Abstract
Quantitative trait loci (QTL) affecting carcass and meat quality located on SSC2 were identified using variance component methods. A large number of traits involved in meat and carcass quality was detected in a commercial crossbred population: 1855 pigs sired by 17 boars from a synthetic line, which where homozygous (A/A) for IGF2. Using combined linkage and linkage disequilibrium mapping (LDLA), several QTL significantly affecting loin muscle mass, ham weight and ham muscles (outer ham and knuckle ham) and meat quality traits, such as Minolta-L* and -b*, ultimate pH and Japanese colour score were detected. These results agreed well with previous QTL-studies involving SSC2. Since our study is carried out on crossbreds, different QTL may be segregating in the parental lines. To address this question, we compared models with a single QTL-variance component with models allowing for separate sire and dam QTL-variance components. The same QTL were identified using a single QTL variance component model compared to a model allowing for separate variances with minor differences with respect to QTL location. However, the variance component method made it possible to detect QTL segregating in the paternal line (e.g. HAMB), the maternal lines (e.g. Ham) or in both (e.g. pHu). Combining association and linkage information among haplotypes improved slightly the significance of the QTL compared to an analysis using linkage information only.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pig breeding programs aim at improving pigs for economically important traits. Carcass quality has been successfully improved in most selection programs because phenotypes are easy to obtain on live animals via ultrasonically measurements of backfat and because these traits show a relatively high heritability. However, although breeding for meat quality has received much attention over the past two decades, it has not been the priority in most selection programs [1–4] because meat quality traits can only be measured on the relatives of selection candidates and late in life. Successful improvement of meat quality may be possible by combining molecular information and traditional measurements because marker data can be obtained on all animals at an early age [5].
Molecular information, i.e. genes and QTL, has rapidly become available via genome scans of experimental crossbred populations (see review by Bidanel and Rothschild [6] and PigQTLdb [7]). In many cases, favourable QTL cannot be exploited due to the poor performance of these exotic breeds with respect to commercially relevant traits. However, the number of QTL studies using commercial populations is increasing [8–22]. Identification of QTL using commercial lines requires a large number of families because fewer heterozygous founders are expected especially for traits under selection such as carcass quality traits.
Most of the studies mentioned above use 'paternal half sib regression' as the statistical method to associate genotypes with phenotypes, which models the segregation of paternal QTL [23]. Variance component methods, based on the theory developed by Fernando and Grossman [24], are currently becoming the method of choice in association studies because they allow for much greater flexibility in the modelling of QTL in arbitrary pedigrees while adjusting simultaneously for systematic environmental effects [13, 25]. A preliminary analysis using eight half-sib families, detected putative QTL on SSC2 [15]. Based on these results, nine additional families were genotyped and analysed to increase the marker density in regions of interest. The goal of this paper is to map QTL affecting meat and carcass quality of commercial finishers and located on SSC2 using variance component methods.
Methods
Population and phenotypes
The 1855 commercial finishers were a cross product of 17 boars of a synthetic sire line (Large White/Pietrain, TOPIGS, The Netherlands) and 239 unregistered hybrid sows. The piglets were born during a two-month period in 2002. Piglets were individually tagged at birth and males were castrated three to five days after farrowing. Pigs were weaned on average at 17 days of age and raised till an average weight of 22.7 kg before being moved to the finishing barns. Diets comprised commercial available feeds and free access to water.
Pigs were loaded in three batches per compartment at an average weight of 118 kg live weight and kept overnight in a lairage at the slaughterhouse. The average age (AGE) of each batch was 164, 172 and 185 days, respectively. During a 70-day period, pigs were slaughtered on 17 different days. Measurements on the carcass were recorded on one half of the carcass. Backfat (BF) and loin depth (LD) were measured at the 10th rib using the Hennessy grading probe HGP Systems Ltd, Auckland NZ). Lean percentage (PLEAN) was calculated as: PLEAN = 58.86 - (0.61 × BF) + (0.12 × LD). Cold carcass weight (CCW) was recorded after temperature equalization. Primal cuts of ham (HAM) and loin (LOIN) were weighed and further dissected into boneless subprimals and individual muscles. Skin and fat were removed from hams removed and four subprimals were weighted: inside ham (IHAM), outer ham (OHAM), knuckle ham (KHAM) and the lite butt ham (LBHAM,i.e. part of the gluteus medius muscle). Together they summed to boneless ham muscle weight (BHAM). Loins were processed to a boneless loin without the fat cover (DLOIN).
Meat quality measurements were taken both on the loin and the ham. Ultimate pH (pHu) was measured in the boneless loin 24–28 h post mortem. Loin Minolta L*, a* and b* (LOINL, LOINA and LOINB) were taken on the fresh cut surface of a 2.5-cm chop removed from the sirloin end using a Minolta CR 300 (Minolta, Osaka, Japan). The same chop was used for a subjective colour score (score 1 to 6, with 1 = pale and 6 = very dark) using the Japanese colour scale (JCScut). The side view of the loin was also scored using this scale (JCSrib). A subjective marbling score (LMARB; 1 to 5, with 1 = devoid and 5 = overly abundant) was given to the chop based on marbling standards of the National Pork Producers Council [26]. Cores were taken from a second 2.5-cm chop using a 25-mm coring device to determine drip loss percentage (DRIP). Samples were weighed and put in pre-weighed tubes and stored in a cooler. After 24 h samples were reweighed and drip loss was calculated [27]. Purge loss (PURGE, %) was determined by weighing a 7.5- to 10-cm piece of the remainder of the boneless loin, cooling it for 5 days in plastic bags and reweighing. Subjective firmness scores (FIRM; 1 to 3, 1 = soft and exudative and 3 = firm) were evaluated using NPPC standards [28].
Meat quality measurements taken on the ham included Minolta L*, a* and b* values on the fresh cut surface of the inside ham muscle (HAML, HAMA and HAMB). A subjective marbling score (HMARB; 1 to 4; 1 = devoid and 4 = abundant) was assigned to the outside ham muscle. General statistics regarding the data is given in van Wijk et al. [29].
Genotyping and linkage map
DNA was extracted from ear or loin tissue samples using the Puregene® DNA Isolation kit (D-70KA, Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, USA). Isolated DNA was tested on 1.2% agarose gel for quality and adjusted in NaCl-Tris-EDTA (STE) buffer to a final concentration of 15 ng/μL. Genotyping was performed in two batches. First eight half-sib families were typed for 10 microsatellite markers on SSC2 [15]. Next, nine additional families were genotyped for eight markers (out of the 10 markers previously used). Subsequently 16 microsatellite markers were added to fine-map regions on SSC2 based on preliminary analyses. All boars were genotyped for IGF2 and they were homozygous (A/A). The markers included in the statistical analysis are shown in Table 1. Genotypes were scored in duplicate and checked against pedigree information. Crimap 2.4 [30] was used to construct a sex-average linkage map. Resulting recombination fractions/cM distances were used in Simwalk version 2.89 [31] to reconstruct haplotypes, which were used in QTL analyses. Distances calculated with the Haldane linkage function were used in QTL analyses while distances calculated with the Kosambi linkage function are reported for comparison with QTL locations given in the literature [7].
Statistical analysis
QTL were mapped based on a combined linkage disequilibrium and segregation analysis using the variance component method because this method uses both the segregation from the sires and the dams, uses linkage disequilibrium among haplotypes in the founders, allows for simultaneously estimation of polygenic-, QTL-, litter- and fixed-effects and allows for complex pedigrees (half- and full-sib structure). Identity by descent (IBD) probabilities of haplotypes, using reconstructed haplotypes, were calculated using the LDLA package [32], which is based on the theory developed by Meuwissen and Goddard [33]. IBD probability matrices were calculated at the midpoint of each bracket of flanking markers. The likelihood at each evaluation point was determined using ASREML [34]. For comparison reasons, models were also fitted ignoring the linkage disequilibrium (LA-only).
Phenotypes were analysed according to the following model. Since the pedigree of the sows was not available a sire-dam model was used (one component model):
y = Xb + Zs + Sc + Wv + e, (1)
where y is a vector containing phenotypic values, b is a vector containing non-genetic effects, s is a vector containing polygenic sire effects, c is a vector containing common litter and dam effects, v is a vector containing haplotype effects due to a putative QTL and e contains the residual effects. Non-genetic effects considered were a barn-group-batch, and sex as class variables and 'cold carcass weight' and 'days in the finishing barn' as linear covariables. The random effects of s, c, v and e were assumed to be normally distributed with zero mean and variances Aσ2 s , Iσ2 c , G p σ2 v and Iσ2 e , respectively where A is the genetic relationship matrix among the sires including five generations of known pedigree, G p is the IBD matrix among the haplotypes at evaluation point p and I is an identity matrix. X, Z, S and W are incidence matrices relating effects to phenotypes.
To relax the assumption of equal variance among the paternal and maternal haplotypes in model 1 the following model (2) was applied:
y = Xb + Zu + Sc + W s v s +W d v d + e. (2)
In model 2, a separate variance component is fitted for the paternal (v s ) and maternal (v d ) haplotypes (two-component model). Since the sires and the anonymous hybrid dams originated from different populations different QTL-alleles may be segregating at the QTL.
Test statistic and significance threshold
To test the hypothesis of the presence of a QTL (H1) versus no QTL (H0) the likelihood ratio test (LRT) was applied. The LRT statistic at each midpoint between adjacent markers was calculated as twice the difference between the log likelihood of model 1 (or 2) minus the log likelihood of a model without a QTL effect. The test statistic plotted along the chromosome gave a LRT-profile. Given this profile, thresholds were calculated which take multiple testing across the chromosome into account using the method described by Piepho [35]. Since different likelihood profiles were obtained for each model and trait specific threshold values were obtained for each combination, significance was tested using this specific threshold.
Results and discussion
Map construction
Genetic linkage maps are presented in Table 1. The order of the markers and the distance among markers is in close agreement with the USDA-MARC.2 genetic linkage map [36] except for marker pair SWR1910-SWR783, which is reversed and separated by 14 cM instead of 1 cM. The average distance among the markers is 6 cM.
QTL
The LRT statistics for traits that exceeded a Piepho-corrected threshold value of 0.05 and the position of their maximum value are given in Table 2. Depending on the trait analysed, the 0.05 threshold obtained corresponded with a nominal p-value of around 0.005. Few false positive QTL will be found at the expense of false negatives using these strict thresholds. Use of a commercial population that has been under selection for several decades might be another reason for the number of QTL observed in this study.
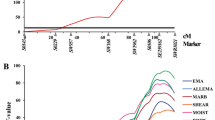
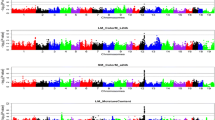
Results are shown for the model applying a single variance component as well as for the two-component model, i.e. allowing for different variances among paternal and among maternal haplotypes. The LRT statistics and position of the QTL were very similar for both models. LRT-profiles for meat quality traits with significant QTL are shown in Figure 1 using LRT-values from the two-component model. In Figure 2 similar profiles are shown for carcass quality traits. Applying an analysis using linkage information only (LA-only) showed fewer and less significant QTL (Table 2). Especially for ham-related traits linkage disequilibrium information seems to be of added value.
Colour
A significant QTL was observed for HAML. The estimated location differed slightly for the two models: 17 cM for the one-component model and 26 cM for the two-component model. Malek et al. [11] also found a QTL for this trait on SSC2 but they were located at 72 and 116 cM. (The locations of QTL from other studies are taken from the pigQTLdb [7] where all the map distances are converted to the USDA-MARC map). For HAMB no QTL have previously been reported on SSC2. The JCSrib QTL is in accordance with the QTL for a similar subjective colour score observed by Malek et al. [11] although their score was on the cut surface of the loin instead of the side-rib-view. The QTL for HAMB and JCSrib were found at almost the same position, which might indicate that it is the same QTL affecting both traits.
pH
The QTL for pHu on SSC2 was observed between markers Sw1686 and Sw2167 (65 cM). Lee et al. [37] observed two QTL for pHu on SCC2 at 42 and 64 cM in a F2-cross between Meishan and Pietrain. Su et al. [38] observed a QTL for pHu at 67 cM. The ultimate pH is usually a good predictor of water holding capacity. Malek et al. [11] showed that two QTL are segregating for this trait on SSC2 (around 75 and 114 cM). However, in this study no significant QTL were found for drip or purge.
Carcass traits
Figure 2 suggests that more than one QTL on SSC2 affect the amount of loin muscle (DLOIN). The most significant QTL for DLOIN at 73 cM on SSC2 has never been reported. Several studies have reported a QTL involving amount of loin at the beginning of SSC2, which is most likely associated with the IGF2-gene [22, 39, 40, 37, 17]. However, Varona et al. [41] and also Lee et al. [37] have reported a QTL for loin depth and percentage lean cuts around 65 cM.
Total kg of ham (HAM) as well as part of this ham (OHAM) showed a significant QTL at 103 cM, but the significant QTL for knuckle ham (KHAM) was situated at the end of SSC2. Duthie et al. [17] have detected a QTL for ham weight on SCC2 at 15 cM like Vidal et al. [14] but this latter study does not give the position.
Variance components
In Table 3, the proportion of total variance due to polygenic (h2), litter (c2) and QTL (v2) as well as the residual and total variance are given for traits mentioned in Table 2 at the evaluation point where the LRT for the QTL was at its maximum. Given the hybrid origin of the population used in this study, i.e. a single strain sire line was crossed with a 3-way cross sow, the two-component model is probably more appropriate than the one-component model because in the two-component model the segregation of the paternal and maternal haplotypes are modelled as independent effects. This is illustrated in Table 3 where contribution of paternal and maternal components is given, i.e. v2s and v2d.
In general, proportions of variance due to polygenic and litter effects are in close agreement with van Wijk et al. [29] in which data was analysed before marker data was available, i.e. they applied a model without QTL effects. The biggest disagreement was observed when comparing the h2 estimates for pHu. The h2 for pHu dropped from 0.11 to 0.02. In both models, the QTL variance (v2) is relatively high indicating that the genetic variance has shifted from polygenic to QTL variance. This might be the result of the specific data analysed. Since it is unlikely that a single QTL explains most of the genetic variance, the QTL variance is most likely overestimated.
Different variance components for sire and dam haplotypes for HAMB and HAM indicate that the underlying QTL are not segregating in dam and sires, respectively. Preferably a two-component model should be applied for crossbred data where different QTL alleles could be segregating in different populations involved in the hybrid offspring.
LDLA
In this study, linkage disequilibrium (LD) information was included when calculating the IBD matrices. However, it is not clear how IBD due to LD should be calculated for crossbred populations. The theory developed by Meuwissen and Goddard [33] assumes a single population 100 generations ago, which is not very likely for very different pig breeds. Uleberg et al. [42] have applied an IBD-value of zero due to LD between base-haplotypes of different breeds. Given that all pigs originate from a domesticated wild boar population this seems to be too extreme because haplotypes could be identical by descent due to the single origin. Biodiversity studies, e.g. Eding and Meuwissen [43], which provide estimates of genetic distance among breeds, could be used to determine IBD within and between breeds simultaneously.
Compared to Meuwissen et al. [44] and Olsen et al. [45] the LRT-profiles (Figures 1 and 2) are less peaked. This might due to the lower marker density used in this study or to the use of cross bred data instead of single population data in the other studies, which have a positive effect on linkage disequilibrium information because IBD among founder haplotypes can be better estimated. In particular, the linkage disequilibrium information decreases the width of the peaks because it takes historic recombination into account [44].
Conclusion
QTL affecting meat and carcass quality were found on SSC2 in this large, commercially produced population. QTL-effects were significant even after correction for multiple testing. The variance component method to detect QTL made it possible to detect QTL segregating in the paternal line (e.g. HAMB), the maternal lines (e.g. Ham) or in both (e.g. pHu). Combining association and linkage information among haplotypes slightly improved the significance of the QTL compared to an analysis using linkage information only.
References
De Vries AG, Wal van der PG, Eikelenboom G, Merks JWM: Genetische variatie in varkensvleeskwaliteit. I.V.O. report B-376. 1992, I.V.O. Zeist, The Netherlands
Hovenier R, Kanis E, van Asseldonk T, Westerink NG: Breeding for pig meat quality in halothane-negative populations – a review. Pig News Inf. 1993, 14: 17N-25N.
Sellier P: Genetics of meat and carcass traits. The genetics of the pig. Edited by: Rothschild MF, Ruvinsky A. 1998, Oxon, UK: CAB International, 463-510.
Knap PW, Sosnicki AA, Klont RE, Lacoste A: Simultaneous improvement of meat quality and growth-and-carcass traits in pigs. Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production. 2002, 31: 339-346.
Heuven HCM, van Wijk HJ, van Arendonk JAM: Combining traditional breeding and genomics to improve pork quality. Outlook on Agriculture. 2003, 32: 235-239.
Bidanel JP, Rothschild M: Current status of quantitative trait locus mapping in pigs. Pig News Inf. 2002, 23: 39-53.
Hu Z-L, Dracheva S, Jang W, Maglott D, Bastiaansen J, Rothschild MF, Reecy J: A quantitative trait loci resource and comparison tool for pigs: PigQTLDB. Mamm Genome. 2005, 15: 792-800. 10.1007/s00335-005-0060-9.
Rohrer GA, Keele JW: Identification of quantitative trait loci affecting carcass composition in swine: II Muscling and wholesale product yield traits. J Anim Sci. 1998, 76: 2255-2262.
Nezer C, Moreau L, Brouwers B, Coppieters W, Detilleux J, Hanset R, Karim L, Kvasz A, Leroy P, Georges M: An imprinted QTL with a major effect on muscle mass and fat deposition maps to the IGF2 locus in pigs. Nat Genet. 1999, 21: 155-156. 10.1038/5935.
Grindflek E, Szyda J, Liu Z, Lien S: Detection of quantitative trait loci for meat quality in a commercial slaughter pig cross. Mamm Genome. 2001, 12: 299-304. 10.1007/s003350010278.
Malek M, Dekkers JCM, Lee HK, Baas TJ, Prusa K, Huff-Lonergan E, Rothschild MF: A molecular genome scan analysis to identify chromosomal regions influencing economic traits in the pig: II. Meat and muscle composition. Mamm Genome. 2001, 12: 637-645. 10.1007/s003350020019.
Evans GJ, Giuffra E, Sanchez E, Kerje S, Davalos G, Vidal O, Illan S, Noguera JL, Varona L, Velander I, Southwood OI, DeKoning DJ, Haley CS, Plastow GS, Andersson L: Identification of quantitative trait loci for production traits in commercial pig populations. Genetics. 2003, 164: 621-627.
DeKoning DJ, Pong-Wong R, Varona L, Evans GJ, Giuffra E, Sanchez A, Plastow G, Noguera JL, Andersson L, Haley CS: Full pedigree quantitative trait locus analysis in commercial pigs using variance components. J Anim Sci. 2003, 81: 2155-2163.
Vidal O, Noguera JL, Amills M, Varona L, Gil M, Jimenez N, Davalos G, Folch JM, Sanchez A: Identification of carcass and meat quality quantitative trait loci in a Landrace pig population selected for growth and leanness. J Anim Sci. 2005, 83: 293-300.
van Wijk HJ, Dibbits B, Baron EE, Brings AD, Harlizius B, Groenen MAM, Knol EF, Bovenhuis H: Identification of quantitative trait loci for carcass composition and pork quality traits in a commercial finishing cross. J Anim Sci. 2006, 84: 789-799.
van Wijk HJ, Buschbell H, Dibbits B, Liefers SC, Harlizius B, Heuven HCM, Knol EF, Bovenhuis H, Groenen MAM: Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci for pork carcass composition and meat quality on SSC4 and SSC11. Anim Genet. 2007, 85: 32-30.
Duthie C, Simm G, Doeschl-Wilson A, Kalm E, Knap PW, Roehe R: Quantitative trait loci for chemical body composition traits in pigs and their positional associations with body tissues, growth and feed intake. Anim Genet. 2008, 39: 130-140. 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01689.x.
Edwards DB, Ernst CW, Raney NE, Doumit ME, Hoge MD, Bates RO: Quantitative trait locus mapping in an F2 Duroc × Pietrain resource population: II. Carcass and meat quality traits. J Anim Sci. 2008, 86: 254-266. 10.2527/jas.2006-626.
Tribout T, Iannucelli N, Druet T, Gilbert H, Riquet J, Gueblez R, Mercat MJ, Bidanel JP, Milan D, Le Roy P: Detection of quantitative trait loci for reproduction and production traits in Large White and French Landrace pig populations. Genet Sel Evol. 2008, 40: 61-78. 10.1051/gse:2007035.
Liu G, Jennen DG, Tholen E, Juengst H, Kleinwaechter T, Hoelker M, Tesfaye D, Un G, Schreinemachers HJ, Murani E, Ponsuksili S, Kim JJ, Schellander K, Wimmers K: A genome scan reveals QTL for growth, fatness, leanness and meat quality in a Duroc-Pietrain resource population. Anim Genet. 2007, 38: 241-252. 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01592.x.
Sanchez MP, Iannucelli N, Basso B, Bidanel P, Billon Y, Gandemer G, Gilbert H, Larzul C, Legault C, Riquet J, Milan D, Le Roy P: Identification of QTL with effects on intramuscular fat content and fatty acid composition in a Duroc × Large White cross. BMC Genet. 2007, 8: 55-10.1186/1471-2156-8-55.
Markljung E, Braunschweig MH, Karlskov-Mortensen P, Bruun CS, Sawera M, Cho I, Hedebro-Velander I, Josell A, Lundstrom K, von Seth G, Jorgensen CB, Fredholm M, Andersson L: Genome-wide identification of quantitative trait loci in a cross between Hampshire and Landrace II: Meat quality traits. BMC Genet. 2008, 9: 22-10.1186/1471-2156-9-22.
Knott SA, Elsen JM, Haley CS: Methods for multiple-marker mapping of quantitative trait loci in half-sib populations. Theor Appl Genet. 1996, 93: 71-80. 10.1007/BF00225729.
Fernando RL, Grossman M: Marker selection using best linear unbiased prediction. Genet Sel Evol. 1989, 21: 467-477. 10.1051/gse:19890407.
Heuven HCM, Bovenhuis H, Janss LLG, van Arendonk JAM: Efficiency of population structures for mapping of Mendelian and imprinted quantitative trait loci (QTL) in outbred pigs using variance component methods. Genet Sel Evol. 2005, 37: 635-655. 10.1051/gse:2005019.
NPPC: Procedures to evaluate market hogs. 1991, National Pork Producers Council, Des Moines, IA, USA, 3
Christensen LB: Drip loss sampling in porcine m. longissimus dorsi. Meat Sci. 2003, 63: 469-477. 10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00106-7.
NPPC: Pork composition and quality assessment procedures. 2000, National Pork Producers Council, Des Moines, IA, USA
van Wijk HJ, Arts DJG, Matthews JO, Webster M, Ducro BJ, Knol EF: Genetic parameters for carcass composition and pork quality estimated in a commercial production chain. J Anim Sci. 2005, 83: 324-333.
Green P, Falls K, Crook S: Documentation for CriMap, Version 2.4. 1990, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA
Sobel E, Lange K: Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker sharing statistics. Am J Hum Genet. 1996, 58: 1323-1337.
Janss LLG, Heuven HCM: LDLA, a package to compute IBD matrices for QTL fine mapping by variance component methods. Abstracts of 56th annual meeting of the European Association for Animal Production. Uppsala, Sweden. 2005
Meuwissen THE, Goddard ME: Prediction of identity by descent probabilities from marker-haplotypes. Genet Sel Evol. 2001, 33: 605-634. 10.1051/gse:2001134.
Gilmour AR, Cullis BR, Welham SJ, Thompson R: ASREML: User manual. 1998, Orange Agricultural Institute, NSW, Australia
Piepho HP: A quick method for computing approximate thresholds for quantitative trait loci detection. Genetics. 2001, 157: 425-432.
Rohrer GA, Alexander LJ, Hu ZL, Smith TLP, Keele JW, Beattie CW: A comprehensive map of the porcine genome. Genome Res. 1996, 6: 371-391. 10.1101/gr.6.5.371.
Lee SS, Chen Y, Moran C, Cepica S, Reiner G, Bartenschlager H, Moser G, Geldermann H: Linkage and QTL mapping for Sus scrofa chromosome 2. J Anim Breed Genet. 2003, 120 (Suppl 1): 11-19. 10.1046/j.0931-2668.2003.00419.x.
Su Y, Ma B, Xiong Y: [Genetic location of body composition traits in pigs]. Yi Chuan. 2004, 26 (2): 163-166.
Jeon JT, Carlborg O, Tornsten A, Giuffra E, Amargar V, Chardon P, Andersson-Eklund L, Andersson K, Hansson I, Lundstrom K, Andersson L: A paternally expressed QTL affecting skeletal and cardiac muscle mass in pigs maps to the IGF2 locus. Nat Genet. 1999, 21: 157-158. 10.1038/5938.
Milan D, Bidanel JP, Iannucelli N, Riquet J, Amigeus Y, Gruand J, Le Roy P, Renard C, Chevalet C: Detection of quantitative trait loci for carcass composition traits in pigs. Genet Sel Evol. 2002, 34: 705-728. 10.1051/gse:2002026.
Varona L, Ovilo C, Clop A, Noguera JL, Perez-Enciso M, Coll A, Folch JM, Barragan C, Toro MA, Babot D, Sanchez A: QTL mapping for growth and carcass traits in an Iberian by Landrace pig intercross: additive, dominant and epistatic effects. Genet Res. 2002, 80 (2): 145-154. 10.1017/S0016672302005803.
Uleberg E, Wideroe IS, Grindflek E, Szyda J, Lien S, Meuwissen THE: Fine mapping of a QTL for intra muscular fat on porcine chromosome 6 using combined linkage and linkage disequilibrium mapping. J Anim Breed Genet. 2005, 122: 1-6. 10.1111/j.1439-0388.2004.00496.x.
Eding H, Meuwissen THE: Marker based estimates of between and within population kinships for the conservation of genetic diversity. J Anim Breed Genet. 2001, 118: 141-159. 10.1046/j.1439-0388.2001.00290.x.
Meuwissen THE, Karlsen A, Lien A, Olsaker I, Goddard ME: Fine mapping a quantitative trait locus for twinning rate using combined linkage and linkage disequilibrium mapping. Genetics. 2002, 161: 373-379.
Olsen HG, Lien S, Svendsen M, Nilsen H, Roseth A, Aasland Opsal M, Meuwissen THE: Fine mapping of milk production QTL on BTA6 by combined linkage and linkage disequilibrium. J Dairy Sci. 2004, 87: 690-698.
Acknowledgements
Technical assistance with collecting the phenotypic data by JO Matthews, M Webster, DJG Arts, Dalland Value Added Pork, Inc and Premium Standard Farms is gratefully acknowledged. R Ariens and A Maciuszonek assisted in the laboratory. The project is financially supported by the Dutch Science Foundation (STW), the Institute of Pig Genetics BV and Hendrix-Genetics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
RvW and EK organized the phenotypes and performed preliminary analysis. BD and TvK created the genotypes. Statistical analyses were done by RvW and HH. HH and HB wrote the article and supervised the project.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Heuven, H.C., van Wijk, R.H., Dibbits, B. et al. Mapping carcass and meat quality QTL on Sus Scrofa chromosome 2 in commercial finishing pigs. Genet Sel Evol 41, 4 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9686-41-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9686-41-4