Abstract
Background
Along with the improvement of high throughput sequencing technologies, the genetics community is showing marked interest for the rare variants/common diseases hypothesis. While sequencing can still be prohibitive for large studies, commercially available genotyping arrays targeting rare variants prove to be a reasonable alternative. A technical challenge of array based methods is the task of deriving genotype classes (homozygous or heterozygous) by clustering intensity data points. The performance of clustering tools for common polymorphisms is well established, while their performance when conducted with a large proportion of rare variants (where data points are sparse for genotypes containing the rare allele) is less known. We have compared the performance of four clustering tools (GenCall, GenoSNP, optiCall and zCall) for the genotyping of over 10,000 samples using the Illumina’s HumanExome BeadChip, which includes 247,870 variants, 90% of which have a minor allele frequency below 5% in a population of European ancestry. Different reference parameters for GenCall and different initial parameters for GenoSNP were tested. Genotyping accuracy was assessed using data from the 1000 Genomes Project as a gold standard, and agreement between tools was measured.
Results
Concordance of GenoSNP’s calls with the gold standard was below expectations and was increased by changing the tool’s initial parameters. While the four tools provided concordance with the gold standard above 99% for common alleles, some of them performed poorly for rare alleles. The reproducibility of genotype calls for each tool was assessed using experimental duplicates which provided concordance rates above 99%. The inter-tool agreement of genotype calls was high for approximately 95% of variants. Most tools yielded similar error rates (approximately 0.02), except for zCall which performed better with a 0.00164 mean error rate.
Conclusions
The GenoSNP clustering tool could not be run straight “out of the box” with the HumanExome BeadChip, as modification of hard coded parameters was necessary to achieve optimal performance. Overall, GenCall marginally outperformed the other tools for the HumanExome BeadChip. The use of experimental replicates provided a valuable quality control tool for genotyping projects with rare variants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
More than 13,500 genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of complex human diseases have been performed since 2008 [1]. The majority of GWAS were conducted using common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays targeting markers that were identified from the international HapMap project [2–4]. These studies are based on the assumption that common traits are driven by common low-penetrance polymorphisms with a frequency of more than one or five percent in the population [5]. A vast proportion of the heritability of complex traits remains unexplained [6]. However, advances in genomic technologies now allow for the search of rare variants of modest to intermediate penetrance [7].
SNP arrays offer the possibility of rapid genotyping of thousands of samples with highly reliable results at low cost. Several commercial arrays now include a large fraction of rare single nucleotide variants (SNV) discovered by high-throughput sequencing technologies. The latter, while still expensive compared to SNP arrays, allows for the discovery of all variants, rare and common, located in the genome of sequenced individuals. The Illumina HumanExome BeadChip provides a compromise between genotyping SNP arrays and next generation sequencing by enabling the genotyping of rare SNVs in thousands of samples at relatively low cost. The HumanExome BeadChip is enriched for rare and low frequency coding variations previously identified from the sequenced exomes of approximately 12,000 individuals of diverse populations for variations seen in more than two individuals and in more than two sequencing projects [8]. Compared to other genotyping platforms targeting millions of markers, the proportion of rare variants (minor allele frequency <5%) included in the HumanExome BeadChip is considerably larger.
A recent review of clustering tools for widely used Illumina BeadChip arrays was presented by Ritchie et al.[9]. They reported that some tools performed marginally better than others for common and rare variants (lowest frequency around 0.05). The authors noted that methods borrowing information from other SNPs (e.g. within-sample information) to genotype rare variants could theoretically outperform reference-based methods, as these would suffer from the limited information available in the training sets for the homozygous and heterozygous clusters of rare alleles. Such within-sample methods are implemented in GenoSNP[10]. Some tools, such as M3[11] and optiCall[12], use a mixture of between- and within-sample approaches. Other tools, such as GenCall (available in the GenomeStudio software) [13], rely on a reference cluster file to cluster marker genotypes one at a time. The zCall tool exclusively genotypes markers that have been previously “missed” by a another tool, and was also recently described [14].
For this project, the performance of GenCall, GenoSNP, optiCall and zCall for clustering markers from the HumanExome BeadChip have been analysed and compared. With the growing interest of the community for studies with rare variants [5, 6, 15, 16], this “head to head” comparison will provide guidance for study design, tool selection and results interpretation.
Methods
Clustering tools
Four clustering tools were compared: GenCall, part of the GenomeStudio software version V2011.1 [13], GenoSNP version 1.3 [10], optiCall version 0.3.3 [12] and zCall version 3.2 [14]. All four tools differ with respect to their genotype calling method.
GenCall (GenomeStudio)
GenCall is Illumina’s proprietary tool and is available through the GenomeStudio software. For a complete description of this tool, refer to Ritchie et al.[9]. In brief, this tool uses the normalized microarray intensities for both alleles (noted X and Y) to compute the associated polar coordinates (r and θ) for each marker/sample pair. Next, using a between-sample model, meaning that it calls one marker by looking at the population of samples, it assigns genotypes by determining the nearest cluster using a reference containing the expected position of each genotype cluster for every marker as determined from the HapMap data. If required, the user may modify the position of each of the expected clusters to be more representative of the data at hand. By pre-assigning the expected position of each cluster, this method can readily provide a genotyping assignation of rare variants for studies having only a small number of samples. However, due to experimental variabilities and genomic variations in different populations, the position of the observed cluster’s centroid might shift when compared with the expected one. A considerable amount of manual cluster adjustments might be needed to achieve good genotype calls.
For this project, a custom cluster file was created by modifying the expected position of the genotype cluster’s centroid for a subset of markers by using all samples from the dataset. The markers selected for manual inspection were: (1) markers with a high heterozygous frequency, (2) markers with a low mean intensity, (3) markers with a low call frequency, (4) markers with a low minor allele frequency with no heterozygous calls, (5) markers showing an excess of heterozygous calls, (6) markers with low AA T means or low BB T meansa, (7) mitochondrial markers, (8) markers on sex chromosomes, (9) markers that fail reproducibility tests, (10) markers with a small cluster separation or (11) markers with low quality score. To compare the efficiency of this modified cluster file, the results from GenCall with the original cluster file were also included in the analysis.
GenoSNP
GenoSNP uses a within-sample model, meaning that it assigns genotypes to all markers of a single sample at once [10]. It uses raw X and Y allele intensities extracted using the GenomeStudio software and calls genotypes by fitting a four-components mixture of Student’s t-distributions on different subsets of markers (separated by Bead Pools) by the mean of a Variational Bayes Expectation Maximization algorithm (VB-EM). The use of this method improves robustness by allowing uncertainty in the statistical model, in contrast to standard expectation maximisation methods. GenoSNP computes the posterior probability of the marker genotype calls. As this tool calls one sample at a time, it offers the flexibility of providing final sample genotyping results before the whole study dataset is ready to be processed. It can also be parallelized by running the tool on multiple samples at a time, and it does not require a reference panel. It is generally expected that this tool would perform well with rare variants, as their genotypes will be clustered with higher frequency variants according to measured X and Y allele intensities (as opposed to between-sample methods, where rare variants are sparsely located in the heterozygous cluster).
To speed up the genotyping process, samples were called using GenoSNP as soon as they were released from the genotyping center. A posterior probability cutoff of 0.8 was used to achieve higher quality calls. To ascertain the quality of the results once all samples were genotyped, the mean and the median intensities of all calls for each sample were plotted.
optiCall
The optiCall tool uses a mixture of between- and within-sample models. It uses a subset of (X,Y) intensities from random samples at a random marker to find a prior distribution to the statistical model used to call genotypes across markers. This distribution is inferred by using an EM algorithm to fit a four-class mixture of Student’s t-distributions. The initial values used by the EM algorithm are obtained by using the kmeans++ algorithm [17] and the individual genotype’s a priori probabilities are assumed to be uniform (0.25 for every cluster, including the outlier’s cluster). Then, a second mixture of t-distributions is used for the between-sample clustering, where the previously estimated priors are used in a Maximum-A-Posteriori (MAP) estimate of its parameters.
To measure the quality of genotype calls, optiCall relies on deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE). The tool will try to improve the genotype calls when the HWE test fails (p<5×10-15) by fitting the previously described model without a prior.
zCall
This tool functions as a post-processing tool (after a default one has been used) [14]. The zCall tool separates the clusters for rare variants by partitioning the (X,Y) intensity space using horizontal and vertical thresholds. Their positions are derived from the mean and variance of the homozygote clusters for common variants that were previously called and are scaled according to a z-score factor to optimize concordance with the default tool. Genotypes are then assigned with respect to their position relative to the z-score scaled coordinates. Accordingly, rare variants are called by defining a distance threshold. The homozygote threshold for the major allele is estimated from the first calling tool’s genotypes, and the rare allele’s threshold is estimated by linear regression from the means and standard deviations of X and Y intensities of common markers.
As recommended by the authors, zCall was used as a post-processing step after GenCall (GenomeStudio). Version 3.2 was used, where all z thresholds were derived from GenomeStudio’s final report, from which samples were filtered out based on call rate and global heterozygosity. A z threshold of 8 was used after comparing the concordance with the original calls (maximum of 99.27%). Only missing genotypes from the original GenomeStudio report were recalled by zCall.
Dataset
The four tools were applied to a dataset consisting of 10,517 unique samples from the Montreal Heart Institute (MHI) Cohort. We also included 95 experimental replicates of NA17281, 15 replicates of NA17251 and 3 replicates of NA12763 from the Coriell Institute (the latter being sequenced by the 1000 Genomes Project[18]). Finally, 93 and 40 MHI cohort samples were replicated 3 and 2 times, respectively. All 10,520 samples (10,856 including replicated ones) were genotyped using the Illumina HumanExome BeadChip, assessing 247,870 markers including 140 insertions/deletions (which were discarded from the present analysis). Some of these markers (214,599) are present in NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project (ESP) database [19], and 93% of these are rare variants with a minor allele frequency (MAF) below 5% in the European American population according to the ESP database [19]. The research protocol was approved by the Montreal Heart Institute research ethics review board and all participants signed an informed consent.
Agreement between tools
We used Cohen’s kappa (κ) and Fleiss’ pi (π), two widely used statistics, to compute the extent of agreement between raters [20], or in this case, genotype calling tools. Cohen’s κ computes the extent of agreement between two tools by first computing the overall agreement probability (Equation 1), using a two-way contingency table (Additional file 1: Table S1), for the distribution of n samples by tools (rater) and genotype category, where n kl indicates the number of samples that tool 1 and 2 classified into genotypes k and l, respectively.
In a comparable contingency table, Cohen’s κ is estimated using Equation 2.
where p a is the observed proportion of agreement (Equation 1) and pe|κ is the proportion of agreement expected by chance.
The data can be summarized in a frequency table (Additional file 1: Table S2), where, for a given sample i and genotype k, r ik represents the total number of tools that called genotype k for sample i. Fleiss’ π is then defined by Equation 3 [21].
The possible set of genotypes included the no call genotype, as all tools might agree that a marker is impossible to be categorized in either of the three genotype clusters (homozygous or heterozygous) due to quality issues (e.g. low intensity).
Error rates
Several methods for error rate estimation (ϵ) with pedigree data have been proposed and reviewed by Liu et al. for their use with unrelated samples [22]. The genotypic model (as defined in Equation 4) provides a proper estimation of the error rate and proposes different constraints on the parameter space in order to make the model parameters identifiable.
The genotypic model was tested by Liu et al. for common variants. However, we found that the possible values of ϵ were out of bounds (i.e. negative or above one) with the HumanExome BeadChip data where a majority of markers are rare. This can be explained by the proportion of the minor allele in the population, p1, which is almost null. For these cases, ϵ was approximated using ϵ≃(C1-C3+1)/3 (Additional file 1: Equation S1).
Results and discussion
Clustering quality
GenoSNP
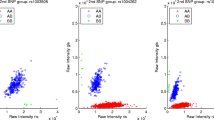
The GenoSNP tool returns the probability of belonging to one of the three genotype clusters (homozygous A, B or heterozygous AB) for each evaluated genotype. The maximal probability is used to define the genotype to be called. We observed a majority of samples with a high proportion of low quality calls (close to the 0.8 quality threshold used). Cluster plots were created for some of the poorly performing samples which raised concern about the calling quality (Figure 1A and 1D). Suspecting a lack of convergence, modifications to the tool were made to increase the number of iterations of the VB-EM procedure. This improved the quality of the clustering for some of the samples (Figure 1B and 1E). Further modifications to the initial X and Y intensities’ variance parameter from 0.1 to 100 (in addition to the increased number of iterations) greatly improved the quality of the clustering tool (Figure 1C and 1F). To efficiently ascertain the effect of the optimized parameters on the calling quality, plots of the mean and the median of the maximal probability of each sample have been created (Figure 2A and 2B respectively), showing a net increase of the probabilities. To further improve the comparison between the original GenoSNP and the modified version (300 iterations and an initial X and Y intensities’ variance of 100), the two tools (original and optimized) were used for comparison with the other tools in this study.
Impact of parameters on GenoSNP’s clustering. Impact of the choice of initial parameters on GenoSNP’s clustering of two samples (MHIC04326 shown in (A), (B) and (C), and MHIC06654 shown in (D), (E) and (F)). The first row shows the clustering results of the two samples using the default parameters (25 EM iterations and an initial variance of 0.1). The second row shows the results when keeping an initial variance of 0.1, but increasing the number of EM iterations to 300. The last row shows the results when increasing both the initial variance and the number of EM iterations to 100 and 300, respectively. In all cases, only markers in the BeadPool 1 are kept. Each point represents the raw B allele intensities against the raw A allele intensities (base two logarithm in both cases) of each marker. The AA, AB and BB genotypes are shown in blue, red and green, respectively. Markers that were below the quality threshold of 0.8 are shown in black.
GenoSNP clustering quality. Quality assessment of GenoSNP’s clustering for original (x axis) against optimized (y axis) parameters. For each sample, both the (A) mean and the (B) median of the posterior probability of all markers are shown. Each point represents a sample. A good clustering has a mean and a median calling probability close to one.
zCall
According to Goldstein et al.[14], the optimal value of the z threshold should be determined by trying different values of z to find the one with the most concordance to the original GenCall calls. Here, the optimal value of z was determined to be 8, having a concordance of 99.27% with the original data.
Missing rates
One important property of a calling tool is its capacity to assign a genotype to the majority of samples and markers (i.e. the calling rate, or inversely, the missing rate). The sample and marker missing rates of the six tools were compared (Figure 3A and 3B respectively). The original version of GenoSNP had the highest missing rate (19% for both sample and marker). The optimized version of GenoSNP increased both the mean sample and marker calling rates by 18.5% (from 80.6% to 99.1%). These rates were inferior to those of the other tools: 99.6%, 99.8%, 99.6% and 99.9% for GenCall (original and optimized cluster file), optiCall and zCall, respectively. It is important to note that the missing rate of zCall is bound to be less than or equal to that of GenCall, as zCall will only call missing genotypes from the results produced by GenCall. Also, the missing rates of GenCall were slightly better when using the optimized cluster file when compared to the original one. A non-parametric Friedman Rank Sum test comparing tools showed a statistically significant difference in both sample and marker missing rates (p-value <2.2×10-16 in both cases), even though the rates seemed similar (Figure 3). Pairwise dependent-samples non-parametric sign tests comparing pairwise tools were also significant (p-value <2.2×10-16 in all cases). More specifically, 0.55- and 0.83-fold decreases, on average, were observed for sample and marker missing rates, respectively, when comparing the original and the optimized cluster file for GenCall.
Locus and sample missing rate. Boxplots showing the distribution of (A) locus and (B) sample missing rates. Values closer to 0 (100% completeness) are preferable. Rates are shown for each of the six tools: GenCall (original and optimized cluster files), GenoSNP (original and optimized), optiCall (without excluding markers failing Hardy-Weinberg) and zCall. The median is shown with a red line and the mean is indicated above each plot. The red dots represent outliers according to the interquartile range. The rates are shown for 10,856 samples and 247,590 markers (markers located on chromosome Y were excluded).
Precision estimates
The dataset contained a high number of technical replicates. The concordance of genotype calls between replicates was computed for the five tools (Figure 4). The optimized version of GenoSNP increased concordance between sample duplicates from a mean of 95.361% to 99.912%, but did not exceed the performance of GenCall (means of 99.996% for both the original and the optimized cluster files). Even though zCall reduced the missing rate from a mean of 0.4% to 0.09%, it added variability in the newly called genotypes, slightly decreasing the concordance between replicated samples when compared with the original results (GenCall, original cluster file). Overall, the call concordance between replicates was similar (> 99% concordance). GenCall had the highest concordance rate with a mean of 99.997% between replicated sample pairs. Optimizing GenCall’s cluster file had only a minor effect on the mean concordance, with a difference of 1.5×10-3%.
Duplicated sample concordance. Boxplots showing the distribution of pairwise concordance of duplicated samples. Red lines are the median and the numbers at the bottom of the plot represent the concordance means. The red dots represent the outliers according to the interquartile range. The six tools are shown (from left to right): GenCall (original and optimized cluster files), GenoSNP (original and optimized), optiCall (without excluding markers failing Hardy-Weinberg) and zCall. A total of 4,892 sample pairs is shown.
Accuracy estimates
One sample sequenced by the 1000 Genomes Project was included three times to the original dataset to assess the concordance with next-generation sequencing. The genotypes called from the different tools were compared to the third release of the 1000 Genomes Project, comprised of low coverage whole genome and high coverage exome sequencing data. The comparison with this gold standard was performed using the pyGenClean tool [23]. Since the majority of markers in the HumanExome BeadChip are located in exons, the results were mostly compared to the high coverage sequencing data (81.6% of the overlapping markers). Table 1 shows the concordance for the three replicates of NA12763. Apart from the original GenoSNP, all the tools had concordance rates greater than 99%. GenCall (optimized cluster file) had the highest concordance rate (mean of 99.897%), closely followed by zCall (mean of 99.879%). GenCall (original cluster file) also performed well, with a mean concordance of 99.855%. Then, calls were categorized according to their allele content: either (1) homozygous calls for the common allele or (2) involving the rare allele (heterozygous or homozygous calls for the rare allele). The frequencies were computed using the corresponding dataset (i.e. tool). Table 2 shows the concordance for the three replicates of NA12763 for genotypes called as homozygous for the common allele. Apart from the original GenoSNP on one replicate, all had concordance rates greater than 99%. GenCall (original cluster file) had the highest concordance rate (mean of 99.948%), closely followed by GenCall (optimized cluster file) and zCall (mean of 99.939% and 99.928% respectively). Table 3 summarizes the concordance rates with the gold standard for genotypes involving the rare allele. GenCall (optimized cluster file) had the highest concordance rate (mean of 99.493%), closely followed by zCall (mean of 99.405%). The other tool had a lower concordance rate (i.e. between 95% and 97%).
Inter-tool agreement
To estimate tool agreement, three coefficients were computed: Cohen’s κ and percent agreement (both shown in Figure 5), and Fleiss’ π (Figure 6). Since GenCall (using the optimized version of the cluster file) provided the best result set, its agreement with the other three tools (excluding the original version of GenoSNP) was considered (Figure 5A and B). The best agreement was between GenCall and zCall, as expected due to the dependence of zCall on the results of GenCall. Both metrics showed a high number of outliers according to the interquartile range dispersionb. To assess the overall agreement between the four tools (excluding GenCall using the original cluster file and the original version of GenoSNP), Fleiss’ κ was computed (Figure 6). The agreement was fairly good between the tools when comparing all markers (common and rare). There was a total of 12,122 outliers according to the interquartile range dispersion, a majority of which (91.3%) were rare variants (MAF <1%, according to frequencies computed using GenCall results) and 5% were markers that were zeroed out while optimizing GenCall’s cluster file. The proportion of rare variants (when compared to common or zeroed out ones) was significantly higher in the outlier group (Wald statistic, p<0.001; logistic regression). Out of the approximately three thousands outlier markers that were comparable with the 1000 Genomes Project data, GenCall had the highest concordance for the three replicates of NA12763 (average of 98.925%), followed by zCall (average of 98.448%) (Additional file 1: Table S3).
Pairwise tool agreement. Boxplots showing the Cohen’s κ coefficient (A) and the percent agreement (B) for all calls when GenCall is compared with the following three tools: GenoSNP (optimized), optiCall (without excluding markers failing Hardy-Weinberg) and zCall. Red lines are median and the numbers at the bottom of the plot represent the concordance means. The red dots represent the outliers according to the interquartile range.
Tool agreement. Distribution of Fleiss’ π coefficient for all 247,730 markers when the following four tools are compared: GenCall (optimized cluster file), GenoSNP (optimized), optiCall (without excluding markers failing Hardy-Weinberg) and zCall. Values closer to 1 indicate good agreement. Using the interquartile range, there were a total of 12,122 outliers (represented as red dots in the boxplot).
Error rate estimates
Error rates were estimated by using the genotypic model (Liu et al.[22]), where the six tools were evaluated (Figure 7). Except for the original version of GenoSNP, all tools showed a comparable estimated error rate mean (approximately 0.002). The zCall tool provided the lowest estimated error rate with a mean of 0.164%, followed by GenCall (optimized cluster file) with a mean of 0.166%. A non-parametric Friedman Rank Sum test comparing tools showed a significant difference in the error rate distributions (p-value <2.2×10-16 in both cases). Pairwise dependent-samples non-parametric sign tests comparing pairwise tools were also significant (p-value <2.2×10-16 in all cases).
Marker error rate distribution. Boxplots showing the marker error rate estimation for each the six tools: GenCall (original and optimized cluster files), GenoSNP (original and optimized), optiCall (without excluding markers failing Hardy-Weinberg) and zCall. The numbers at the top of the plot represent the mean of the error rate distribution and the red lines are the median of each distribution. Red dots represent the outliers according to the interquartile range. Values above 1/3 were discarded since it’s not plausible to have such a large error rate in practice [22].
Conclusions
This study compares the performance of widely used clustering tools when applied to genotyping data from Illumina’s HumanExome BeadChip. This genotyping array includes a large proportion of rare variants that were previously identified by sequencing technologies. The dataset used here included 10,520 unique samples along with a high number of technical replicates for quality assessment.
Contrary to our original expectations, GenoSNP, which relies on a within-sample model, did not perform well when used straight “out of the box”. This might be explained by the high density of markers in each BeadPool, which is higher than for Illumina’s Human 1M BeadChip (comprising an overall higher number of markers). The latter was successfully tested by GenoSNP’s authors. This problem was mostly obvious with cluster plots (Figure 1) and with graphs showing the summarized quality of the calls per sample (Figure 2). The concordance of results from the original GenoSNP tool with the 1000 Genomes Project, however, remained high (mean of 87.87%). The optimized tool (modified initial variance and number of iterations) increased the concordance to a mean of 99.61%. The quality threshold of 0.8 provided a better separation of the three clusters, but increased the missing rate of both sample and marker (mean of 0.87%).
GenCall relies on a between-sample model that requires reference parameters to perform its clustering. As such, it is common practice to manually modify the reference cluster parameters to ensure the best quality of results when the population analyzed is different from the one used to generate the reference parameters. This task requires a significant amount of manual labor which increases with the number of samples and markers. Loading the raw data, normalizing and modifying the original cluster file took one person 5 work days, compared to only a few days to generate the intensity files for the other tools. When we compared the genotype results from GenCall using the original cluster file with the ones generated with the optimized cluster file, we saw only limited improvement in the overall concordance of genotype calls with those of the gold standard. When partitioning calls according to their allele content, we saw a limited decrease in the concordance of homozygous calls involving the common allele when compared with the gold standard, while the concordance of calls involving the rare allele improved by approximately 0.5%. A limited improvement in the concordance between technical replicates was observed. However, the optimization of the cluster file had a greater impact on the missing rate per sample and per loci (0.19% improvement in both cases). According to normal quality control procedures, a filter to remove samples and markers with a missing rate greater than 2% is typically imposed prior to genetic analysis [23]. By optimizing the cluster file, an average of 2,963 markers (1.2%) per sample could be rescued by lowering the marker missing rate below the 2% quality threshold.
It should be noted that this study was limited by the lack of an independent gold standard for concordance analysis. GenCall’s (and zCall’s) concordance with the 1000 Genomes Project might be overestimated due to the nature of its reference parameters. Indeed, the reference cluster file was created by using estimated cluster position for each of the markers in the HapMap population. Hence, the sample NA12763 is expected to have a higher concordance value than samples from the Montreal Heart Institute Cohort owing to the CEU HapMap population. One possible way to overcome this limitation would be to sequence a few of our own cohort samples, however, it could be argued that the sequencing technology itself would not provide an adequate gold standard in this situation.
Many study designs will plan to include experimental replicates chosen from the genotyped cohort to assess the reproducibility of the genotyping pipeline and the precision of the results. Including a reference sample to the study design offers the additional possibility of assessing the accuracy of the results. High precision is particularly important as it provides optimal power for statistical analysis [24] and can prevent type I errors due to plate biases or subgroup effects [25]. GenCall (using the original or the optimized cluster file) provided the highest concordance rate between experimental replicates (99.997%) when compared to other tools. The other tools (except for the original GenoSNP) performed relatively well, all providing a mean concordance greater than 99%.
All clustering tools had a high accuracy (>99.8%) when calling common markers (except for GenoSNP at only one of the three replicates of NA12763). Other metrics have shown that all the tools (once optimized) performed almost at the same efficiency level on the HumanExome BeadChip. The major difference arose when in the presence of rare markers, where the accuracy of all the tools decreased below 99.5% (as low as 96% for some) for genotypes involving the rare allele. Within-sample tools like GenoSNP can process samples in an efficient manner by running single samples and smaller batches of samples in parallel instead of having to wait for a large amount of samples to be genotyped and normalized. Unfortunately, even with the proper optimization of initial parameters, GenoSNP could not outperform the other tools. However, GenCall, Illumina’s proprietary tool, performed better than the other tested tools with respect to concordance with the gold standard for genotypes involving the rare allele (accuracy) and slightly better for the concordance in between technical replicates (precision). The fact that zCall has been run as a post-process of GenCall without the use of the reference cluster file optimization (since it is not mandatory) might explain why it’s accuracy was not as high as the optimized GenCall for calls involving the rare allele. Since the third version of zCall derives its thresholds from GenomeStudio’s report, the call rate will increase and better accuracy might be possible if the original cluster file is optimized beforehand.
Recommending a single clustering tool according to the metrics shown in this report is not straightforward. In general, GenCall (optimized cluster file) outperformed the other tools in terms of precision and accuracy (overall, and for the calls involving the rare allele). Its accuracy was also higher for the markers with low inter-tool agreement. However, when using the optimized cluster file, GenCall’s accuracy for the homozygous calls (common allele) was lower than when using the default cluster file. When considering missing and estimated error rates, zCall outperformed the other tools, closely followed by GenCall (optimized cluster file). It is important to mention that the task of optimizing the cluster file is time consuming. Furthermore, all the other tools presented here require intensity data provided by the GenomeStudio software and possible file conversion, which increase the total execution time.
The parallel use of multiple clustering tools offers the possibility of identifying discordant markers which can be further investigated. But notably, the manual optimization of GenCall’s cluster file at those loci and the visual inspection of the cluster plots should provide high quality datasets for downstream analysis.
Endnotes
aθ values of the center of the AA and BB clusters in normalized polar coordinates, respectively.
b Outliers are observations that fall below Q1-1.5(I Q R) or above Q3+1.5(I Q R), where Q1 and Q3 are respectively the first and third quartiles and I Q R=Q3-Q1 is the interquartile range.
References
Hindorff LA, MacArthur J, Morales J, Junkins HA, Hall PN, Klemm AK, Manolio TA: A Catalog of Published Genome-Wide Association Studies. 2013, [http://www.genome.gov/gwastudies],
The International HapMap Consortium: A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature. 2005, 437 (7063): 1299-1320. 10.1038/nature04226.
The International HapMap Consortium: A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature. 2007, 449 (7164): 851-861. 10.1038/nature06258.
The International HapMap 3 Consortium: Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature. 2010, 467 (7311): 52-58. 10.1038/nature09298.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ, McCarthy MI, Ramos EM, Cardon LR, Chakravarti A, Cho JH, Guttmacher AE, Kong A, Kruglyak L, Mardis E, Rotimi CN, Slatkin M, Valle D, Whittemore AS, Boehnke M, Clark AG, Eichler EE, Gibson G, Haines JL, Mackay TF, McCarroll SA, Visscher PM: Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature. 2009, 461 (7265): 747-753. 10.1038/nature08494.
Zuk O, Hechter E, Sunyaev SR, Lander ES: The mystery of missing heritability: genetic interactions create phantom heritability. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012, 109 (4): 1193-1198. 10.1073/pnas.1119675109.
Kaiser J: Genetic influences on disease remain hidden. Science. 2012, 338 (6110): 1016-1017. 10.1126/science.338.6110.1016.
llumina Inc: Data Sheet: Human Exome BeadChips. 2013, [http://res.illumina.com/documents/products/datasheets/datasheet_humanexome_beadchips.pdf],
Ritchie ME, Liu R, Carvalho BS, Irizarry RA, Australia and New Zealand Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (ANZgene): Comparing genotyping algorithms for Illumina’s Infinium whole-genome SNP BeadChips. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011, 12: 68-10.1186/1471-2105-12-68.
Giannoulatou E, Yau C, Colella S, Ragoussis J, Holmes CC: GenoSNP: a variational Bayes within-sample SNP genotyping algorithm that does not require a reference population. Bioinformatics. 2008, 24 (19): 2209-2214. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn386.
Li G, Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Zhao H: M3: an improved SNP calling algorithm for Illumina BeadArray data. Bioinformatics. 2012, 28 (3): 358-365. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr673.
Shah T, Liu J, Floyd J, Morris J, Wirth N, Barrett J, Anderson C: optiCall: a robust genotype-calling algorithm for rare, low-frequency and common variants. Bioinformatics. 2012, 28 (12): 1598-1603. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts180.
llumina Inc: GenomeStudio Software v2011.1 Release Notes. 2011, [http://support.illumina.com/documents/MyIllumina/1f2d00ae-b759-489b-82f9-0163ce085ae7/GenomeStudio_2011.1_Release_Notes.pdf],
Goldstein JI, Crenshaw A, Carey J, Grant GB, Maguire J, Fromer M, O’Dushlaine C, Moran JL, Chambert K, Stevens C, Sklar P, Hultman CM, Purcell S, McCarroll SA, Sullivan PF, Daly MJ, Neale BM, Swedish Schizophrenia Consortium, ARRA Autism Sequencing Consortium: zCall: a rare variant caller for array-based genotyping Genetics and population analysis. Bioinformatics. 2012, 28 (19): 2543-2545. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts479.
Maher B: The case of the missing heritability. Nature. 2008, 456 (7218): 18-21. 10.1038/456018a.
Eichler EE, Flint J, Gibson G, Kong A, Leal SM, Moore JH, Nadeau JH: Missing heritability and strategies for finding the underlying causes of complex disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2010, 11 (6): 446-450. 10.1038/nrg2809.
Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S: k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, SODA ’07. 2007, Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1027-1035. [http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1283383.1283494],
Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE, Kang HM, Marth GT, McVean GA, 1000 Genomes Project Consortium: An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012, 491 (7422): 56-65. 10.1038/nature11632.
NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project (ESP): Exome Variant Server. 2013, [http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/],
Gwet KL: Computing inter-rater reliability and its variance in the presence of high agreement. Br J Math Stat Psychol. 2008, 61: 29-48. 10.1348/000711006X126600.
Fleiss JL: Measuring nominal scale agreement among many raters. Psychol Bull. 1971, 76 (5): 378-382.
Liu N, Zhang D, Zhao H: Genotyping error detection in samples of unrelated individuals without replicate genotyping. Hum Hered. 2009, 67 (3): 154-162. 10.1159/000181153.
Lemieux Perreault LP, Provost S, Legault MA, Barhdadi A, Dubé MP: pyGenClean: efficient tool for genetic data clean up before association testing. Bioinformatics. 2013, 29 (13): 1704-1705. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt261.
Powers S, Gopalakrishnan S, Tintle N: Assessing the impact of non-differential genotyping errors on rare variant tests of association. Hum Hered. 2011, 72 (3): 153-160. 10.1159/000332222.
Mayer-Jochimsen M, Fast S, Tintle NL: Assessing the impact of differential genotyping errors on rare variant tests of association. PloS One. 2013, 8 (3): e56626-10.1371/journal.pone.0056626.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Montreal Heart Institute Foundation and by the Centre of Excellence in Personalized Medicine. We would like to acknowledge the team at the Beaulieu-Saucier Université de Montréal Pharmacogenomics Center who performed the genotyping of more than 10,000 samples of the Montreal Heart Institute Cohort on the HumanExome BeadChip together with all the participants of the cohort and the ones responsible for their recruitment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
LPLP worked on the experimental design, optimized GenoSNP’s initial parameters, performed analyses, compared the tools, implemented the statistical tests and drafted the manuscript. MAL contributed to the analysis and to the manuscript. AB contributed to the statistical analyses and the manuscript. SP contributed to the experimental design, analysis and the manuscript. VN contributed to the manual optimization of GenCall and the manuscript. JCT leads the Montreal Heart Institute Cohort and directs the genomic project with the HumanExome BeadChip. MPD supervised the project, participated in the design and coordination of the study, supervised the laboratory and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12859_2013_6317_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1: Additional materials. Supplemental Equation S1: The genotypic model for error rate estimation was tested by Liu et al. for common variants only. However, we found that the possible values of ϵ were out of bound (i.e. negative or above one) for a majority of rare markers. For those cases, ϵ was approximated using ϵ≃(C1-C3+1)/3. Supplemental Table S1: Distribution of n samples by calling tool in q categories. The set of possible categories are all possible genotypes (i.e. q∈{AA,AB,BB,00}, where 00 represents the no call category). This table is computed for each marker and for each pair of calling tools. The overall agreement probability and Cohen’s κ are shown in Equation 1 and 2 of the main text, respectively. Supplemental Table S2: Distribution of r calling tools by n samples and q response categories. The set of possible categories are all possible genotypes (i.e. q∈{AA,AB,BB,00}, where 00 represents the no call category). This table is computed for each marker and for each calling tool. Fleiss’ π is explained in Equation 3 of the main text. Supplemental Table S3: Call concordance and number of compared markers for the three control replicates when compared to the 1000 Genomes Project for the markers that were outliers for their Fleiss’ π values. The following four tools were compared: GenCall (optimized cluster file), GenoSNP (optimized), optiCall (without excluding markers failing Hardy-Weinberg) and zCall. (PDF 218 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Perreault, LP.L., Legault, MA., Barhdadi, A. et al. Comparison of genotype clustering tools with rare variants. BMC Bioinformatics 15, 52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-15-52
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-15-52