Abstract
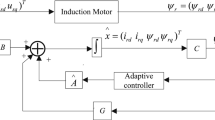
The conventional internal model control (IMC) has been used widely due to its advantages of less computational burden and simple implementation. Since the internal model controller has a fixed filter, disturbances created by mismatched models, parameter variations and other unstructured dynamic uncertainties in induction motors (IMs) cannot be eliminated by a fixed IMC. To solve these problems, the control strategy of an induction motor using internal model control with an extended state observer (IMC-ESO) was proposed. IM parameter variations and other unstructured dynamic uncertainties are considered in IM drives. Based on this model, an ESO is defined as a hypothetical equivocal function. Then the estimated disturbance is applied as a feed-forward compensation to accurately control the current loop. Since the designed ESO works concurrently with IMC, the fast dynamic response of the IMC is maintained. The feasibility and validity of the proposed method are validated by experimental results.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α, β :
-
Stationary reference frame axes
- d, q :
-
Rotary reference frame axes
- isα, isβ :
-
α-axis and β-axis stator currents, A
- isd, isq :
-
d-axis and q-axis stator currents, A
- iu, iv, iw :
-
a-axis, b-axis and c-axis stator currents, A
- usα, usβ :
-
α-axis and β-axis stator voltages, V
- usd, usq :
-
d-axis and q-axis stator voltages, V
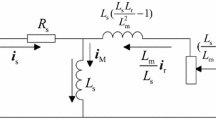
- Lm, Ls,Lr :
-
Mutual inductance, stator inductance and rotor inductance, H
- ωf, ωs :
-
Slip frequency and synchronous angular velocity, rad/s
- n :
-
Angular rotor speed, r/min
- u, v, w :
-
Three-phase reference frame axes
- 0*:
-
Reference quantity
- σ :
-
(= 1 − (L2m/LsLr)) Total leakage coefficient
- θ :
-
Rotor position, rad
- Rs, Rr :
-
Stator and rotor resistances, Ω
- T r :
-
(= Lr/Rr) Rotor time constant
- U dc :
-
DC link voltage, V
- T L :
-
Load torque, N m
- εd, εq :
-
Unstructured uncertainties
- U N :
-
Rated voltage, V
- P N :
-
Rated power, kW
- I N :
-
Rated current, A
- f N :
-
Rated frequency, Hz
- δd, δq :
-
Disturbances caused by parameter variations and other unmodeled dynamics uncertainties.
References
Lee, S.B., Wiedenbrug, E., Younsi, K.: ECCE 2013 tutorial: testing and diagnostics of induction machines in an industrial environment. In: Presented at ECCE 2013, Denver, CO, USA (2013)
Jose, A.A-D., Quijano-Lopez, A., Fuster-Roig, V., Nevot, C.: Case stories on induction motors fault diagnosis based on current analysis. In: Proceedings of PCIC Europe 2016, Berlin, Germany, June 2016, pp. 115–123
Lee, S.B.: SDEMPED 2013 tutorial: testing and monitoring of medium/high voltage induction machines. In: Presented at the SDEMPED 2013, Valencia, SPAIN, Sep 2013
Mosaad, Mohamed I.: Model reference adaptive control of STATCOM for grid integration of wind energy systems. IET Electr. Power Appl. 12(5), 605–613 (2018)
Nguyen, A.T., Rafaq, M.S., Choi, H.H., Jung, J.-W.: A model reference adaptive control-based speed controller for a surface-mountedpermanent magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1149/TIE-pel.2018.2826480
Al-Maliki, A.Y., Iqbal, K.: FLC-based PID controller tuning for sensorless speed control of DC motor. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT). https://doi.org/10.1109/icit 2018
Dominguez, J.R., et al.: Copper and core loss minimization for induction motors using high-order sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(7), 2877–2889 (2012)
Singh, V.K., Pillai, G.N.: Non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control of general class of chaotic system. In: 2011 IEEE 6th IEEE Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), pp. 4–6 (2017)
Liu, J.-X., Vazquez, S., Wu, L.-G., Marquez, A., Gao, H.J., Franquelo, L.G.: Extended state observer-based sliding-mode control for three-phase power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(1), 22–31 (2017)
Levant, A.: Higher-order sliding modes, differentiation and output feedback control. Int. J. Control 76(9–10), 924–941 (2003)
Rodríguez, J., et al.: State of the art of finite control set model predictive control in power electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 9(2), 1003–1016 (2013)
Cortes, P., Kazmierkowski, M., Kennel, R., Quevedo, D., Rodriguez, J.: Predictive control in power electronics and drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55(12), 4312–4324 (2008)
Xia, C., Yan, Y., Song, P., Shi, T.: Voltage disturbance rejection for matrix converter-based PMSM drive system using internal model control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(1), 361–372 (2015)
Garcia, C.E., Morari, M.: Internal model control. 1. a unifying review and some new results. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 21, 308–323 (1982)
Economous, C.G., Morari, M., Palsson, B.O.: Internal model control. 5. Extension to nonlinear systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 25, 403–411 (1986)
Sethi, B.K., Vinayak, J.R., Sivakumaran, N.: Internal model controller for CFBC boiler using neural networks. In: 2018 Indian Control Conference (ICC) January 4–6, IIT Kanpur, India (2018)
Shiva, C.K., Mukherjee, V.: Comparative performance assessment of a novel quasi-oppositional harmony search algorithm and internal model control method for automatic generation control of power system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 9(11), 1137–1150 (2015)
Zhu, Q., Yin, Z.-G., Zhang, Y.-Q., Niu, J.-B., Li, Y., Zhong, Y.-R.: Research on two-degree-of-freedom internal model control strategy for induction motor based on immune algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(3), 1981–1992 (2016)
Bazaei, A., Yong, Y.-K., Moheimani, S.O.R.: Combining spiral scanning and internal model control for sequential AFM imaging at video rate. IEEE Trans. Mechatron. 22(1), 371–380 (2017)
Cui, P., Zhang, D.-C., Yang, S., Li, H.-T.: Friction compensation based on time delay control and internal model control for gimbal system in MSCMG. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(5), 3798–3807 (2017)
Qiu, Zeng, Santillo, Mario, Jankovic, Mrdjan, Sun, Jing: Composite adaptive internal model control and its application to boost pressure control of a turbocharged gasoline engine. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 23(6), 371–380 (2015)
Sun, X.-D., Shi, Z., Chen, L., Yang, Z.-B.: Internal model control for a bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor based on inverse system method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 31(4), 1539–1548 (2016)
Zuo, S., Song, Y.D., Lewis, F.L., Davoudi, A.: Output containment control of linear heterogeneous multi-agent systems using internal model principle. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(8), 2099–2109 (2017)
Mohamed, Y.A.R.I.: Design and implementation of a robust current-control scheme for a PMSM vector drive with a simple adaptive disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 54(4), 1981–1988 (2007)
Liu, C., Liu, G., Fang, J.C.: Feedback linearization and extended state observer-based control for rotor-AMBs system with mismatched uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(2), 1313–1322 (2017)
Aharon, I., Shmilovitz, D.: Uncertainty and disturbance estimator-based controllers design under finite control bandwidth constraint. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(2), 1439–1449 (2018)
Dal, M., Teodorescu, R., Blaabjerg, F.: Complex state variable- and disturbance observer based current controllers for AV drives: an experimental comparison. IET Power Electron. 6(9), 1792–1802 (2013)
Kósi, K., Tar, J.K., Haidegger, T. et al.: Application of Luenberger’s Observer in RFPT-based adaptive control—a case study. In: 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics, pp. 365–369 (2013)
Accetta, A., Cirrincione, M., Pucci, M., Vitale, G.: Neural sensorless control of linear induction motors by a full-order luenberger observer considering the end effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 50(3), 1891–1904 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Yin, Z., Bai, C. et al. Internal model control of induction motors based on extended state observer. J. Power Electron. 20, 163–175 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-019-00025-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-019-00025-2