Abstract
Introduction
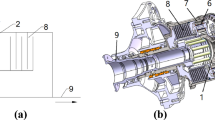
Based on the characteristics of the helicopter main reduction gearbox, and combined with the advantages of face gear and cylindrical gear power dividing, a new configuration of helicopter main gearbox with twice split paths is proposed. A bending–torsional coupled dynamic model of the system is developed through the lumped parameter method, and the influence of stiffness, damping and backlash are considered.
Methods
The dynamic equation is solved by Runge–Kutta method, and the load sharing and the dynamic load coefficients are obtained, as well as their variation with the backlash.
Results
Results show that with the increase of the backlash, the load-sharing coefficient decreases, the dynamic load coefficient increases, but the other drive stages are almost unaffected. Compared with split torque stages and power confluence stages, the load sharing and dynamic load coefficient of power input stages are the most sensitive to the backlash of the power input stage, and the appropriate increase of the backlash can effectively improve the dynamic properties.
Conclusion
Therefore, in order to obtain better dynamic performance, it is necessary to allocate the backlash reasonably.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b :
-
Backlash
- c :
-
Meshing damping
- c Dm, c ifp, c ijsjh :
-
Torsional damping of the corresponding shaft
- e :
-
Eccentric error
- f l(Y t):
-
Gap function
- F ifx, F ify, F ifz :
-
Component forces of the meshing force of the face gear pairs
- F ijx, F ijy :
-
Component force on the split shaft
- F inmf, F inpjs,F inBjh :
-
Meshing forces of Zm and Zif, Zip and Zijs, ZB and Zijh
- F ipx, F ipy, F ipz :
-
Component forces on duplicate shaft
- F l :
-
Meshing force
- F mx, F mz :
-
Component force on the input shaft
- F Bx, F By :
-
Component force on the output shaft
- Gl :
-
Dynamic load coefficient
- I m, I if, I ip, I ijs, I ijh, I B :
-
Moment of inertia of Zm, Zif, Zip, Zijs, Zijh and ZB
- k m :
-
Average meshing stiffness
- k 0 :
-
Variation amplitude of meshing stiffness
- K Dm, K ifp, K ijsjh, K Bo :
-
Torsional stiffness of the input shaft, duplicate shaft, split shaft and output shaft
- K l,:
-
Meshing stiffness
- K ipx, K ipy, K ipz :
-
Support stiffness of duplicate shaft
- K inmf, K inpjs, K inBjh :
-
Time-varying meshing stiffness of Zif and Zm, Zip and Zijs, ZB and Zijh
- K mx, K mz :
-
Support stiffness of input shaft
- m m, m if, m ip, m ijs, m ijh, m B :
-
Lumped mass of Zm, Zif, Zip, Zijs, Zijh and ZB
- P l :
-
Static load of gear pairs
- Ωimf, Ωijs, Ωijh :
-
Load sharing coefficient
- r ibp, r ibjs, r ibjh, r bB :
-
Base circle radius of Zip, Zijs, Zijh and ZB
- r if :
-
Equivalent meshing radius of face gear
- r ifp, r ijsjh :
-
Equivalent radius of duplicate shaft and split shaft
- r m :
-
Radius of pitch circle of Zm
- r Dm, r Bo :
-
Equivalent radius of the input shaft and output shaft
- T D, T o :
-
Input torque and the load
- X inp, Y inp, Z inp :
-
Displacement of duplicate shaft along the coordinate direction
- X ij, Y ij :
-
Transverse displacement of split shaft
- X nm, Z nm :
-
Transverse and axial displacement of input shaft
- X B, Y B :
-
Transverse displacement of output shaft
- Z if, Z ijh :
-
Face gear, the pinion of power confluence stage
- Z ip, Z ijs :
-
Driving and driven gear of split torque stage
- φ D, φ m, φ B, φ o :
-
Torsional displacement of input, Zm, ZB and output
- φ if, φ ip, φ ijs, φ ijh :
-
Torsional displacement of gear Zif, Zip, Zijs and Zijh
- θ ip, θ ij, θ iB, θ B :
-
Installation angle
- i :
-
R, L
- j :
-
1, 2
- l :
-
inmf, inpjs and inBjh
References
White G (1974) New family of high-ratio reduction gear with multiple drive paths. Proc Inst Mech Eng 188(1):281–288
White G (1974) Design study of a 375 kW helicopter transmission with split-torque epicyclic and bevel drive stages. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 197(4):213–224
Smirnov G (1990) Multiple-power-path nonplanetary main gearbox of the Mi-26 heavy-lift transport helicopter, Vertiflite. Mil Design Bureau, Moscow, pp 20–23
Gokcek M (2012) Mechanical Engineering. InTech, Rijeka, Croatia
Heath GF, Bossler RB Jr (1993) Advanced rotorcraft transmission (ART) program-final report. NASA Contractor Report 191057, Lewi, USA
Handschuh RE, Lewicki DG, Heath GF, et al (1996) Experimental evaluation of face gears for aerospace drive system application, NASA Technical Memorandum 107227, San Diego, USA
Krantz TL (1994) Dynamics of a split torque helicopter transmission, NASA TM-106410, USA
Krantz TL, Rashidi M (1995) Vibration analysis of a split path gearbox. In: 31st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE joint propulsion conference and exhibit, San Diego, USA
Yang Z, Wang S, Fan Y (2008) Nonlinear dynamics characteristics of split torque gear transmission system. Chin J Mech Eng 44(7):52–57
Gui Y, Zhu R, Bibo F et al (2014) Impact of torsional stiffness on dynamic load sharing of cylindrical gear split-torque transmission system. J Aerosp Power 29(9):2265–2268
Dong J, Wang S, Lin H et al (2015) Parameters effect on dual-path helical gear transmission dynamic load and load sharing characteristic. J Aerosp Power 30(5):1260–1266
Jin GH, Xiong YP, Gui YF et al (2017) Sensitive parameter and its influence law on load sharing performance of double input split torque transmission system. J Mech Sci Technol 5(6):583–595
Litvin FL, Fuentes A, Howkins M (2001) Design, generation and TCA of new type of asymmetric face-gear drive with modified geometry. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(43):5837–5865
Litvin FL, Fuentes A, Zanzi C et al (2002) Face-gear drive with spur involute pinion: geometry, generation by a worm, stress analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191(25):2785–2813
Li Z, Zhu R (2010) Load tooth contact analysis on face gear driver. J Nanjing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 42(2):219–223
Chen G, Chen G, Li Y et al (2009) Dynamic response analysis of gear drive with face-gears. J Aerosp Power 24(10):2391–2396
Yang Z, Wang S, Fan Y et al (2010) Nonlinear dynamics of face-gear transmission system. J Vib Shock 29(9):218–221
Hu Z, Tang J, Chen S et al (2013) Effect of mesh stiffness on the dynamic response of face gear transmission system. ASME J Mech Des 135(7):1–7
Jin G, Zhu R, Li Z et al (2011) Impact of coefficient of tooth width on bending stress of face gear. J Cent South Univ 42(5):1303–1309
Wang J, Wang Y (2005) Combination resonance of spur gear system analyzed using multi-scale approach. J Xian Univ Technol 21(1):5–10
Li G, Guangbin Yu, Wen J et al (2008) Method of multiplescalesin solving nonlinear dynamic diffrential equations of gear system. J Jilin Univ 38(1):75–79
Li W, Wang L, Chang S et al (2013) Impact of tooth surface friction on harmonic resonance of gear system. J Jilin Univ 43(5):1290–1294
Yao H, Qi X, Mao L et al (2013) Incremental harmonic balance method for coupled bending and torsional vibration in planetary gear system. J Northeast Univ 34(10):1452–1455
Zhang Z, Chen Y (2014) Harmonic balance method with alternating frequency/time domain technique for nonlinear dynamical system with fractional exponential. Appl Math Mech 35(4):423–436
Wang X, Wang Y, Zhao X et al (2015) Study on super-harmonic resonance for gear transmission based on teeth surface friction. J Mech Sci Technol 29(11):4631–4638
Li H, Chen Y, Hou L et al (2016) Periodic response analysis of a misaligned rotor system by harmonic balance method with alternating frequency/time domain technique. Science China Technol Sci 59(11):1717–1729
Wang S, Zhu C, Song C et al (2017) Effects of gear modifications on the dynamic characteristics of wind turbine gearbox considering elastic support of the gearbox. J Mech Sci Technol 31(3):1079–1088
Chen R, Zhou J, Sun W (2018) Dynamic characteristics of a planetary gear system based on contact status of the tooth surface. J Mech Sci Technol 32(1):69–80
Zhu Z, Zhu R, Bao H et al (2011) Impact of run out and meshing frequency errors on dynamic load-sharing for encased differential herringbone train. J Aerosp Power 26(11):2601–2609
Acknowledgements
The work is fully supported by National Natural Science Foundation of PRC (Grant No. 51475226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, G., Ren, W., Zhu, R. et al. Influence of Backlash on Load Sharing and Dynamic Load Characteristics of Twice Split Torque Transmission System. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 7, 565–577 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-019-00150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-019-00150-z