Abstract
Background
A novel sarcomeric myosin heavy chain gene, MYH14, was identified following the completion of the human genome project. MYH14 contains an intronic microRNA, miR-499, which is expressed in a slow/cardiac muscle specific manner along with its host gene; it plays a key role in muscle fiber-type specification in mammals. Interestingly, teleost fish genomes contain multiple MYH14 and miR-499 paralogs. However, the evolutionary history of MYH14 and miR-499 has not been studied in detail. In the present study, we identified MYH14/miR-499 loci on various teleost fish genomes and examined their evolutionary history by sequence and expression analyses.
Results
Synteny and phylogenetic analyses depict the evolutionary history of MYH14/miR-499 loci where teleost specific duplication and several subsequent rounds of species-specific gene loss events took place. Interestingly, miR-499 was not located in the MYH14 introns of certain teleost fish. An MYH14 paralog, lacking miR-499, exhibited an accelerated rate of evolution compared with those containing miR-499, suggesting a putative functional relationship between MYH14 and miR-499. In medaka, Oryzias latipes, miR-499 is present where MYH14 is completely absent in the genome. Furthermore, by using in situ hybridization and small RNA sequencing, miR-499 was expressed in the notochord at the medaka embryonic stage and slow/cardiac muscle at the larval and adult stages. Comparing the flanking sequences of MYH14/miR-499 loci between torafugu Takifugu rubripes, zebrafish Danio rerio, and medaka revealed some highly conserved regions, suggesting that cis-regulatory elements have been functionally conserved in medaka miR-499 despite the loss of its host gene.
Conclusions
This study reveals the evolutionary history of the MYH14/miRNA-499 locus in teleost fish, indicating divergent distribution and expression of MYH14 and miR-499 genes in different teleost fish lineages. We also found that medaka miR-499 was even expressed in the absence of its host gene. To our knowledge, this is the first report that shows the conversion of intronic into non-intronic miRNA during the evolution of a teleost fish lineage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
To meet the constantly changing functional demands, the physiological properties of skeletal muscle are highly adjustable and are achieved through a process of switching muscle fiber-types, such as slow and fast muscle fibers, in response to internal and external stimuli, a process termed muscle fiber-type plasticity [1]. Myosin heavy chains (MYHs) form a large gene family that includes sarcomeric MYHs, major contractile proteins of striated muscles that are expressed in a spatio-temporal manner defining the functional properties of different muscle fiber subtypes [1]. In humans, sarcomeric MYHs form two clusters on the genome where skeletal and cardiac MYHs are arrayed in tandem on chromosome Chr17 and Chr14, respectively [2–5]. Upon completion of the human genome project, a novel MYH named MYH14 (MYH7b) was identified on Chr20 [6], recently, there has been increasing interest in its direct involvement in muscle fiber-type plasticity. Mammalian MYH14 has a microRNA, miR-499, in its 19th intron that suppresses the expression of genes involved in muscle fiber-type specification [7–11]; thus, miR-499 seemingly acts to support normal slow-muscle formation in mammals.
Our previous studies revealed that teleost fish also have MYH14 in their genomes [12, 13]. Expression analysis in torafugu Takifugu rubripes Abe 1949 and zebrafish Danio rerio Hamilton 1822 revealed that MYH14 is one of the major components of the MYH repertoire expressed in the slow and cardiac muscles of teleost fish [14, 15], suggesting its role in teleost muscle formation. Consistent with functional conservation with mammals, Wang et al. [16] showed that the transcriptional network of Sox6/MYH14/miR-499 plays an essential role in maintaining slow muscle lineage in larval zebrafish muscle. Our previous study also showed that teleost fish contain a higher number of MYHs in their genomes than do their mammalian counterparts [12, 13, 17, 18]. Two MYH14 paralogs, MYH M3383 and MYH M5 , were identified in the torafugu genome by phylogenetic and syntenic analyses [13]. Moreover, we have also previously found that medaka Oryzias latipes lacks MYH14 in the syntenic region [15]. These lines of evidence allowed us to speculate on the existence of a highly varied distribution and function of MYH14 and miR-499 in teleost fish.
The aim of this study was to elucidate the evolutionary history of MYH14/miR-499 in fish. MYH14 and miR-499 genes were screened from available vertebrate genome databases, and their evolutionary history was examined by synteny and phylogenetic analyses. In this study, we confirm the conversion of intronic into intergenic miRNA during fish evolution.
Results
Distribution of MYH14 and miR-499 in teleost fish genomes
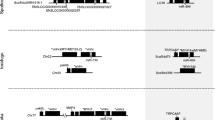
Using the genomic databases available for different vertebrates, we examined the syntenic organization of human MYH14 and miR-499 with their orthologs. The locations and IDs of MYH14 and miR-499 used in this study are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1. Our results show that the tandem arrayed location of the ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 2 gene (EDEM2), transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 4 associated protein gene (TRPC4AP), and MYH14 containing miR-499 were conserved in humans, chickens, and coelacanths Latimeria chalumnae. The synteny was also found LG18 in spotted gar Lepisosteus oculatus. In zebrafish Chr11, MYH14 containing miR-499 was located next to TRPC4AP. In addition, two MYH14s were also found on Chr23 located near a putative TRPC4AP paralog. Both zebrafish MYH14 contained miR-499, totaling three MYH14/miR-499 pairs in this species. Ikeda et al. [13] reported two MYH14 paralogs, MYH M5 and MYH M3383 , in the torafugu genome. The former was located on scaffold79 and the latter on scaffold398. MYH M5 was located next to TRPC4AP and contained miR-499, whereas MYH M3383 was located next to sulfatase 2 gene (SULF2) and did not contain miR-499 in its intron. In tetrapods, however, SULF2 is located in the same chromosome as MYH14/miR-499, but far from the locus. Based on the synteny, two putative MYH14s, one containing miR-499 and the other lacking it, were also found in green spotted puffer Tetraodon nigroviridis and tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Interestingly, in Atlantic cod Gadus morhua, stickleback Gasterosteus aculeatus, platyfish Xiphophorus maculatus, and medaka, miR-499 was present within the expected syntenic region that contained TRPC4AP, NDRG3, SULF2. However, MYH14 was absent in each case. Cod and stickleback retained a single MYH14 paralog lacking miR-499 in the other syntenic region that contained SULF2. SULF2 seems to be consistently located next to MYH14 in most teleost fish species. Interestingly, the medaka genome was lacking MYH14. Although we screened the MYH14 sequence from the Ensembl medaka genome and medaka EST data sets deposited to DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank using tBLASTn and the torafugu MYH14-1 (MYHM5) protein sequence as a query, no MYH14 sequence was retrieved.
Genomic organization of MYH14 and miR-499 in various vertebrates. Orthologous genes are connected by solid and dotted lines. Genes displayed above the midline are in forward strands (+ orientation, from left to right), whereas those displayed below are in reverse strands (− orientation, from right to left). MYH14 and miR-499 paralogs found in one species are distinguished by numbers (see Table 1). Abbreviations used: Chr, chromosome; TRPC4AP, transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 4 associated protein; EDEM2, ER degradation enhancer, mannosidase alpha-like 2; SLA2, Src-like-adaptor 2; NDRG3, N-myc downstream regulated family member 3; PHF20, PHD finger protein 20; SULF2, sulfatase 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of MYH14 and miR-499
Phylogenetic analyses based on the MYH14 coding and miR-499 stem-loop sequences were performed to clarify the evolutionary history of the MYH14/miR-499 locus in teleost fish. Figure 2A and Additional file 1: Figure S1A show neighbor-joining (NJ) and maximum-likelihood (ML) trees of the MYH14s. Both trees show almost the same phylogenetic relationship, indicating the reliability of the phylogenetic relationships observed in this study. MYH14 was monophyletic in the amniote lineage, including humans, chickens, and coelacanths, but was duplicated in the ray-finned fish lineage, except for the spotted gar (Figure 2A). Therefore, both MYH14s in teleost fish are paralogous genes that diverged at the base of neoteleostei lineage. MYH14 paralogs were separated, except for zebrafish, according to the presence or absence of miR-499 in their introns. Note that accelerated evolution was clearly observed in MYH14s lacking miR-499 by their large genetic distance from MYH14 possessing miR-499, suggesting a functional relationship between MYH14 and miR-499.
The miR-499s phylogenetic relationships (Figure 2B and Additional file 1: Figure S1B) were consistent with those of the MYH14s. Although the bootstrap value in each node was quite low, three zebrafish miR-499 paralogs, miR-499-1, -2, and −3, were divided into two clades. Zebrafish miR-499-1 formed a single cluster with other teleost fish miR-499s.
The combined phylogenetic and synteny analyses suggest that the MYH14/miR-499 locus was duplicated early in teleost evolution and one of the duplicated miR-499 genes was lost in the common ancestor to cod and the Acanthopterygii, after the split from the zebrafish lineage. Additionally, MYH14s have seemingly been lost at independent points of teleost evolution.
miR-499 expression in medaka
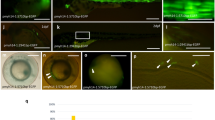
To find out whether miRNA-499 can be expressed despite lacking its host gene, its expression in medaka was examined by in situ hybridization and next-generation sequencing. We observed that medaka miR-499 was expressed at the embryonic stage in the notochord (Figure 3A), miR-499 expression in the notochord has not been previously reported in other animals. At the hatching stage, miR-499 was expressed in cardiac and trunk skeletal muscles (Figure 3B, C). The transverse sections of the medaka larva clearly showed miR-499 expression in the heart (Figure 3D) and the lateral surface of the myotomal muscle (Figure 3E) where slow muscle fibers are present. These expression patterns are consistent with those of their mammalian and zebrafish counterparts. To localize miR-499 transcripts in adult medaka, in situ hybridization was performed with transverse sections of trunk skeletal and cardiac muscles. Unlike the embryonic and larval stages, the adult medaka only exhibited strong miR-499 expression in the cardiac muscle (Figure 3F-H). This miR-499 expression pattern in the adult stage was also confirmed by next-generation sequencing (Figure 3I). Although miR-499 was detected in the adult medaka tissues examined, much higher miR-499 reads were obtained from the cardiac muscle (reads per million [RPM] = 20,624) when compared with skeletal muscle (544), eye (256), brain (40), intestine (22), testis (11), and ovary tissues (0) (Figure 3I).
miR-499 expression in medaka. Whole mount of a medaka embryo at 5 days post fertilization (dpf) (A) and a hatching larva at 10 dpf (B). miR-499 transcripts were detected in the notochord of the embryo and in cardiac and trunk skeletal muscles in the hatching larva. C) Ventral view of miR-499 expression in the heart of a 10-dpf larva. D) Transverse section of cardiac muscle at the position indicated in panel B. E) Transverse section from trunk skeletal muscle at the position indicated in panel B. Arrows indicate miR-499 expression in superficial slow muscle fibers. Transverse sections of adult cardiac (F) and trunk skeletal muscles (G). H) Higher magnification of the square indicated in panel G. miR-499 was expressed in cardiac but not in trunk muscle at the adult stage. I) miR-499 expression confirmed by next-generation sequencing. Vertical axis indicates miR-499 read numbers in each tissue. Scale bars: A-C, 500 μm; D-H, 200 μm.
Sequence analysis of MYH14/miR-499 locus flanking regions
Intronic miRNAs can be independently transcribed from their host gene by using their own promoter positioned immediately upstream of miRNAs [19]. For medaka, miR-499 is transcribed lacking its host gene MYH14, which suggests the presence of its own promoter for transcription. Figure 4A shows comparisons of torafugu MYH14-1 (MYH M5 ) flanking regions with corresponding regions in zebrafish MYH14-1 and medaka miR-499. In the case of medaka, MYH14 was completely absent, with the exception of miR-499 (Figure 4A and Additional file 2: Figure S2) and an intron immediately downstream of miR-499 (intronic conserved region in Figure 4A, Additional file 3: Figure S3). Interestingly, the torafugu and zebrafish MYH14s 5′-flanking sequences showed clear similarity with those of medaka miR-499 (5′-upstream conserved regions in Figure 4A, Additional file 4: Figure S4). Although the conservation in the zebrafish MYH14-1 5′-flanking region was not so obvious, it still contained several highly conserved regions (Additional file 4: Figure S4).
Medaka miR-499 characteristics. (A) Comparison of the flanking and related sequences of torafugu MYH14-1 (MYH M5 ) with zebrafish MYH14-1 and medaka miR-499. Highly conserved (>75%) regions between the two sequences are indicated by red-shaded peaks. Several highly conserved regions were identified at the MYH14/miR-499 5′-flanking and intron, as shown in blue boxes. (B) Putative secondary structures of mirtron (Caenorhabditis elegans miR-62) and miR-499.
Secondary structure of the miR-499 stem-loop sequence
Intronic miRNA is transcribed as pre-mRNA from a part of an intron in the host gene [20]. miRNA endowed by an intron folds to form a local double-stranded stem-loop structure called the primary miRNA (pri-miRNA). In animals, RNase III drosha crops pri-miRNA at the stem-loop during splicing and produces a precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA), which is then processed by dicer to form mature miRNA. From these canonical intronic miRNAs, a new type of intronic miRNA called mirtron has been discovered. Mirtrons are embedded in short introns, and their biogenesis does not require drosha cropping. The pre-miRNA of mirtron is produced directly by splicing [21–23]. Figure 4B shows miR-499 predicted stem-loop structures from medaka, torafugu, and the representative mirtron, miR-62, from Caenorhabditis elegans. miR-499s have longer stem-loop regions than those of mirtrons and are processed by drosha to produce pre-miRNAs. The torafugu MYH14 intron containing miR-499 is 247 bp in length (see Additional file 2: Figure S2), which is long enough to produce canonical miRNA hairpins to be cut by drosha. These results combined suggest that miR-499 is not a mirtron but a canonical intronic miRNA. However, experimental proof is required to confirm whether miR-499 requires drosha processing.
Discussion
Figure 5 shows the putative evolutionary history of the MYH14/miR-499 locus in teleost fish. It has been proven that after two rounds of whole genome duplication (WGD) in a common ancestor of vertebrates, a third WGD occurred in the fish lineage [24–28]. This fish-specific WGD occurred at the base of the Teleostei lineage, after diverging from ancient fish groups such as Polypteriformes, Acipenseriformes, and Lepisosteidae [29]. Our phylogenetic analysis clearly shows duplication of the MYH14/miR-499 locus after the divergence of spotted gar, indicating that the teleostei-specific WGD provided present-day MYH14/miR-499 paralogs in teleost fish. TRPC4AP and SULF2 genes located next to MYH14, were also duplicated in the fish-specific WGD. However, information on Osteoglossomorpha, Elopomorpha, Clupeomorpha, and Protacanthopterygii, which are important fish groups comprised of neoteleostei, was not reviewed in this study. Therefore, further analysis is required to fully reveal MYH14/miR-499 evolution in fish.
Putative evolutionary history of MYH14 and miR-499 in the fish lineage. The common ancestor of amniotes and fish had a single miR-499 containing MYH14. Neoteleostei-specific whole genome duplication formed two sets of MYH14/miR-499 pairs. In the zebrafish lineage, additional tandem duplication resulted in three MYH14/miR-499 pairs. In torafugu, green spotted puffer, and tilapia, redundancy in miR-499 caused the deletion of one of the two miR-499 paralogs. In the stickleback and Atlantic cod lineage, an additional gene loss occurred in one of the two MYH14 paralogs and loss of the remaining MYH14 gene resulted in its complete elimination from the medaka genome.
The existence of multiple MYH14 and miR-499 genes in various teleost fish suggests their expressional and functional versatilities. Torafugu MYH14-1 (MYH M5 ) expression was observed in both slow and cardiac muscles in the developmental and adult stages, whereas MYH14-2 (MYH M3383 ) expression was restricted to adult slow muscle [13, 14]. Zebrafish MYH14-1 was expressed in both slow and cardiac muscles in the early developmental stages and in slow and intermediate muscles in the adult stage [15]. Furthermore, our present study demonstrates that medaka miR-499 expression differed from the above-mentioned MYH14expression patterns (see Figure 3). It would be interesting to determine whether such differences in MYH14 and miR-499 are related to physiological and ecological variations among teleost fish species. Fish are the most diverse vertebrate group consisting of over 22,000 species. In response to the wide range of environmental and physiological conditions they encounter, the characteristics of fish musculature, including muscle fiber-type composition, are also highly diverse. Medaka makes a particularly interesting subject because of the complete elimination of MYH14 from its genome. Although muscle fiber-type composition has not been well characterized in medaka, Ono et al. [30] reported an MYH gene specifically expressed in slow muscle fibers at the horizontal myoseptum. Such MYH expression has never been reported in other teleost fish species. In contrast, medaka fast muscle exhibits high plasticity to adapt to temperature fluctuations by changing MYH expression [18, 31]. Further comparative analyses of MYH14 and miR-499 may shed light on the mechanisms involved in the formation of species-specific musculature evolution.
The loss of the intronic miRNA in the ancestor of cod and the Acanthopterygii might be explained by functional redundancy. The loss of intronic miRNA from the host gene is possible if mutations are introduced into an intron without any effect on the function and expression of the host gene. Stickleback, medaka, and Atlantic cod display the opposite pattern with the intronic miRNA lacking its host gene. Intronic miRNAs are transcribed with their host genes, and thus, coordinated expression between an intronic miRNA and its host gene is frequently observed [32]. In the present study, however, medaka miR-499 was actually expressed in various tissues despite the absence of MYH14 (see Figure 3). How does intronic miRNA remain after the loss of its host gene? We speculate that miR-499 is a canonical intronic miRNA produced by drosha cropping (see Figure 4B). Recent studies have revealed that splicing and pre-miRNA cropping by drosha are independent processes, indicating that splicing is not essential for intronic miRNA production [33]. In other words, severe mutations of the host gene may not affect the production of intronic miRNAs in the presence of the host gene transcriptional system. Interestingly, sequence comparison analysis showed highly conserved 5′-flanking regions between torafugu MYH M5 and medaka miR-499 (see Figure 5A). The spatio-temporal expression of the major skeletal MYHs in teleost fish is regulated by small regions scattered throughout the 5′-flanking sequence [18, 30, 34, 35]. Recently, Yeung et al. [36] reported promoter activity in a 6.2-kb upstream sequence of mouse MYH14 that mimics endogenous MYH14 and miR-499 expression. Therefore, these conserved regions in the 5′-flanking sequence may act as a promoter for the spatio-temporal expression of MYH14, and the regulatory sequences are conserved in medaka miR-499 despite the loss of the MYH14 gene. We could also speculate that miR-499 has its own promoter as do some intronic miRNAs. In fact, Matthew et al. [37] reported uncoupled MYH14 and miRNA-499 expression in mice, suggesting the independent transcriptional regulation of miR-499 from MYH14. Isik et al. [38] found a conserved region immediately upstream of some intronic miRNAs in C. elegans and demonstrated in promoter activity the conserved region. An intronic sequence immediately downstream of miR-499 is conserved among zebrafish, torafugu, and medaka, as shown in Figure 4A, which could be the miR-499 promoter. These findings can potentially explain why miR-499 has remained despite the loss of MYH14 in some teleost fish genomes. To our knowledge, this is the first report that describes the conversion of intronic into non-intronic miRNA during evolution. Comparative analysis of transcriptional regulation between intronic and intergenic miR-499s will provide new insights into miRNA evolution.
Methods
Fish
All procedures in this study were performed according to the Animal Experimental Guidelines for The University of Tokyo. Live adult medaka specimens (average body weight of 0.78 g) were reared in local tap water with a circulating system at 28.5°C under a 14:10-h light–dark photoperiod, at a fish rearing facility in the Department of Aquatic Bioscience, The University of Tokyo. Tissue for RNA extraction was dissected after instant euthanasia by decapitation and stored in RNAlater (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA, USA). Embryos were obtained by natural spawning and raised at 28.5°C. The developmental stage was determined by the number of days post fertilization.
Construction of a physical map around MYH14 and miR-499
The Ensembl genome browser (http://www.ensembl.org/index.html) was used to determine the syntenic organization in the region surrounding MYH14 and/or miR-499 in vertebrates. The database versions used were as follows: human (GRCh37), chicken (Galgal4), coelacanth L. chalumnae (LatCha1), zebrafish D. rerio (Zv9), torafugu T. rubripes (FUGU4), green spotted puffer T. nigroviridis (TETRAODON8), tilapia O. niloticus (Orenil1.0), Atlantic cod G. morhua (gadMor1), stickleback G. aculeatus (BROADS1), platyfish X. maculatus (Xipmac4.4.2), and medaka O. latipes (MEDAKA1). The pre Ensembl browser (http://pre.ensembl.org/index.html) was used for analysis of spotted gar L. oculatus (LepOcu1).
Bioinformatics analysis
The MYH14 and miR-499 sequence data were retrieved from the available genome databases mentioned above (Table 1). NJ and ML trees were constructed on the basis of the MYH14 coding and miR-499 stem-loop sequences using MEGA5 [39] with 1000 bootstrap replications. The Nei and Gojyobori method [40] (Jukes-Cantor) was employed to consider synonymous and non-synonymous substitutions for the MYH14 NJ tree. The Tajima-Nei model [41] was employed for the miR-499 NJ tree, whereas the Tamura-Nei model [42] was used for the MYH14 and miR-499 ML trees. The torafugu MYH14-1 (MYH M5 ), zebrafish MYH14-1 5′- and 3′-flanking sequences, and the medaka miR-499 stem-loop sequences, which contain Snai1 and TRPC4AP genes, were retrieved from the Ensembl genome browser. The homology search on the flanking sequences was carried out using the mVISTA alignment program through the vista server (http://genome.lbl.gov/vista/index.shtml). Putative secondary structures of the miR-499 from medaka and torafugu stem-loop sequences and that of the C. elegans mirtron miR-62 (miRBase accession number: MI0000033) were predicted using the RNA fold program CentroidFold (http://www.ncrna.org/centroidfold).
Small RNA library construction and sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from the muscle, intestine, eye, brain, heart, ovary, and testis of adult medaka using a mirVana™ miRNA Isolation Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Small RNAs (less than 40 nucleotides in size) were purified from total RNA using a flashPAGE™ Fractionator (Applied Biosystems), and the small RNA libraries were constructed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Library sequencing was performed with SOLiD™ next-generation sequencer (Applied Biosystems). After elimination of low-quality reads using perl scripts of our own design, 102, 602, 452 reads of 35 nucleotides were obtained. The 18–25 nucleotide reads were subjected to a Blast search against known mature miRNA sequences deposited in miRBase 18.0 (http://www.mirbase.org/). The sequences with their seed regions (2–8 nucleotides from the 5′-end) showing 100% identity to those of known mature miR-499 sequences were annotated as medaka miR-499. Gene expression was represented as reads per million (RPM), which corresponds to (total reads of a given gene/total reads in the tissue) × 106. Sequence data sets used in this study were deposited at the DDBJ Sequence Read Archive under the accession number DRA001039 and DRA001040.
In situ hybridization
We used a digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled MiRCURY detection probe (Exiqon, Copenhagen, Denmark), an LNA-modified oligo DNA probe containing the miR-499 mature sequence (5′-AAACATCACTGCAAGTCTTAA-3′), to detect miR-499 transcripts. In situ hybridizations were performed according to Kloosterman et al. [43]. The adult, embryo, and larval medaka trunk skeletal and cardiac muscles were fixed in 4% PFA at 4°C overnight. Transverse sections of the tissues were cut at 16-μm thickness. All hybridizations were performed at 66°C, which was 20°C below the predicted melting temperature (Tm) of the LNA probe. Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-DIG antibody (Roche Diagnostics, Penzberg, Germany) and nitroblue tetrazolium chloride/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate were used for signal detection with an MVX10 stereomicroscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
References
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C: Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 2011, 91: 1447-1531. 10.1152/physrev.00031.2010.
Mahdavi V, Chambers AP, Nadal-Ginard B: Cardiac alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes are organized in tandem. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984, 81: 2626-2630. 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2626.
Saez LJ, Gianola KM, McNally EM, Feghali R, Eddy R, Shows TB, Leinwand LA: Human cardiac myosin heavy chain genes and their linkage in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15: 5443-5459. 10.1093/nar/15.13.5443.
Weiss A, McDonough D, Wertman B, Acakpo-Satchivi L, Montgomery K, Kucherlapati R, Leinwand L, Krauter K: Organization of human and mouse skeletal myosin heavy chain gene clusters is highly conserved. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999, 96: 2958-2963. 10.1073/pnas.96.6.2958.
Shrager JB, Desjardins PR, Burkman JM, Konig SK, Stewart SK, Su L, Shah MC, Bricklin E, Tewari M, Hoffman R, Rickels MR, Jullian EH, Rubinstein NA, Stedman HH: Human skeletal myosin heavy chain genes are tightly linked in the order embryonic-IIa-IId/x-ILb-perinatal-extraocular. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000, 21: 345-355. 10.1023/A:1005635030494.
Desjardins PR, Burkman JM, Shrager JB, Allmond LA, Stedman HH: Evolutionary implications of three novel members of the human sarcomeric myosin heavy chain gene family. Mol Biol Evol. 2002, 19: 375-393. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004093.
van Rooij E, Quiat D, Johnson BA, Sutherland LB, Qi X, Richardson JA, Kelm RJ, Olson EN: A family of microRNAs encoded by myosin genes governs myosin expression and muscle performance. Dev Cell. 2009, 17: 662-673. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.10.013.
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004, 116: 281-297. 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5.
McCarthy JJ, Esser AK, Peterson AC, Dupont-Versteegden EE: Evidence of MyomiR network regulation of β-myosin heavy chain gene expression during skeletal muscle atrophy. Physiol Genomics. 2009, 39: 219-226. 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00042.2009.
Hagiwara N, Yeh M, Liu A: Sox6 is required for normal fiber type differentiation of fetal skeletal muscle in mice. Dev Dyn. 2007, 236: 2062-2076. 10.1002/dvdy.21223.
von Hofsten J, Elworthy S, Gilchrist MJ, Smith JC, Wardle FC, Ingham PW: Prdm1- and Sox6-mediated transcriptional repression specifies muscle fiber type in the zebrafish embryo. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9: 683-689. 10.1038/embor.2008.73.
Watabe S, Ikeda D: Diversity of the pufferfish Takifugu rubripes fast skeletal myosin heavy chain genes. Comp Biochem Physiol. 2006, 1: 28-34.
Ikeda D, Ono Y, Snell P, Edwards YJ, Elgar G, Watabe S: Divergent evolution of the myosin heavy chain gene family in fish and tetrapods: evidence from comparative genomic analysis. Physiol Genomics. 2007, 32: 1-15. 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00278.2006.
Akolkar DB, Kinoshita S, Yasmin L, Ono Y, Ikeda D, Yamaguchi H, Nakaya M, Erdogan O, Watabe S: Fibre type-specific expression patterns of myosin heavy chain genes in adult torafugu Takifugu rubripes muscles. J Exp Biol. 2010, 213: 137-145. 10.1242/jeb.030759.
Kinoshita S, Bhuiyan SS, Ceyhun SB, Asaduzzaman M, Asakawa S, Watabe S: Species-specific expression variation of fish MYH14, an ancient vertebrate myosin heavy chain gene orthologue. Fish Sci. 2011, 77: 847-853. 10.1007/s12562-011-0375-2.
Wang X, Ono Y, Tan CS, Chai RJ, Philip C, Ingham PW: Prdm1a and miR-499 act sequentially to restrict Sox6 activity to the fast-twitch muscle lineage in the zebrafish embryo. Development. 2011, 138: 4399-4404. 10.1242/dev.070516.
Ikeda D, Clark MS, Liang CS, Snell P, Edwards YJK, Elgar G, Watabe S: Genomic structural analysis of the pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain genes. Mar Biotechnol. 2004, 6: S462-S467.
Liang CS, Kobiyama A, Shimizu A, Sasaki T, Asakawa S, Shimizu N, Watabe S: Fast skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain gene cluster of medaka Oryzias latipes enrolled in temperature adaptation. Physiol Genomics. 2007, 29: 201-214.
Monteys AM, Spengler RM, Wan J, Tecedor L, Lennox KA, Xing Y, Davidson BL: Structure and activity of putative intronic miRNA promoters. RNA. 2010, 16: 495-505. 10.1261/rna.1731910.
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC: Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009, 10: 126-139. 10.1038/nrm2632.
Berezikov E, Chung WJ, Willis J, Cuppen E, Lai EC: Mammalian mirtron genes. Mol Cell. 2007, 28: 328-336. 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.028.
Okamura K, Hagen JW, Duan H, Tyler DM, Lai EC: The mirtron pathway generates microRNA-class regulatory RNAs in drosophila. Cell. 2007, 130: 89-100. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.028.
Ruby JG, Jan CH, Bartel DP: Intronic microRNA precursors that bypass drosha processing. Nature. 2007, 448: 83-86. 10.1038/nature05983.
Amores A, Force A, Yan YL, Joly L, Amemiya C, Fritz A, Ho RK, Langeland J, Prince V, Wang YL, Westerfield M, Ekker M, Postlethwait JH: Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science. 1998, 282: 1711-1714.
Elgar G, Clark MS, Meek S, Smith S, Warner S, Edwards YJ, Bouchireb N, Cottage A, Yeo GS, Umrania Y, Williams G, Brenner S: Generation and analysis of 25 Mb of genomic DNA from the pufferfish Fugu rubripes by sequence scanning. Genome Res. 1999, 9: 960-971. 10.1101/gr.9.10.960.
Postlethwait JH, Woods IG, Ngo-Hazelett P, Yan YL, Kelly PD, Chu F, Huang H, Hill-Force A, Talbot WS: Zebrafish comparative genomics and the origins of vertebrate chromosomes. Genome Res. 2000, 10: 1890-1902. 10.1101/gr.164800.
Woods IG, Kelly PD, Chu F, Ngo-Hazelett P, Yan YL, Huang H, Postlethwait JH, Talbot WS: A comparative map of the zebrafish genome. Genome Res. 2000, 10: 1903-1914. 10.1101/gr.10.12.1903.
Smith SF, Snell P, Gruetzner F, Bench AJ, Haaf T, Metcalfe JA, Green AR, Elgar G: Analyses of the extent of shared synteny and conserved gene orders between the genome of Fugu rubripes and human 20q. Genome Res. 2002, 12: 776-784.
Hoegg S, Brinkmann H, Taylor JS, Meyer A: Phylogenetic timing of the fish-specific genome duplication correlates with the diversification of the teleost fish. J Mol Evol. 2004, 59: 190-203. 10.1007/s00239-004-2613-z.
Ono Y, Kinoshita S, Ikeda D, Watabe S: Early development of medaka Oryzias latipes muscles as revealed by transgenic approaches using embryonic and larval types of myosin heavy chain genes. Dev Dyn. 2010, 239: 1807-1817. 10.1002/dvdy.22298.
Liang CS, Ikeda D, Kinoshita S, Shimizu A, Sasaki T, Asakawa S, Shimizu N, Watabe S: Myocyte enhancer factor 2 regulates expression of medaka Oryzias latipes fast skeletal myosin heavy chain genes in a temperature-dependent manner. Gene. 2008, 407: 42-53. 10.1016/j.gene.2007.09.016.
Baskerville S, Bartel DP: Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. 2005, 11: 241-247. 10.1261/rna.7240905.
Kim YK, Kim VN: Processing of intronic microRNAs. EMBO J. 2007, 26: 775-783. 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601512.
Yasmin L, Kinoshita S, Akolkar DB, Asaduzzaman M, Ikeda D, Ono Y, Watabe S: A 5′-flanking region of embryonic-type myosin heavy chain gene, MYH M743-2 , from torafugu (Takifugu rubripes) regulates developmental muscle-specific expression. Comp Biochem Physiol. 2010, 6: 76-81.
Asaduzzaman M, Kinoshita S, Bhuiyan SS, Asakawa S, Watabe S: Multiple cis-elements in the 5′-flanking region of embryonic/larval fast-type of the myosin heavy chain gene of torafugu, MYH M743-2 , function in the transcriptional regulation of its expression. Gene. 2011, 489: 41-54. 10.1016/j.gene.2011.08.005.
Yeung F, Chung E, Guess MG, Bell ML, Leinwand LA: Myh7b/miR-499 gene expression is transcriptionally regulated by MRFs and EOS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40: 7303-7318. 10.1093/nar/gks466.
Matthew LB, Massimo B, Leslie AL: Uncoupling of expression of an intronic microRNA and its myosin host gene by exon skipping. Mol Cell Biol. 2010, 30: 1937-1945. 10.1128/MCB.01370-09.
Isik M, Hendrik CK, Berezikov E: Expression patterns of intronic microRNAs inCaenorhabditis elegans. Silence. 2010, 1: 1-5. 10.1186/1758-907X-1-1.
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S: MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011, 28: 2731-2739. 10.1093/molbev/msr121.
Nei M, Gojobori T: Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986, 3: 418-426.
Tajima F, Nei M: Estimation of evolutionary distance between nucleotide sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 1984, 1: 269-285.
Tamura K, Nei M: Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol. 1993, 10: 512-526.
Kloosterman WP, Wienholds E, de Bruijn E, Kauppinen S, Plasterk RH: In situ detection of miRNAs in animal embryos using LNA-modified oligonucleotide probes. Nat Methods. 2006, 3: 27-29. 10.1038/nmeth843.
Acknowledgment
This study was partly supported by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors have no financial or other competing interests to declare.
Authors’ contributions
B.S.S. and K.S. were involved in the conception and design, and data acquisition and interpretation. W.C. carried out next-generation sequencing data retrieval and analysis, and A.M. assisted in fish breeding and data analysis. A.S. and S.W. participated in research design, coordination, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Sharmin Siddique Bhuiyan, Shigeharu Kinoshita contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
12862_2012_2425_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1: Figure S1: MYH14 and mIR-499 phylogenetic analysis. MYH14 (A) and miR-499 (B) maximum-likelihood (ML) trees. Bootstrap values from 1000 replicates analysis are given at the nodes as percentage values. (PDF 177 KB)
12862_2012_2425_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Additional file 2: Figure S2: Sequence comparison of the intron containing miR-499 among torafugu, zebrafish, and medaka. Shaded sequences are highly conserved regions among the three fish species. Mature miR-499 sequences are boxed. Bold letters indicate 5′ and 3′ intron splice sites. Numbers on the right indicate the positions of the MYH14 (torafugu and zebrafish) start codon and mature miR-499 (medaka) 5′-end. Nucleotide sequences were aligned by CLUSTALW. (PDF 89 KB)
12862_2012_2425_MOESM3_ESM.zip
Additional file 3: Figure S3: Intronic conserved regions in MYH14 among torafugu, zebrafish, and medaka. The red box shows highly conserved regions among the three fish species. Bold letters indicate 5′ and 3′ splice intron sites. Numbers on the right indicate the positions of the MYH14 (torafugu and zebrafish) start codon and mature miR-499 (medaka) 5′-end. Nucleotide sequences were aligned by CLUSTALW. (ZIP 138 KB)
12862_2012_2425_MOESM4_ESM.zip
Additional file 4: Figure S4: 5′-flanking conserved regions in MYH14 among torafugu, zebrafish, and medaka. The red and gray boxes show highly conserved regions between torafugu and medaka, and among the three fish species, respectively. Bold letters indicate 5′ and 3′ splice intron sites. Numbers on the right indicate the positions of the MYH14 (torafugu and zebrafish) start codon and mature miR-499 (medaka) 5′-end. Nucleotide sequences were aligned by CLUSTALW. (ZIP 170 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuiyan, S.S., Kinoshita, S., Wongwarangkana, C. et al. Evolution of the myosin heavy chain gene MYH14 and its intronic microRNA miR-499: muscle-specific miR-499 expression persists in the absence of the ancestral host gene. BMC Evol Biol 13, 142 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-142
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-142