Abstract
Reconfigurable machine tools are emerging as new generation machine tools for dealing with the fluctuating market scenario and immense competition between original equipment manufacturers. New approaches, mechanism and designs principles are required for the development of these machine tools in manufacturing systems. A lot of research work has been done in reconfigurable machine tool (i.e. lathe, milling, shaper, NC, CNC etc.) but still less work has been conducted to develop reconfigurable drilling machine. This paper presents a modular approach to develop Reconfigurable Drilling Machine Tool, which will allow the machine not only to reconfigure the modules in a certain way for performing a specific task but also to develop a new type of machine which can incorporate all the features of reconfiguration for the production of multiple part families on a single platform. A module library, which includes basic and auxiliary modules, is implemented on this machine tool to explain the core features (i.e. scalability, modularity, convertibility and flexibility). Probably, this proposed design contributes a theoretical approach for the reconfiguration features of drilling machine in Reconfigurable Manufacturing System and this proposed design is illustrated through a figure, which is developed on design software (i.e. solid works platform).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
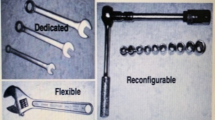
In the 21st century, individualization of customer demand, intensification of global market and uncertainty of product life are increasing day by day. Due to all these issues, the manufacturing companies are facing a lot of pressure to reconfigure machine structure in manufacturing system. Therefore traditional manufacturing system (i.e. Dedicated manufacturing system and flexible manufacturing system) are not enabled for solving these issues. Experts from different manufacturing industries have developed a new type of manufacturing system known as Reconfigurable Manufacturing System (RMS).Yomen Koren was the first scientist who developed this RMS in 1999 after that a lot of researcher has worked in this field. Dedicated Manufacturing System (DMS) is generally used for mass production in which, conventional machines are used with fixed tooling condition and automation. These machines have no flexibility, convertibility and scalability features of machine tool. Whereas Flexible Manufacturing Systems have a configuration with fixed hardware but programmable software to handle changes in work orders, production schedules, part-programs, and tooling for several types of parts. Therefore, a new generation machine tool and manufacturing system are required with better functionality, responsiveness and robustness. RMS is designed for cost- effective response in market oriented manufacturing environments at a low cost and rapid time. Reconfigurable Manufacturing System (RMS) combines both the advantages of DMS and FMS. The main components of RMS are reconfigurable material handling, reconfigurable inspection system and reconfigurable machine tool but RMT is the heart of RMS. The modularity, scalability, convertibility, flexibility, diognasability, integrability are the core features of RMT that helps to reconfiguration the machine structure as per requirement. To achieve this, many computer aided design (CAD) of machine tool have been proposed and developed. Virtual Arch type machine, machine with multi spindle, modular scalable machine tool and many more machines have been developed at University of Michigan. For example, arc type reconfigurable machine [1] and multi spindle machine [2] is shown below in the Fig. 1a, b.
These machines are designed on the basis of modularity, scalability principles [3, 4]. In RMT, reconfiguration can be done on at any level (i.e. at machine hardware level, software level and system level) to reconfigure the existing modules parts for performing of new specific operation. By doing this, convertibility, modularity and scalability of machine tool increases. Abdi [5] discussed a fuzzy analytical hierarchical process (FAHP) mode to integrate machine reconfiguration and equipment selection. The life cycle cost of different modular parts of machine tool can be reduced with the help of concepts of reconfiguration [6]. Xu et al. [7] had implemented the reconfiguration concepts for developing MRMT with minimum number of modules. He also discussed the module components library and reconfigurability. Consequently, reconfigurability also plays a vital role in machine tool. As per Gumasta et al. [8] reconfigurability is defined as the ability to frequently change and rearrange the machine tool components (both hardware and software) in a cost effective way.
In this paper, a reconfigurable drill machine tool has been proposed, which is designed with the help of Solid works platform. Module library, which consists of basic and auxiliary parts are also explained. The second section briefly emphasis the literature review work related to reconfigurable machine (i.e. lathe, milling, shaper, slotter, CNC, NC etc.). In the third section, reconfigurable principles and RMT are explained. In forth section, different designing steps of RDMT is also explained and highlighting the operational achievement of RDMT. Finally, the last fifth section concludes the article and point up the constraint of the study.
2 Literature review
See Table 1.
3 Reconfigurable machine tool
An innovative concept and development of reconfigurable machine tool had started at university of Michigan at 1999. Since then, various types of reconfigurable machine tool have been developed [22, 27,28,29,30]. The structures of this machine tool are modular in nature. Therefore, different machine configuration can be obtained to produce desired shape of any family of part. Machine hardware and software are the basic elements of RMT as shown in Fig. 2. Further, machine hardware parts consist of basic and auxiliary modules, which are further classified into three categories: Function operated modules, motion operated modules and accessory operated modules.
Different machine configuration through basic modules and auxiliary modules [31]
Function modules are modules which can be changed to provide a new machining process. Each function enables one of the following machining processes: drilling, milling, tapping, boring, grinding, polishing, engraving, and turning. Motion modules are modules which through their integration enables some kind of motion, whether it be liner or angular. Thus, they help in positioning and feeding of the tool post. Accessory modules are those modules which are not necessary for the machining operation but are used to make machining easier and simpler, like work clamps and stabilizers. Bed, column, legs, work piece table, arbor are the basic module and tool post, spindle, carriage, tail stock etc. are the auxiliary parts of lathe machine [9]. Modularity, Convertibility, Integrability, Scalability etc. are the core characteristics of RMT [1, 17, 24, 32]. Modularity means that both hardware and software modules of RMT should be modular so that it can be easily added or replace as per requirements [2, 33, 34]. Gadalla and Xue [23] proposed a machine tool configuration on modularity and convertibility principal with minimum reconfiguration efforts to change from one machine configuration to another machine configuration. In his research, he implemented modular hardware parts to perform drilling, milling and turning operation on RMT, which is illustrated in the Fig. 3.
Two configurations of a RMT, a modules library, b milling/drilling configuration and c turning configuration [35]
3.1 Module library to develop reconfigurable drill machine tool (RDMT)
Modules are the heart of machine tool which allows developing multiple set of machine configuration and variation on machining operation (such as milling, drilling, cutting etc.) on single platform. Therefore, the synthesis of module library (i.e. basic and auxiliary) is building blocks to develop any reconfigurable machine tool [36]. They are generally selected from module library to provide required machine configuration. Padayachee et al. [14] listed a set of mechanical modules library (such as tail stock, tool post, rotary 4 column, end effectors, rotary arm, rotary bed, lathe front, column, power back etc.) that were used to develop a machine configuration which provide a different machining process: drilling, milling, boring and tapping. Figure 3b, c illustrates this concept. In this paper, different basic and auxiliary modules are used. All of them have been designed on solid works designing platform, which are shown in Fig. 4. Basic modules are generally heavy in weight and the shape and size are large as compared to auxiliary modules. In RDMT base, vertical column and work piece table are basic modules and guide way, tool post, arch type plate, actuator are auxiliary modules. Table 2 outlines the characteristics of basic and auxiliary modules.
4 Mechanism to develop Reconfigurable Drilling Machine tool (RDMT)
Modular Reconfigurable Machines (MRM) is constructed using basic and auxiliary modules, which can be added or removed from the machine tool [37, 38] in order to enhance the required capacity, modularity, scalability and functionality. The proposed machine discussed in this paper consists of the Basic Structure (Fig. 5) to which the various modules are added and also supports the work table bench, Arch-Shaped Guideways etc. The Arch-Shaped Guideways (Fig. 6) are symmetrically located around the table and can be moved perpendicular to the surface of the table with help of Telescopic Lifts. On the Arch-Type Guideways, modules for the motion of tool in X- and Y- Direction (parallel to the plane of the work table) are placed. Each module has arrangement so that they can be attached to a fellow module or another module. This is done by making each module independent of extra accessories i.e. the module itself consist of motor or actuator which makes them less dependent and since they are similar in their build they can be integrated together with minimal extra accessories. Each additional DOF is added through the integration of a motion module. By adding a new motion module, a new degree of freedom is achieved which, by the use of multiple spindles increases the modularity. A 360° Rotating Module is attached on top of the Y-Axis Motion Module which can conveniently make fine angular variations to the direction of feed (Fig. 7). Tool changing is done by 180° rotation of The Multi-tool Spindle (Fig. 8) The Multi-Tool Spindle contains modular interface for attaching two different tools on either side (front and back) of the spindle. In this machine tool, twist drill bit can generally used for drilling in all type of work piece and the material of drill tool is high speed steel and typically have a length of 9–14 times its cutting diameter. The motor which drives the spindle can be accommodated within the spindle housing in such a way, that power is transferred across both the tools. Hence two different machining operations can be performed by the same spindle alternately as per the machining requirement. The modules or combination of modules and the multi-tool spindle can be arranged independently on each of the Arch-Shaped Guideways. Hence, two faces of a workpiece can be machined simultaneously on the single work table by doing this machine convertibility increased. The machining operations can be independently performed by each spindle so that asymmetric parts can be machined in a single pass. On the other hand, a symmetric part can be machined quickly by performing identical operations on both the spindles. A vertical column (Fig. 9), that can slide in only one direction, carries a third spindle for machining the top face of the workpiece. An Arch-Plate is attached to the column which enables angular placement of the spindle, by changing the plate we can also change the type of machining operations which can be achieve by using the vertical column. This Spindle can be used for drilling holes or milling cylinder bores on surfaces inclined to the horizontal.
When using the machine at its full potential it will have all the motion and function modules assembled together (Fig. 10). Multiple spindles will ensure speedy production and independent operations will ensure the fabrication of a complete part in one go, along with fabrication of another part of the same family. When using the machine at its full potential it will have all the motion and function modules assembled together (Fig. 10). Multiple spindles will ensure speedy production and independent operations will ensure the fabrication of a complete part in one go, along with fabrication of another part of the same family. We can use any of the four different configurations as shown in Fig. 11, which best matches the production requirement. If drilling on inclined surfaces is the only requirement, the First Configuration may be used. If only the lateral sides of the workpiece need to be machined, the Second Configuration may be used. If a product requires both side as well as top faces to be machined the Third Configuration may be used.
5 Conclusion
This paper classified the features of traditional drilling machine and Reconfigurable Drilling Machine Tool (RDMT) and also discussed the concept of Reconfigurable Manufacturing System. Further, this research paper provides an overview of the literature work related to the design and development of reconfigurable machine tool (RMT) in manufacturing system. Based on these design principles, we have proposed a Reconfigurable Drilling machine (RDMT) in which mechanical modules library (consists of basic and auxiliary modules) has been implemented for filling the space between conventional machine and flexible machine. In this machine tool, more than four manufacturing operations (vertical drilling, horizontal drilling, inclined drilling and milling operations) can be performed on a single platform through just replacing or adding basic and auxiliary modules which are proposed in Fig. 4. By doing this, we can enhance the core characteristics of machine tool (i.e. scalability, convertibility, flexibility and modularity). This machine and different types of modules have been designed on solid works designing platform. The authors are of the view that the reconfigurabilitry of Reconfigurabile Machine Tool (RMT) are depend on several modules parts and mechanism [9]. Some of these might have been not mentioned in this work. Therefore,some auxiliary reconfigurable mechanism can be used to develop next generation machine tool i.e. Industry 4.0. Further research work can be extended to implement measurement of cutting forces through Finite Elementary Analysis (FEA) during operation and to deploy active vibration damping for the development of light based modular structure of Reconfigurable Drilling Machine Tool (RDMT). In future, reconfigurability value can be assessed which is associated with multi spindle tool, material handling tool, reliability of different auxiliary modules.
References
Katz R (2007) Design principles of reconfigurable machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(5–6):430–439
Bi ZM, Lang SY, Verner M, Orban P (2008) Development of reconfigurable machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39(11–12):1227–1251
Landers RG (2000) A new paradigm in machine tools: reconfigurable machine tools, Japan–USA. In: Symposium on flexible automation, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Mori M, Fujishima M (2009) Reconfigurable machine tools for a flexible manufacturing system. In: ElMaraghy AH (ed) Changeable and reconfigurable manufacturing system. Springer, London, pp 101–109
Abdi MR (2009) Fuzzy multi-criteria decision model for evaluating reconfigurable machines. Int J Prod Econ 117(1):1–15
Mpofu K, Kumile CM, Tale NS (2008) Adaption of commercial off the shelf modules for reconfigurable machine tool design. In: 2008 15th International conference on mechatronics and machine vision in practice. IEEE, Auckland, pp 144–150
Xu Z, Xi F, Liu L, Chen L (2017) A method for design of modular reconfigurable machine tools. Machines 5(1):1–16
Gumasta K, Kumar Gupta S, Benyoucef L, Tiwari MK (2011) Developing a reconfigurability index using multi-attribute utility theory. Int J Prod Res 49(6):1669–1683
Singh A, Asjad M, Gupta P, Quamar J (2019) An approach to develop shaper cum slotter mechanism: a reconfigurable machine tool. South Asian J Bus Manag Case. https://doi.org/10.1177/2277977919833765
Singh A, Gupta P, Asjad M (2019a) Reconfigurable Manufacturing System (Rms): accelerate towards industries 4.0 (March 18, 2019). In: Proceedings of international conference on sustainable computing in science, technology and management (SUSCOM-2019), Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3354485. 26–28 Feb 2019
Ren G, Chen X (2019) Basic research on reconfigurable intelligent manufacturing system. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol 242, No. 3, IOP Publishing, Bristol, p 032059. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/242/3/032059
Majija N, Mpofu K, Modungwa D (2013) Conceptual development of modular machine tools for Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems. In: Advances in sustainable and competitive manufacturing systems, Springer, Heidelberg, pp 467–477
Padayachee J, Bright G, Masekamela I (2009) Modular reconfigurable machine tools: design, control and evaluation. S Afr J Ind Eng 20(2):127–143
Padayachee J, Masekamela I, Bright G, Kumile C, Tlale NS (2008) Modular reconfigurable machines incorporating open architecture control. In: 15th International conference on mechatronics and machine vision in practice (M2VIP’08), Auckland, New Zealand, 2–4 Dec 2008
Padayachee J, Bright G (2012) Modular machine tools: design and barriers to industrial implementation. J Manuf Syst 31(2):92–102
Vafadar A, Tolouei-Rad M, Hayward K, Abhary K (2016) Technical feasibility analysis of utilizing special purpose machine tools. J Manuf Syst 39:53–62
Lader RG, Min BK, Koren Y (2001) Reconfigurable machine tool. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 50(1):269–274
Pasek ZJ (2006) Challenges in the design of reconfigurable machine tools. In: Reconfigurable manufacturing systems and transformable factories. Springer, Berlin, pp 141–154
Yao Y, Liu M, Du J, Zhou L (2019) Design of a machine tool control system for function reconfiguration and reuse in network environment. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 56:117–126
Katz R, Moon Y-M (2000) Virtual arch type reconfigurable machine tool design. The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Dhupia J, Powalka B, Katz R, Ulsoy AG (2007) Dynamics of the arch-type reconfigurable machine tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(2):326–334
Son H, Choi HJ, Park HW (2010) Design and dynamic analysis of an arch-type desktop reconfigurable machine. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(6):575–584
Gadalla M, Xue D (2017) Recent advances in research on reconfigurable machine tools: a literature review. Int J Prod Res 55(5):1440–1454
Aguilar A, Roman-Flores A, Huegel JC (2013) Design, refinement, implementation and prototype testing of a reconfigurable lathe-mill. J Manuf Syst 32(2):364–371
Linke B, Harris P, Zhang M (2015) Development of desktop multipurpose grinding machine for educational purposes. Proc Manuf 1:740–746
Fadlovich CH, Brown RA, Whalen-Robinson DJ, Woogerd MG, Davis EJ, Mtm Robotics LLC (2019) Self-contained modular manufacturing tool. U.S. Patent Application 10/252,421
Gwangwava N, Mpofu K, Tlale N, Yu Y (2014) A methodology for design and reconfiguration of Reconfigurable Bending Press Machines (RBPMs). Int J Prod Res 52(20):6019–6032
Ponce P, Molina A, Bastida H, MacCleery B (2015) Real-time hardware ANN-QFT robust controller for reconfigurable micro-machine tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(1–4):1–20
Azulay H, Mills JK, Benhabib B (2014) A multi-tier design methodology for reconfigurable milling machines. J Manuf Sci Eng 136(4):041007
Ersal T, Stein JL, Louca LS (2004) A modular modeling approach for the design of reconfigurable machine tools. In: ASME 2004 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp 393–399
Pattanaik LN, Jain PK, Mehta NK (2007) Cell formation in the presence of reconfigurable machines. Int J Manuf Technol 34(3):335–345
Singh A, Gupta S, Asjad M, Gupta P (2017) Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems: journey and the road ahead. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8(Suppl. 2):1849–1857
Mehrabi MG, Ulsoy AG, Koren Y (2000) Reconfigurable manufacturing systems: key to future manufacturing. J Intell Manuf 11(4):403–419
Bi ZM, Lang SYT, Shen W, Wang L (2008) Reconfigurable manufacturing systems: the state of the art. Int J Prod Res 46(4):967–992
Zhong H, Zheng W (2012) Reconfigurable machine tools design methodology. Master Thesis. Stockholm: Department of Production Engineering and Management, Royal Institute of Technology
Goyal PK, Jain PK, Jain M (2012) Optimal configuration selection for Reconfigurable Manufacturing System using NSGA II and TOPSIS. Int J Prod Res 50(15):4175–4191
Abele E, Wörn A (2009) Reconfigurable Machine Tools and equipment. In: ElMaraghy Hoda A (ed) changeable and reconfigurable manufacturing systems. Springer, London, pp 111–125
Abele E, Wörn A, Fleischer J, Wieser J, Martin P, Klöpper R (2007) Mechanical module interfaces for Reconfigurable Machine Tools. Prod Eng Res Devel 1(4):421–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Asjad, M. & Gupta, P. A conceptual development of reconfigurable drill machine tool (RDMT). SN Appl. Sci. 1, 1141 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1194-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1194-9