Abstract
Epigenetics is the term used to describe heritable changes in gene expression that are not coded in the DNA sequence itself but by post-translational modifications in DNA and histone proteins. These modifications include histone acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation and phosphorylation. Epigenetic regulation is not only critical for generating diversity of cell types during mammalian development, but it is also important for maintaining the stability and integrity of the expression profiles of different cell types. Until recently, the study of human disease has focused on genetic mechanisms rather than on non-coding events. However, it is becoming increasingly clear that disruption of epigenetic processes can lead to several major pathologies, including cancer, syndromes involving chromosomal instabilities, and mental retardation. Furthermore, the expression and activity of enzymes that regulate these epigenetic modifications have been reported to be abnormal in the airways of patients with respiratory disease. The development of new diagnostic tools might reveal other diseases that are caused by epigenetic alterations. These changes, despite being heritable and stably maintained, are also potentially reversible and there is scope for the development of 'epigenetic therapies' for disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The genetic code cannot be the sole arbiter of cell fate since each cell in a blastocyst can differentiate into the many different cell types found in multicellular organisms each with a unique function and gene expression pattern. This has led to the idea that additional information beyond that generated by the genetic code must be important for the regulation of genomic expression. Over 60 years ago the term "epigenetics" was introduced to describe this information and this is now understood to mean all meiotically and mitotically heritable changes in gene expression that are not coded in the DNA sequence itself [1]. Epigenetic regulation is not only critical for generating diversity of cell types during mammalian development, but it is also important for maintaining the stability and integrity of the expression profiles of different cell types. Interestingly, whereas these epigenetic changes are heritable and normally stably maintained, they are also potentially reversible, as evidenced by the success of cloning entire organisms by nuclear transfer methods using nuclei of differentiated cells [2]. Therefore, understanding the basic mechanisms that mediate epigenetic regulation is invaluable to our knowledge of cellular differentiation and genome programming.
Studies of the molecular basis of epigenetics have largely focused on mechanisms such as DNA methylation and chromatin modifications [3]. In fact, emerging evidence indicates that both mechanisms act in concert to provide stable and heritable silencing in higher eukaryotic genomes. Interestingly, the recently described process of RNA silencing, originally utilised by the cell to protect itself against viral infection, also involves the same mechanisms used to sustain epigenetic silencing. These components (DNA methylation, chromatin modifications and RNA-associated silencing) interact and often disruption of one component will affect the activity/expression of the other two leading to inappropriate expression or silencing of genes, resulting in 'epigenetic diseases' [1, 3].
It is possible for epigenetic marks to be transmitted along chromosomes. Drosophila and plants exhibit a characteristic known as position-effect variegation (PEV) whereby euchromatic genes can become transcriptionally silenced when juxtaposed to heterochromatic sequences [1]. The extent of this cis-spreading silencing phenomenon varies and involves a number of proteins which have roles in heterochromatin formation e.g. E(var)s (enhancers of PEV) or Su(var)s (suppressors of PEV) [4]. Su(var) 2–5 for example encodes the chromatin-binding nuclear protein heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) [5] which has a critical role in initiating and maintaining the condensed chromatin conformation of heterochromatin through its actions on histone methylation and chromatin remodelling.
Epigenetic marks
DNA methylation
One of the most fundamental epigenetic marks is the widespread methylation of the C5 position of cytosine residues in DNA [1, 6]. The maintenance of these methyl CpG marks is due to the action of a number of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) which add the universal methyl donor S-adenosyl-L-methionine to cytosine (Table 1). These enzymes have been implicated in many processes including transcriptional regulation, genomic stability, chromatin structure modulation, X chromosome inactivation, and the silencing of parasitic DNA transposable elements [7]. Overall, DNA methylation exerts a stabilizing effect which promotes genomic integrity and ensures proper temporal and spatial gene expression during development. In contrast, DNA demethylation is probably a passive event and no bona fide DNA demthylase has been identified to-date [8]. The importance of DNA methylation is highlighted by the fact that many human disease result from abnormal control [9]. In addition, cytosine methylation is highly mutagenic, causing a C to T mutation resulting in loss of the CpG methyl-acceptor site, and aberrant methylation of CpG islands is a characteristic of many human cancers and may be found in early carcinogenesis [3, 10, 11].
It has been estimated that as much as 80% of all CpG dinucleotides in the mammalian genome are methylated [1]. The remaining unmethylated CpG residues are mostly located in the promoter regions of constitutively active and/or inducible genes and are referred to as CpG islands. CpG islands generally consist of regions of >500 base pairs with a GC content greater than 55% [9, 12]. When methylated these CpG islands result in stable inherited transcriptional silencing. How sequences are targeted for de novo methylation in mammals remains largely unknown. Several triggers have been proposed to target DNA methylation including: (i) sequence, composition or secondary structure of the DNA itself; (ii) RNAs that might target regions on the basis of sequence homology; and (iii) specific chromatin proteins, histone modifications or higher-order chromatin structures and these are clearly not mutually exclusive [13].
Early models for the control of DNA methylation proposed two-steps: 'de novo methylation' by DNMTs active on unmethylated DNA e.g. DNMT3a and 3b [14], followed by 'maintenance methylation' by DNMT3a or by DNMT1 which is specific for the hemi-methylated DNA resulting from replication [15]. However, the validity of this model has recently been questioned [9]. There are a number of DNMTs and DNMT-interacting proteins reported mostly distinguished on the basis of structural similarity, sequence specificity but rarely primary function. Indeed most predicted proteins have been designated as being DNMTs solely because they have most, or all, of the conserved motifs observed in the catalytic domain of known DNMTs [9, 10]. The problem is compounded by the fact that DNMTs may also form complexes with each other [16].
Mammalian Dnmt1 is considered to be a maintenance DNMT as knockout studies and antisense approaches show a global effect on methylation [9, 17]. Furthermore, DIM-2, a relative of Dnmt1, is responsible for all known DNA methylation in Neurospora [13]. Some potential DNMTs include proteins for which little or no enzymatic activity has been found in mammalian cells [13], thus, mammalian DNMT2 has little or no DNMT activity in vitro [18], and deletion of Dnmt2 in mouse embryonic stem cells had no noticeable effect on DNA methylation [13]. In contrast, depletion of Drosophila Dnmt2 by RNAi, however, resulted in loss of the little DNA methylation detectable by immunolocalization, and overexpression appeared to induce hypermethylation [19].
DNA methylation can repress transcription through several mechanisms including direct inhibition of transcription factor DNA binding and indirectly through the effects of methyl CpG binding proteins (Table 1). As such, methyl-CpG binding proteins e.g. MeCP2 and MBDs are recruited to methylated CpG where they can act as mediators of transcriptional repression through the association with HDAC containing repressor complexes. Interestingly, Mbd2 knockout cells can express IL-4 in cells where this gene is normally silent [20]. In contrast, CpG methylation blocks DNA binding of the chromatin boundary element binding protein (CTCF), which can block interactions between an enhancer and its promoter when placed between the two elements resulting in gene induction. Generally loss of MBDs is less profound than that of DNMT loss since DNMTs greatly reduce the extent of genomic DNA methylation and therefore interfere with all proteins that interpret the DNA methylation signal whereas loss of one methyl-CpG binding protein will enable other proteins that recognize the DNA methylation signal.
DNA methylation, in conjunction with post-translational modifications of histones, is involved in the regulation of chromatin states that are either mutually reinforcing or mutually inhibitory possibly acting through feedback loops [17]. This may polarize chromatin, committing it to enable either transcriptional activity or transcriptional silence with uncommitted states being rare. This would imply that an active mechanism must be involved in switching between transcriptionally active and silenced states. Recently, clear evidence for cross-talk between these epigenetic processes has been provided. Thus, the polycomb group (PcG) protein EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste homolog 2) serves as a recruitment platform for DNMTs indicating a direct link between the two major epigenetic repression systems [21]. Similarly, histone H1 depletion induced marked changes in chromatin structure such as decreasing global nucleosome spacing and reducing local chromatin compaction without affecting global DNA methylation. However, many of the genes whose expression was regulated by H1 depletion showed evidence for reduced methylation of specific CpGs within their regulatory regions thereby suggesting that linker histones can also play a role in the maintenance or establishment of specific DNA methylation patterns [22].
Chromatin structure and histone modifications
Chromatin is made up of nucleosomes which are particles consisting of 146 bp of DNA wrapped around an octomer of two molecules each of the core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H4 and H4). Nucleosomal DNA can be further compacted by association with the linker histone H1 and additional nonhistone proteins, as well as by higher order looping and folding of the chromatin fibre. In the resting cell DNA is wound tightly around these basic core histones, presenting an impenetrable barrier to large protein complexes such as RNA polymerase II, which produce unspliced primary messenger RNA transcripts. Alterations in the structure of chromatin are critical to the regulation of gene expression [1, 23, 24].
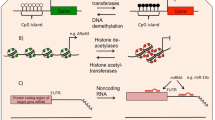
Over 100 years ago cytologists appreciated the link between chromatin compaction and cell activation status. Thus chromatin was divided into two major forms: heterochromatin and euchromatin [1]. Heterochromatin was defined as condensed regions of the nucleus that do not decondense during interphase, whereas euchromatin was noted to readily decondense upon exit of mitosis. It was postulated that heterochromatin is the functionally inactive regions of the genome and euchromatin is where gene activity occurs (Figure 1). We now know that heterochromatin regions less susceptible to nuclease activity; contain few actively expressed genes, and replicate late in the S-phase [1, 25]. In contrast, euchromatin is more open and accessible to nucleases, is rich in actively transcribing genes, and replicates early during S-phase [1, 25].
Heterochromatin is the compacted "closed" form of chromatin associated with gene silencing. Activation of chromatin to its more "open" form which allows gene expression to occur is regulated by modification of core histones by specific co-activator complexes containing enzymes which can acetylate, phosphorylate or methylate histone tails. Removal of the linker histone H1 and changes in DNA methylation state are also important in this process. This is reversed by corepressor complexes that include histone deacetylases (HDACs) and both DNA and histone methylases, thereby causing gene silencing.
Allfrey and colleagues [26] initially described a role for histone acetylation in de novo mRNA synthesis in 1964 however it wasn't until the mid 1990s that a molecular appreciation of the events linking histone acetylation and gene expression were made. In these later studies it was reported that transcriptional co-activator proteins act as the molecular switches that control gene transcription and all have intrinsic histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity [27, 28]. Gene transcription occurs when the chromatin structure is opened up, with loosening of the tight nucleosomal structure allowing RNA polymerase II and basal transcription complexes to interact with DNA and initiate transcription. When transcription factors are activated they bind to specific recognition sequences in DNA and subsequently recruit large coactivator proteins, such as cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP), p300 and PCAF (p300-CBP associated factor) and other complexes to the site of gene expression [23].
The N-terminal tails of the histone molecules protrude through and beyond the DNA coil presenting accessible targets for post-translational modifications such as acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, sumoylation and ubiquitination of selective amino acid residues (Figure 2). Some modifications, including acetylation and phosphorylation, are reversible and dynamic and are often associated with inducible expression of individual genes. Thus, lysine residues in the tails of histone H3 and H4 may be acetylated forming bromodomains enabling the association of other co-activators such as TATA box binding protein (TBP), TBP-associated factors, chromatin modifying engines and RNA polymerase II [23, 28](Figure 3). This molecular mechanism is common to all genes, including those involved in differentiation, proliferation and activation of cells. Just as acetylation of histones is associated with gene induction, removal of acetyl groups by histone deacetylases (HDAC)s is generally associated with re-packing of chromatin and a lack of gene expression or gene silencing [29]. Other modifications, such as methylation, are generally more stable and are involved in the long-term maintenance of expression status. Since these modifications occur on multiple but specific sites it has been suggested that modified histones can act as signalling templates, integrating upstream signalling pathways to elicit appropriate nuclear responses such as transcription activation or repression [30]. The Histone Code Hypothesis proposes that different combinations of histone modifications may result in distinct outcomes in terms of chromatin-regulated functions [31].
Epigenetic modifications within the nucleosomes. A number of distinct post-translational modifications including acetylation (orange flag), phosphorylation (red circle), ubiquitination (blue star) and methylation (green flag) occur at the N termini of histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Other modifications are known and may also occur in the globular domain. Methylation of C5 on cytosine residues within CpG regions of DNA are also important markers for epigenetic effects. The histones are depicted in single-letter amino-acid code with the residue number shown underneath.
Histone modifications act by serving as a node for the assembly of coactivators and corepressor complexes through the recognition of these modifications by proteins that contain bromodomains (recognize acetylated lysines) or chromodomains (recognize methylated lysines). This, rather than an effect on chromatin structure per se, determines effects on gene expression. Recruitment of heterochromatin protein (HP)1 through a chromodomain may also affect local DNA methylation through recruitment of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and methyl binding domain (MBD) proteins. This may lead to further assembly of other histone methyl transferases (HMTs) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) complexes which enable further gene silencing to occur. Gene activation, in contrast, requires recruitment of an acrivation complex involving the TATA binding protein (TBP) and its associated factors (TAFs), chromatin remodeling complexes such as mating type switching/sucrose non-fermenting (SWI/SNF) and RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II).
Histone acetylation
Recruitment of a histone modifying enzyme to the right place at the right time is only the first step in establishing a combination of histone marks that may direct a biological outcome. The second step in this process revolves around the specificity of the enzyme for individual histone tails and for specific histone residues [23]. For example, Gcn5 (general control non-derepressible 5) and PCAF preferentially acetylate H3 K9 and K14 whereas NuA4 HAT complexes preferentially acetylate K4, K8, K12 and K16 of histone H4 [32] (Table 1).
It was originally proposed that histone acetylation would alter the electrostatic interaction between histones and DNA by altering the charge on the lysine residue leading to an "open" structure. However, at best, full acetylation of histone H3 is likely to lead to a 10–30% decrease in positive charge which is unlikely to affect interactions with DNA [32]. The major role of acetylated histones is to direct the binding of nonhistone proteins. For example, bromodomains specify binding to acetylated lysines but this does not show much specificity. For instance, acetylation of K8 within histone H4 can promote the recruitment of the ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzyme, human SWI/SNF – via a bromodomain within the Brg1 subunit – but a similar bromodomain within the Swi2 subunit of the yeast SWI/SNF complex interacts with a broader range of acetylated H3 and H4 tails [32, 33]. Thus, the major role of the bromodomain, and the chromodomain (see later), is to serve as the nidus for assembly of co-activator vs. co-repressor complexes (Figure 3).
HATs are divided into five families. These include the Gcn5 (general control non-derepressible 5)-related acetyltransferases (GNATs); the MYST (for 'MOZ, Ybf2/Sas3, Sas2 and Tip60)-related HATs; p300/CBP HATs; the general transcription factor HATs, which include the TFIID subunit TAF250 (TBP-associated factor of 250 kDa); and the nuclear hormone-related HATs SRC1 (steroid receptor coactivator 1) and ACTR (activator of retinoid receptor) [34]. In addition to these three major groups of HATs, more than a dozen other proteins have been shown to possess acetyltransferase activity [34].
Most HATs exist as stoichiometric multisubunit complexes in vivo [35]. The complexes are typically more active than their respective catalytic subunits and display distinct substrate specificities [36, 37], suggesting that associated subunits regulate the activities of the respective catalytic subunits. In addition, non-catalytic subunits are also involved in recruiting substrates for targeted action to ensure the specificity. One HAT can be the catalytic subunit of multiple complexes thus, GCN5L forms at least two distinct multisubunit complexes [35], and yeast Gcn5 is the catalytic subunit of four complexes [34]. Increasingly levels of complexity are being found e.g. recent studies indicate that Ubp8, a deubiquitinating enzyme present in two Gcn5 complexes, controls the deubiquitination of histone H2B and methylation of histone H3 [38]. Incorporation of HATs into complexes also alters lysine specificity. On free histones Gcn5 alone acetylates mainly H3 lysine 14, SAGA acetylates lysines 9, 14, 18 and 23, and ADA acetylates 9, 14 and 18 [35, 39]. Thus, HAT complexe subunits not only specify histone modification, but also transcriptional function in targeting of these complexes to promoters.
Histone deacetylases
HDACs play a critical role in reversing the hyperacetylation of core histones. Lysine acetylation is reversible and is controlled by the opposing actions of HATs and HDACs in vivo (Figure 4). Since histones were thought to be the major cellular proteins modified by lysine acetylation, most lysine HATs and HDACs were initially identified as histone acetyltransferases and HDACs [23, 40].
The histone switch. Targeted modifications under the control of histone methylases (HMTs), histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) alter the histone code at gene regulatory regions. This establishes a structure that contains bromo- and chromo-domains that permits recruitment of ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling factors to open promoters and allow further recruitment of the basal transcription machinery. Deacetylation, frequently followed by histone methylation, establishes a base for highly repressive structures, such as heterochromatin. Acetylated histone tails are shown as yellow stars. Methylation (Me) is shown to recruit heterochromatin protein 1 (HP-1).
HDACs are divided into four classes: I (HDAC1, -2, -3, and -8), II (HDAC4, -5, -6, -7, -9, and -10), III (Sirt1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, and -7) and IV (HDAC11) [41–43]. The widely expressed class I HDACs are exclusively localized to the nucleus whereas the more restricted class II HDACs shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm (Table 2). There is evidence that these different HDACs target different patterns of acetylation and regulate different genes [40]. The different HDACs are also likely to be regulated differently. HDACs interact with corepressor molecules, such as nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR), ligand-dependent corepressor (LCoR), NuRD (nucleosomes remodelling and decatylase) and mSin3 (Switch independent 3), all of which aid HDACs in gene repression and may provide specificity by selecting which genes are switched off by HDAC [41, 44, 45] (Figure 5).
Composition of HDAC repressor complexes. HDACs lack intrinsic repressor activity and require co-factors for optimal HDAC activity. The co-repressor proteins involved in the major HDAC complexes NuRD (nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase), Sin3 (Switch insensitive 3), Co-REST (Co-repressor of REST (RE1 silencing transcription factor)) and N-CoR and SMRT complexes are shown. NuRD and sin3 complexes share the retinoblastoma associated protein (RbAp)46 and 48 proteins and also contain distinct sets of proteins. Abbreviations: Co-REST, Co-repressor of REST (RE1 silencing transcription factor); MBD3, Methyl CpG binding domain 3; Mi2, Mi2 autoantigen; MTA-2, Metastasis-associated gene family, member 2; N-CoR, Nuclear receptor co-repressor; NuRD, Nucleosome remodelling and deacetylating; RbAp46, Retinoblastoma associated protein of 46 kDa; SAP18, Sin3 associated protein of 18kDa; SDS3, Suppressor of defective silencing 3; Sin3, Switch insensitive 3; SMRT, Silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors; ZNF217, Zn finger factor 217 kDa.
The activities of most if not all HDACs are regulated by protein-protein interactions. In addition, many HDACs are regulated by post-translational modifications as well as by subcellular localization. HDACs generally exist as a component of stable large multi-subunit complexes, and most, if not all, HDACs interact with other cellular proteins. With the exception of mammalian HDAC8, most purified recombinant HDACs are enzymatically inactive [46]. Any protein that associates with HDACs, therefore, has the potential to activate or inhibit the enzymatic activity of HDACs. Likewise, HDACs, in general, have no DNA binding activity, therefore, any DNA-binding protein that targets HDACs to DNA or to histones potentially can affect HDAC function.
Human HDAC1 and HDAC2 exist together in at least three distinct multi-protein complexes called the Sin3, the NuRD, and the Co-repressor of REST (RE1 silencing transcription factor, CoREST) complexes [46](Figure 5). Sin3 and NuRD complexes share a core comprised of four proteins: HDAC1, HDAC2, retinoblastoma associated protein (RbAp)46, and RbAp48. In addition, each complex contains unique polypeptides (Sin3, sin3 associated protein (SAP)18, and SAP30 in the Sin3 complex; Mi2, metastasis-associated gene family (MTA)-2, and methyl CpG binding domain (MBD)3 in the NuRD complex) which are essential for HDAC activity and function [47, 48]. Thus the NuRD complex may link acetylation and methylation in the regulation of gene expression [46]. Similar results are seen for HDAC activity within the CoREST complex [49]. Furthermore, HDAC3 activity is dependent upon silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid receptor (SMRT) and nuclear receptor corepressor (N-CoR) association [46].
Unlike HDAC3, the class II HDACs cannot be activated by SMRT/N-CoR alone. Instead, the enzymatic activity of HDAC4, 5, and 7 is dependent on the association with the HDAC3/SMRT/N-CoR complex [46]. These studies suggest that HDAC4, 5, and 7 are not active deacetylases but recruit preexisting enzymatically active SMRT/N-CoR complexes containing HDAC3 [50] (Figure 5).
All mammalian HDACs possess potential phosphorylation sites and many of them have been found to be phosphorylated in vitro and in vivo. HDAC1 phosphorylation may either alter its conformation into a more favourable enzymatic active form or affect the ability of HDAC1 to interact with proteins, such as MTA2 and SDS3, which can subsequently stimulate its activity and consequently enhance its enzymatic activity [46]. Similarly, HDAC2 phosphorylation is necessary for both enzymatic activity and association with the corepressors mSin3 and Mi2 [46]. The activity of class II HDACs may also be regulated by phosphorylation via modulating their subcellular localization [46]. HDACs must reside in the nucleus in order to deacetylate histones and to repress transcription, therefore, signals that enhance HDAC nuclear localization must affect HDAC activity. HDAC1, 2, and 8 are predominantly nuclear proteins but in contrast, HDAC3 can be found both in the nucleus and cytoplasm and the nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio depends on cell types and stimuli [46]. Thus, in response to IL-1β stimulation, the N-CoR/TAB2/HDAC3 corepressor complex undergoes nuclear to cytoplasmic translocation, resulting in derepression of a specific subset of NF-κB-regulated genes [51].
In contrast, experiments in cardiac myocytes shows that class II HDACs shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm where they associate with 14-3-3 proteins [52, 53]. The binding of class II HDACs to 14-3-3 is absolutely dependent on phosphorylation of conserved N-terminal serine residues and this association results in sequestration of HDACs to the cytoplasm [52, 53]. Furthermore, CaMK-mediated phosphorylation of HDACs 4, 5, 7, and 9 promotes their association with 14-3-3 proteins resulting in increased retention of HDACs in the cytoplasm. Binding of 14-3-3 has been suggested to mask an N-terminal nuclear localization signal [52, 53].
Interestingly, HDACs can autoregulate their own expression by feedback mechanisms utilising the DNA binding actions of transcription factors such as NF-Y (nuclear factor Y) and Sp1. Furthermore, some degree of cross-talk in this regulation must also occur as changes in HDAC1 expression can also affect the expression of other class I HDACs [46]. Recent evidence [54] has shown that nitration of HDAC2 can lead to protein degradation. Proteasomal degradation appears to be a major mechanism of regulation of HDAC function [46].
Histone methylation
Histone methylation has been implicated for over 40 years in the control of gene expression [26]. Histones may be methylated on either lysine (K) or arginine (R) residues. Due to their small size and their charged nature it is unlikely that these marks alter chromatin structure. It is therefore believed that methylation of K or R residues forms a binding site or interacting domain allowing other regulatory proteins to be recruited. Methyl-K residues may exist in either the mono-, di- or tri-methylated forms. In contrast, R methylation may be either mono-methylated or di-methylated although a further complexity is added by the ability of di-Me-R to be symmetrical or asymmetrical [30]. Currently, there are at least 17 K and 7 R residues known to be methylated suggesting a large number of possible combinations.
Most of our knowledge concerning the role of methylation in gene expression has come from experiments in yeast and Drosophila however, general principles appear to hold true in man [30]. Histone H3 and H4 methylation has been most studied and distinct forms are presence within heterochromatin (condensed, heritable and transcriptionally inert chromatin) and euchromatin (loosely packed and transcriptionally active chromatin). Thus methylated forms of H3K9, H3K27, H3K79 and H4K20 are found to be associated with heterochromatin whereas activated genes with euchromatin are associated with methylated H3K4 and H3K36 histones. Upon selective gene activation further methylation of these histones (H3K4 & H3K36) within the 5' controlling regions of genes occurs [30]. These posttranslational modifications are carried out by histone methyl-transferases (HMT), which covalently modify lysines and arginines on histones. These modifications, in combination with acetylations, are thought to inscribe a histone pattern that recruits factors that affect transcription [55].
The discovery that one of the well-studied Su(var) genes encoded a histone methyltransferase (HMT) was a major breakthrough in the understanding the function of H3K-methylation [1]. The Drosophila Su(var)3–9 gene was originally pulled out of a genetic screen for transcriptional silencing associated with heterochromatin [56]. Subsequently, the human homolog, Suv39H1, was shown to specifically methylate histone H3 at K9 [57]. Structure-function analyses of Suv39H1 and other HMTs indicated that the SET domain was responsible for HMT activity. The highly conserved SET domain is named after three proteins all with silencing properties: Su(var)3–9, enhancer of zeste [E(Z)], and trithorax (TRX) [56]. Many SET domain-containing proteins have high specificity for different sites on H3 and H4 but it is important to note that not all SET domain-containing proteins are HMTs, nor are the activities of all HMTs mediated by SET domains [1]. For example, Dot1p is a non-SET domain-containing enzyme that methylates H3 at Lys79 [1, 58].
As with acetylation, the functional consequence of histone K methylation depends upon the proteins that recognize the particular modification. Protein that induce gene repression, such as heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) (Figure 3) or the Drosophila Polycomb (PC) protein, contain a chromodomain that allows them to specifically recognize the appropriate repressive methylation mark (H3K9 and H3K27 respectively) [30], whereas the activating protein chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 1 (CHD1) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae uses its chromodomain to bind the activating methylated H3K4 [59]. Other domains, important for the recognition of distinct methylated lysine residues have also evolved e.g. for the recruitment of proteins involved in DNA repair (see later) although it is not known generally how recruitment of distinct proteins to particular methylated lysines leads to the desired functional effect [30].
Demethylation of lysines
The enzyme LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) which is able to demethylate H3K4 has recently been identified [60]. The ability to target the activating methylated H3K4 site correlates with its expression in a number of repressor complexes [30]. However, LSD1 can only demethylate the mono- or di-methylated forms of H3K4 despite the fact that the tri-methylated state is most closely associated with active genes. This suggests that other enzymes must exist although the action of co-factors may also be important. In addition, it has been reported that the androgen receptor may be able to alter the specificity of LSD1 from H3K4 to H3K9, and thereby converts the demethylase from a repressor to an activator of transcription [61]. This data is controversial and requires confirmation. The recent discovery of demethylases has opened up a new area of research and suggested that methyl marks are not necessarily permanent. This agrees with evidence from stem cells and cell lines indicates that patterns of gene expression thought to be under epigenetic control can be reversed [2, 62].
Arginine methylation and demethylation
There are a number of protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) and R methylation is only found on chromatin when genes are actively transcribed particularly in response to oestrogen receptor activation although a methyl R binding protein has not been reported [63]. Interestingly, during oestrogen-mediated gene induction, H3R2 methylation appears to be transient or even cyclical [64] which suggest the existence of enzymes that reverse R methylation. Recently, an enzyme peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) has been found which removes the methyl group mono-methyl R residues in H3 and H4 [65, 66]. PAD14 converts the R residue to citrulline but whether citrulline can be removed or converted back to R is unknown as is the answer to the question as to whether citrulline itself can act as an epigenetic mark. Interestingly, PAD14 activity is linked to the repression of an oestrogen-controlled gene, pS2 [30].
Cross-talk between histone marks
Cross-talk between different histone marks can also have a profound effect on enzyme activity [1]. For instance, ubiquitylation of H2B K123 by the E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme Rad6 is required for subsequent di-methylation of H3 K4 by Set1p or H3 K79 by Dot1p [38]. Prior histone marks can also inhibit subsequent modifications [1]. For example, H3 S10 phosphorylation inhibits subsequent H3 K9 methylation, and of course H3 K9 methylation can also block acetylation of this same residue. More recently it has been demonstrated that S10 phosphorylation by Aurora B kinase can lead to the dissociation of HP1 from heterochromatin without affecting K9 methylation status [67, 68]. An excellent example of even more complex cross-talk is exemplified during p53-dependent transcriptional activation in vitro [69]. In this case methylation of H4 R3 by PRMT1 stimulates CBP-p300 acetylation of H4 K5, K8, K12 and K16, which in turn promotes the methylation of H3 R2, R17 and R26 by another PRMT family member, CARM1. Thus, positive and negative crosstalk ultimately generates the complex patterns of gene or locus-specific histone marks associated with distinct chromatin states.
Histone variants
Chromatin arrays also contain novel types of nucleosome that harbour one or more variant isoforms of the core histones [1]. For instance, nucleosomes assembled at yeast and mammalian centromeres contain a histone H3 variant, Cse4/CENP-A, which is essential for centromere function or assembly. Another histone H3 variant, H3.3, replaces canonical histone H3 during transcription, generating a mark of the transcription event [1]. Several variants of histone H2A have also been identified. The macro-H2A variant is restricted to metazoans and functions in X chromosome inactivation, while H2AZ (also known as H2A.F/Z or H2AvD) is found in all eukaryotes. Surprisingly, H2AZ is required for one or more essential roles in chromatin structure that cannot be replaced by bona fide histone H2A [70]. In most cases, it is not known how histone variants alter nucleosome structure or change the folding properties of nucleosomal arrays [70]. Once a histone variant is targeted to a specific locus, there is the potential for creation of novel chromatin domains that have distinct regulatory properties. For instance, the amino-terminal tail of CENP-A lacks the phosphorylation and acetylation sites that are normally modified in histone H3 at transcriptionally active regions [71].
Methylation and RNA interference (RNAi)
DNA methylation has long been shown to have a transcriptional silencing function which may reflect the fact that several HDAC-containing complexes possess methyl-DNA binding motifs [1]. Furthermore, Suv39H1/2 knockout cells from mice have an abnormal pericentric heterochromatin DNA methylation pattern [72]. Mutually reinforcing relationships between histone modifications and DNA methylation have been found such as H3-K9 methylation is a prerequisite for DNA methylation and DNA methylation can also trigger H3-K9 methylation [1, 3, 73]. It is likely that both DNA and histone methylation pathways leave epigenetic marks that are required for stable and long-term epigenetic silencing. However, it is unclear what initiates the recruitment of the different epigenetic modifiers to their specific target sequences [1, 3].
Since its discovery in 1990 as a means of controlling Petunia colour [74] and the more recent demonstration in mammalian cells there has been great interest in the mechanisms by which RNA interference (RNAi) controls mitotically heritable transcriptional silencing [75, 76]. It is clear that components of the RNAi machinery can exist in complexes with the chromodomain protein CHP1 which may enable targeting to specific methyl K residues [75, 76]. In addition, deletion of components of the RNAi machinery results in impaired centromere function, a derepression of transgenes integrated at centromeres, and a loss of the characteristic H3-K9 methylation and HP1 association [75, 76]. Furthermore, miRNAs and antisense RNAs are involved in the silencing of some mammalian imprinted genes [77] and in dosage compensation in mammals [75, 76] suggesting that RNA is able to direct histone modifications (for example, H3-K9 methylation) and DNA methylation to specific loci, thereby evoking heritable and stable silencing [75, 76]. Finally, there is a report of a case of α-thalassaemia showing how antisense transcription could lead to DNA methylation and stable silencing of the HBA2 globin gene [78].
Inheritance of epigenetic marks on histones
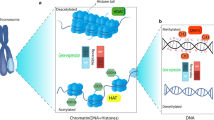
Little detail concerning the mechanisms for inheritance of histone modifications is known in contrast to that for the inheritance of DNA methylation through mitotic cell division [1]. Methylated K residues do not have a rapid turnover rate and early studies looking at the turnover rate of histone methylation found that the half-life of the methyl mark on histones was equal to that of the protein itself indicating an irreversible modification that persisted through cell division [79]. In addition, even the highly dynamic acetyl K modifications are maintained during mitosis and inheritance of acetylation patterns may be essential to maintain gene expression profiles through successive generations [80]. Thus, successful propagation of histone modification patterns requires a way of copying/replicating preexisting modifications onto the newly assembled nucleosomes [1]. During DNA replication, preexisting nucleosomes of the parental genome are recycled and deposited onto the newly generated daughter strands, and therefore, any stable histone modifications can potentially be transferred from one generation to the next [1] (Figure 6).
During replication, parental nucleosomes are recycled and deposited onto the two daughter strands. In the random segregation model, the parent histone octamers (red cylinders) are intact and pass to the two daughter strands in a random manner. Newly assembled nucleosomes (grey cylinders) fill in the gaps not occupied by the parental octamers and histone-modifying enzymes copy the parental histone modifications (e.g. Acetylated groups, Ac) to newly assembled nucleosomes. In the semi-conservative model, the parent histone octamers split in half and are equally distributed among the two daughter strands (red halves). Nucleosome assembly complexes then deposit newly synthesized histones to complement the existing halves of the nucleosomes (grey halves) present on the daughter strands. In this case, histone modifying enzymes would copy the modifications (e.g. Ac) to the new half of the nucleosomes from the old half (symbolized by the green arrows).
Parental nuclesomes may divide in a semiconservative manner whereby the parental histone octamer is split into H2A-H2B/H3-H4 heterodimers that are then equally segregated onto the two daughter DNA strands [81]. The nucleosome assembly complex then deposits newly synthesized histones to complete the preexisting half of the nucleosomes raising the potential to faithfully and equally transmit histone-associated information from parent to daughter DNA strands [1, 81]. In the DNA methylation process, copying of the methylation pattern during replication is mediated by DNMT1 that preferentially methylates hemimethylated DNA [1]. A similar mechanism could be invoked for HMTs and HATs whereby recruitment to selectively modified histone residues may be afforded by the use of chromo- and bromo-domains within the enzymes themselves.
Role of epigenetics in DNA damage/repair
Following a double stranded strand break (DSB) DNA repair processes such as homologous recombination and single-strand annealing occur and the chromatin adjacent to this DSB plays a role in the repair and signalling events. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of histone H2AX (a variant of histone H2A) is an early event following DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation or by HO endonuclease activity. This is a result of the action of two related PI3K-like kinases called ATR and ATM [82, 83]. Phosphorylation of H2AX forms a binding interface that allows recruitment of cohesions or adaptor proteins to the site of DSB and subsequent recruitment of the repair machinery [82, 83].
Chromatin remodeling complexes such as NuA4 are also recruited to DSB via proximal H2AX [83, 84] possibly allowing the access to or processing of DNA by repair proteins. Interestingly, NuA4 also contains histone acetyltransferase activity and can acetylate histone H4, which is important for resistance to DNA-damaging agents [84]. Importantly, abrogation of NuA4 function sensitizes cells to DSB-inducing agents [83, 84].
Other histone modifications such as ubiquitination, acetylation, and methylation have also been implicated in the DNA damage checkpoint and repair pathways [82, 83]. Despite bulk histone methylation not changing after DNA damage [85] histone methylation does appear to contribute to the repair process directly interacting with checkpoint adaptor proteins. For example, in mammals, H3-K79-Me is important for localization of the adaptor protein 53BP1 [85] and cells deficient in Dot1, the HMT responsible for lysine 79 methylation, are unable to form 53BP1 foci after DNA damage. However, the process is more complex as neither chromatin remodelling complexes nor histone modifications are absolutely required for adaptor proteins to function in the repair of DSB due to ionizing radiation [82, 83].
Epigenetic diseases
Heritable patterns of gene silencing are essential to maintain normal development and cell differentiation in man. Many inherited or somatically acquired diseases which involve learning disorders are associated with chromosomal alterations [3]. Examples of these include mutations in the ATRX gene which results in consistent changes in the pattern of methylation of ribosomal DNA, and fragile X syndrome which occurs when a CGG repeat in the FMR1 5' untranslated region expands and becomes methylated [3], causing the gene to be silenced and creating a visible 'fragile' site on the X chromosome. The gross chromosomal anomalies seen in these diseases points to a central role for epigenetic mechanisms in chromosome architecture. Furthermore, mutations in the DNMT3b gene causes ICF (immunodeficiency, centromeric region instability and facial anomalies) syndrome [14, 86].
A number of the features of complex diseases that are not explained by genetics may be explained, at least in part, by the inheritability, partial stability and reversibility of epigenetic regulation [87]. Epigenetic regulation has been proposed to account for age-of-onset effects, sex effects, parent-of-origin effects (which are very important in asthma and COPD), disease fluctuations and might provide an explanation for the phenotypic discordance often observed among monozygotic twins (70% for multiple sclerosis, 30% to 50% for diabetes, and 25% for asthma) [87, 88]. Interestingly, PADI4 polymorphisms have been associated with rheumatoid arthritis in some, but not all, populations [89, 90]. More recently, global histone modification patterns have been shown to predict the risk of prostate cancer recurrence [91].
Epigenetic control of inflammatory gene expression in lung and airway cells
Induction of inflammatory genes by nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)
Although numerous different pathways are activated during the inflammatory response, nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB) is thought to be of paramount importance in asthmatic inflammation because it is activated by numerous extracellular stimuli including cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor-α (TNFα) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), viruses and immune challenges [92]. In addition, it is a major target for glucocorticoids [93]. NF-κB is ubiquitously expressed within cells, and it not only controls induction of inflammatory genes in its own right but also enhances the activity of other cell- and signal-specific transcription factors [92, 94]. Activation of NF-κB allows it to translocate into the nucleus where it associates with sequence specific DNA binding elements in the promoter region of responsive genes [95].
NF-κB can induce histone acetylation and other histone modifications in a temporal manner [96, 97] leading to recruitment of other co-activator and remodelling complexes and the induction of inflammatory gene expression [95]. NF-κB-induced acetylation occurs preferentially on histone H4, rather than histones 2A, 2B or 3, in epithelial cells and is directed primarily towards lysine residues 8 and 12 at NF-κB responsive regulatory elements [96]. It is not known whether modifications on H2A and H2B occur after NF-κB association/activation. The "histone code" would suggest that even small changes in histone tail modifications could have marked structural changes and allow recruitment of distinct co-activator complexes. Upon DNA binding, NF-κB recruits a large co-activator complex that contains the HAT proteins cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) binding protein (CBP) and p300/CBP (PCAF), although neither of these are the major HAT activated by NF-κB [96]. Several other HATs have been reported to be associated with NF-κB, including transcriptional intermediary factor-2 (TIF-2), also known as glucocorticoid receptor interacting protein-1 (GRIP)-1; p300; and members of the p160 family and steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) [98].
Recently it has become apparent that NF-κB activated by distinct cellular stimuli controls the expression of different patterns of genes [99–101] due to differing temporal profiles of NF-κB activation and nuclear retention. These results suggest that subtle alterations in NF-κB activation conditions may have marked effects on co-factor/remodelling complex recruitment and subsequent gene induction. Furthermore, it has also become clear that small changes in the consensus κB binding site and surrounding bases can have profound effects on the subsequent ability of activated NF-κB to activate gene expression [102]. NF-κB is predominantly composed of the p50/p65 heterodimer [92] and subtle changes in p65 phosphorylation are also influential in regulating NF-κB activity; for example, inactive p65 is nonphosphorylated and is associated predominantly with HDAC1, whereas p65 is phosphorylated following IKK-2 stimulation and is able to bind to coactivator molecules such as p300/CBP [103].
The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A has been reported to enhance NF-κB-driven inflammatory gene transcription in a number of cell lines [96,103\ensash 105]. Two major mechanisms for this effect have been proposed. In the first case it has been reported that NF-κB has an associated HDAC when bound to DNA that acts as a break on the ability of NF-κB to activate local HAT activity. Inhibition of this associated HDAC leads to increased local HAT activity and elevated inflammatory gene transcription [96, 103–105]. Warner Greene and colleagues [105] have proposed an alternative mechanism whereby HDAC3 modifies NF-κB nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling and association with IκBα resulting in enhance nuclear retention of activated p65 that is insensitive to inactivation by IκBα. More recently using overexpression systems it has been suggested that IκBα can sequester HDAC1 and HDAC3 in the cytoplasm enhancing NF-κB activity [106].
Suppression of NF-κB by glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are 21-carbon steroid hormones [107] which are thought to freely diffuse from the circulation into cells across the cell membrane and bind to a cytoplasmic receptor (GR). Once the GR is activated, it translocates to the nucleus, binds to specific DNA sequences in the promoter regions of responsive genes and in a process analogous to that seen with NF-κB above recruits a number of coactivators proteins including CBP and SRC-1 to produce a DNA-protein structure that allows enhanced gene transcription [108]. However, despite the ability of glucocorticoids to induce the transcription of anti-inflammatory genes, such as annexin-1, IL-10, and the inhibitor of NF-κB, IκBα, the major anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids are through repression of inflammatory and immune genes induced by NF-κB [109]. This interaction does not appear to alter DNA binding per se, thus treatment of asthmatic patients with high doses of inhaled corticosteroids that suppress airway inflammation is not associated with any reduction in NF-κB binding to DNA [110].
The interaction between NF-κB and GR may result in differing effects on histone modifications such as acetylation/deacetylation at the activated p65 transcriptional complex, either through GR binding to, or recruiting, nuclear receptor corepressors such as NCoR, or interestingly under some conditions by the co-activator GRIP-1, and HDACs [96, 111] or direct repression of NF-κB- associated HAT activity [96] resulting in alterations in histone modifications at the GM-CSF promoter in epithelial cells [96] resulting in attenuation of gene expression. Similar data has also been reported in primary airway smooth muscle cells where fluticasone was able to attenuate TNFα-induced p65 association with the native CCL11 promoter and block TNFα-induced histone H4 acetylation [112].
Using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays we have demonstrated that corticosteroids reverse the acetylation of the promoter of inflammatory genes such as GM-CSF [96]. Other genes are not recognised through this mechanism, so corticosteroids do not switch off genes involved in basal cell functions, proliferation or survival. Furthermore this explains why corticosteroids are relatively safe, as side effects may be mediated mainly by gene activation mechanisms, which requite higher concentrations of corticosteroids, rather than via gene repression and HDAC recruitment.
It has become clear that histones are not the only targets for histone acetylases and recent evidence has suggested that acetylation of transcription factors can modify their activity. For example, the p65 component of NF-κB can also be acetylated thus modifying its transcriptional activity [113]. We have recently reported that GR is also acetylated upon ligand binding at K494 and K495 and that deaceylation by HDAC2 is critical for interaction with p65, at least at low concentrations of dexamethasone, without affecting the ability of GR to associate with GREs [113]. Furthermore, specific knockdown of HDAC2 by RNA interference resulted in reduced sensitivity to dexamethasone suppression of IL-1β-stimulated GM-CSF release and prevented p65 association with GR. In addition, site -directed mutagenesis of K494 and K495 reduced GR acetylation and the ability to repress NF-κB-dependent gene expression became insensitive to TSA. Finally, we have shown that overexpression of HDAC2 in glucocorticoid insensitive alveolar macrophages from patients with COPD is able to restore glucocorticoid sensitivity [113]. This data suggests that reduction of HDAC2 plays a critical role in glucocorticoid insensitivity in repressing NF-κB, but not GRE, -mediated gene expression.
HATS/HDACs in airway diseases
Little or no data is available about epigenetic marks in respiratory diseases probably due to a lack of research rather than a lack of epigenetic marks. In bronchial biopsies from patients with asthma there is a marked increase in HAT and a small reduction in HDAC activity compared to normal airways [114] (Table 3). Similar changes are found in alveolar macrophages obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with asthma [115]. Changes in activity are associated with reductions in select proteins e.g. there is a small reduction in the expression of HDAC1, but expression of HDAC2 and 3 is normal in these cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (lymphocytes and monocytes) appear to have normal HAT and HDAC activity, indicating that these changes occur locally in the airways of asthmatic patients. Interestingly, in patients with asthma who smoke there is a significantly greater reduction of HDAC activity in bronchial biopsies than in non-smoking asthmatic patients (unpublished observations) and this may account for why these smoking asthmatics have more severe asthma and perhaps a relative steroid insensitivity [116].
In contrast to asthma, in COPD there is no change in HAT activity but a marked reduction in HDAC activity in the lung parenchyma and this decrease is correlated with disease severity [117]. The reduction in HDACs in peripheral lung and BAL macrophages is selective with a marked reduction in HDAC2, with lesser reduction in HDAC5 and HDAC8 expression, but normal expression of the other class 1 and 2 HDACs. Furthermore, HDAC5 expression is predominantly cytoplasmic rather than nuclear in patients with COPD. The reduction in HDAC activity is also related to the intensity of inflammation, as measured by expression of IL-8 and the number of inflammatory cells in small airways [118]. In addition, the lack of clinical efficacy of corticosteroids in COPD compared with marked effects in asthma [119–121] may be explained, at least in part, by an inhibitory effect of cigarette smoking and oxidative stress on HDAC function [122]. Asthmatic patients who smoke have more severe disease and are also resistant to the anti-inflammatory effects of corticosteroids [116, 123]. Alveolar macrophages from normal smokers show a reduction in HDAC activity and expression of HDAC2 (Table 3) and this is correlated with an increase in release of TNF-α and IL-8 in response to an inflammatory stimulus Similarly, in smoking rats there is a reduced expression and activity of HDAC2 which is associated with increased inflammatory gene expression and reduced corticosteroid sensitivity [124].
In addition to subjects with COPD, patients with asthma who smoke cigarettes also show resistance to the anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids and this persists to some extent even in ex-smokers [116, 123]. Cigarette smoking is an oxidative stress and may affect several aspects of steroid function including effects on nuclear cofactors [125, 126]. Importantly, these effects are reversed by antioxidants [125–127]. Intriguingly, there is also a marked increase in oxidative stress in severe glucocorticoid insensitive asthma [128, 129] which also shows reduced HDAC2 expression [115]. This suggests that anti-oxidants or NOS inhibitors, which would reduce the formation of peroxynitrite, may therefore be effective therapies and restore glucocorticoid responsiveness in COPD, severe asthma and asthmatic subjects who smoke (Figure 7).
Oxidative stress can increase the expression inflammatory genes such as interleukin (IL)-8, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP) by up-regulating NF-κB activity (a). Oxidative stress can also prevent glucocorticoid receptor (GR) function by (b) suppression of GR-associated histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) activity and expression since HDAC2 is recruited by GR to NF-κB to switch off inflammatory gene expression.
Recent evidence also suggests that changes in DNA hypersensitivity related to altered methylation patterns and to histone acetylation can occur at the IL-10 locus during T-cell differentiation into Th2 cells and in IL-10-producing regulatory T cells enabling optimal IL-10 gene expression [130]. Similar results occur for other Th2 cytokines in human cells [131].
Virus infections
Adenovirus infection increases the expression of inflammatory genes in epithelial cells in vitro and this appears to be mediated via the adenoviral E1A protein, which is capable of interacting with HAT-containing coactivators such as CBP [132]. In COPD lungs there is evidence for latent adenovirus infection and increased expression of E1A protein, so that this may be a mechanism for amplification of inflammation in COPD patients [133, 134]. Interestingly, adenovirus infection in guinea pigs amplifies the inflammatory response to allergen [135] and is associated with a significant reduction in HDAC activity in the lungs in ovalbumin-sensitized animals [136]. Persistence of adenovirus infections has also been implicated in steroid-resistance in children with asthma [137]. Other virus infections may also impair the action of HDAC2 and thus induce steroid resistance, but this still needs to be explored. Thus, increased gene transcription in inflammatory diseases may be due to increased HAT, decreased HDAC or a combination of both.
Lung cancer
Global hypomethylation, dysregulation of DNA methyltransferase and regional hypermethylation in normally unmethylated CpG islands have all been implicated in lung cancer [138]. Specific CpG island methylation seen in the promoter regions of many genes associated with neoplasias such as p16 suggests that abnormal expression or regulation of Dnmt1 may be important in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [139]. Methylation of the promoter regions in multiple genes has been reported in adenocarcinimas and NSCLC with increasing numbers of methylated genes being associated with tumour progression [140, 141]. The ability to detect these changes in peripheral blood and sputum suggest a useful marker for early detection and/or chemoprotective interventions [142].
Epigenetic therapy
Since many human diseases, in particular cancer, have an epigenetic aetiology investigators have used drugs targeting these processes as novel therapies [3]. Several of these agents including histone deacetylase inhibitors (e.g. SAHA & MS275) and DNA methylase inhibitors (e.g. 5-azacytidine) have been tested in clinical trials with the intention of reactivating the expression of genes that have undergone epigenetic silencing [3]. Results, however, have not proved as successful as predicted from cell line data possibly as a result of cytotoxicity [143]. The prototype methylase inhibitors, 5-azacytidine (5-aza-CR) and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-aza-CdR) are converted to the deoxynucleotide triphosphates and are then incorporated in place of cytosine into replicating DNA. They are therefore active only in S-phase cells, where they serve as powerful mechanism-based inhibitors of DNA methylation [3]. DNA methyltransferases get trapped on DNA containing these modified bases (e.g. azacytosine) resulting in the formation of heritably demethylated DNA [144]. However, covalent attachment of the various DMTs to modified DNA may also be responsible for the cytotoxic effects seen severely limiting their utility [3]. In addition, it is no means that that the therapeutic mechanism of action of DNA methylation and HDAC inhibitors is through epigenetic effects. HDAC inhibitors and DNA methylation inhibitors are cytotoxic agents and induce cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis by upregulating p21 and/or p53 [3, 145]. Furthermore, loss of genomic methylation causes p53-dependent apoptosis, and p53 represses DNMT1, suggesting a feedback loop between the two proteins [3, 146]. Clinical trials with antisense oligonucleotides that target the DNA methyltransferases are also underway [147].
We have shown that the anti-inflammatory effects of theophylline with respect to resduced eosinophilia in bronchial biopsies from asthmatic patients may be mediated via activation of HDAC and that this effect is independent of PDE inhibition [148]. Theophylline appears to preferentially activate class I HDACs, including HDAC2 [149]. However, the exact mechanism whereby theophylline activates HDAC is not yet certain, but is likely to be through signal transduction pathways, probably kinases, that regulate HDAC activity or co-factor association. The effects of theophylline on HDAC appear to be enhanced under conditions of oxidative stress, making it more efficient as a regulator of inflammatory genes [149]. This means that the dose of theophylline does not have to be increased as the disease becomes more severe as the increase in oxidative stress would increase drug activity.
This predicts that theophylline will enhance the anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids and therapeutic concentrations of theophylline markedly potentiate the anti-inflammatory effects of corticosteroids in vitro [149]. This may explain why adding a low dose of theophylline is more effective than increasing the dose of inhaled corticosteroids in patients who are not adequately controlled [150–152].
Summary & conclusions
The recognition that epigenetic modifications of DNA and histones regulate inflammatory gene expression and play a role in diverse functions such as DNA repair, proliferation, RNA interference and in several diseases indicates the global importance of these effects. Their role in lung cancer has become increasingly clear and evidence is accumulating that epigenetic changes may account for some of the heritable effects of cigarette smoking. The reversible nature of these modifications raises the possibility of future therapies directed against these changes.
Abbreviations
- 53BP1 p53-:
-
binding proteinACTR activator of retinoid receptor
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein-1
- ATM:
-
ataxia telangiectasiamutated proteinATR ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related proteinATRX α--thalassemia mental retardation X-linked
- Brg1:
-
Brahma homolog
- CARM1:
-
Co-activator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1
- CBP:
-
CREB binding protein
- CHD1:
-
chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 1
- Co-REST:
-
Co-repressor of REST (RE1 silencing transcription factor)
- CREB:
-
cAMP response element binding protein
- DNMT:
-
DNA methyltransferase
- Dot1p:
-
disruptor of telomeric silencing 1
- DSB:
-
double stranded strand breakE (var) enhancers of PEV
- E(Z):
-
enhancer of zeste
- FMR1:
-
Familial Mental Retardation gene 1
- FOXO1:
-
Forkhead box protein O1
- Gcn5:
-
general control non-derepressible 5
- GNAT:
-
general control non-derepressible 5 related acetyltransferases
- HAT:
-
Histone acetyltransferase
- Hda1:
-
Histone deacetylase 1 (yeast)
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HMT:
-
histone methyl-transferaseHP1 heterochromatin protein 1
- ICF immunodeficiency:
-
centromeric region instability and facial anomalies syndrome
- LCoR:
-
Ligand dependent corepressor
- LCoR:
-
ligand-dependent corepressor
- LSD1:
-
lysine-specific demethylase 1
- MBD3:
-
Methyl CpG binding domain 3
- Mi2:
-
Mi2 autoantigen
- miRNA microRNAMTA-2 Metastasis-associated gene family:
-
member 2
- MYST MOZ:
-
Ybf2/Sas3, Sas2 and Tip60
- N-CoR:
-
Nuclear receptor co-repressor
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- NuA4:
-
Nucleosome histone acetyltransferase of histone 4
- NuRD:
-
Nucleosome remodelling and deacetylating
- PADI4:
-
peptidyl arginine deiminase 4
- PC Drosophila :
-
Polycomb
- PCAF:
-
p300-CBP associated factorPDE Phosphodiesterase
- PEV:
-
position-effect variegation
- PRMT:
-
arginine methyltransferase
- RbAp46:
-
Retinoblastoma associated protein of 46 kDa
- Rpd3:
-
Reduced potassium dependency 3
- SAGA:
-
Spt-Ada-Gen5-acetyltransferase
- SAHA:
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid
- SAP18:
-
Sin3 associated protein of 18kDa
- SDS3:
-
Suppressor of defective silencing 3
- SET Su(var)3–9:
-
Enhancer-of-zeste, Trithorax
- Sin3:
-
Switch insensitive 3
- Sir2:
-
Silent information regulator 2
- SMRT:
-
Silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors
- SRC1:
-
steroid receptor coactivator 1
- Su(var):
-
suppressors of PEV
- SWI/SNF:
-
mating type switching/sucrose non-fermenting
- TAF250:
-
TBP associated factor of 250 kDa
- TBP:
-
TATA box binding protein
- TRX:
-
trithorax
References
Cheung P, Lau P: Epigenetic regulation by histone methylation and histone variants. Mol Endocrinol 2005, 19:563–573.
Wilmut I, Beaujean N, de Sousa PA, Dinnyes A, King TJ, Paterson LA, Wells DN, Young LE: Somatic cell nuclear transfer. Nature 2002, 419:583–586.
Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA: Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature 2004, 429:457–463.
Grewal SI, Elgin SC: Heterochromatin: new possibilities for the inheritance of structure. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2002, 12:178–187.
Eissenberg JC, James TC, Foster-Hartnett DM, Hartnett T, Ngan V, Elgin SC: Mutation in a heterochromatin-specific chromosomal protein is associated with suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990, 87:9923–9927.
Holliday R: The inheritance of epigenetic defects. Science 1987, 238:163–170.
Song F, Smith JF, Kimura MT, Morrow AD, Matsuyama T, Nagase H, Held WA: Association of tissue-specific differentially methylated regions (TDMs) with differential gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102:3336–3341.
Zardo G, Fazi F, Travaglini L, Nervi C: Dynamic and reversibility of heterochromatic gene silencing in human disease. Cell Res 2005, 15:679–690.
Robertson KD: DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 2005, 6:597–610.
Jones PA, Baylin SB: The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2002, 3:415–428.
Feinberg AP, Tycko B: The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat Rev Cancer 2004, 4:143–153.
Takai D, Jones PA: The CpG island searcher: a new WWW resource. In Silico Biol 2003, 3:235–240.
Freitag M, Selker EU: Controlling DNA methylation: many roads to one modification. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2005, 15:191–199.
Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E: DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 1999, 99:247–257.
Chen T, Ueda Y, Dodge JE, Wang Z, Li E: Establishment and maintenance of genomic methylation patterns in mouse embryonic stem cells by Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23:5594–5605.
Chedin F, Lieber MR, Hsieh CL: The DNA methyltransferase-like protein DNMT3L stimulates de novo methylation by Dnmt3a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99:16916–16921.
Jaenisch R, Bird A: Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet 2003, 33 Suppl:245–254.
Goll MG, Bestor TH: Eukaryotic Cytosine Methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem 2004.
Kunert N, Marhold J, Stanke J, Stach D, Lyko F: A Dnmt2-like protein mediates DNA methylation in Drosophila. Development 2003, 130:5083–5090.
Hutchins AS, Mullen AC, Lee HW, Sykes KJ, High FA, Hendrich BD, Bird AP, Reiner SL: Gene silencing quantitatively controls the function of a developmental trans-activator. Mol Cell 2002, 10:81–91.
Vire E, Brenner C, Deplus R, Blanchon L, Fraga M, Didelot C, Morey L, Van EA, Bernard D, Vanderwinden JM, Bollen M, Esteller M, Di CL, de LY, Fuks F: The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 2005.
Fan Y, Nikitina T, Zhao J, Fleury TJ, Bhattacharyya R, Bouhassira EE, Stein A, Woodcock CL, Skoultchi AI: Histone h1 depletion in mammals alters global chromatin structure but causes specific changes in gene regulation. Cell 2005, 123:1199–1212.
Urnov FD, Wolffe AP: Chromatin remodeling and transcriptional activation: the cast (in order of appearance). Oncogene 2001, 20:2991–3006.
Adcock IM, Ito K, Barnes PJ: Glucocorticoids: effects on gene transcription. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2004, 1:247–254.
Holmquist GP: Role of replication time in the control of tissue-specific gene expression. Am J Hum Genet 1987, 40:151–173.
Allfrey VG, Faulkner R, Mirsky AE: Acetylation and methylation of histones and their possible role in the regulation of RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1964, 51:786–794.
Ogryzko VV, Schiltz RL, Russanova V, Howard BH, Nakatani Y: The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 1996, 87:953–959.
Roth SY, Denu JM, Allis CD: Histone acetyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem 2001, 70:81–120.
Gao L, Cueto MA, Asselbergs F, Atadja P: Cloning and functional characterization of HDAC11, a novel member of the human histone deacetylase family. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:25748–25755.
Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T: Reversing histone methylation. Nature 2005, 436:1103–1106.
Rice JC, Allis CD: Code of silence. Nature 2001, 414:258–261.
Peterson CL, Laniel MA: Histones and histone modifications. Curr Biol 2004, 14:R546-R551.
Fischle W, Wang Y, Allis CD: Binary switches and modification cassettes in histone biology and beyond. Nature 2003, 425:475–479.
Carrozza MJ, Utley RT, Workman JL, Cote J: The diverse functions of histone acetyltransferase complexes. Trends Genet 2003, 19:321–329.
Yang XJ: The diverse superfamily of lysine acetyltransferases and their roles in leukemia and other diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 2004, 32:959–976.
Ogryzko VV, Kotani T, Zhang X, Schiltz RL, Howard T, Yang XJ, Howard BH, Qin J, Nakatani Y: Histone-like TAFs within the PCAF histone acetylase complex. Cell 1998, 94:35–44.
Marmorstein R, Berger SL: Structure and function of bromodomains in chromatin-regulating complexes. Gene 2001, 272:1–9.
Zhang Y: Transcriptional regulation by histone ubiquitination and deubiquitination. Genes Dev 2003, 17:2733–2740.
Brownell JE, Allis CD: Special HATs for special occasions: linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1996, 6:176–184.
Peterson CL: HDAC's at work: everyone doing their part. Mol Cell 2002, 9:921–922.
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB: Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J 2003, 370:737–749.
Yang XJ, Gregoire S: Class II Histone Deacetylases: from Sequence to Function, Regulation, and Clinical Implication. Mol Cell Biol 2005, 25:2873–2884.
Porcu M, Chiarugi A: The emerging therapeutic potential of sirtuin-interacting drugs: from cell death to lifespan extension. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2005, 26:94–103.
Jones PL, Shi YB: N-CoR-HDAC corepressor complexes: roles in transcriptional regulation by nuclear hormone receptors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2003, 274:237–268.
Fernandes I, Bastien Y, Wai T, Nygard K, Lin R, Cormier O, Lee HS, Eng F, Bertos NR, Pelletier N, Mader S, Han VK, Yang XJ, White JH: Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor LCoR functions by histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Mol Cell 2003, 11:139–150.
Sengupta N, Seto E: Regulation of histone deacetylase activities. J Cell Biochem 2004, 93:57–67.
Zhang Y, Ng HH, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Bird A, Reinberg D: Analysis of the NuRD subunits reveals a histone deacetylase core complex and a connection with DNA methylation. Genes Dev 1999, 13:1924–1935.
Lechner T, Carrozza MJ, Yu Y, Grant PA, Eberharter A, Vannier D, Brosch G, Stillman DJ, Shore D, Workman JL: Sds3 (suppressor of defective silencing 3) is an integral component of the yeast Sin3[middle dot]Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex and is required for histone deacetylase activity. J Biol Chem 2000, 275:40961–40966.
You A, Tong JK, Grozinger CM, Schreiber SL: CoREST is an integral component of the Co. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98:1454–1458.
Fischle W, Kiermer V, Dequiedt F, Verdin E: The emerging role of class II histone deacetylases. Biochem Cell Biol 2001, 79:337–348.
Baek SH, Ohgi KA, Rose DW, Koo EH, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG: Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. Cell 2002, 110:55–67.
McKinsey TA, Zhang CL, Olson EN: Identification of a signal-responsive nuclear export sequence in class II histone deacetylases. Mol Cell Biol 2001, 21:6312–6321.
McKinsey TA, Zhang CL, Lu J, Olson EN: Signal-dependent nuclear export of a histone deacetylase regulates muscle differentiation. Nature 2000, 408:106–111.
Tomita K, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: The effect of oxidative stress on histone acetylation and IL-8 release. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003, 301:572–577.
Ehrenhofer-Murray AE: Chromatin dynamics at DNA replication, transcription and repair. Eur J Biochem 2004, 271:2335–2349.
Jenuwein T, Laible G, Dorn R, Reuter G: SET domain proteins modulate chromatin domains in eu- and heterochromatin. Cell Mol Life Sci 1998, 54:80–93.
Rea S, Eisenhaber F, O'Carroll D, Strahl BD, Sun ZW, Schmid M, Opravil S, Mechtler K, Ponting CP, Allis CD, Jenuwein T: Regulation of chromatin structure by site-specific histone H3 methyltransferases. Nature JID - 0410462 2000, 406:593–599.
Feng Q, Wang H, Ng HH, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Struhl K, Zhang Y: Methylation of H3-lysine 79 is mediated by a new family of HMTases without a SET domain. Curr Biol 2002, 12:1052–1058.
Pray-Grant MG, Daniel JA, Schieltz D, Yates JRIII, Grant PA: Chd1 chromodomain links histone H3 methylation with. Nature 2005, 433:434–438.
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P, Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA, Shi Y: Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 2004, 119:941–953.
Metzger E, Wissmann M, Yin N, Muller JM, Schneider R, Peters AH, Gunther T, Buettner R, Schule R: LSD1 demethylates repressive histone marks to promote androgen-receptor-dependent transcription. Nature 2005, 437:436–439.
Rugg-Gunn PJ, Ferguson-Smith AC, Pedersen RA: Human Embryonic Stem Cells as a Model for Studying Epigenetic Regulation During Early Development. Cell Cycle 2005., 4:
Lee DY, Teyssier C, Strahl BD, Stallcup MR: Role of protein methylation in regulation of transcription. Endocr Rev 2005, 26:147–170.
Metivier R, Penot G, Hubner MR, Reid G, Brand H, Kos M, Gannon F: Estrogen receptor-alpha directs ordered, cyclical, and combinatorial recruitment of cofactors on a natural target promoter. Cell 2003, 115:751–763.
Cuthbert GL, Daujat S, Snowden AW, Erdjument-Bromage H, Hagiwara T, Yamada M, Schneider R, Gregory PD, Tempst P, Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T: Histone deimination antagonizes arginine methylation. Cell 2004, 118:545–553.
Vossenaar ER, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ: PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays 2003, 25:1106–1118.
Hirota T, Lipp JJ, Toh BH, Peters JM: Histone H3 serine 10 phosphorylation by Aurora B causes HP1 dissociation from heterochromatin. Nature 2005, 438:1176–1180.
Fischle W, Tseng BS, Dormann HL, Ueberheide BM, Garcia BA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Funabiki H, Allis CD: Regulation of HP1-chromatin binding by histone H3 methylation and phosphorylation. Nature 2005, 438:1116–1122.
An W, Kim J, Roeder RG: Ordered cooperative functions of PRMT1, p300, and CARM1 in transcriptional activation by p53. Cell 2004, 117:735–748.
Henikoff S, Ahmad K: Assembly of Variant Histones into Chromatin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2005.
Ouspenski II, Van Hooser AA, Brinkley BR: Relevance of histone acetylation and replication timing for deposition of centromeric histone CENP-A. Exp Cell Res 2003, 285:175–188.
Wen J, Huang S, Pack SD, Yu X, Brandt SJ, Noguchi CT: Tal1/SCL binding to pericentromeric DNA represses transcription. J Biol Chem 2005, 280:12956–12966.
Bender J: DNA methylation and epigenetics. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2004, 55:41–68.
Napoli C, Lemieux C, Jorgensen R: Introduction of a Chimeric Chalcone Synthase Gene into Petunia Results in Reversible Co-Suppression of Homologous Genes in trans. Plant Cell 1990, 2:279–289.
Bayne EH, Allshire RC: RNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammals. Trends Genet 2005, 21:370–373.
Stevenson DS, Jarvis P: Chromatin silencing: RNA in the driving seat. Curr Biol 2003, 13:R13-R15.
Migeon BR, Chowdhury AK, Dunston JA, McIntosh I: Identification of TSIX, encoding an RNA antisense to human XIST, reveals differences from its murine counterpart: implications for X inactivation. Am J Hum Genet 2001, 69:951–960.
Tufarelli C, Stanley JA, Garrick D, Sharpe JA, Ayyub H, Wood WG, Higgs DR: Transcription of antisense RNA leading to gene silencing and methylation as a novel cause of human genetic disease. Nat Genet 2003, 34:157–165.
Byvoet P, Shepherd GR, Hardin JM, Noland BJ: The distribution and turnover of labeled methyl groups in histone fractions of cultured mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 1972, 148:558–567.
Jeppesen P: Histone acetylation: a possible mechanism for the inheritance of cell memory at mitosis. Bioessays 1997, 19:67–74.
Tagami H, Ray-Gallet D, Almouzni G, Nakatani Y: Histone H3.1 and H3.3 complexes mediate nucleosome assembly pathways dependent or independent of DNA synthesis. Cell 2004, 116:51–61.
Pilch DR, Sedelnikova OA, Redon C, Celeste A, Nussenzweig A, Bonner WM: Characteristics of gamma-H2AX foci at DNA double-strand breaks sites. Biochem Cell Biol 2003, 81:123–129.
Vidanes GM, Bonilla CY, Toczyski DP: Complicated tails: histone modifications and the DNA damage response. Cell 2005, 121:973–976.
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 2002, 16:6–21.
Huyen Y, Zgheib O, Ditullio RAJ, Gorgoulis VG, Zacharatos P, Petty TJ, Sheston EA, Mellert HS, Stavridi ES, Halazonetis TD: Methylated lysine 79 of histone H3 targets 53BP1 to DNA double-strand breaks. Nature 2004, 432:406–411.
Kumar A: Rett and ICF syndromes: methylation moves into medicine. J Biosci 2000, 25:213–214.
Vercelli D: Genetics, epigenetics, and the environment: switching, buffering, releasing. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004, 113:381–386.
Petronis A: Human morbid genetics revisited: relevance of epigenetics. Trends Genet 2001, 17:142–146.
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, Tokuhiro S, Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Nakayama-Hamada M, Kawaida R, Ono M, Ohtsuki M, Furukawa H, Yoshino S, Yukioka M, Tohma S, Matsubara T, Wakitani S, Teshima R, Nishioka Y, Sekine A, Iida A, Takahashi A, Tsunoda T, Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K: Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 2003, 34:395–402.
Barton A, Bowes J, Eyre S, Spreckley K, Hinks A, John S, Worthington J: A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population is not associated in a United Kingdom population. Arthritis Rheum 2004, 50:1117–1121.
Seligson DB, Horvath S, Shi T, Yu H, Tze S, Grunstein M, Kurdistani SK: Global histone modification patterns predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Nature 2005, 435:1262–1266.
Baldwin ASJ: Series introduction: the transcription factor NF-kappaB and human disease. J Clin Invest 2001, 107:3–6.
Barnes PJ, Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 1997, 336:1066–1071.
Ohmori Y, Schreiber RD, Hamilton TA: Synergy between interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in transcriptional activation is mediated by cooperation between signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and nuclear factor kappaB. J Biol Chem JID - 2985121R 1997, 272:14899–14907.
Ghosh S, Karin M: Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 2002, 109 Suppl:S81-S96.
Ito K, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: Glucocorticoid receptor recruitment of histone deacetylase 2 inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced histone H4 acetylation on lysines 8 and 12. Mol Cell Biol 2000, 20:6891–6903.
Lee KY, Ito K, Hayashi R, Jazrawi EP, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: NF-{kappa}B and Activator Protein 1 Response Elements and the Role of Histone Modifications in IL-1{beta}-Induced TGF-{beta}1 Gene Transcription. J Immunol 2006, 176:603–615.
Jenkins BD, Pullen CB, Darimont BD: Novel glucocorticoid receptor coactivator effector mechanisms. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2001, 12:122–126.
Covert MW, Leung TH, Gaston JE, Baltimore D: Achieving stability of lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB activation. Science 2005, 309:1854–1857.
Werner SL, Barken D, Hoffmann A: Stimulus specificity of gene expression programs determined by temporal control of IKK activity. Science 2005, 309:1857–1861.
Ogawa S, Lozach J, Benner C, Pascual G, Tangirala RK, Westin S, Hoffmann A, Subramaniam S, David M, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK: Molecular determinants of crosstalk between nuclear receptors and toll-like receptors. Cell 2005, 122:707–721.
Leung TH, Hoffmann A, Baltimore D: One nucleotide in a kappaB site can determine cofactor specificity for NF-kappaB dimers. Cell 2004, 118:453–464.
Zhong H, May MJ, Jimi E, Ghosh S: The phosphorylation status of nuclear NF-kappa B determines its association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol Cell 2002, 9:625–636.
Ashburner BP, Westerheide SD, Baldwin ASJ: The p65 (RelA) subunit of NF-kappaB interacts with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressors HDAC1 and HDAC2 to negatively regulate gene expression. Mol Cell Biol JID - 8109087 2001, 21:7065–7077.
Chen L, Fischle W, Verdin E, Greene WC: Duration of nuclear NF-kappaB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science JID - 0404511 2001, 293:1653–1657.
Viatour P, Legrand-Poels S, Van Lint C, Warnier M, Merville MP, Gielen J, Piette J, Bours V, Chariot A: Cytoplasmic IkappaBalpha increases NF-kappaB-independent transcription through binding to histone deacetylase (HDAC) 1 and HDAC3. J Biol Chem 2003, 278:46541–46548.
Johnson M: Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of inhaled glucocorticoids. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1996, 97:169–176.
Karin M: New twists in gene regulation by glucocorticoid receptor: is DNA binding dispensable? Cell 1998, 93:487–490.
Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: How do corticosteroids work in asthma? Ann Intern Med 2003, 139:359–370.
Hart L, Lim S, Adcock I, Barnes PJ, Chung KF: Effects of inhaled corticosteroid therapy on expression and DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor kappaB in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000, 161:224–231.
Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK: Coregulator codes of transcriptional regulation by nuclear receptors. J Biol Chem 2001, 276:36865–36868.
Nie M, Knox AJ, Pang L: beta2-Adrenoceptor agonists, like glucocorticoids, repress eotaxin gene transcription by selective inhibition of histone H4 acetylation. J Immunol 2005, 175:478–486.
Ito K, Yamamura S, Essilfie-Quaye S, Cosio B, Ito M, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: Histone deacetylase 2-mediated deacetylation of the glucocorticoid receptor enables NF-{kappa}B suppression. J Exp Med 2005.
Ito K, Caramori G, Lim S, Oates T, Chung KF, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: Expression and activity of histone deacetylases in human asthmatic airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002, 166:392–396.
Cosio BG, Mann B, Ito K, Jazrawi E, Barnes PJ, Chung KF, Adcock IM: Histone acetylase and deacetylase activity in alveolar macrophages and blood mononocytes in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004, 170:141–147.
Chaudhuri R, Livingston E, McMahon AD, Thomson L, Borland W, Thomson NC: Cigarette smoking impairs the therapeutic response to oral corticosteroids in chronic asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 168:1308–1311.
Ito K, Ito M, Eliott WM, Cosio B, Caramori G, Kon OM, B. B, Hayashi S, Adcock IM, Hogg JC, Barnes PJ: Decreased Histone Deacetylase Activity in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Relationship to Disease Severity. N Engl J Med 2005, In Press.
Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, Buzatu L, Cherniack RM, Rogers RM, Sciurba FC, Coxson HO, Pare PD: The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2004, 350:2645–2653.
Keatings VM, Jatakanon A, Worsdell YM, Barnes PJ: Effects of inhaled and oral glucocorticoids on inflammatory indices in asthma and COPD. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997, 155:542–548.
Culpitt SV, Maziak W, Loukidis S, Nightingale JA, Matthews JL, Barnes PJ: Effect of high dose inhaled steroid on cells, cytokines, and proteases in induced sputum in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999, 160:1635–1639.
Loppow D, Schleiss MB, Kanniess F, Taube C, Jorres RA, Magnussen H: In patients with chronic bronchitis a four week trial with inhaled steroids does not attenuate airway inflammation. Respir Med 2001, 95:115–121.
Ito K, Lim S, Caramori G, Chung KF, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: Cigarette smoking reduces histone deacetylase 2 expression, enhances cytokine expression, and inhibits glucocorticoid actions in alveolar macrophages. FASEB J 2001, 15:1110–1112.
Chalmers GW, Macleod KJ, Little SA, Thomson LJ, McSharry CP, Thomson NC: Influence of cigarette smoking on inhaled corticosteroid treatment in mild asthma. Thorax 2002, 57:226–230.
Marwick JA, Kirkham PA, Stevenson CS, Danahay H, Giddings J, Butler K, Donaldson K, Macnee W, Rahman I: Cigarette smoke alters chromatin remodeling and induces proinflammatory genes in rat lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2004, 31:633–642.
Barnes PJ, Ito K, Adcock IM: Corticosteroid resistance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: inactivation of histone deacetylase. Lancet 2004, 363:731–733.
Ito K, Hanazawa T, Tomita K, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM: Oxidative stress reduces histone deacetylase 2 activity and enhances IL-8 gene expression: role of tyrosine nitration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004, 315:240–245.
Okamoto K, Tanaka H, Ogawa H, Makino Y, Eguchi H, Hayashi S, Yoshikawa N, Poellinger L, Umesono K, Makino I: Redox-dependent regulation of nuclear import of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem 1999, 274:10363–10371.
Kharitonov SA, Barnes PJ: Nitric oxide, nitrotyrosine, and nitric oxide modulators in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2003, 3:121–129.
Katsoulis K, Kontakiotis T, Leonardopoulos I, Kotsovili A, Legakis IN, Patakas D: Serum total antioxidant status in severe exacerbation of asthma: correlation with the severity of the disease. J Asthma 2003, 40:847–854.
Saraiva M, Christensen JR, Tsytsykova AV, Goldfeld AE, Ley SC, Kioussis D, O'Garra A: Identification of a macrophage-specific chromatin signature in the IL-10 locus. J Immunol 2005, 175:1041–1046.
Santangelo S, Cousins DJ, Winkelmann NE, Staynov DZ: DNA methylation changes at human Th2 cytokine genes coincide with DNase I hypersensitive site formation during CD4(+) T cell differentiation. J Immunol 2002, 169:1893–1903.
Higashimoto Y, Elliott WM, Behzad AR, Sedgwick EG, Takei T, Hogg JC, Hayashi S: Inflammatory mediator mRNA expression by adenovirus E1A-transfected bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002, 166:200–207.
Retamales I, Elliott WM, Meshi B, Coxson HO, Pare PD, Sciurba FC, Rogers RM, Hayashi S, Hogg JC: Amplification of inflammation in emphysema and its association with latent adenoviral infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001, 164:469–473.
Hogg JC: Role of latent viral infections in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001, 164:S71-S75.
Yamada K, Elliott WM, Brattsand R, Valeur A, Hogg JC, Hayashi S: Molecular mechanisms of decreased steroid responsiveness induced by latent adenoviral infection in allergic lung inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002, 109:35–42.
Ito M, Yamada K, Vitalis TZ, Elliott WM, To Y, Hayashi S, Adcock IM, Hogg JC, Barnes PJ, Ito K: Latent adenovirus infection decreases histone deacetylase activity in the lungs of ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004, 169:A78.
Macek V, Sorli J, Kopriva S, Marin J: Persistent adenoviral infection and chronic airway obstruction in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994, 150:7–10.
Herman JG: Epigenetics in lung cancer: focus on progression and early lesions. Chest 2004, 125:119S-122S.
Belinsky SA, Nikula KJ, Palmisano WA, Michels R, Saccomanno G, Gabrielson E, Baylin SB, Herman JG: Aberrant methylation of p16(INK4a) is an early event in lung cancer and a potential biomarker for early diagnosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95:11891–11896.
Zochbauer-Muller S, Fong KM, Virmani AK, Geradts J, Gazdar AF, Minna JD: Aberrant promoter methylation of multiple genes in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res 2001, 61:249–255.
Zochbauer-Muller S, Fong KM, Maitra A, Lam S, Geradts J, Ashfaq R, Virmani AK, Milchgrub S, Gazdar AF, Minna JD: 5' CpG island methylation of the FHIT gene is correlated with loss of gene expression in lung and breast cancer. Cancer Res 2001, 61:3581–3585.
Zochbauer-Muller S, Lam S, Toyooka S, Virmani AK, Toyooka KO, Seidl S, Minna JD, Gazdar AF: Aberrant methylation of multiple genes in the upper aerodigestive tract epithelium of heavy smokers. Int J Cancer 2003, 107:612–616.
Moradei O, Maroun CR, Paquin I, Vaisburg A: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: latest developments, trends and prospects. Curr Med Chem Anti -Canc Agents 2005, 5:529–560.
Zhou L, Cheng X, Connolly BA, Dickman MJ, Hurd PJ, Hornby DP: Zebularine: a novel DNA methylation inhibitor that forms a covalent complex with DNA methyltransferases. J Mol Biol 2002, 321:591–599.
Marks PA, Richon VM, Miller T, Kelly WK: Histone deacetylase inhibitors. Adv Cancer Res 2004, 91:137–168.
Karpf AR, Moore BC, Ririe TO, Jones DA: Activation of the p53 DNA damage response pathway after inhibition of DNA methyltransferase by 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine. Mol Pharmacol 2001, 59:751–757.
Yan L, Nass SJ, Smith D, Nelson WG, Herman JG, Davidson NE: Specific inhibition of DNMT1 by antisense oligonucleotides induces re-expression of estrogen receptor-alpha (ER) in ER-negative human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther 2003, 2:552–556.
Ito K, Lim S, Caramori G, Cosio B, Chung KF, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ: A molecular mechanism of action of theophylline: Induction of histone deacetylase activity to decrease inflammatory gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99:8921–8926.
Cosio BG, Tsaprouni L, Ito K, Jazrawi E, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ: Theophylline restores histone deacetylase activity and steroid responses in COPD macrophages. J Exp Med 2004, 200:689–695.
Evans DJ, Taylor DA, Zetterstrom O, Chung KF, O'Connor BJ, Barnes PJ: A comparison of low-dose inhaled budesonide plus theophylline and high-dose inhaled budesonide for moderate asthma. N Engl J Med 1997, 337:1412–1418.
Ukena D, Harnest U, Sakalauskas R, Magyar P, Vetter N, Steffen H, Leichtl S, Rathgeb F, Keller A, Steinijans VW: Comparison of addition of theophylline to inhaled steroid with doubling of the dose of inhaled steroid in asthma. Eur Respir J 1997, 10:2754–2760.
Lim S, Jatakanon A, Gordon D, Macdonald C, Chung KF, Barnes PJ: Comparison of high dose inhaled steroids, low dose inhaled steroids plus low dose theophylline, and low dose inhaled steroids alone in chronic asthma in general practice. Thorax 2000, 55:837–841.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of Asthma UK, The Clinical Research Committee (RBH), The Medical Research Council (UK), The National Institutes of Health USA, The Wellcome Trust, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, GlaxoSmithKline, Mitsubishi (Japan), Novartis and Pfizer for supporting research in our laboratories.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests
Authors' contributions
All authors contributed equally towards the writing of this review.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Adcock, I.M., Ford, P., Ito, K. et al. Epigenetics and airways disease. Respir Res 7, 21 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-7-21
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-7-21