Abstract
Purpose
Psychiatry still needs objective biomarkers. In the context of schizophrenia, there are speech abnormalities such as tangentiality, derailment, alogia, neologisms, poverty of speech, and aprosodia. There is a growing interest in speech signals features as possible indicators of schizophrenia. This article aims to develop an intelligent tool for detection of schizophrenia using vocal patterns and machine learning techniques. The main advantages of this type of solution are the low cost, high performance, and for being non-invasive.
Methods
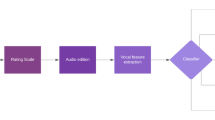
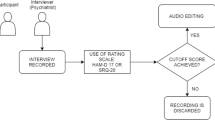
Thirty-one individuals over 18 years old were selected, 20 with previous diagnosis of schizophrenia, and 11 healthy controls. Their speech was audio-recorded in naturalistic settings, during a routine medical assessment for psychiatric patients. In the case of healthy patients, the recordings were made in different environments. Recordings were pre-processed, excluding non-participant voices. We extracted 33 features. We used the particle swarm optimization algorithm for feature selection.
Results
The classifiers’ performance was analyzed with four metrics: accuracy, sensibility, specificity, and kappa index. Best results were achieved when considering all 33 extracted features. Within machine models, support vector machines (SVM) models provided the greatest classification performance, with mean accuracy of 91.76% for PUK kernel. Our results outperform those from most studies published so far for the detection of schizophrenia based on acoustic patterns.
Conclusion
The use of machine learning classifiers using vocal parameters, in particular SVM, has shown to be very promising for the detection of schizophrenia. Nevertheless, further experiments with a larger sample will be necessary to validate our findings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberto P, Arndis S, Vibeke B, Riccardo F. Voice patterns in schizophrenia: a systematic review and Bayesian Meta-analysis. Voice Schizophrenia Rev Meta-anal. 2019;1–40.
Alpert M, Anderson LT. Imagery mediation of vocal emphasis in flat affect. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977;34(2):208–12.
Alpert M, Rosenberg SD, Pouget ER, Shaw RJ. Prosody and lexical accuracy in flat affect schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2000;97:107–18.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). DSM-5 - Manual Diagnóstico e Estatístico de Transtornos Mentais. Artmed (5.). Porto Alegre: Artmed. 1011769780890425596.
Baca-Garcia E, Perez-Rodriguez MM, Basurte-Villamor I, Fernandez Del Moral AL, Jimenez-Arriero MA, Gonzalez De Rivera JL, et al. Diagnostic stability of psychiatric disorders in clinical practice. Br J Psychiatry. 2007;190(MAR):210–6. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.106.024026.
Bedi G, Carrillo F, Cecchi GA, Slezak DF, Sigman M, Mota NB, et al. Automated analysis of free speech predicts psychosis onset in high-risk youths. Nature Partner Journals. 2015;1:15030. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjschz.2015.30.
Bzdok D, Meyer-lindenberg A. Machine learning for precision psychiatry: opportunities and challenges. Biologic Psychiat Cognit Neurosci Neuroimag. 2018;3:223–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2017.11.007.
Cannizzaro MS, Cohen H, Rappard F, Snyder PJ. Bradyphrenia and Bradykinesia both contribute to altered speech in schizophrenia: a quantitative acoustic study. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2005;18(4):206–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wnn.0000185278.21352.e5.
Chakraborty D, Xu S, Yang Z, Han Y, Chua V, Tahir Y, et al. Prediction of negative symptoms of schizophrenia from objective linguistic, acoustic and non-verbal conversational cues. In: IEEE 2018 international conference on Cyberworlds prediction; 2018a. p. 280–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/CW.2018.00057.
Chakraborty, D, Yang, Z, Tahir, Y, Maszczyk, T, Dauwels, J, Thalmann, N, … Lee, J (2018b). Prediction of Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia From Emotion Related Low-Level Speech Signals. IEEE, 6024–6028.
Chuanwen J, Bompard E. A hybrid method of chaotic particle swarm optimization and linear interior for reactive power optimisation. Math Comput Simul. 2005;68(1):57–65.
Cohen AS, Alpert M, Nienow TM, Dinzeo TJ, Docherty NM. Computerized measurement of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:827–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.08.008.
Cohen AS, Mitchell KR, Docherty NM, Horan WP. Vocal expression in schizophrenia: less than meets the ear. J Abnorm Psychol. 2016;125(2):299–309. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000136.
Cohen AS, Najolia GM, Kim Y, Dinzeo TJ. On the boundaries of blunt affect/alogia across severe mental illness: implications for research domain criteria. Schizophr Res. 2012;140(1–3):41–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2012.07.001.
Commowick O, Istace A, Kain M, Laurent B, Leray F, Simon M, et al. Objective evaluation of multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using a data management and processing infrastructure. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1–17.
Compton MT, Lunden A, Cleary SD, Pauselli L, Alolayan Y, Halpern B, et al. The aprosody of schizophrenia: computationally derived acoustic phonetic underpinnings of monotone speech. In: Schizophrenia Research; 2018. p. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2018.01.007.
Covington MA, Lunden SLA, Cristofaro SL, Wan CR, Bailey CT, Broussard B, et al. Phonetic measures of reduced tongue movement correlate with negative symptom severity in hospitalized patients with first-episode schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. Schizophr Res. 2012;142:93–5.
Cruz T, Cruz T, Santos W. Detection and classification of lesions in mammographies using neural networks and morphological wavelets. IEEE Lat Am Trans. 2018;16(3):926–32.
de Lima SM, da Silva-Filho AG, dos Santos WP. Detection and classification of masses in mammographic images in a multi-kernel approach. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. 2016;134:11–29.
de Santana MA, Pereira JMS, da Silva FL, de Lima NM, de Sousa FN, de Arruda GMS, et al. Breast cancer diagnosis based on mammary thermography and extreme learning machines. Res Biomed Eng. 2018;34(1):45–53.
dos Santos WP, De Assis FM, De Souza RE, Mendes PB, De Souza Monteiro HS, Alves HD. A dialectical method to classify Alzheimer’s magnetic resonance images. Evol Comput. 2009;473.
dos Santos, WP, de Souza, RE, & dos Santos Filho, PB (2007). Evaluation of Alzheimer’s disease by analysis of MR images using multilayer perceptrons and Kohonen SOM classifiers as an alternative to the ADC maps. In 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (pp. 2118–2121).
Eberhart, R, & Kennedy, J (1995). A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In MHS'95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science (pp. 39-43). IEEE.
Eberhart RC, Shi Y. Computational intelligence: concepts to implementations. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2011.
Elite A, Pedrão LJ, Zamberlan-Amorim NE, Carvalho AMP, Bárbaro AM. Comportamento comunicativo de indivíduos com esquizofrenia. Rev CEFAC. 2014;16(4):1283–93.
Elvevåg B, Foltz PW, Rosenstein M, DeLisi LE. An automated method to analyze language use in patients with schizophrenia and their first-degree relatives. J Neurolinguistics. 2010;23(3):270–84. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.956839.
García-Nieto J, Alba E, Jourdan L, Talbi E. Sensitivity and specificity based multiobjective approach for feature selection: application to cancer diagnosis. Inf Process Lett. 2009;109(16):887–96.
Gonçalves DM, Stein AT, Kapczinski F. Avaliação de desempenho do Self-Reporting Questionnaire como instrumento de rastreamento psiquiátrico: Um estudo comparativo com o Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR. Cad Saude Publica. 2008;24(2):380–90. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2008000200017.
Higuchi M, Tokuno S, Nakamura M, Shinohara S. Classification of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, and healthy state using voice. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2018;11(3):89–93. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11s3.30042.
Hu, X, Eberhart, RC, & Shi, Y (2003). Engineering optimization with particle swarm. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium. SIS'03 (cat. No. 03EX706) (pp. 53-57). IEEE.
Huys QJM, Maia TV, Frank MJ. Computational psychiatry as a bridge from neuroscience to clinical applications. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19(3):404–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4238.
Iwabuchi SJ, Liddle PF, Palaniyappan L. Clinical utility of machine-learning approaches in schizophrenia: improving diagnostic confidence for translational neuroimaging. Front Psych. 2013;4(August):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00095.
Jiang H, Hu B, Liu Z, Wang G, Zhang L, Li X, et al. Detecting Depression Using an Ensemble Logistic Regression Model Based on Multiple Speech Features. Comput Math Methods Med. 2018;2018:6508319. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6508319.
Kayi, ES, Diab, M, Pauselli, L, Compton, M, & Coppersmith, G (2017). Predictive linguistic features of schizophrenia. Proceedings Ofthe 6th Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics, 241–250.
Kennedy, J, & Eberhart, R (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN'95-International Conference on Neural Networks (Vol. 4, pp. 1942-1948). IEEE.
Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of Brief psychiatric rating scale scores. Br J Psychiatry. 2005;187(2):366–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.03.040.
Mac-Kay A, Jerez I, Pesenti P. Speech-language intervention in schizophrenia: an integrative review. Rev CEFAC. 2018;20(2):238–46. https://doi.org/10.1590/1982-0216201820219317.
Martínez-Sánchez F, Muela-Martínez JA, Cortés-soto P, José J, Meilán G, Antonio J, et al. Can the acoustic analysis of expressive prosody discriminate schizophrenia? Span J Psychol. 2015;18(86):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2015.85.
Moraglio A, Di Chio C, Poli R. Geometric particle swarm optimisation. In: European conference on genetic programming. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2007. p. 125–36.
Mundt JC, Snyder PJ, Cannizzaro MS, Chappie K, Geralts DS. Voice acoustic measures of depression severity and treatment response collected via interactive voice response (IVR) technology. J Neurolinguistics. 2007;20:50–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroling.2006.04.001.
Mundt JC, Vogel AP, Feltner DE, Lenderking WR. Vocal acoustic biomarkers of depression severity and treatment response. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72(7):580–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.03.015.Vocal.
Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychol Rep. 1962;10:799–812.
Petzschner FH, Weber LAE, Gard T, Stephan KE. Review computational psychosomatics and computational psychiatry : toward a joint framework for differential diagnosis. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.05.012.
Rapcan V, D’Arcy S, Yeap S, Afzal N, Thakore J, Reilly RB. Acoustic and temporal analysis of speech: a potential biomarker for schizophrenia. Med Eng Phys. 2010;32:1074–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.07.013.
Russell SJ, Norvig P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (third). Harlow: Pearson Education; 2016.
Sadock B, Sadock V, Ruiz P. Compêndio de Psiquiatria: Ciência do Comportamento e Psiquiatria Clínica (11.). Porto Alegre: Artmed; 2017.
Santos WP, Assis FM. Algoritmos dialéticos para inteligência computacional. Recife: Editora Universitária UFPE; 2013.
Santos KOB, Araújo TM, Pinho PS, Silva ACC. Avaliação de um Instrumento de Mensuração de Morbidade Psíquica. Revista Baiana de Saúde Pública. 2010;34(3):544–60.
Shi, Y, & Krohling, RA (2002). Co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization to solve min-max problems. In Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC'02 (cat. No. 02TH8600) (Vol. 2, pp. 1682-1687). IEEE.
Tahir Y, Yang Z, Id DC, Thalmann N, Thalmann D, Maniam Y, et al. Non-verbal speech cues as objective measures for negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. PLoS One. 2019;14:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214314.
Tovar A, Fuentes-Claramonte P, Soler-Vidal J, Ramiro-Sousa N, Rodriguez-Martinez A, Sarri-Closa C, et al. The linguistic signature of hallucinated voice talk in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2019;206:111–7.
Trelea IC. The particle swarm optimization algorithm: convergence analysis and parameter selection. Inf Process Lett. 2003;85(6):317–25.
Van der Merwe, DW, & Engelbrecht, AP (2003). Data clustering using particle swarm optimization. In The 2003 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 2003. CEC'03. (Vol. 1, pp. 215-220). IEEE.
Xue B, Zhang M, Member S, Browne WN. Particle swarm optimization for feature selection in classification: a multi-objective approach. In: Ieee Transactions on Cybernetics; 2012. p. 1–16.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Brazilian research-funding agency CNPq, for the partial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espinola, C.W., Gomes, J.C., Pereira, J.M.S. et al. Vocal acoustic analysis and machine learning for the identification of schizophrenia. Res. Biomed. Eng. 37, 33–46 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-020-00097-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-020-00097-1