Abstract
Background
FOXP2 is a forkhead transcription factor critical for normal development of language in humans, but little is known of its broader function and regulation during central nervous system (CNS) development. We report here that lef1, a member of the Lef/Tcf family of transcription factors activated by Wnt signaling, regulates foxP2 during embryogenesis, and we isolate novel foxP2 enhancers which are lef1-dependent.
Results
Loss, knock down, or inhibition of lef1 led to loss of foxP2 expression. We isolated DNA fragments from the foxP2 genomic region that function as enhancers to drive GFP expression in the CNS during development, including in the telencephalon, diencephalon, eye, tectum, and hindbrain. Three of these enhancers, foxP2-enhancerA.1, foxP2-enhancerB, and foxP2-enhancerD, contain putative Lef1 binding sites, and are regulated by lef1. However, two other genomic fragments containing Lef1 sites failed to function in vivo as enhancers. Chromatin immunoprecipitation confirmed that Lef1 binds to sites in foxP2-enhancerA.1 and foxP2-enhancerB.
Conclusion
This work shows that lef1 is necessary for expression of foxP2 in the tectum, mid-hindbrain boundary, and hindbrain during CNS development, and is the first insight into the upstream regulation of foxP2 during development. We also demonstrate that in silico prediction of potential lef1 binding sites poorly predicts their ability to function in vivo as enhancers. The foxP2 enhancers we identified will allow dissection of foxP2's role during CNS development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
FOXP2 is a forkhead domain transcription factor whose mutation has been associated with severe deficits in language [1–6]. Its cloning and expression during development have been described in humans, mouse, songbird, frog, medaka, and zebrafish [7–16]. CNS expression during development in the different vertebrate species is remarkably similar, with conserved expression in the telencephalon, basal ganglia, thalamus, tectum, tegmentum, cerebellum, and hindbrain. However, the function of FOXP2 during CNS development is poorly understood. Homozygous knockout or point mutation of Foxp2 in mice leads to early postnatal death, with reports of disordered Purkinje cell layers [17–19] and smaller cerebellar size [18, 20]. In songbirds, FoxP2 appears to be necessary for vocal learning and is expressed in neurons during active song learning [9, 21, 22].
The neural circuits and genetic cascades in which FOXP2 participates remain uncharacterized. Chromatin immunoprecipitation methods have identified potential downstream targets of FOXP2 [23, 24], but in vivo function and importance of the identified targets is uncertain. To understand in greater detail the role of foxP2 in CNS development, we sought to identify how foxP2 expression is regulated. The conservation of six predicted lef1 binding sites between pufferfish, zebrafish, mouse, and human in the foxP2 genomic region (this study; [25], and the overlapping expression of lef1 and foxP2 in the zebrafish CNS during development, led us to consider whether lef1 might regulate foxP2. Lef1 is a transcription factor activated by the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which has been shown to play a critical role in proliferation, tissue patterning, CNS neuronal cell fate specification, and axon pathfinding [26]. We found that loss or knockdown of lef1 led to a loss of foxP2 expression in the tectum, mid-hindbrain boundary, and hindbrain. Of six conserved potential lef1 binding sites predicted in the foxP2 genomic region [25], we show that only three lie in genomic fragments that function in vivo as enhancers, underscoring the importance of in vivo testing of predicted enhancers. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), we demonstrated that lef1 can bind directly to the functional enhancer sites, and showed that in the absence of lef1 these enhancers fail to function. The foxP2 enhancers will be useful for dissection of foxP2 function by allowing detailed analysis of axon pathfinding and synaptogenesis in foxP2-expressing neurons.
Results
foxP2 and lef1have sequential and overlapping expression in the CNS during embryogenesis
We noted that 6 binding sites for Tcf/Lef transcription factors are conserved between mouse and pufferfish in the FOXP2 genomic region, which is more than for any other putative Tcf/Lef target gene (Table S6 of [25]. This finding, and our prior observations that foxP2 and lef1 are expressed in the tectum and hindbrain during CNS embryogenesis [7, 27], raised the possibility that lef1 might regulate foxP2 expression. We performed in situ labeling for foxP2 and lef1 to investigate whether they shared temporal and/or spatial domains of expression. We found that lef1 is expressed in the mid-hindbrain boundary (MHB) starting at 24 hpf, and in the tectum starting at 30 hpf (Figure 1A–C). foxP2 expression in the MHB and tectum becomes apparent at 36 hpf (Figure 1D–F). Other domains of lef1 and foxP2 expression, including the telencephalon, hypothalamus, and dorsal diencephalon, had non-overlapping expression. To confirm that foxP2 and lef1 are indeed co-expressed in the same cells, rather than in distinct subsets of cells in the same region, we performed double in situs, and found that foxP2 and lef1 are co-expressed in tectal cells at 36 hpf (Figure 2A–D). This sequentially overlapping pattern of expression in the MHB, and contemporaneous overlap in the tectum, confirmed that lef1 was present in a relevant pattern to potentially direct foxP2 expression.
Sequential expression of foxP2 and lef1 in the CNS during embryogenesis. Whole-mount in situs for lef1 (A-C) and foxP2 (D-F) at 24 hpf, 30 hpf, and 36 hpf. Lateral views, anterior to left, dorsal up; eyes have been removed to facilitate visualization. Scale bar = 50 μm. (Abbreviations: dd, dorsal diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; mhb, mid-hindbrain boundary; tec, tectum; tel, telencephalon.) (A-C): lef1 is expressed in the hypothalamus, dorsal midbrain, and MHB at 24 hpf, with expression extending to the tectum at 30 hpf. By 36 hpf expression is confined primarily to the hypothalamus and tectum. (D-F): foxP2 is expressed in the tectum and MHB starting at 36 hpf. Earlier expression (24 hpf and 30 hpf) is confined to the telencephalon.
Co-expression of foxP2 and lef1 in the tectum. Whole-mount double in situ confocal imaging for foxP2 and lef1 at 36 hpf, dorsal views, anterior up. Abbreviations: hb, hindbrain; tec, tectum; tel, telencephalon. (A) Z-stack projection of foxP2 (green) overlaid on brightfield image of lef1 expression in the tectum. The region shown in higher magnification in (B-D) is boxed in yellow. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B-D) Single optical plane showing lef1 (red- BM Purple), foxP2 (green- Alexa 488), and co-expression in the tectum. Arrow points to a representative co-expressing cell. Scale bar = 25 μm.
Knockdown of lef1 causes loss of foxP2expression
Based on this overlap of expression, we hypothesized that lef1 might regulate foxP2. To test this, we used several approaches. First, we used a morpholino to knockdown lef1 [27], and evaluated foxP2 in situ expression. Knockdown of lef1 causes a near-complete loss of foxP2 expression in the tectum, MHB, and hindbrain at 36 hpf (Figure 3A, B) in 85% of injected embryos (n = 61), compared with 0% of uninjected embryos (n = 53). This effect is specific to lef1, since a morpholino against a different Lef/Tcf family member, tcf3b [28], which is also expressed in the tectum and hindbrain [28], showed no effect on foxP2 expression (n = 48, data not shown). The loss of foxP2 expression in the hindbrain, where lef1 expression is not detectable by in situ (Figure 1A–C), is presumably an indirect effect, perhaps via loss of an inductive signal from the MHB. Alternatively, this could be a direct effect, for example, if lef1 is expressed at very low levels in the hindbrain, or if some lef1-positive neurons migrate from the MHB to the hindbrain.
Loss of lef1 leads to absent foxP2 expression in the tectum, mid-hindbrain boundary, and hindbrain. Whole-mount in situs at 36 hpf; anterior to left, dorsal up, eyes removed. Scale bar = 50 μm. (Conditions: hs:Δtcf, Tg(hsp70l:Δtcf-GFP)w26; lef1 mo, lef1 morphants; wt, wild type; x8, homozygous Df(LG01)x8. Abbreviations: hb, hindbrain; mhb, mid-hindbrain boundary; tec, tectum; tel, telencephalon.) (A, B) lef1 morphant (B) lacks expression in tectum, MHB, and hindbrain (arrows), compared to wild-type (A). (C) Df(LG01)x8 homozygote lacks expression in tectum, MHB, and hindbrain (arrows). (D) Tg(hsp70l:Δtcf:GFP)w26 embryo, three hours post-heat shock, lacks expression in tectum, MHB, and hindbrain (arrows). (E, F) mbx in situs; staining in tectum and hindbrain is indistinguishable between wild type and lef1 morphants (F).
To confirm that loss of foxP2 expression was due to knockdown of lef1 and not a non-specific morpholino effect, we utilized two alternative means to remove lef1 expression. First, we examined expression of foxP2 in Df(LG01)x8 mutant embryos. Df(LG01)x8 is a deletion on chromosome 1 which contains lef1 (but not foxP2); homozygous deficiency mutants do not express lef1 [27, 29]. We found that homozygous Df(LG01)x8 mutants do not express foxP2 in the tectum, MHB, or hindbrain (Figure 3C) (100%, n = 25 embryos).
Second, we examined whether a dominant negative construct which inhibits lef1 function would cause a loss of foxP2 expression. We used embryos carrying the transgene hsp70l:Δtcf-GFP, which expresses an N-terminal deletion of Tcf3a fused to GFP. In the absence of its N-terminal DNA-binding domain, Tcf3a acts as a dominant repressor of Wnt-mediated transcription [30]. Following heat-shock at 32 hpf for 1 hour, embryos were collected 3 hours post-heat shock. There was loss of foxP2 expression in the tectum, MHB, and hindbrain (Figure 3D) in 61% of transgenic embryos (n = 38), and in 0% of non-transgenic siblings (n = 82). Decrease of foxP2 telencephalic expression is presumably due to a dominant effect of the transgene, since the decrease was not seen using the morpholino or Df(LG01)x8.
The loss of foxP2 expression in the tectum and hindbrain is not secondary to an absence of cells, as expression of the tectal marker mbx [31] is indistinguishable between wild type and lef1 morphants (Figure 3E, F). Other markers for the tectum (emx2), and hindbrain (isl1, zash1a) of lef1 morphants also appear as wild type patterns and levels [27]; J.E.L. and R.I.D., unpublished data). Furthermore, the loss of foxP2 expression persists at 48 hpf (Additional File 1). These results show that loss of lef1 specifically causes loss of foxP2 expression in the tectum, MHB, and hindbrain.
Identification of foxP2genomic enhancers and Lef1 binding sites
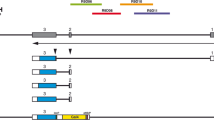
6 potential conserved binding sites for lef/tcf family transcription factors were identified in the FOXP2 genomic locus of mouse and pufferfish using in silico analysis [25]. This algorithm (enhancer element locator) aligns transcription factor sequence sites from orthologous genomic regions between two species, with scoring of the sites determined by conservation, affinity, and clustering of sites. Based on conserved synteny between zebrafish, mouse, and pufferfish, we initially were able to identify 5 of these sites in the zebrafish foxP2 genomic locus using Sanger Centre genome assembly Zv6 (see Methods; Figure 4A).
Genomic structure and identification of enhancers of foxP2. (A) foxP2 genomic region (not to scale). Coding exons are shown as solid black boxes. Predicted lef1 binding sites are shown as ovals. DNA fragments tested for enhancer activity are shown. (B) Schematic of cloning strategy for DNA fragments. PCR primers for the genomic region of interest (red box) are designed with attB4 and attB1 sites (blue boxes), and the region is amplified and cloned using a BP reaction into an entry clone. A LR reaction is performed to recombine the entry clone (containing the genomic DNA fragment) into a Tol2 destination vector, placing the genomic fragment upstream of a basal promoter and EGFP (green box). (C) Summary table of expression patterns of the different enhancers at 72 hpf in the CNS.
Because the foxP2 genomic assembly is incomplete in the region upstream of the 2nd coding exon (J.L.B., unpublished data), we sought to identify the sixth predicted lef1 binding site. In human FOXP2 this site is 8.8 kb upstream of the first coding exon. We obtained the sequence for this region in zebrafish from the unassembled BAC DKEY-116L11. Using the enhancer element locator algorithm [25], we compared the 9 kb regions immediately upstream of the first coding exon of foxP2 from the human and zebrafish genomes. We found conservation of this same element (zebrafish: ttgtgggctGCTTTCATCtgtgggttaa; human: atgatcagtGCTTTCATCtttattttaa) located 8.5 kb upstream of the first coding exon in zebrafish (contained within foxP2-enhancerA).
To identify foxP2 enhancers, and to determine whether any of the potential lef1 sites might function in vivo in the context of enhancer elements, we cloned genomic fragments containing the sites into a Tol2 transposon-based vector (Figure 4B) [32–34]. To visualize expression controlled by the potential enhancers, each DNA fragment was cloned immediately upstream of GFP under control of a minimal promoter [32]. In total we cloned nine genomic DNA fragments (Figure 4A), from five different regions, containing the six predicted lef1 sites (two sites are contained in foxP2-fragmentC). To test for expression, we injected one cell stage embryos and assayed GFP expression from 12 hpf through 96 hpf (Figure 4C). Subsequent analysis used stable transgenic lines, which mostly reproduced the same patterns of expression. Three of the regions, foxP2-enhancerA, B, and D, drove GFP expression in patterns partially recapitulating foxP2 expression (Figure 5). Potential enhancers foxP2-fragmentC and foxP2-fragmentE had no expression.
Confocal live whole-mount images of foxP2 enhancers. Pictures show GFP expression at 72 hpf (except foxP2-enhancerD, taken at 48 hpf). The eye has been removed in panels E and G to facilitate visualization. Scale bar = 100 μm. (A, C, E, G, I): lateral views, anterior left, dorsal up. (B, D, F, H, J): dorsal views, anterior up. (Abbreviations: di, diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; tec, tectum; tel, telencephalon; arrows, GFP-expressing cells in the eye. (A, B) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA:EGFP)zc42; (C, D) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44; (E, F) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.2:EGFP)zc46; (G, H) Tg(foxP-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41; (I, J) Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47.
foxP2-enhancerA drove expression in the eye, diencephalon, tectum, hindbrain, and telencephalon (Figure 5A, B). GFP expression was first noted in the telencephalon at 24 hpf, then at 48 hpf in the eye, tectum and hindbrain, becoming maximal at 72 hpf. By 80 hpf expression in the CNS diminished significantly, while jaw expression became visible. Subcloning of foxP2-enhancerA to yield enhancerA.1 and A.2 revealed very similar patterns to foxP2-enhancerA (Figure 5C–F). However, enhancerA.2 had significantly fewer labeled cells, suggesting that the more proximal region of enhancerA and enhancerA.1 contains necessary elements. foxP2-enhancerB expression in the telencephalon began at 24 hpf, with eye and hindbrain expression apparent by 72 hpf (Figure 5G, H). foxP2-enhancerD expression in the eye, dorsal diencephalon, and tectum began at 36 hpf, was maximal at 48 hpf, and decreased by 72 hpf (Figure 5I, J).
The enhancers we have identified partially mirror endogenous foxP2 expression [7]. While the enhancer fragments were chosen based on in silico prediction of potential lef1 binding sites [25], our analysis shows the importance of in vivo validation, since only 3 of the 6 predicted binding sites appear to lie in functional enhancer elements for the stages analyzed.
lef1knockdown leads to loss of expression from foxP2-enhancers A.1, B, and D
Based on our observations that foxP2-enhancers A.1, B, and D show expression in a pattern mirroring lef1 expression in the tectum and hindbrain, and contained putative binding sites for Lef1, we tested whether knockdown of lef1 led to loss of GFP expression. We injected lef1 morpholino into stable transgenic foxP2 enhancer lines (Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44, Tg(foxP2-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41, Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47), and looked for GFP expression in the tectum and hindbrain at 36 hpf. To detect enhancer-driven transcription with maximum sensitivity, we used an in situ probe for gfp. Morphants showed a loss of GFP expression in the tectum and hindbrain, but maintenance of telencephalic expression, in 89% of enhancerA.1 embryos (n = 71), 100% of enhancerB embryos (n = 22), and 100% of enhancerD embryos (n = 27) (Figure 6A–F). In contrast, in uninjected embryos only 2%, 0%, and 0% (n = 58, 15, and 16), respectively, showed loss of tectum and hindbrain expression. Further, the lef1-mediated loss of expression from the enhancers was visible at 52 hpf by visualization of GFP (Additional File 2).
lef1 is necessary for expression from foxP2-enhancerA.1, foxP2-enhancerB, and foxP2-enhancerD. Whole-mount gfp in situs at 36 hpf; anterior to left, dorsal up, eyes removed. Scale bar = 50 μm. Conditions (wild type, wt; or lef1 morphant, lef1 MO) are shown above the panels, enhancer names to left. (Abbreviations: dd, dorsal diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; tec, tectum; tel, telencephalon.) (A) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44expresses in telencephalon, tectum, and hindbrain. (B) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44embryo injected with lef1 morpholino lacks GFP expression in tectum and hindbrain (arrows), although telencephalic expression persists. (C) Tg(foxP2-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41expresses in telencephalon and hindbrain. (D) Tg(foxP2-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41embryo injected with lef1 morpholino lacks GFP expression in the hindbrain (arrow), but telencephalic expression is present. (E) Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47expresses in dorsal diencephalon and tectum. (F) Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47embryo injected with lef1 morpholino lacks GFP expression in the tectum (arrow), but dorsal diencephalic expression persists. (G) Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8embryo shows GFP expression in all post-mitotic neurons. (H) Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8embryo injected with lef1 morpholino still has GFP expression in the tectum and hindbrain.
To demonstrate that loss of GFP expression in the lef1 morphants was not simply due to absence of the GFP-expressing cells, we injected lef1 morpholino into transgenic fish lines Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8(also known as HuC:GFP) and Tg(pax2a:GFP)e1. Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8expresses GFP in all post-mitotic neurons [35], while Tg(pax2a:GFP)e1expresses GFP in a pattern mirroring pax2a expression, including in the MHB, cerebellum, and hindbrain [36]. In both lines we found that lef1 morphants still expressed GFP in the tectum, MHB, and hindbrain (Figure 6G, H, and Additional File 2). In addition, using Tg(isl3:GFP)zc7 to label retinal axons (A. Pittman and C.B.C., unpublished), we observed that the pattern of retinotectal projections appeared normal in 48 hpf morphants (data not shown). Although overall numbers of GFP-expressing cells appeared reduced in lef1 morphants of Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8and Tg(pax2a:GFP)e1, in the foxP2 enhancer lines there was a complete lack of GFP-expressing cells in the tectum and hindbrain. These results show that loss of tectal and hindbrain expression observed with the lef1 morpholino in foxP2-enhancerA.1, foxP2-enhancerB, and foxP2-enhancerD is not simply due to a loss of neurons, but instead indicates a requirement for lef1 in these enhancers' function.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation identifies critical Lef1 binding sites in foxP2-enhancerA.1 and foxP2-enhancerB
To test whether Lef1 can bind to foxP2-enhancerA.1 and foxP2-enhancerB to regulate foxP2 expression, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using a polyclonal antibody against zebrafish Lef1 [27]. We designed PCR amplicons to test different regions of foxP2-enhancerA.1 and foxP2-enhancerB (Figure 7A), using chromatin extracted from 30 hpf embryos. For foxP2-enhancerA.1, we found that PCR amplicon FP2700 (centered around base pair 2700 in the enhancerA.1 DNA fragment) showed significant enrichment compared to controls (no antibody, and extracts from homozygous Df(LG01)x8 embryos) (Figure 7B). Interestingly, amplicon FP300, encompassing the predicted Lef1 binding site in foxP2-enhancerA.1 (Figure 7A), showed minimal enrichment (Figure 7B). Further, a deletion construct of foxP2-enhancerA:GFP, removing the region containing FP300, did not cause loss of GFP expression (data not shown). This suggests that maximal Lef1 binding for foxP2-enhancerA.1 is centered around FP2700. For foxP2-enhancerB, we found that FPb2600 had significant enrichment compared to controls (Figure 7C). This PCR amplicon contains a predicted Lef1 binding site [25] (Figure 7A). We therefore conclude that Lef1 directly interacts with regulatory regions of foxP2 in 30 hpf zebrafish embryos.
ChIP analysis of foxP2-enhancerA.1 and foxP2-enhancerB genomic regions at 30 hpf. (A) Diagram of foxP2-enhancerA.1 and foxP2-enhancerB regions. PCR amplicon locations and names are indicated above the genomic region; predicted Lef1 binding sites are shown as ovals. (B) Agarose gel analysis of ChIP PCR for foxP2-enhancerA.1, showing the PCR products for FP2700, FP300, and B3end. In wild type (wt) embryos, ChIP shows significant enrichment of the FP2700 product and slight enrichment of the FP300 product, compared to both the no antibody (Ab) control, and the ChIP of homozygous Df(LG01)x8 embryos (Mock: water control for the PCR reaction.) In contrast, the B3end product showed no enrichment relative to the Df(LG01)x8 embryos. (C) Agarose gel analysis of ChIP PCR for foxP2-enhancerB, showing the FPb2600 PCR product. In wt embryos, ChIP shows significant enrichment of the FPb2600 product, compared to both the no antibody and homozygous Df(LG01)x8 controls.
Discussion
Our data show that lef1 and foxP2 expression overlap in the developing CNS, and that lef1 is necessary for foxP2 expression in the tectum, MHB, and hindbrain. We identified Lef1binding sites in the foxP2 regulatory regions, based on the identification of foxP2 enhancers that depend on lef1 for expression, and ChIP analysis showing binding of Lef1 to these enhancers.
lef1 regulation appears to be a combination of both direct and indirect effects on foxP2 (Figure 8). In the tectum and MHB, lef1 expression precedes foxP2 expression. Loss of lef1 leads to loss of both endogenous foxP2 expression, and expression from foxP2 enhancers. In the hindbrain loss of lef1 also leads to a loss of foxP2 expression. Since lef1 expression is not detectable in the hindbrain, we hypothesize that loss of foxP2 expression occurs both via an inductive effect of lef1 expression in the MHB, and through a second gene regulated by lef1 (Figure 8). This model would explain why we observe foxP2 expression (both by in situ and by expression from its enhancers) in the hindbrain (where lef1 is not expressed), as well as why foxP2 expression persists after lef1 expression in the MHB stops. In addition, our data demonstrate that foxP2 expression in the telencephalon, including the subpallium/basal ganglia, is regulated independently of lef1.
Model of foxP2 regulation in the CNS. In the telencephalon, an unknown factor X activates foxP2 expression. In the tectum (and MHB) Lef1 directly binds to enhancer elements of foxP2, leading to foxP2 expression. In the hindbrain expression of foxP2 is Lef1-dependent, but indirectly, since Lef1 is not expressed in the hindbrain.
Since foxP2 expression in the telencephalon is not lef1-dependent, other factors must regulate foxP2. Conversely, in regions where lef1 is expressed but foxP2 is not, for example the dorsal diencephalon, lack of foxP2 expression could either reflect an absence of some necessary co-factors, or the presence of an inhibitor of expression, or both mechanisms. We have tried to globally activate foxP2 by heat-shock induction of a constitutively active form of tcf3 (RID, unpublished data), but did not observe any ectopic foxP2 expression (data not shown), implying stringent, multifactorial control of foxP2 expression.
Previous computer algorithm-based methods identified several other potential Lef1 binding sites in the foxP2 genomic region [25], but our in vivo analysis failed to support a role for them. Another recently described in silico method to identify transcription factor target genes would also fail to identify the lef1 enhancers for foxP2, as this method only included the 5 kb regions immediately upstream of transcriptional start sites [37]. Our work shows the importance of actual in vivo testing for analysis of enhancer gene regulation.
Since we analyzed expression up to 96 hours after fertilization, enhancers responsible for controlling expression at later times might have been missed. Given that all of the CNS domains of expression for foxP2 are present by 72 hpf [7, 11], we feel that this is unlikely. However, we can not exclude the possibility that untested genomic regions might regulate expression, or that several independent regions might function in concert.
This study identified three regions functioning as enhancers for foxP2, specifically driving expression in the telencephalon, eye, diencephalon, tectum, and hindbrain. Their expression reveals that foxP2 is expressed in multiple brain regions, under strict temporal and spatial control, regulated through both lef1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. These transgenic lines label multiple distinct axon tracts (data not shown), and will allow analysis of subsets of foxP2 neurons and axons, in both wild type and mutant backgrounds, as well as misexpression and rescue experiments.
The role of foxP2 in CNS development has remained elusive, despite multiple genetic studies in humans demonstrating its necessity for normal language development [1–6]. In affected members of the human KE family, who carry a heterozygous point mutation which disrupts the function of one copy of FOXP2, voxel-based morphometric MRI analyses suggest disturbances in Broca's area, the basal ganglia, and the cerebellum [38, 39]. Studies of FoxP2 knockout or point mutation mice have consistently shown cerebellar involvement. Homozygotes have been reported to have disordered Purkinje cell layering [17–19, 40] and smaller cerebellar size [18, 20], while heterozygotes are noted to display impaired motor learning and altered Purkinje cell synaptic plasticity [19, 20]. Our identification of lef1 as a regulator of foxP2 expression in the MHB and hindbrain is a first step towards understanding the foxP2 genetic network involved in cerebellar development. The role of the cerebellum in language function is at least partially understood [41], but it is uncertain whether the oromotor apraxia of the KE family is due to defects of cerebellar or striatal pathways (or both) [40, 42, 43]. Importantly, other domains of foxP2 expression, for example in the telencephalon (including the subpallium), appear to be regulated independently of lef1.
Conclusion
Wnt signaling has multiple roles in neuronal specification and the development of connectivity in the CNS [26], as does lef1, which is activated by the canonical Wnt signaling cascade. lef1 is necessary for development of dentate gyrus neurons [44], for neurogenesis and specification of neuronal subsets in the hypothalamus [27], and for expression of the transcription factors zic2a and zic5 in the tectum [45]. Here we show that lef1 regulates foxP2 expression in the tectum, MHB, and hindbrain. Interestingly, ChIP studies suggest that FOXP2 may in turn regulate components of the Wnt signaling pathway [23, 24]. The identification of components of the foxP2 signaling cascade, including upstream, interacting, and downstream members, will be important for understanding foxP2 function, and for elucidating the genes and neural circuits involved in language development.
Methods
Fish stocks and embryo raising
Adult fish were bred according to standard methods. Embryos were raised at 28.5°C in E3 embryo medium with 0.003% phenylthiourea to inhibit pigment formation and staged by time and morphology [46]. For in situ staining, embryos were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) (in PBS) for 3 h at room temperature (RT) or overnight (O/N) at 4°C, washed briefly in PBS, dehydrated, and stored in 100% MeOH at -20°C until use.
Transgenic fish lines and alleles used were as follows: Df(LG01)x8 [29]; Tg(hsp70l:Δtcf-GFP)w26[30]; Tg(foxP2-enhancerA:EGFP)zc42; Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44; Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.2:EGFP)zc46; Tg(foxP2-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41; Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47; Tg(pax2a:GFP)e1[36]; Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8[35]. Df(LG01)x8 homozygotes were identified by their smaller forebrain and flattened hindbrain phenotype (J.E.L. and R.I.D., unpublished). Tg(hsp70l:Δtcf-GFP)w26embryos were identified by GFP expression after heat shock.
Heat shock was performed by incubation of 32 hpf embryos for 1 hour at 37°C, then collecting 3 hours after the end of the heat shock.
In situhybridization
Whole-mount in situ labeling for foxP2, gfp, and lef1 was performed as previously described [7, 27, 47]; the mbx RNA probe derived from full-length mbx cDNA cloned into pBluescript [31]. Double in situs were performed using a DNP-labeled probe for foxP2 and digoxigenin-labeled probe for lef1. Following standard hybridization and washes, DNP probe was detected using an anti-DNP HRP conjugate diluted 1:200 in TNTB block at 4°C overnight (PerkinElmer; [48]), followed by detection using Alexa Fluor 488 Tyramide diluted 1:250 (Molecular Probes) with 0.0015% hydrogen peroxide for 1 hour. Embryos were washed in TNT, blocked in TNTB, incubated with anti-digoxigenin alkaline phosphatase diluted 1:5000 in TNTB at 4°C overnight, and then detected with a standard BM Purple color reaction.
Genomic PCR and Enhancer Cloning
PCR primers to clone foxP2 genomic fragments were as follows (forward and reverse primers, sequences 5' to 3'; size in kb listed immediately following the enhancer name): foxP2-enhancerA (9.7 kb): FP2.12L GTCGTAATTGCTCGGTGAC, FP2.3R GTGTGAATGCCAGCGATAGA; foxP2-enhancerA.1 (6.8 kb): FP2.12L, FP2.16R CGTCTCGACTGAGCAGAGTT; foxP2-enhancerA.2 (5.1 kb): FP2.12L, FP2.46R ACAACTGGCGTGTAAGGTGT; foxP2-fragment A.3 (4.7 kb): FP2.41L GACACCTTACACGCCAGTTG, FP2.3R; foxP2-fragment A.4 (2.3 kb): FP2.41L, FP2.40R CAGGGTGTGTTATAAACATGCAT; foxP2-enhancerB (4.6 kb): FP2.39L GACACTCTGGAGGAACTATG, FP2.38R GGAAACGGTGCAGTATGTGT; foxP2-fragment C (1.6 kb): F.FP1 GGCGGGTACCTGGTCATATT, F.RP2 TTTCCACCCAACCATAAATCA; foxP2-enhancerD (1.2 kb): H.FP1 CCAGCTATCCGAGAGGTTCA, H.RP2 CCGCCTGTTCAAATCAGAAT; foxP2-fragment E (0.69 kb): G.FP1 TGACCTCTGTGTAGCCTTGC, G.RP2 CATTGCTAGGGGAACGTGAT.
PCR was performed using standard conditions (TaKaRa LA PCR amplification kit 2.1, Millipore) from total genomic DNA, and PCR fragments gel purified prior to cloning (Qiagen gel purification kit). BP and LR reactions (Gateway cloning system, Invitrogen) were performed to clone the DNA fragments upstream of an adenovirus E1b minimal promoter and carp β-actin transcriptional start fused to EGFP (pENTRbasEgfp) in a Tol2 plasmid backbone (pTolR4-R2) [32, 33, 49]. BP reactions were performed by adding attB4 sequence to the 5' primer (5'-GGGGACAACTTTGTATAGAAAAGTTG-gene specific primer-3'), and attB1 sequence to the 3' primer (5'-GGGGACTGCTTTTTTGTACAAACTTG-gene specific primer-3'). The identity of the genomic fragments was confirmed by restriction enzyme digests and partial sequencing.
Injection of DNA constructs and raising of stable transgenic lines was performed essentially as described [33, 49]. 20 pg of each enhancer:EGFP-Tol2 construct was co-injected with 20 pg of Tol2 transposase RNA in a total volume of 1 nL at the 1-cell stage. Embryos were screened for GFP expression from 12 hpf through 96 hpf. Patterns of enhancer expression were confirmed by multiple independent transient injections of the plasmid (> 5 injections for all constructs, > 100 embryos per injection), as well as isolation of 2 or more independent stable transgenic lines (in cases where stable transgenics were isolated).
Morpholino oligonucleotide sequences
The lef1 and tcf3b splice-blocking morpholinos (MO) were synthesized by Gene Tools (Philomath, OR); efficacy and use were as previously described [27, 28, 50, 51]. For lef1, 2 ng of morpholino E7I7 was injected; for tcf3b, 5 ng was injected.
Microscopy and image analysis
Whole-mount images were taken using brightfield microscopy with embryos mounted in 80% glycerol. Confocal microscope images of live embryos were taken after mounting embryos anesthetized using tricaine (0.004%) in 1.5% low melt agarose dissolved in 0.33× PBS/7.3% glycerol. Image acquisition and analysis were performed as described previously [52]. Confocal images of double in situs were taken on an Olympus FV1000 after mounting embryos in 80% glycerol. BM Purple fluorescence was imaged with 633 nm excitation, collecting emission from 700–800 nm [53].
Sequence Analysis
We used coordinate conversion ("convert" function) in the UCSC genome web server http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/hgTracksHelp.html#Convert[54] to identify conserved lef1 binding sites in the foxP2 region of zebrafish, based on predicted Tcf4 binding sites positions in the human genome (since Tcf4 and Lef1 bind to a shared motif) [25]. The genomic upstream sequence of foxP2 was obtained by performing a BLAST search against unfinished sequences in the Sanger Centre Danio rerio sequencing project (sequence for foxP2-enhancerA is contained in BAC DKEY-116L11; GenBank accession CU468733). To identify the sixth potential Lef1 binding site in the foxP2-enhancerA region predicted by Hallikas et al. [25], we used the enhancer element locator algorithm (available at http://www.cs.helsinki.fi/u/kpalin/EEL/, and compared the 9 kb regions upstream of the first coding exon of human and zebrafish FOXP2 using the Tcf4 consensus binding motif.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
ChIP was performed as previously described [27, 55] with the following modifications. 80–120 embryos of each genotype (wild type or homozygous Df(LG01)x8) were collected between 28 hpf and 30 hpf, dechorionated, and fixed in 2.2% formaldehyde for 15 minutes at room temperature. Embryos were rinsed in 0.125 M glycine, followed by PBS, and then lysed. The Df(LG01)x8 lysate was checked by genomic PCR for the lef1 gene to confirm that no PCR product was obtained. PCR products were visualized on ethidium bromide-stained agarose gels. Primers used for ChIP analysis of the foxP2-enhancerA.1 genomic region were the following (forward and reverse primers, sequences 5' to 3'): FP300, CGACTCTCCGCGAAACAC, CATTGCCATTATCACCAGCA; FP900, CCTATCAAAGGCAGGCAGA, TTATCGCACTAAACAAGCTATTACAC; FP1800, CACAGAGTGAAGTCATGGAGAAA, AGCGCACGCACAACTAATC; FP2700, AGAGAAACGGATAAACAGTGAGAAG, CCCTCTCGAACCCTCAAAA; B3end, TGATTAACGCCGTCTTTTCC, AGCGCACGCACAATAAAATA. Primers used for ChIP analysis of the foxP2-enhancerB genomic region were (forward and reverse primers, sequences 5' to 3'): FPb200, AGCTGGAAGGAAGTGTCTGG, TTTTGGCATGTGCAAAGAAG; FPb1500, GCGTATGTATGCTTGTCAGGTT, TGCGTGGTGTTTTACTTGGA; FPb2600, CAGATCGACGGATGATACACA, TTCCGCCAATTATCATGTCA; FPb3800, GACCCCTTCGCAATGTCTAAT, TTCGAGAAATGCTTGCACAC.
Abbreviations
- ChIP:
-
chromatin immunoprecipitation
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- MHB:
-
mid-hindbrain boundary
References
Lai CS, Fisher SE, Hurst JA, Vargha-Khadem F, Monaco AP: A forkhead-domain gene is mutated in a severe speech and language disorder. Nature. 2001, 413: 519-23.
Feuk L, Kalervo A, Lipsanen-Nyman M, Skaug J, Nakabayashi K, Finucane B, Hartung D, Innes M, Kerem B, Nowaczyk MJ, et al: Absence of a paternally inherited FOXP2 gene in developmental verbal dyspraxia. Am J Hum Genet. 2006, 79: 965-72.
Lennon PA, Cooper ML, Peiffer DA, Gunderson KL, Patel A, Peters S, Cheung SW, Bacino CA: Deletion of 7q31.1 supports involvement of FOXP2 in language impairment: clinical report and review. Am J Med Genet A. 2007, 143: 791-8.
MacDermot KD, Bonora E, Sykes N, Coupe AM, Lai CS, Vernes SC, Vargha-Khadem F, McKenzie F, Smith RL, Monaco AP, et al: Identification of FOXP2 truncation as a novel cause of developmental speech and language deficits. Am J Hum Genet. 2005, 76: 1074-80.
Zeesman S, Nowaczyk MJ, Teshima I, Roberts W, Cardy JO, Brian J, Senman L, Feuk L, Osborne LR, Scherer SW: Speech and language impairment and oromotor dyspraxia due to deletion of 7q31 that involves FOXP2. Am J Med Genet A. 2006, 140: 509-14.
Shriberg LD, Ballard KJ, Tomblin JB, Duffy JR, Odell KH, Williams CA: Speech, prosody, and voice characteristics of a mother and daughter with a 7;13 translocation affecting FOXP2. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2006, 49: 500-25.
Bonkowsky JL, Chien CB: Molecular cloning and developmental expression of foxP2 in zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 2005, 234: 740-6.
Ferland RJ, Cherry TJ, Preware PO, Morrisey EE, Walsh CA: Characterization of Foxp2 and Foxp1 mRNA and protein in the developing and mature brain. J Comp Neurol. 2003, 460: 266-79.
Haesler S, Wada K, Nshdejan A, Morrisey EE, Lints T, Jarvis ED, Scharff C: FoxP2 expression in avian vocal learners and non-learners. J Neurosci. 2004, 24: 3164-75.
Lai CS, Gerrelli D, Monaco AP, Fisher SE, Copp AJ: FOXP2 expression during brain development coincides with adult sites of pathology in a severe speech and language disorder. Brain. 2003, 126: 2455-62.
Shah R, Medina-Martinez O, Chu LF, Samaco RC, Jamrich M: Expression of FoxP2 during zebrafish development and in the adult brain. Int J Dev Biol. 2006, 50: 435-8.
Shu W, Yang H, Zhang L, Lu MM, Morrisey EE: Characterization of a new subfamily of winged-helix/forkhead (Fox) genes that are expressed in the lung and act as transcriptional repressors. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276: 27488-97.
Takahashi K, Liu FC, Hirokawa K, Takahashi H: Expression of Foxp2, a gene involved in speech and language, in the developing and adult striatum. J Neurosci Res. 2003, 73: 61-72.
Teramitsu I, Kudo LC, London SE, Geschwind DH, White SA: Parallel FoxP1 and FoxP2 expression in songbird and human brain predicts functional interaction. J Neurosci. 2004, 24: 3152-63.
Schon C, Wochnik A, Rossner A, Donow C, Knochel W: The FoxP subclass in Xenopus laevis development. Dev Genes Evol. 2006, 216: 641-6.
Itakura T, Chandra A, Yang Z, Xue X, Wang B, Kimura W, Hikosaka K, Inohaya K, Kudo A, Uezato T, et al: The medaka FoxP2, a homologue of human language gene FOXP2, has a diverged structure and function. J Biochem. 2007
Shu W, Cho JY, Jiang Y, Zhang M, Weisz D, Elder GA, Schmeidler J, De Gasperi R, Sosa MA, Rabidou D, et al: Altered ultrasonic vocalization in mice with a disruption in the Foxp2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 102: 9643-8.
French CA, Groszer M, Preece C, Coupe AM, Rajewsky K, Fisher SE: Generation of mice with a conditional Foxp2 null allele. Genesis. 2007, 45: 440-6.
Fujita E, Tanabe Y, Shiota A, Ueda M, Suwa K, Momoi MY, Momoi T: Ultrasonic vocalization impairment of Foxp2 (R552H) knockin mice related to speech-language disorder and abnormality of Purkinje cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 3117-22.
Groszer M, Keays DA, Deacon RM, de Bono JP, Prasad-Mulcare S, Gaub S, Baum MG, French CA, Nicod J, Coventry JA, et al: Impaired synaptic plasticity and motor learning in mice with a point mutation implicated in human speech deficits. Curr Biol. 2008, 18: 354-62.
Rochefort C, He X, Scotto-Lomassese S, Scharff C: Recruitment of FoxP2-expressing neurons to area X varies during song development. Dev Neurobiol. 2007, 67: 809-17.
Haesler S, Rochefort C, Georgi B, Licznerski P, Osten P, Scharff C: Incomplete and inaccurate vocal imitation after knockdown of FoxP2 in songbird basal ganglia nucleus Area X. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5: e321-
Spiteri E, Konopka G, Coppola G, Bomar J, Oldham M, Ou J, Vernes SC, Fisher SE, Ren B, Geschwind DH: Identification of the transcriptional targets of FOXP2, a gene linked to speech and language, in developing human brain. Am J Hum Genet. 2007, 81: 1144-57.
Vernes SC, Spiteri E, Nicod J, Groszer M, Taylor JM, Davies KE, Geschwind DH, Fisher SE: High-throughput analysis of promoter occupancy reveals direct neural targets of FOXP2, a gene mutated in speech and language disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 2007, 81: 1232-50.
Hallikas O, Palin K, Sinjushina N, Rautiainen R, Partanen J, Ukkonen E, Taipale J: Genome-wide prediction of mammalian enhancers based on analysis of transcription-factor binding affinity. Cell. 2006, 124: 47-59.
Ciani L, Salinas PC: WNTs in the vertebrate nervous system: from patterning to neuronal connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005, 6: 351-62.
Lee JE, Wu SF, Goering LM, Dorsky RI: Canonical Wnt signaling through Lef1 is required for hypothalamic neurogenesis. Development. 2006, 133: 4451-61.
Dorsky RI, Itoh M, Moon RT, Chitnis A: Two tcf3 genes cooperate to pattern the zebrafish brain. Development. 2003, 130: 1937-47.
Phillips BT, Kwon HJ, Melton C, Houghtaling P, Fritz A, Riley BB: Zebrafish msxB, msxC and msxE function together to refine the neural-nonneural border and regulate cranial placodes and neural crest development. Dev Biol. 2006, 294: 376-90.
Lewis JL, Bonner J, Modrell M, Ragland JW, Moon RT, Dorsky RI, Raible DW: Reiterated Wnt signaling during zebrafish neural crest development. Development. 2004, 131: 1299-308.
Kawahara A, Chien CB, Dawid IB: The homeobox gene mbx is involved in eye and tectum development. Dev Biol. 2002, 248: 107-17.
Villefranc JA, Amigo J, Lawson ND: Gateway compatible vectors for analysis of gene function in the zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 2007, 236: 3077-87.
Kwan KM, Fujimoto E, Grabher C, Mangum BD, Hardy ME, Campbell DS, Parant JM, Yost HJ, Kanki JP, Chien CB: The Tol2kit: A multisite gateway-based construction kit for Tol2 transposon transgenesis constructs. Dev Dyn. 2007, 236: 3088-3099.
Kawakami K: Transgenesis and gene trap methods in zebrafish by using the Tol2 transposable element. Methods Cell Biol. 2004, 77: 201-22.
Park HC, Kim CH, Bae YK, Yeo SY, Kim SH, Hong SK, Shin J, Yoo KW, Hibi M, Hirano T, et al: Analysis of upstream elements in the HuC promoter leads to the establishment of transgenic zebrafish with fluorescent neurons. Dev Biol. 2000, 227: 279-93.
Picker A, Scholpp S, Bohli H, Takeda H, Brand M: A novel positive transcriptional feedback loop in midbrain-hindbrain boundary development is revealed through analysis of the zebrafish pax2.1 promoter in transgenic lines. Development. 2002, 129: 3227-39.
Del Bene F, Ettwiller L, Skowronska-Krawczyk D, Baier H, Matter JM, Birney E, Wittbrodt J: In vivo validation of a computationally predicted conserved Ath5 target gene set. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3: 1661-71.
Liegeois F, Baldeweg T, Connelly A, Gadian DG, Mishkin M, Vargha-Khadem F: Language fMRI abnormalities associated with FOXP2 gene mutation. Nat Neurosci. 2003, 6: 1230-7.
Belton E, Salmond CH, Watkins KE, Vargha-Khadem F, Gadian DG: Bilateral brain abnormalities associated with dominantly inherited verbal and orofacial dyspraxia. Hum Brain Mapp. 2003, 18: 194-200.
Alcock KJ, Passingham RE, Watkins KE, Vargha-Khadem F: Oral dyspraxia in inherited speech and language impairment and acquired dysphasia. Brain Lang. 2000, 75: 17-33.
Ackermann H: Cerebellar contributions to speech production and speech perception: psycholinguistic and neurobiological perspectives. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31: 265-72.
Vargha-Khadem F, Gadian DG, Copp A, Mishkin M: FOXP2 and the neuroanatomy of speech and language. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005, 6: 131-8.
Vargha-Khadem F, Watkins K, Alcock K, Fletcher P, Passingham R: Praxic and nonverbal cognitive deficits in a large family with a genetically transmitted speech and language disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995, 92: 930-3.
Galceran J, Miyashita-Lin EM, Devaney E, Rubenstein JL, Grosschedl R: Hippocampus development and generation of dentate gyrus granule cells is regulated by LEF1. Development. 2000, 127: 469-82.
Nyholm MK, Wu SF, Dorsky RI, Grinblat Y: The zebrafish zic2a-zic5 gene pair acts downstream of canonical Wnt signaling to control cell proliferation in the developing tectum. Development. 2007, 134: 735-46.
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF: Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 1995, 203: 253-310.
Dorsky RI, Sheldahl LC, Moon RT: A transgenic Lef1/beta-catenin-dependent reporter is expressed in spatially restricted domains throughout zebrafish development. Dev Biol. 2002, 241: 229-37.
Denkers N, Garcia-Villalba P, Rodesch CK, Nielson KR, Mauch TJ: FISHing for chick genes: Triple-label whole-mount fluorescence in situ hybridization detects simultaneous and overlapping gene expression in avian embryos. Dev Dyn. 2004, 229: 651-7.
Fisher S, Grice EA, Vinton RM, Bessling SL, Urasaki A, Kawakami K, McCallion AS: Evaluating the biological relevance of putative enhancers using Tol2 transposon-mediated transgenesis in zebrafish. Nat Protoc. 2006, 1: 1297-305.
Bonner J, Gribble SL, Veien ES, Nikoaus OB, Weidinger G, Dorsky RI: Distinct pathways mediate patterning and proliferation in the dorsal spinal cord downstream of canonical Wnt signaling. Dev Biol.
Bonner J, Gribble SL, Veien ES, Nikolaus OB, Weidinger G, Dorsky RI: Proliferation and patterning are mediated independently in the dorsal spinal cord downstream of canonical Wnt signaling. Dev Biol. 2008, 313: 398-407.
Suli A, Mortimer N, Shepherd I, Chien CB: Netrin/DCC signaling controls contralateral dendrites of octavolateralis efferent neurons. J Neurosci. 2006, 26: 13328-37.
Trinh LA, McCutchen MD, Bonner-Fraser M, Fraser SE, Bumm LA, McCauley DW: Fluorescent in situ hybridization employing the conventional NBT/BCIP chromogenic stain. BioTechniques. 2007, 42: 756-759.
Karolchik D, Baertsch R, Diekhans M, Furey TS, Hinrichs A, Lu YT, Roskin KM, Schwartz M, Sugnet CW, Thomas DJ, et al: The UCSC Genome Browser Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31: 51-4.
Weinmann AS, Bartley SM, Zhang T, Zhang MQ, Farnham PJ: Use of chromatin immunoprecipitation to clone novel E2F target promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 2001, 21: 6820-32.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Chien and Dorsky labs for their assistance. This work was supported by a PCMC Foundation grant and CHRC grant to JLB, NIH K12 HD001410 and K08 DA024753 to JLB, and NIH R01 NS053897 to RID.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
JLB and EF jointly carried out cloning and in situs. XW performed ChIP. JLB and JEL performed expression analysis. JLB, CBC, and RID conceived the study, and participated in its design and coordination. JLB was largely responsible for writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12861_2008_387_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Additional file 1: Loss of lef1 leads to absent foxP2 expression in the tectum, mid-hindbrain boundary, and hindbrain. Whole-mount in situs at 48 hpf; anterior to left, dorsal up, eyes removed. Scale bar = 50 μm. (Conditions: hs:Δtcf- Tg(hsp70l:Δtcf:GFP)w26, lef1 mo- lef1 morphants, wt- wild type, x8- homozygous Df(LG01)x8. Abbreviations: hb: hindbrain; mhb: mid-hindbrain boundary; tec: tectum; tel: telencephalon.) (A, B) lef1 morphant (B) lacks expression in tectum and has diminished expression in the hindbrain (arrows), compared to wild-type (A). (C) In Df(LG01)x8 homozygote, expression is absent in the tectum and hindbrain (arrows). (D) In Tg(hsp70l:Δtcf:GFP)w26 embryo, collected four hours after heat shocking, expression is absent from the tectum and hindbrain (arrows). MHB expression is reduced but not absent, perhaps because lef1 induction of foxP2 expression is already sufficiently established by the time of heat-shock. (TIFF 6 MB)
12861_2008_387_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
Additional file 2: lef1 is necessary for expression from foxP2-enhancerA.1, foxP2-enhancerB, and foxP2-enhancerD. Whole-mount confocal images at 52 hpf (except foxP2-enhancerD), lateral view, anterior left, dorsal up. Conditions (wild type- wt, or lef1 morphant- lef1 MO) are shown above the panels, while the enhancer name is to the left of the panels. (Abbreviations: hb: hindbrain; tec: tectum; tel: telencephalon.) (A) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44expresses in telencephalon, tectum, and hindbrain. (B) Tg(foxP2-enhancerA.1:EGFP)zc44embryo injected with lef1 morpholino: GFP expression is absent in the tectum and hindbrain (arrows), although telencephalic expression persists. (C) Tg(foxP2-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41expresses in telencephalon, tectum, and hindbrain. (D) Tg(foxP2-enhancerB:EGFP)zc41embryo injected with lef1 morpholino: GFP expression is absent in the hindbrain (arrow), but still present in the telencephalon. (E) Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47expresses in tectum. (F) Tg(foxP2-enhancerD:EGFP)zc47embryo injected with lef1 morpholino: GFP expression is absent in the tectum (arrow). (G) Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8embryo shows GFP expression in all post-mitotic neurons. (H) Tg(elavl3:EGFP)zf8embryo injected with lef1 morpholino: GFP expression is still present in the tectum and hindbrain. (I) Tg(pax2a:GFP)e1embryo shows expression in the MHB and hindbrain. (J) Tg(pax2a:GFP)e1embryo injected with lef1 morpholino has persistent expression in the MHB and hindbrain. (TIFF 20 MB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Bonkowsky, J.L., Wang, X., Fujimoto, E. et al. Domain-specific regulation of foxP2 CNS expression by lef1. BMC Dev Biol 8, 103 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-8-103
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-8-103