Summary.
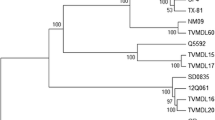
The viruses were isolated from the blood of sentinel cattle and Culicoides biting midges in the Kyushu district, southwestern Japan, in 1999 and identified by neutralization tests as Peaton (PEA) viruses. Before this study, PEA virus had been isolated in Australia only. The nucleotide identity of the nucleocapsid (N) protein encoded by the S segment ranged from 91.1 to 91.6% between the Australian and Japanese strains. A phylogenetic analysis of the N protein sequence revealed that the PEA virus strains are closely related to Aino (AIN) virus and suggested reassortment events for PEA and AIN viruses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 13, 2001 Accepted October 15, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumori, Y., Inai, K., Yanase, T. et al. Serological and genetic characterization of newly isolated Peaton virus in Japan. Arch. Virol. 147, 401–410 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s705-002-8328-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s705-002-8328-4