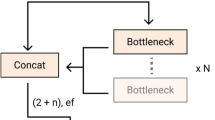
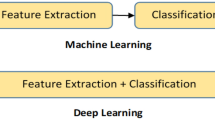
Abstract
Automatic systems for pavement inspection can significantly enhance the performance of the Pavement Management Systems (PMSs). Cracking is the most current distress in any type of pavement. Progress of various technologies leads to a lot of effort in developing an automatic system for pavement cracking inspection. In the early image-based systems, the feature extraction process for crack classification must be done by using various image processing techniques in an expert-based system. In recent years, the new machine learning techniques such as a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) provide more efficient models with the ability of automatic feature extracting, but these models need a lot of labeled data for training. Transfer learning is a technique that solves this problem using pre-trained models. In this research, several pre-trained models (AlexNet, GoogleNet, SqueezNet, ResNet-18, ResNet-50, ResNet-101, DenseNet-201, and Inception-v3) have been used to retrain based on pavement images using transfer learning. This study aims to evaluate the efficiency of retrained DCNNs in the detection and classification of the pavement cracking. Also, it presents a more effective algorithm based on a developed wavelet transform module with more regulizer parameters for crack segmentation. The result indicated that retrained classifier models provide reliable outputs with a range of 0.94 to 0.99 in confusion matrix-based performance, but the speed of some models is significantly higher than others. Also, the results clarified that the developed wavelet module could segment crack pixels with a high level of clarity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Y. Chan, B. Huang, X. Yan, S. Richards, Investigating effects of asphalt pavement conditions on traffic accidents in Tennessee based on the pavement management system (PMS), J. Adv. Transp. 44 (3) (2010) 150–161.
D. A. Noyce, H. Bahia, J. Yambo, J. Chapman, A. J. W. Bill, Incorporating road safety into pavement management: Maximizing surface friction for road safety improvements, Report Number MRUTC 04-04. Traffic Operations and Safety Laboratory, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA, 2007.
M. Y. Shahin, Pavement management for airports, roads, and parking lots, Springer, NY, USA, 1994, p.2–5.
F. M. Nejad, H. Zakeri, “The Hybrid Method and its Application to Smart Pavement Management,” in Metaheuristics in Water, Geotechnical and Transport Engineering, ed. By X.-S. Yang, A. H. Gandomi, S. Talatahari, A. H. Alavi, Elsevier, Oxford, 2013, p. 439–484.
H. Zakeri, F. M. Nejad, A. Fahimifar, Image Based Techniques for Crack Detection, Classification and Quantification in Asphalt Pavement: A Review, Archives Comput. Methods Eng. 24 (4) (2017) 935–977.
V. Ananth, P. Ananthi, V. Elakkiya, J. Priyadharshini, R. Shiyamili, Automatic Pavement Crack Detection Algorithm, Inter. Innov.Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2 (1) (2017) 86–89.
K. Zhang, H. Cheng, B. Zhang, Unified Approach to Pavement Crack and Sealed Crack Detection Using Preclassification Based on Transfer Learning, J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 32 (2) (2018) 04018001.
B. Mataei, F. Moghadas Nejad, M. Zahedi, H. Zakeri, Evaluation of pavement surface drainage using an automated image acquisition and processing system, Autom. Constr. 86 (1) (2018) 240–255.
Z. Hong, Exact extraction method for road rutting laser lines, Analysis, vol. 106070, p. 19, 2018.
C. Ting, W. Weixing, Y. Nan, G. Ting, W. Fengping, Detection method for the depth of pavement broken block in cement concrete based on 3D laser scanning technology, Infrared Laser Engineering, 2 (1) (2017) 013.
S. Dai and K. Hoegh, 3D step frequency GPR Asphalt pavement stripping detection: Case study evaluating filtering approaches. In Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (IWAGPR), 9th International Workshop, Edinburgh, Scotland, 2017, pp. 1–7.
S. Li, C. Yuan, D. Liu, H. Cai, Integrated processing of image and GPR data for automated pothole detection, J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 30 (6) (2016) 04016015.
X. Chapeleau, J. Blanc, P. Hornych, J.-L. Gautier, J. Carroget, Use of distributed fiber optic sensors to detect damage in a pavement, 12th ISAP Conference on Asphalt pavement, Raleigh, North Carolina, USA, 2014.
M. R. Carlos, M. E. Aragón, L. C. González, H. J. Escalante, F. Martínez, Evaluation of Detection Approaches for Road Anomalies Based on Accelerometer Readings—Addressing Who’s Who, IEEE Transactions Intelligent Transp. Syst. 19 (10) (2018) 3334–3343.
A. Fox, B. V. Kumar, J. Chen, F. Bai, “Multi-lane pothole detection from crowdsourced undersampled vehicle sensor data, IEEE Transactions Mobile Comput. 16 (12) (2017) 3417–3430.
S. Nakashima, S. Aramaki, Y. Kitazono, S. Mu, K. Tanaka, S. Serikawa, Application of ultrasonic sensors in road surface condition distinction methods, Sensors 16 (10) (2016) 1678.
R. Madli, S. Hebbar, P. Pattar, V. Golla, Automatic detection and notification of potholes and humps on roads to aid drivers, IEEE Sensors J. 15 (8) (2015) 4313–4318.
J. Mehta, V. Mathur, D. Agarwal, A. Sharma, K. Prakasha, Pothole Detection and Analysis System (Pol) AS) for Real Time Data Using Sensor Networks, J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 12 (12) (2017) 3090–3097.
M. Solla, S. Lagüela, H. González-Jorge, P. Arias, Approach to identify cracking in asphalt pavement using GPR and infrared thermographic methods: Preliminary findings, NDT & E Inter. 62 (1) (2014) 55–65.
J. Huang, W. Liu, X. Sun, A pavement crack detection method combining 2D with 3D information based on Dempster-Shafer theory, Computer-Aided Civ. Infrast. Eng. 29 (4) (204) 299–313.
Y. O. Ouma and M. Hahn, Wavelet-morphology based detection of incipient linear cracks in asphalt pavements from RGB camera imagery and classification using circular Radon transform, Adv. Eng. Informatics 30 (3) (2016) 481–499.
S. Mathavan, K. Kamal, M. Rahman, A Review of Three-Dimensional Imaging Technologies for Pavement Distress Detection and Measurements, IEEE Transactions Intelligent Transp. Syst. 16 (5) (2015) 2353–2362.
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G. Hinton, Deep learning, Nature, 521 (1) (2015) 436.
L. Deng, D. Yu, Deep learning: methods and applications, Foundations Trends® in Signal Process. 7 (3–4) (2014) 197–387.
H. Lokeshwor, L. K. Das, S. Goel, Robust method for automated segmentation of frames with/without distress from road surface video clips, J. Transp. Eng. 140 (1) (2013) 31–41.
Y. ZHANG and H. ZHOU, “Automatic pavement cracks detection and classification using radon transform, J. Infor. Comput. Sci. 9 (17) (2012) 5241–5247.
Y. J. Tsai, V. Kaul, A. Yezzi, Automating the crack map detection process for machine operated crack sealer, Autom. Constr. 31 (1) (2013) 10–18.
S. Varadharajan, S. Jose, K. Sharma, L. Wander, C. Mertz, Vision for road inspection. In IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, USA, 2014, pp. 115–122.
W. Xu, Z. Tang, J. Zhou, J. Ding, Pavement crack detection based on saliency and statistical features. In IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 2013, pp. 4093–4097.
H. Zakeri, F. M. Nejad, A. Fahimifar, Rahbin: A quadcopter unmanned aerial vehicle based on a systematic image processing approach toward an automated asphalt pavement inspection, Autom. Constr. 72 (2) (2016) 211–235.
S. Hongxun, W. Weixing, W. Fengping, W. Linchun, W. Zhiwei, Pavement crack detection by ridge detection on fractional calculus and dual-thresholds, Inter. J. Multimedia Ubiquitous Eng. 10 (4) (2015) 19–30.
C. A. Lettsome, Y.-C. J. Tsai, V. Kaul, Enhanced adaptive filter-bank-based automated pavement crack detection and segmentation system, J. Electronic Imaging 21 (4) (2012) 043008.
F. M. Nejad and H. Zakeri, An optimum feature extraction method based on Wavelet-Radon Transform and Dynamic Neural Network for pavement distress classification, Expert Syst. Appl. 38 (8) (2011) 9442–9460.
H. Ceylan, M. B. Bayrak, K. Gopalakrishnan, Neural networks applications in pavement engineering: A recent survey, Int. J. Pavement Eng. 7 (6) (2014) 434–444.
N.-D. Hoang, Q.-L. Nguyen, D. Tien Bui, Image processing-based classification of asphalt pavement cracks using support vector machine optimized by artificial bee colony, J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 32 (5) (2018) 04018037.
T. Wang, K. Gopalakrishnan, O. Smadi, A. K. Somani, Automated shape-based pavement crack detection approach, Transp. 33 (3) (2018) 598–608.
W. R. L. d. Silva and D. S. d. Lucena, Concrete Cracks Detection Based on Deep Learning Image Classification. In Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings, 18th International Conference on Experimental Mechanics (ICEM18), Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
H. Maeda, Y. Sekimoto, T. Seto, T. Kashiyama, H. Omata, Road Damage Detection Using Deep Neural Networks with Images Captured Through a Smartphone, Comput. Aided Civ. Infras. Eng. 33 (12) (2018) 1127–1141.
Y.-J. Cha, W. Choi, O. Büyüköztürk, Deep Learning-Based Crack Damage Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks, Comput. Aided Civ. Infras. Eng. 32 (5) (2017) 361–378.
Y. Liu, J. Yao, X. Lu, R. Xie, L. Li, DeepCrack: A Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning Architecture for Crack Segmentation, Neurocomput. 338 (1) (2019) 139–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.01.036
K. Gopalakrishnan, S. K. Khaitan, A. Choudhary, A. Agrawal, Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with transfer learning for computer vision-based data-driven pavement distress detection, Constr. Build. Mater. 157 (2017) 322–330.
C. V. Dung, Autonomous concrete crack detection using deep fully convolutional neural network, Automation Constr. 99 (2019) 52–58.
S. Albelwi and A. Mahmood, A framework for designing the architectures of deep convolutional neural networks, Entropy 19 (6) (2017) 242.
Z. Tong, J. Gao, Z. Han, Z. Wang, Recognition of asphalt pavement crack length using deep convolutional neural networks, Road Mater. Pavement Des. 19 (6) (2018) 1334–1349.
A. Bhandare, M. Bhide, P. Gokhale, R. Chandavarkar, Applications of Convolutional Neural Networks, Inter. J. Computer Sci. Infor. Technol. 7 (5) (2016) 2206–2215.
C. Kyriakou, S. E. Christodoulou, L. Dimitriou, Detecting and Classifying Roadway Pavement Cracks, Rutting, Raveling, Patching, and Potholes Utilizing Smartphones, In Transportation Research Board 97th Annual Meeting, Washington DC, USA, 2018.
S. Gao, Z. Jie, Z. Pan, F. Qin, R. Li, Automatic Recognition of Pavement Crack via Convolutional Neural Network, In Transactions on Edutainment XIV, ed. By Z. Pan, A. D. Cheok, W. Müller, Springer, Berlin, 2018, p. 82–89.
B. Li, K. C. Wang, A. Zhang, E. Yang, G. Wang, Automatic classification of pavement crack using deep convolutional neural network, Inter. J. Pavement Eng. 21 (4) (2018) 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2018.1485917.
M. A. Nielsen, Neural networks and deep learning. Determination press, USA, 2015.
S. Dorafshan, R. J. Thomas, M. Maguire, Comparison of deep convolutional neural networks and edge detectors for image-based crack detection in concrete, Constr. Build. Mater. 186 (2018) 1031–1045.
D. C. Ciresan, U. Meier, J. Masci, L. Maria Gambardella, J. Schmidhuber, Flexible, high performance convolutional neural networks for image classification, In Proceedings-International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Barcelona, Spain, 2011.
S. J. Pan and Q. Yang, A survey on transfer learning, IEEE Transactions Knowledge Data Eng. 22 (10) (2010) 1345–1359.
O. Russakovsky et al., Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge, Inter. J. Comput. Vision 115 (3) (2015) 211–252.
A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G. E. Hinton, Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, In Advances in neural information processing systems, Harrah’s Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 2012.
F. N. Iandola, S. Han, M. W. Moskewicz, K. Ashraf, W. J. Dally, K. Keutzer, Squeezenet: Alexnet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and < 0.5 mb model size, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Cornell University, USA, 2016.
C. Szegedy et al., Going deeper with convolutions, IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Boston, USA, 2015, pp. 1–9.
K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, J. Sun, Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification, IEEE international conference on computer vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015, pp. 1026–1034.
K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, J. Sun, Deep residual learning for image recognition, IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016, pp. 770–778.
G. Huang, Z. Liu, L. Van Der Maaten, K. Q. Weinberger, Densely connected convolutional networks, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017.
C. Szegedy, V. Vanhoucke, S. Ioffe, J. Shlens, Z. Wojna, Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision, in IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016, pp. 2818–2826.
P. S. Addison, The illustrated wavelet transform handbook: introductory theory and applications in science, engineering, medicine and finance. CRC press, 2017.
P. Prasad and G. Umamadhuri, Biorthogonal Wavelet-based Image Compression, in Artificial Intelligence and Evolutionary Computations in Engineering Systems, ed. By S. Dash, P. Chandra, B. Naidu, R. Bayindir, S. Das, Springer, Singapore, 2018, pp. 391–404.
P. Luo, X. Qu, X. Qing, J. Gu, CT Image Denoising Using Double Density Dual Tree Complex Wavelet with Modified Thresholding, 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Business Analytics (ICDSBA), Changsha, China, 2018, pp. 287–290: IEEE.
X. Wang and X. Feng, Pavement distress detection and classification with automated image processing, 2011 International Conference on Transportation, Mechanical, Electrical Engineering (TMEE), Changchun, China, 2011, pp. 1345–1350: IEEE.
B. Sun and Y. Qiu, Automatic Pavement Surface Cracking Recognition Using Wavelet Transforms Technology, Second International Conference on Transportation Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2009, pp. 2201–2206.
C. Ma, W. Wang, C. Zhao, F. Di, Z. Zhu, Pavement cracks detection based on FDWT, International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering (CiSE), Wuhan, China, 2009, pp. 1–4: IEEE.
J. Zhou, P. S. Huang, F.-P. Chiang, Wavelet-based pavement distress detection and evaluation, Optical Eng. 45 (2) (2006) 027007.
F. M. Nejad, N. Karimi, H. Zakeri, Automatic image acquisition with knowledge-based approach for multidirectional determination of skid resistance of pavements, Autom. Constr. 71 (2) (2016) 414–429.
G. Yang, Q. J. Li, Y. J. Zhan, K. C. Wang, C. Wang, Wavelet based macrotexture analysis for pavement friction prediction, KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 22 (1) (2018) 117–124.
R. Abbasnia and A. Farsaei, Corrosion detection of reinforced concrete beams with wavelet analysis, Inter. J. Civ. Eng., Transaction A: Civ. Eng. 11 (3) (2013) 160–169.
A. Dixit and S. Majumdar, Comparative analysis of coiflet and daubechies wavelets using global threshold for image denoising, Inter. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 6 (5) (2013) 2247–2252.
D. Wei and A. C. Bovik, Generalized coiflets with nonzero-centered vanishing moments, IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems II: Analog Digital Signal Process. 45 (8) (1998) 988–1001.
D. Wei and H. Cheng, Representations of stochastic processes using coiflet-type wavelets, in Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing, Pocono Manor, USA, 2000, pp. 549–553.
R. Nigam and S. K. Singh, Crack detection in a beam using wavelet transform and photographic measurements, Struct. 25 (2020) 436–447.
V. L. Fox, M. Milanova, S. Al-Ali, Scene Analysis Using Morphological Mathematics and Fuzzy Logic, in Computer Vision in Control Systems-1, ed. By M.N. Favorskaya, L.C. Jain, Springer, Switzerland, 2015, p. 239–259.
P. Soille, Morphological image analysis: principles and applications, Springer Science & Business Media, Switzerland, 2013.
R. C. Gonzalez and R. E. Woods, Digital image processing, 2nd edn. Pearson Education International, London, UK, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Peer review under responsibility of Chinese Society of Pavement Engineering.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjbar, S., Nejad, F.M. & Zakeri, H. An image-based system for pavement crack evaluation using transfer learning and wavelet transform. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 14, 437–449 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-020-0098-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-020-0098-9