Abstract
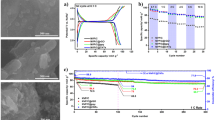
Metallic antimony (Sb) is considered as a promising anode material for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) owing to its high theoretical capacity (660 mAh/g) based on alloying/dealloying reactions with sodium ions. The main issues of Sb, however, are its large volume expansion upon cycling. In this study, we synthesized Sb-reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composite material by reduction of Sb2O3 nanoparticles. We confirmed that ~ 5 nm sized Sb nanoparticles are well distributed onto the rGO sheets, and Sb–rGO composite electrodes showed higher capacity and better cycling performance compared to bare Sb nanoplatelets. This improvement is attributed to increased electrical conductivity owing to incorporation of rGO, which also acts as a buffer against volume expansion of Sb particles during electrochemical reactions. The moderate rate performance of Sb–rGO composite materials was further improved by electrode formulation modification using a carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) binder. An electrode architecture containing Sb–rGO composite material with CMC binder achieved a high capacity (~ 400 mAh g−1) at a high rate (~ 30 C).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.S. Hou, C.E. Banks, M.J. Jing, Y. Zhang, X.B. Ji, Carbon quantum dots and their derivative 3d porous carbon frameworks for sodium-ion batteries with ultralong cycle life. Adv. Mater. 27(47), 7861–7866 (2015)
T.F. Liu, Y.P. Zhang, Z.G. Jiang, X.Q. Zeng, J.P. Ji, Z.H. Li, X.H. Gao, M.H. Sun, Z. Lin, M. Ling, J.C. Zheng, C.D. Liang, Exploring competitive features of stationary sodium ion batteries for electrochemical energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 12(5), 1512–1533 (2019)
H.L. Pan, Y.S. Hu, L.Q. Chen, Room-temperature stationary sodium-ion batteries for large-scale electric energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 6(8), 2338–2360 (2013)
M.D. Slater, D. Kim, E. Lee, C.S. Johnson, Sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23(8), 947–958 (2013)
G. Wang, X.H. Xiong, D. Xie, X.X. Fu, Z.H. Lin, C.H. Yang, K.L. Zhang, M.L. Liu, A scalable approach for dendrite-free alkali metal anodes via room-temperature facile surface fluorination. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11(5), 4962–4968 (2019)
M. Dahbi, N. Yabuuchi, K. Kubota, K. Tokiwa, S. Komaba, Negative electrodes for Na-ion batteries. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(29), 15007–15028 (2014)
M.K. Datta, R. Epur, P. Saha, K. Kadakia, S.K. Park, P.N. Kuma, Tin and graphite based nanocomposites: potential anode for sodium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 225(1), 316–322 (2013)
S.Y. Hong, Y. Kim, Y. Park, A. Choi, N.S. Choi, K.T. Lee, Charge carriers in rechargeable batteries: Na ions vs. Li ions. Energy Environ. Sci. 6(7), 2067–2081 (2013)
D. Kundu, E. Talaie, V. Duffort, L.F. Nazar, The emerging chemistry of sodium ion batteries for electrochemical energy storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 54(11), 3431–3448 (2015)
J.Y. Dong, Y.M. Xue, C. Zhang, Q.H. Weng, P.C. Dai, Y.J. Yang, M. Zhou, C.L. Li, Q.H. Cui, X.H. Kang, C.C. Tang, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, X. Wang, Improved Li+ storage through homogeneous n-doping within highly branched tubular graphitic foam. Adv. Mater. 29(6), 1603692 (2017)
D.A. Stevens, J.R. Dahn, High capacity anode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 147(4), 1271–1273 (2000)
Y. Wen, K. He, Y.J. Zhu, F.D. Han, Y.H. Xu, I. Matsuda, Y. Ishii, J. Cumings, C.S. Wang, Expanded graphite as superior anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 5, 4033 (2014)
C.J. Chen, Y.W. Wen, X.L. Hu, X.L. Ji, M.Y. Yan, L.Q. Mai, P. Hu, B. Shan, Y.H. Huang, Na+ intercalation pseudocapacitance in graphene-coupled titanium oxide enabling ultra-fast sodium storage and long-term cycling. Nat. Commun. 6, 6929 (2015)
Y. Xu, E.M. Lotfabad, H.L. Wang, B. Farbod, Z.W. Xu, A. Kohandehghan, D. Mitlin, Nanocrystalline anatase TiO2: a new anode material for rechargeable sodium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 49(79), 8973–8975 (2013)
Y.C. Yang, X.B. Ji, M.J. Jing, H.S. Hou, Y.R. Zhu, L.B. Fang, X.M. Yang, Q.Y. Chen, C.E. Banks, Carbon dots supported upon n-doped TiO2 nanorods applied into sodium and lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(10), 5648–5655 (2015)
W.H. Li, S.H. Hu, X.Y. Luo, Z.L. Li, X.Z. Sun, M.S. Li, F.F. Liu, Y. Yu, Confined amorphous red phosphorus in mof-derived n-doped microporous carbon as a superior anode for sodium-ion battery. Adv. Mater. 29(16), 1605820 (2017)
J.F. Qian, X.Y. Wu, Y.L. Cao, X.P. Ai, H.X. Yang, High capacity and rate capability of amorphous phosphorus for sodium ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 52(17), 4633–4636 (2013)
Y.J. Zhu, Y. Wen, X.L. Fan, T. Gao, F.D. Han, C. Luo, S.C. Liou, C.S. Wang, Red phosphorus single-walled carbon nanotube composite as a superior anode for sodium ion batteries. ACS Nano 9(3), 3254–3264 (2015)
W.W. Deng, X.M. Liang, X.Y. Wu, J.F. Qian, Y.L. Cao, X.P. Ai, J.W. Feng, H.X. Yang, A low cost, all-organic Na-ion battery based on polymeric cathode and anode. Sci. Rep. 3, 2671 (2013)
Y. Park, D.S. Shin, S.H. Woo, N.S. Choi, K.H. Shin, S.M. Oh, K.T. Lee, S.Y. Hong, Sodium terephthalate as an organic anode material for sodium ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 24(26), 3562–3567 (2012)
Z.Q. Zhu, H. Li, J. Liang, Z.L. Tao, J. Chen, The disodium salt of 2,5-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone as anode material for rechargeable sodium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 51(8), 1446–1448 (2015)
J. Duan, W. Zhang, C. Wu, Q.J. Fan, W.X. Zhang, X.L. Hu, Y.H. Huang, Self-wrapped Sb/C nanocomposite as anode material for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 16, 479–487 (2015)
C. Nithya, S. Gopukumar, RGO/nano Sb composite: a high performance anode material for Na+ ion batteries and evidence for the formation of nanoribbons from the nano RGO sheet during galvanostatic cycling. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2(27), 10516–10525 (2014)
T.J. Wu, H.S. Hou, C.Y. Zhang, P. Ge, Z.D. Huang, M.J. Jing, X.Q. Qiu, X.B. Ji, Antimony anchored with nitrogen-doping porous carbon as a high-performance anode material for Na-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9(31), 26118–26125 (2017)
J.H. Song, P.F. Yan, L.L. Luo, X.G. Qi, X.H. Rong, J.M. Zheng, B.W. Xiao, S. Feng, C.M. Wang, Y.S. Hu, Y.H. Lin, V.L. Sprenkle, X.L. Li, Yolk-shell structured Sb@C anodes for high energy Na-ion batteries. Nano Energy. 40, 504–511 (2017)
X.J. Wei, X.P. Wang, X. Tan, Q.Y. An, L.Q. Mai, Nanostructured conversion-type negative electrode materials for low-cost and high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(46), 1804458 (2018)
A.S. Arico, P. Bruce, B. Scrosati, J.M. Tarascon, W. Van Schalkwijk, Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nat. Mater. 4(5), 366–377 (2005)
B. Lestriez, S. Desaever, J. Danet, P. Moreau, D. Plee, D. Guyomard, Hierarchical and resilient conductive network of bridged carbon nanotubes and nanofibers for high-energy Si negative electrodes. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 12(4), A76–A80 (2009)
V. Sivasankaran, C. Marino, M. Chamas, P. Soudan, D. Guyomard, J.C. Jumas, P.E. Lippens, L. Monconduit, B. Lestriez, Improvement of intermetallics electrochemical behavior by playing with the composite electrode formulation. J. Mater. Chem. 21(13), 5076–5082 (2011)
R. Wang, L.L. Feng, W.R. Yang, Y.Y. Zhang, Y.L. Zhang, W. Bai, B. Liu, W. Zhang, Y.M. Chuan, Z.G. Zheng, H.J. Guan, Effect of different binders on the electrochemical performance of metal oxide anode for lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12(1), 575 (2017)
L.J. Cote, F. Kim, J.X. Huang, Langmuir-blodgett assembly of graphite oxide single layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(3), 1043–1049 (2009)
S. Komaba, T. Ishikawa, N. Yabuuchi, W. Murata, A. Ito, Y. Ohsawa, Fluorinated ethylene carbonate as electrolyte additive for rechargeable Na batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 3(11), 4165–4168 (2011)
H. Nakai, T. Kubota, A. Kita, A. Kawashima, Investigation of the solid electrolyte interphase formed by fluoroethylene carbonate on Si electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158(7), A798–A801 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) Institutional Program [Project no. 2E29642].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, S., Lee, J. & Kim, H. Development of electrode architecture using Sb–rGO composite and CMC binder for high-performance sodium-ion battery anodes. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 57, 91–97 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-019-00012-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-019-00012-0