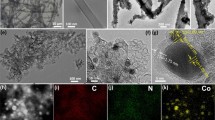
Abstract
Developing cost-effective electrocatalysts with high activity and stability especially at high current density is of great significance for the large-scale commercial application of electrochemical water splitting to hydrogen production but still remains challenging. Herein, we report an effective confinement pyrolysis strategy to fabricate embedded ruthenium–cobalt nanoclusters supported on N-doped porous two-dimensional carbon nanosheets (RuCo@CN). Markedly, the embedded structure can effectively prevent the migration, agglomeration, and leaching of nanoparticles, thus endowing the RuCo@CN catalyst with high stability. To be exact, high stability with up to 650 h can be achieved at high current density (− 500 and − 1000 mA·cm−2). Besides, the RuCo@CN catalysts also exhibit highly reactive with low overpotentials of only 11 mV at − 10 mA·cm−2. Density functional theory calculations reveal that the introduction of cobalt reduces the decomposition barrier of H2O for RuCo@CN alloy, thus promoting hydrogen evolution reaction.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data produced are available on the reasonable request from the corresponding authors.
References
Sanati S, Morsali A, García H. First-row transition metal-based materials derived from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks as highly efficient electrocatalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Energy Environ Sci. 2022;15:3119.
Zhang JC, Chen GB, Liu QC, Fan C, Sun D, Tang Y, Sun H, Feng X. Competitive adsorption: reducing the poisoning effect of adsorbed hydroxyl on Ru single-atom site with SnO2 for efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2022;9:486.
Yang M, Zhang S, Wang T, Shi B, Liu J, Tang Y, Xu Z, Sarwar MT, Tang A, Yang H. Multiple interface Ni(PO3)2-CoP4/CoMoO4 nanorods for highly efficient hydrogen evolution in alkaline water/seawater electrolysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022;10:12423.
Hou X, Zhou H, Zhao M, Cai Y, Wei Q. MoS2 nanoplates embedded in Co-N-doped carbon nanocages as efficient catalyst for HER and OER. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2020;8:5724.
Zou X, Zhang Y. Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:5148.
Xu Z, Yeh CL, Chen JL, Lin JT, Ho KC, Lin RY-Y. Metal-organic framework-derived 2D NiCoP nanoflakes from layered double hydroxide nanosheets for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting at high current densities. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022;10:11577.
Danilov FI, Tsurkan AV, Vasil’eva EA, Protsenko VS. Electrocatalytic activity of composite Fe/TiO2 electrodeposits for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solutions. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2016;41:7363.
Jiang P, Liu Q, Sun X. NiP2 nanosheet arrays supported on carbon cloth: an efficient 3D hydrogen evolution cathode in both acidic and alkaline solutions. Nanoscale. 2014;6:13440.
Li R, Chu B, Liu J, Wang F, Chen Z, Pang Q, Li B, Fan M, Dong L. Interfacial coupling and defect-induced dual effects enabling superhydrophilic Ni2P/V2O3–x heteronanosheets to accelerate alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022;10:12262.
Wu C, Yang Y, Dong D, Zhang Y, Li J. In situ coupling of CoP polyhedrons and carbon nanotubes as highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst. Small. 2017;13:1602873.
Tung CW, Kuo TR, Huang YP, Chu YC, Hou CH, Li Y, Suen NT, Han J, Chen HM. Dynamic Co(µ-O)2Ru moiety endowed efficiently catalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv Energy Mater. 2022;12:2200079.
Huang H, Jung H, Park CY, Kim S, Lee A, Jun H, Choi J, Han JW, Lee J. Surface conversion derived core-shell nanostructures of Co particles@RuCo alloy for superior hydrogen evolution in alkali and seawater. Appl Catal B. 2022;315: 121554.
Madhu R, Jayan R, Karmakar A, Selvasundarasekar SS, Kumaravel S, Bera K, Nagappan S, Dhandapani HN, Islam MM, Kundu S. Rationally constructing chalcogenide-hydroxide heterostructures with amendment of electronic structure for overall water-splitting reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022;10:11299.
Jian J, Kang H, Qiao X, Cui K, Liu Y, Li Y, Qin W, Wu X. Cobalt and aluminum co-optimized 1T phase MoS2 with rich edges for robust hydrogen evolution activity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2022;10:10203.
Song C, Zhao Z, Sun X, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang D. In situ growth of Ag nanodots decorated Cu2O porous nanobelts networks on copper foam for efficient HER electrocatalysis. Small. 2019;15:1804268.
Lin H, Shi Z, He S, Yu X, Wang S, Gao Q, Tang Y. Heteronanowires of MoC-Mo2C as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Sci. 2016;7:3399.
Tiwari JN, Harzandi AM, Ha M, Sultan S, Myung CW, Park HJ, Kim DY, Thangavel P, Singh AN, Sharma P, Chandrasekaran SS, Salehnia F, Jang JW, Shin HS, Lee Z, Kim KS. High-performance hydrogen evolution by Ru single atoms and nitrided-Ru nanoparticles implanted on N-doped graphitic sheet. Adv Energy Mater. 2019;9:1970101.
Wu W, Wu Y, Zheng D, Wang K, Tang Z. Ni@Ru core-shell nanoparticles on flower-like carbon nanosheets for hydrogen evolution reaction at All-pH values, oxygen evolution reaction and overall water splitting in alkaline solution. Electrochim Acta. 2019;320: 134568.
He Q, Zhou Y, Shou H, Wang X, Zhang P, Xu W, Qiao S, Wu C, Liu H, Liu D, Chen S, Long R, Qi Z, Wu X, Song L. Synergic reaction kinetics over adjacent ruthenium sites for superb hydrogen generation in alkaline media. Adv Mater. 2022;34:2110604.
Liu ZL, Li BQ, Feng YJ, Jia D, Li C, Zhou Y. N-doped sp2/sp3 carbon derived from carbon dots to boost the performance of ruthenium for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Small Methods. 2022;6:2200637.
Zhu J, Cai L, Tu Y, Zhang L, Zhang W. Emerging ruthenium single-atom catalysts for the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A. 2022;10:15370.
Liu Y, Wang Q, Zhang J, Ding J, Cheng Y, Wang T, Li J, Hu F, Yang HB, Liu B. Recent advances in carbon-supported noble-metal electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction: syntheses, structures, and properties. Adv Energy Mater. 2022;12:2200928.
Wang J, Wei Z, Mao S, Li H, Wang Y. Highly uniform Ru nanoparticles over N-doped carbon: pH and temperature-universal hydrogen release from water reduction. Energy Environ Sci. 2018;11:800.
Li Y, Zhang LA, Qin Y, Chu F, Kong Y, Tao Y, Li Y, Bu Y, Ding D, Liu M. Crystallinity dependence of ruthenium nanocatalyst toward hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 2018;8:5714.
Liu Y, Yang Y, Peng Z, Liu Z, Chen Z, Shang L, Lu S, Zhang T. Self-crosslinking carbon dots loaded ruthenium dots as an efficient and super-stable hydrogen production electrocatalyst at all pH values. Nano Energy. 2019;65: 104023.
Yu J, Guo Y, She S, Miao S, Ni M, Zhou W, Liu M, Shao Z. Bigger is surprisingly better: agglomerates of larger RuP nanoparticles outperform benchmark Pt nanocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Mater. 2018;30:1800047.
Li P, Duan X, Wang S, Zheng L, Li Y, Duan H, Kuang Y, Sun X. Amorphous ruthenium-sulfide with isolated catalytic sites for Pt-like electrocatalytic hydrogen production over whole pH range. Small. 2019;15:1904043.
Zhao J, Pan T, Sun J, Gao H, Guo J. Cu-Ru nanoalloys on carbon black for efficient production of hydrogen in neutral and alkaline conditions. Mater Lett. 2020;262: 127041.
Liu G, Zhou W, Chen B, Zhang Q, Cui X, Li B, Lai Z, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Gu L, Zhang H. Synthesis of RuNi alloy nanostructures composed of multilayered nanosheets for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy. 2019;66: 104173.
Zhang Z, Li P, Wang Q, Feng Q, Tao Y, Xu J, Jiang C, Lu X, Fan J, Gu M, Li H, Wang H. Mo modulation effect on the hydrogen binding energy of hexagonal-close-packed Ru for hydrogen evolution. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7:2780.
Yang Y, Wu D, Li R, Rao P, Li J, Deng P, Luo J, Huang W, Chen Q, Kang Z, Shen Y, Tian X. Engineering the strong metal support interaction of titanium nitride and ruthenium nanorods for effective hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl Catal B. 2022;317: 121796.
Mao J, He CT, Pei J, Chen W, He D, He Y, Zhuang Z, Chen C, Peng Q, Wang D, Li Y. Accelerating water dissociation kinetics by isolating cobalt atoms into ruthenium lattice. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4958.
Su J, Yang Y, Xia G, Chen J, Jiang P, Chen Q. Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14969.
Zhang M, Li H, Chen J, Yi L, Shao P, Xu CY, Wen Z. Nitrogen-doped graphite encapsulating RuCo nanoparticles toward high-activity catalysis of water oxidation and reduction. Chem Eng J. 2021;422: 130077.
Yoo JM, Shin H, Chung DY, Sung YE. Carbon shell on active nanocatalyst for stable electrocatalysis. ACC Chem Res. 2022;55:1278.
Su F, Lee FY, Lv L, Liu J, Tian XN, Zhao XS. Sandwiched ruthenium/carbon nanostructures for highly active heterogeneous hydrogenation. Adv Funct Mater. 2007;17:1926.
Wei Z, Lou J, Su C, Guo D, Liu Y, Deng S. An efficient and reusable embedded ru catalyst for the hydrogenolysis of levulinic acid to gamma-valerolactone. Chemsuschem. 2017;10:1720.
Su H, Zhang KX, Zhang B, Wang HH, Yu QY, Li XH, Antonietti M, Chen JS. Activating cobalt nanoparticles via the mott-schottky effect in nitrogen-rich carbon shells for base-free aerobic oxidation of alcohols to esters. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139:811.
Zheng Y, Jiao Y, Zhu Y, Cai Q, Vasileff A, Li LH, Han Y, Chen Y, Qiao SZ. Molecule-level g-C3N4 coordinated transition metals as a new class of electrocatalysts for oxygen electrode reactions. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139:3336.
Zhang F, Zhu Y, Chen Y, Lu Y, Lin Q, Zhang L, Tao S, Zhang X, Wang H. RuCo alloy bimodal nanoparticles embedded in N-doped carbon: a superior pH-universal electrocatalyst outperforms benchmark Pt for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A. 2020;8:12810.
Zhang J, Chen G, Liu Q, Fan C, Sun D, Tang Y, Sun H, Feng X. Competitive adsorption: reducing the poisoning effect of adsorbed hydroxyl on Ru single-atom site with SnO2 for efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61:202209486.
Yu P, Wang F, Shifa TA, Zhan X, Lou X, Xia F, He J. Earth abundant materials beyond transition metal dichalcogenides: a focus on electrocatalyzing hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy. 2019;58:244.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. D5000220257, D5000220443), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22002120), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (No. cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0750), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2019A1515110507), the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (No. 2023-YBGY-322).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YLC and HPZ conceived the presented idea. JHW carried out catalyst synthesis, characterization studies, and wrote the article. TSW carried out all the DFT calculations. JHW, SWY, FBM, YKZ, ZYX, DC, HDS, SNZ, and KZ carried out the catalytic experiments. QYZ provided funding acquisition. YLC, TSW, and HPZ helped with article modification. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis, and manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JH., Yang, SW., Ma, FB. et al. RuCo alloy nanoparticles embedded within N-doped porous two-dimensional carbon nanosheets: a high-performance hydrogen evolution reaction catalyst. Tungsten 6, 114–123 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-023-00223-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-023-00223-3