Abstract
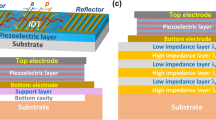
Natural fibre based sandwich composite wave absorbing structures were prepared and characterized for stealth and radome applications. The principal aim of this research was to develop a novel sandwich radar wave absorbing composite structure and evaluating their wave transmission and flexural properties. Fibres such as wool, silk, E-glass, aramid and wave absorbing foams like balsa wood, PVC and PMI were used for making wave absorbing sandwich composites. The composites were prepared using autoclave vacuum bag degassing method followed by post curing at 120 °C. The radar wave transmission characteristics were investigated using stealth radomes by partially replacing the traditional E-glass and aramid fibre structure with a frequency selective surface (FSS) with standard parameters. The free space measurement technique was used to examine the radar wave transmission characteristics in the X-band frequency range (8.2–12.4 GHz). Three point bending test also performed to identify the flexural strength of sandwich composite setup to ensure the bending rigidity. A highest wave transmission of 87.7% at bandwidth 0.83 GHz in − 1 dB with flexural strength of 44.2 MPa was observed for sandwich composite type 3c, which contains aramid/epoxy composite + balsa wood + silk/epoxy structure. The SEM micrographs showed highly reacted and toughness improved matrix phase for type 3c composite sandwich.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Rao, S.P. Mahulikar, Integrated review of stealth technology and its role in airpower. Aeronaut. J. 106, 629–641 (2002)
S.P. Mahulikar, H.R. Sonawane et al., Infrared signature studies of aerospace vehicles. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 43, 218–245 (2007)
W.S. Chin, D.G. Lee, Binary mixture rule for predicting the dielectric properties of unidirectional E-glass/epoxy composite. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 74, 153–162 (2006)
P.C. Kim, D.G. Lee, Composite sandwich constructions for absorbing the electromagnetic waves. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 87, 161–167 (2009)
P.C. Kim, W.S. Chin et al., EM characteristics of the RAS composed of E-glass/epoxy composite and single dipole FSS element. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 75, 601–609 (2006)
I.S. Seo, W.S. Chin et al., Characterization of electromagnetic properties of polymeric composite materials with free space method. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 66, 533–542 (2004)
W.S. Chin, D.G. Lee, Development of the composite RAS (radar absorbing structure) for the X-band frequency range. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 77, 457–465 (2007)
P.C. Kim, D.G. Lee et al., Nanocomposite stealth radomes with frequency selective surfaces. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 86, 299–305 (2008)
I. Choi, J.G. Kim et al., Effects of a damaged composite face to the electromagnetic wave transmission characteristics of low-observable radomes. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 93, 2740–2747 (2011)
P.C. Kim, D.G. Lee et al., Low-observable radomes composed of composite sandwich constructions and frequency selective surfaces. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 68, 2163–2170 (2008)
K.T. Annil, J. Inayathullah et al., Development of hybrid composite radar wave absorbing structure for stealth applications. Bull. Mater. Sci. 39, 279–284 (2016)
I. Choi, J.G. Kim et al., Aramid/epoxy composites sandwich structures for low-observable radomes. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 71, 1632–1638 (2011)
W.S. Chin, D.G. Lee, Laminating rule for predicting the dielectric properties of E-glass/epoxy laminate composite. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 77, 373–382 (2007)
M.S. Naidu, V. Kamaraju, High Voltage Engineering, 5th edn. (Tata McGraw Hill Education, Noida, 2013), p. 79
W. Middleton, M.E.V. Valkenburg, Reference Data for Engineers, 9th edn. (Newnes, Amsterdam, 2001), p. 102
W.B. Westphal, A. Sils, Dielectric Constant and Loss Data. Report, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA, April 1972.
P.C. Kim, D.G. Lee et al., Polarization characteristics of a composite stealth radome with a frequency selective surface composed of dipole elements. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 90, 242–246 (2009)
I. Choi, J.G. Kim et al., Design of the hybrid composite face with electromagnetic wave transmission characteristics of low-observable radomes. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 94, 3394–3400 (2012)
I. Choi, J.G. Kim et al., Radar absorbing sandwich construction composed of CNT, PMI foam and carbon/epoxy composite. Sci. Direct – Elsevier Compos. Struct. 94, 3002–3008 (2012)
V.R. Arun Prakash, R. Viswanathan, Microwave-shielding behavior of silanized Cu and Cu–Fe3O4 compound particle-reinforced epoxy resin composite in E-, F-, I-, and J-band frequencies. Polym. Bull. 75, 4207–4225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2262-1
T. Merizgui, A. Hadjadj, M. Kious, V.A. Prakash, B. Gaoui, Effect of magnetic iron(III) oxide particle addition with MWCNTs in kenaf fibre-reinforced epoxy composite shielding material in ‘E’, ‘F’, ‘I’ and ‘J’ band microwave frequencies. Mater. Res. Express 23, 22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/20531591/11f9de
A. Vincent, G. Ramesh, S.M. Kumar, Microwave shielding behaviour of surface treated MWCNT-epoxy composites in I & J band-A note. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 24, 89–92 (2018)
V.R. Arunprakash, A. Rajadurai, Radio frequency shielding behavior of silane treated Fe2O3/E-glass fibre reinforced epoxy hybrid composite. Appl. Phys. A 122, 875–822 (2016)
M. John Prabhahar, S. Julyes Jaisingh, V.R. Arun Prakash, Role of Magnetite (Fe3O4)–Titania (TiO2) hybrid particle on mechanical, thermal and microwave attenuation behaviour of flexible natural rubber composite in X and Ku band frequencies. Mater. Res. Express 7(2020), 016106 (2019)
V.R. Arun Prakash, A. Rajadurai, V. Jayaseelan, S. Jerome Dass, M. Murali, ‘Role of silanized magnetic Fe2O3 particle in heat dissipation and microwave shielding behavior of E-glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composite. Mater. Res. Express 6, 076113 (2019)
T. Merizgui, A. Hadjadj, M. Kious, V.R. Arun Prakash, Effect of temperature and frequency on microwave shielding behaviour of functionalized kenaf fibre-reinforced MWCNTs/iron(III) oxide modified epoxy hybrid composite. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-020-00179-y
V.R. Arunprakash, R. Viswanathan, Fabrication and characterization of echinoidea spike particles and kenaf natural fibre-reinforced Azadirachta-indica blended epoxy multi-hybrid bio composite. Composites: A 118, 317–326 (2019)
V.R. Arun Prakash, A. Rajadurai, Thermo-mechanical characterization of siliconized E-glass fibre/Hematite particles reinforced epoxy resin hybrid composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 384(16), 99–106 (2016)
M. Arul Murugan, V. Jayaseelan, D. Jayabalakrishnan, T. Maridurai, S. Selva Kumar, G. Ramesh, V.R. Arun Prakash, Low velocity impact and mechanical behaviour of shot blasted SiC wire-mesh and silane-treated aloevera/hemp/flax reinforced SiC whisker modified epoxy resin composites. Silicon (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00297-0
V.R. Arun Prakash, R. Viswanathan, Fabrication and characterization of silanized echinoidea fillers and kenaf fibre-reinforced Azadirachta-indica blended epoxy multi-hybrid biocomposite. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 23, 207–217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12588-019-09251-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antony Vincent, V., Kailasanathan, C., Ramesh, G. et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Hybrid Natural Fibre-Reinforced Sandwich Composite Radar Wave Absorbing Structure for Stealth Radomes. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 22, 794–802 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-021-00299-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-021-00299-z