Fang G, Petit-Conil M, Bourbonnais R, Robert JL, Asther M, Sigoillot JC: Efficient enzymatic delignification of wheat straw pulp by a sequential xylanase-laccase treatment. J Pulp Paper Sci. 2002, 28: 67-71.
Camarero S, Garcia O, Vidal T, Colom J, del Rio JC, Gutierrez AM, Gras J, Monje R, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT: Efficient bleaching of non-wood high-quality paper pulp using laccase-mediator system. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2004, 35: 113-120.
Sigoillot C, Record E, Belle V, Robert J-L, Levasseur A, Punt PJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Fournel A, Sigoillot J-C, Asther M: Natural and recombinant fungal laccases for paper pulp bleaching. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004, 64: 346-352.
Ravalason H, Herpoel-Gimbert I, Record E, Bertaud F, Grisel S, de Weert S, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Asther M, Petit-Conil M, Sigoillot JC: Fusion of a family 1 carbohydrate binding module of Aspergillus niger to the Pycnoporus cinnabarinus laccase for efficient softwood kraft pulp biobleaching. J Biotechnol. 2009, 142: 220-226.
Eugenio ME, Santos SM, Carbajo JM, Martin JA, Martin-Sampedro R, Gonzales AE, Villar JC: Kraft pulp biobleaching using an extracellular enzymatic fluid produced by Pycnoporus sanguineus. Bioresour Technol. 2010, 101: 1866-1870.
Camarero S, Ibarra D, Martínez MJ, Martínez A: Lignin-derived compounds as efficient laccase mediators for decolorization of different types of recalcitrant dyes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005, 71: 1775-1784.
Lu L, Zhao M, Zhang B-B, Yu S-Y, Bian X-J, Wang W, Wang Y: Purification and characterization of laccase from Pycnoporus sanguineus and decolorization of an anthraquinone dye by the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007, 74: 1232-1239.
Uzan E, Nousiainen P, Balland V, Sipila J, Piumi F, Navarro D, Asther M, Record E, Lomascolo A: High redox potential laccases from the ligninolytic fungi Pycnoporus coccineus and Pycnoporus sanguineus suitable for white biotechnology: from gene cloning to enzyme characterization and applications. J Appl Microbiol. 2010, 108: 2199-2213.
Jaouani A, Guillén F, Penninckx MJ, Martínez AT, Martínez MJ: Role of Pycnoporus coccineus laccase in the degradation of aromatic compounds in olive oil mill wastewater. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2005, 36: 478-486.
Berrio J, Plou FJ, Ballesteros A, Martínez AT, Martínez MJ: Immobilization of Pycnoporus coccineus laccase on Eupergit C: Stabilization and treatment of olive oil mill wastewaters. Biocatal Biotransform. 2007, 25: 130-134.
Yahaya YA, Mashitah MD, Bhatia S: Biosorption of copper (II) onto immobilized cells of Pycnoporus sanguineus from acqueous solution: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Hazard Mater. 2009, 161: 189-195.
Osma JF, Toca-Herrera JL, Rodríguez-Couto S: Uses of laccases in the food industry. Enzyme Res. 2010, 2010: 918761-
Gil ES, Muller L, Santiago MF, Garcia TA: Biosensor based on brut extract from laccase (Pycnoporus sanguineus) for environmental analysis of phenolic compounds. J Portuguese Electrochem Society. 2009, 27: 215-225.
Kudanga T, Nyanhongo GS, Guebitz GM, Burton S: Potential applications of laccase-mediated coupling and grafting reactions: a review. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2011, 48: 195-208.
Lomascolo A, Cayol JL, Roche M, Guo L, Robert JL, Record E, Lesage-Meessen L, Ollivier B, Sigoillot JC, Asther M: Molecular clustering of Pycnoporus strains from various geographic origins and isolation of monokaryotic strains for laccase hyperproduction. Mycol Res. 2002, 106: 1193-1203.
Wessels JGH, Mulder GH, Springer J: Expression of dikaryon-specific and non-specific mRNAs of Schizopyllum commune in relation to environmental conditions and fruiting. J Gen Microbiol. 1987, 13: 2557-2561.
Meza JC, Lomascolo A, Casalot L, Sigoillot JC, Auria R: Laccase production by Pycnoporus cinnabarinus grown on sugar-cane bagasse: influence of ethanol vapors as inducer. Process Biochem. 2005, 40: 3365-3371.
Meza JC, Auria R, Lomascolo A, Sigoillot JC, Casalot L: Role of ethanol on growth, laccase production and protease activity in Pycnoporus cinnabarinus ss3 grown on sugarcane bagasse. Enzyme Microbiol Technol. 2007, 41: 162-163.
Espagne E, Lespinet O, Malagnac F, Da Silva C, Jaillon O, Porcel BM, Couloux A, Aury JM, Ségurens B, Poulain J, Anthouard V, Grossetete S, Khalili H, Coppin E, Déquard-Chablat M, Picard M, Contamine V, Arnaise S, Bourdais A, Berteaux-Lecellier V, Gautheret D, de Vries RP, Battaglia E, Coutinho PM, Danchin EG, Henrissat B, Khoury RE, Sainsard-Chanet A, Boivin A, Pinan-Lucarré B, et al: The genome sequence of the model ascomycete fungus Podospora anserina. Genome Biol. 2008, 9: R77-
Mariette J, Escudié F, Allias N, Salin G, Noirot C, Thomas S, Klopp C: NG6: Integrated next generation sequencing storage and processing environment. BMC Genomics. 2012, 13: 462-
Mariette J, Noirot C, Klopp C: Assessment of replicate bias in 454 pyrosequencing and a multi-purpose read-filtering tool. BMC Res Notes. 2011, 4: 149-
Stanke M, Tzvetkova A, Morgenstern B: AUGUSTUS at EGASP: using EST, protein and genomic alignments for improved gene prediction in the human genome. Genome Biol. 2006, 7 (S11): 1-8.
Li L, Stoeckert CJ, Roos DS: OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 2003, 13: 2178-2189.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G: Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology: the gene ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 2000, 25: 25-29.
Price AL, Jones NC, Pevzner PA: De novo identification of repeat families in large genomes. Bioinformatics. 2005, 21: 351-358.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ: Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990, 215: 403-410.
Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J: Repbase Update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005, 110: 462-467.
Mc Carthy E, Mc Donald JF: LTR_STRUC: a novel search and identification program for LTR retrotransposons. Bioinformatics. 2003, 19: 362-367.
Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P: RepeatMasker Open-3.0. 1996–2010. http://www.repeatmasker.org,
Benson G: Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27: 573-580.
Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B: The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42: D490-D495.
Levasseur A, Drula E, Lombard V, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B: Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnology for Biofuels. 2013, 6: 41-
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR: HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39: W29-W37.
Breathnach R, Benoist C, O’Hara K, Chambon P: Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978, 75: 4853-4857.
Couturier M, Navarro D, Olivé C, Chevret D, Haon M, Favel A, Lesage-Meessen L, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Berrin JG: Post-genomic analyses of fungal lignocellulosic biomass degradation reveal the unexpected potential of the plant pathogen Ustilago maydis. BMC Genomics. 2012, 13: 57-
Arfi Y, Chevret D, Henrissat B, Berrin JG, Levasseur A, Record E: Characterization of salt-adapted secreted lignocellulolytic enzymes from the mangrove fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. Nat Commun. 2013, 4: 1810-
Pel HJ, de Winde JH, Archer DB, Dyer PS, Hofmann G, Schaap PJ, Turner G, de Vries RP, Albang R, Albermann K, Andersen MR, Bendtsen JD, Benen JA, van den Berg M, Breestraat S, Caddick MX, Contreras R, Cornell M, Coutinho PM, Danchin EG, Debets AJ, Dekker P, van Dijck PW, van Dijk A, Dijkhuizen L, Driessen AJ, d’Enfert C, Geysens S, Goosen C, Groot GS, et al: Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat Biotechnol. 2007, 25: 221-231.
Fernandez-Fueyo E, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Ferreira P, Floudas D, Hibbett DS, Canessa P, Larrondo LF, James TY, Seelenfreund D, Lobos S, Polanco R, Tello M, Honda Y, Watanabe T, Watanabe T, Ryu JS, Kubicek CP, Schmoll M, Gaskell J, Hammel KE, StJohn FJ, Vanden Wymelenberg A, Sabat G, Splinter BonDurant S, Syed K, Yadav JS, Doddapaneni H, Subramanian V, Lavín JL, Oguiza JA, et al: Comparative genomics of Ceriporiopsis subvermispora and Phanerochaete chrysosporium provide insight into selective ligninolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109: 5458-5463.
Martínez D, Larrondo LF, Putnam N, Gelpke MD, Huang K, Chapman J, Helfenbein KG, Ramaiya P, Detter JC, Larimer F, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B, Berka R, Cullen D, Rokhsar D: Genome sequence of the lignocellulose degrading fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium strain RP78. Nat Biotechnol. 2004, 22: 695-700.
Levasseur A, Pontarotti P, Poch O, Thompson JD: Strategies for reliable exploitation of evolutionary concepts in high throughput biology. Evol Bioinform Online. 2008, 4: 121-137.
Levasseur A, Orlando L, Bailly X, Milinkovitch MC, Danchin EG, Pontarotti P: Conceptual bases for quantifying the role of the environment on gene evolution: the participation of positive selection and neutral evolution. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2007, 82: 551-572.
Levasseur A, Pontarotti P: The role of duplications in the evolution of genomes highlights the need for evolutionary-based approaches in comparative genomics. Biol Direct. 2011, 6: 11-
Murat C, Payen T, Petitpierre D, Labbé J: Repeated elements in filamentous fungi and comparative genomic of wood-decay fungi. The Ecological Genomics of Fungi. Edited by: Francis M. 2013, Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell
Ohm RA, de Jong JF, Lugones LG, Aerts A, Kothe E, Stajich JE, de Vries RP, Record E, Levasseur A, Baker SE, Bartholomew KA, Coutinho PM, Erdmann S, Fowler TJ, Gathman AC, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Knabe N, Kües U, Lilly WW, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Magnuson JK, Piumi F, Raudaskoski M, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Schwarze FW, van Kuyk PA, Horton JS, et al: Genome sequence of the model mushroom Schizophyllum commune. Nat Biotechnol. 2010, 28: 957-963.
Eastwood DC, Floudas D, Binder M, Majcherczyk A, Schneider P, Aerts A, Asiegbu FO, Baker SE, Barry K, Bendiksby M, Blumentritt M, Coutinho PM, Cullen D, de Vries RP, Gathman A, Goodell B, Henrissat B, Ihrmark K, Kauserud H, Kohler A, LaButti K, Lapidus A, Lavin JL, Lee YH, Lindquist E, Lilly W, Lucas S, Morin E, Murat C, Oguiza JA, et al: The plant cell wall-decomposing machinery underlies the functional diversity of forest fungi. Science. 2011, 333: 762-765.
Guillén F, Gómez-Toribio V, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT: Production of hydroxyl radical by the synergistic action of fungal laccase and aryl alcohol oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000, 383: 142-147.
Sigoillot C, Lomascolo A, Record E, Robert JL, Asther M, Sigoillot JC: Lignocellulolytic and hemicellulolytic system of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: isolation and characterization of a cellobiose dehydrogenase and a new xylanase. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2002, 31: 876-883.
Bey M, Berrin JG, Poidevin L, Sigoillot JC: Heterologous expression of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus cellobiose dehydrogenase in Pichia pastoris and involvement in saccharification processes. Microb Cell Fact. 2011, 10: 113-
Caffall KH, Mohnen D: The structure, function, and biosynthesis of plant cell wall pectic polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 2009, 344: 1879-1900.
Eggert C, Lafayette P, Temp U, Eriksson KEL, Dean JFD: Molecular analysis of a laccase gene from the white-rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998, 6: 1766-1772.
Otterbein L, Record E, Chereau D, Herpoël I, Asther M, Moukha S: Isolation of a new laccase isoform from the white-rot fungi Pycnoporus cinnabarinus strain ss3. Can J Microbiol. 2000, 46: 759-763.
Yaver DS, Golightly EJ: Cloning and characterization of three laccase genes from the white-rot basidiomycete Trametes villosa: genomic organization of the laccase gene family. Gene. 1996, 181: 95-102.
Hoshida H, Nakao M, Kanazawa H, Kubo K, Hakukawa T, Morimasa K, Akada R, Nishizawa Y: Isolation of five laccase gene sequences from the white rot fungus Trametes sanguineus by PCR, and cloning, characterization and expression of the laccase cDNA in yeasts. J Biosci Bioeng. 2001, 92: 372-380.
Wahleithner JA, Xu F, Brown KM, Brown SH, Golightly EJ, Halkier T, Kauppinen S, Pederson A, Schneider P: The identification and characterization of four laccases from the plant pathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Curr Genet. 1996, 29: 395-403.
Litvintseva AP, Henson JM: Cloning, characterization, and transcription of three laccase genes from Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici, the take-all fungus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002, 68: 1305-1311.
Xiao YZ, Hong YZ, Li JF, Hang T, Tong PG, Fang W, Zhou CZ: Cloning of novel laccase isozyme genes from Trametes sp. AH28-2 and analyses of their differential expression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006, 71: 493-501.
Soden DM, Dobson ADW: Differential regulation of laccase gene expression in Pleurotus sajor-caju. Microbiology. 2001, 147: 1755-1763.
Rodriguez E, Ruiz-Duenas FJ, Kooistra R, Ramb A, Martínez AT, Martínez MJ: Isolation of two laccase genes from the white-rot fungus Pleurotus eryngii and heterologous expression of the pel3 encoded protein. J Biotechnol. 2008, 134: 9-19.
Pezzella C, Autore F, Giardina P, Piscitelli A, Sannia G, Faraco V: The Pleurotus ostreatus laccase multi-gene family: isolation and heterologous expression of new family members. Curr Genet. 2009, 55: 45-57.
Kilaru S, Hoegger PJ, Kües U: The laccase multi-gene family in Coprinopsis cinerea has seventeen different members that divide into two distint subfamilies. Curr Genet. 2006, 50: 45-60.
Hoegger PJ, Kilaru S, James TY, Thacker JR, Kües U: Phylogenetic comparison and classification of laccase and related multicopper oxidase protein sequences. FEBS J. 2006, 273: 2308-2326.
Perry CR, Matcham SE, Wood DA, Thurston CF: The structure of laccase protein and its synthesis by the commercial mushroom Agaricus bisporus. J Gen Microbiol. 1993, 39: 171-178.
Giardina P, Faraco V, Pezzella C, Piscitelli A, Vanhulle S, Sannia G: Laccases: a never-ending story. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010, 67: 369-385.
Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Fernández E, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT: Pleurotus ostreatus heme peroxidases: An in silico analysis from the genome sequence to the enzyme molecular structure. CR Biol. 2011, 334: 795-805.
Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Morales M, García E, Miki Y, Martínez MJ, Martínez AT: Substrate oxidation sites in versatile peroxidase and other basidiomycete peroxidases. J Exp Bot. 2009, 60: 441-452.
Bordoli L, Kiefer F, Arnold K, Benkert P, Battey J, Schwede T: Protein structure homology modeling using SWISS-MODEL workspace. Nat Protoc. 2009, 4: 1-13.
Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Lundell T, Floudas D, Nagy LG, Barrasa JM, Hibbett DS, Martínez AT: Lignin-degrading peroxidases in Polyporales: an evolutionary survey based on ten sequenced genomes. Mycologia. 2013, 105: 1428-1444.
Hofrichter M, Ullrich R, Pecyna MJ, Liers C, Lundell T: New and classic families of secreted fungal heme peroxidases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010, 87: 871-897.
Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Martínez AT: Structural and functional features of peroxidases with a potential as industrial biocatalysts. Biocatalysts based on heme peroxidases. Edited by: Torres E, Ayala M. 2010, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 37-59.
Morin E, Kohler A, Baker AR, Foulongne-Oriol M, Lombard V, Nagy LG, Ohm RA, Patyshakuliyeva A, Brun A, Aerts AL, Bailey AM, Billette C, Coutinho PM, Deakin G, Doddapaneni H, Floudas D, Grimwood J, Hildén K, Kües U, Labutti KM, Lapidus A, Lindquist EA, Lucas SM, Murat C, Riley RW, Salamov AA, Schmutz J, Subramanian V, Wösten HA, Xu J, et al: Genome sequence of the button mushroom Agaricus bisporus reveals mechanisms governing adaptation to a humic-rich ecological niche. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109: 17501-17506.
Hofrichter M, Ullrich R: Heme-thiolate haloperoxidases: versatile biocatalysts with biotechnological and environmental significance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006, 71: 276-288.
Johansson T, Nyman PO: A cluster of genes encoding major isozymes of lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Gene. 1996, 170: 31-38.
Pointing SB, Pelling AL, Smith GJD, Hyde KD, Reddy CA: Screening of basidiomycetes and xylariaceous fungi for lignin peroxidase and laccase gene specific sequences. Mycology Research. 2005, 109: 115-124.
Morgenstern I, Robertson D, Hibbett DS: Characterization of three mnp genes of Fomitiporia mediterranea and report of additional class II peroxidases in the order Hymenochaetales. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010, 76: 6431-6440.
Rajakumar S, Gaskell SJ, Cullen D, Lobos S, Karahanian E, Vicuna R: Lip-like genes in Phanerochaete sordida and Ceriporiopsis subvermispora, white rot fungi with no detectable lignin peroxidase activity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996, 62: 2660-2663.
Fernández-Fueyo E, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Ferreira P, Floudas D, Hibbett DS, Canessa P, Larrondo L, James TY, Seelenfreund D, Lobos S, Polanco R, Tello M, Honda Y, Watanabe T, Watanabe T, Ryu JS, Kubicek CP, Schmoll M, Gaskell J, Hammel KE, St. John FJ, Vanden Wymelenberg A, Sabat G, Bondurant SS, Syed K, Yadav J, Doddapaneni H, Subramanian V, Lavín JL, Oguiza JA, et al: Comparative genomics of Ceriporiopisis subvermispora and Phanerochaete chrysosporium provide insight into selective ligninolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109: 5458-5463.
Evans CS, Dutton MV, Guillén F, Veness RG: Enzymes and small molecular mass agents involved with lignocellulose degradation. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994, 13: 235-240.
Vanden Wymelenberg A, Sabat G, Mozuch M, Kersten PJ, Cullen D, Blanchette RA: Structure, organization and transcriptional regulation of a family of copper radical oxidase genes in the lignin degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006, 72: 4871-4877.
Whittaker MM, Kersten PJ, Cullen D, Whittaker JM: Identification of catalytic residues in glyoxal oxidase by targeted mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1999, 274: 36226-36232.
Rogers MS, Tyler EM, Akyumani N, Kurtis CR, Spooner RK, Deacon SE, Tamber S, Firbank SJ, Mahmoud K, Knowles PF, Phillips SEV, McPherson MJ, Dooley DM: The stacking tryptophan of galactose oxidase: a second coordination sphere residue that has profound effects on tyrosyl radical behavior and enzyme catalysis. Biochemistry. 2007, 46: 4606-4618.
Songulashvili G, Elisashvili V, Wasser SP, Nevo E, Hadar Y: Basidiomycetes laccase and manganese peroxidase activity in submerged fermentation of food industry wastes. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2007, 41: 57-61.
Elisashvili V, Kachlishvili E, Penninckx M: Effect of growth substrate, method of fermentation, and nitrogen source on lignocellulose-degrading enzymes production by white-rot basidiomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008, 35: 1531-1538.
Elisashvili V, Kachlishvili E, Tsiklauri N, Metreveli E, Khardziani T, Agathos SN: Lignocellulose-degrading enzyme production by white-rot Basidiomycetes isolated from the forests of Georgia. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009, 25: 331-339.
Sathishkumar P, Murugesan K, Palvannan T: Production of laccase from Pleurotus florida using agro-wastes and efficient decolorization of reactive blue 198. J Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50: 360-367.
Osma JF, Moilanen U, Toca-Herrera JL, Rodriguez-Couto S: Morphology and laccase production of white-rot fungi grown on wheat bran flakes under semi-solid-state fermentation conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011, 318: 27-34.
Poidevin L, Berrin JG, Bennati-Granier C, Levasseur A, Herpoël-Gimbert I, Chevret D, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B, Heiss-Blanquet S, Record E: Comparative analyses of Podospora anserina secretomes reveal a large array of lignocellulose-active enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014, In press
Janusz G, Kucharzyk KH, Pawlik A, Staszczak M, Paszczynski AJ: Fungal laccase, manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase: gene expression and regulation. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2013, 52: 1-12.
Koseki T, Fushinobu S, Ardiansyah , Shirakawa H, Komai M: Occurrence, properties, and applications of feruloyl esterases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009, 84: 803-810.
Saha BC: Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003, 30: 279-291.
Kohno K: Stress-sensing mechanisms in the unfolded protein response: similarities and differences between yeast and mammals. J Biochem. 2010, 147: 27-33.
Berends E, Ohm RA, de Jong JF, Rouwendal G, ten HA W, Lugones LG, Bosch D: Genomic and biochemical analysis of N glycosylation in the mushroom-forming basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009, 75: 4648-4652.
Tefsen B, Ram AF, van Die I, Routier FH: Galactofuranose in eukaryotes: aspects of biosynthesis and functional impact. Glycobiology. 2012, 22: 456-469.
Nobles MK, Frew BP: Studies in wood-inhabiting hymenomycetes. V. The genus Pycnoporus Karst. Can J Bot. 1962, 40: 987-1016.
Casselton LA, Olesnicky : Molecular genetics of mating type recognition in basidiomycete fungi. Microbiolo Mol Biol Rev. 1998, 62: 55-70.
Kües U, James TY, Heitman J: Mating type in basidiomycetes: Unipolar, bipolar, and tetrapolar patterns of sexuality. The mycota, Volume XIV. Edited by: Pöggeler S, Wöstemeyer J. 2011, Heidelberg: Evolution of fungi and fungal-like organisms. Springer, 97-160.
Kües U, Casselton LA: Homeodomains and regulation of sexual development in basidiomycetes. Trends Genet. 1992, 8: 154-155.
Asante-Owusu RN, Banham AH, Böhnert HU, Mellor EJ, Casselton LA: Heterodimerization between two classes of homeodomain proteins in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus brings together potential DNA-binding and activation domains. Gene. 1996, 172: 25-31.
Niculita-Hirzel H, Labbé J, Kohler A, Le Tacon F, Martin F, Sanders IR, Kües U: Gene organization of the mating type regions in the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor reveals distinct evolution between the two mating type loci. New Phytol. 2008, 180: 329-342.
James TY, Kües U, Rehner SA, Vilgalys R: Evolution of the gene encoding mitochondrial intermediate peptidase and its cosegregation with the A mating type locus of mushroom fungi. Fungal Genet Biol. 2004, 41: 381-390.
James TY, Lee M, van Diepen LTA: A single mating-type locus composed of homeodomain genes promotes nuclear migration and heterokaryosis in the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Eukaryot Cell. 2011, 10: 249-262.
James TY, Sun S, Li WJ, Heitman J, Kuo HC, Lee YH, Asiegbu FO, Olsen Å: Polyporales genomes reveal the genetic architecture underlying tetrapolar and bipolar mating systems. Mycologia. 2013, 105: 1374-1390.
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S: MEGA: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011, 28: 2731-2739.
Kües U, Navarro-González M: Mating-type orthologous genes in the primarily homothallic Moniliophthora perniciosa, the causal agent of Witches’ Broom Disease in cacao. J Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50: 442-451.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Commission of the European Communities through the BIORENEW project (NMP2-CT-2006-026456 “White Biotechnology for added-value products from re newable plant polymers: Design of tailor-made biocatalysts and new industrial bioprocesses”) and the PEROXICATS project (KBBE-2010-4-265397 “Novel and more robust fungal peroxidases as industrial biocatalysts.”), and by the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MINECO) through the HIPOP project (BIO2011-26694, “Screening and engineering of new high-redox-potential peroxidases”). The authors also thank the MICA and CEPIA departments of the INRA [French National Institute for Agricultural Research] for their support. Francisco J. Ruiz-Dueñas received a Ramon y Cajal contract from the Spanish MINECO. We thank Anne-Hélène Jan and Julie Pitrat (School of Biological Engineering and Applied Microbiology Polytech Marseille, France) for their assistance in the in silico annotation of oxidoreductases, and Peter J. Punt and Marie Noëlle Rosso for their insightful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contribution
AL, ALo, ER designed the research; AL, ALo, OC, EBU, FP, MH, YA, DC, ED, MJK, PG, LLM, VL, JM, CN, JP, AP, JCS, AW, CK performed the research; AL, ALo, FJRD, EBU, UK, AFJR CM, IB, HABW, FM, PMC, RPdV, ATM, CK, PP, BH analyzed the data; AL, ALo, ER wrote the paper; AL coordinated the study. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12864_2014_6245_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Additional file 2: Table S2: List of the lignocellulolytic repertoire encoding-genes in P. cinnabarinus BRFM137.(DOCX 28 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Additional file 3: Table S3: Annotation of the lignin oxidoreductases predicted from the genome of P. cinnabarinus BRFM137.(DOCX 15 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM8_ESM.docx
Additional file 8: Figure S2: Molecular characterization of peroxidase genes (A) and schematic organization of peroxidase gene clusters on genomic DNA from P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 (B).(DOCX 64 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM10_ESM.docx
Additional file 10: Table S6: Annotation of the AA5_1 proteins predicted from the genome of P. cinnabarinus BRFM137. (DOCX 14 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM12_ESM.docx
Additional file 12: Figure S3: Molecular characterization of AA5_1 genes (A) and schematic organization of glyoxal oxidase gene clusters on genomic DNA from P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 (B). (DOCX 50 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM14_ESM.docx
Additional file 14: Figure S4: Modeling of the active site of the theoretical Glox1 predicted in P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 and comparison with galactose oxidase from Dactylium dendroides. (DOCX 701 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM15_ESM.docx
Additional file 15: Data S4: Structural comparison between Glox1 and Gaox proteins [97]. (DOCX 14 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM16_ESM.xlsx
Additional file 16: Table S8: List of lignocellulolytic enzymes identified in the secretomes of P. cinnabarinus BRFM137 in different growth conditions. (XLSX 30 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM17_ESM.docx
Additional file 17: Table S9: List of unique and common genes identified in the different growth conditions. (DOCX 18 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM19_ESM.docx
Additional file 19: Table S11: P. cinnabarinus genome annotation related to protein glycosylation pathways. (DOCX 32 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM20_ESM.docx
Additional file 20: Figure S5: Alignments of the N-terminal regions of HD1 (A) and HD2 mating type proteins (B) of Pycnoporus and other Agaricomycetes. (DOCX 182 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM21_ESM.docx
Additional file 21: Figure S6: Alignment of sequences of putative G protein-coupled transmembrane pheromone receptors deduced from EST contigs of P. cinnabarinus (Pci) and sequences of pheromone receptors of P. chrysosporium (Pch; for nomenclature, see James et al.[117]). (DOCX 2 MB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM22_ESM.docx
Additional file 22: Figure S7: Neighbour-joining trees (bootstrap values: 500) of sequences of A. (nearly) complete, B. N-terminal and C. C-terminal halves of pheromone receptors of P. cinnabarinus and P. chrysosporium (for nomenclature see James et al.[117]). The classification in non-mating type and B orthologs follows the analysis of Niculita-Hierzel et al.[115]. (DOCX 38 KB)
12864_2014_6245_MOESM23_ESM.docx
Additional file 23: Figure S8: Alignment of sequences of putative B mating type pheromone precursors (Ph1 and Ph2) and of putative precursors for non-mating-type pheromone-like peptides (Phl1 to Phl3). (DOCX 42 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Levasseur, A., Lomascolo, A., Chabrol, O. et al. The genome of the white-rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: a basidiomycete model with a versatile arsenal for lignocellulosic biomass breakdown. BMC Genomics 15, 486 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-486
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-486