Abstract
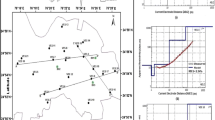
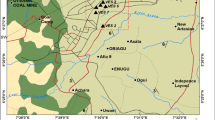
Electrical resistivity investigation was carried out at different sections of University of Ilorin main campus, Ilorin Southwestern Nigeria with the aim of evaluating groundwater potential and properties of the aquifers. Data were acquired at different locations using vertical electrical sounding (VES) method. Hydraulic conductivity, transmissivity, transverse unit resistance, longitudinal conductance, fracture contrast and reflection coefficient were estimated and used for evaluating the groundwater potential and aquifer vulnerability. The results revealed three–five geo-electric layers which correspond to the top soil, lateritic layer, weathered rock layer, fractured rock layer and the fresh basement rock. The top soil has apparent resistivity values ranging from 72.0 to 8117.3 Ωm and thickness range of 0.4–1.6 m while the last geo-electric layer is the infinite fresh basement having apparent resistivity greater than 300 Ωm. The VES curve types obtained are KH, H, A, AKH, HKH and HA with the H curve type covering about 50% of the study area. Aquifers in most part of the study areas are prone to contamination because of low protective capacity of the overburden material. Low groundwater potential covers about 56.79% of the total area and limited to northwestern corner, parts of the north, southwest and northeast. High potential for groundwater was observed at the eastern, northern and southern part of the study area covering about 12.35%. All areas that have thick overburden, high transmissivity, low fracture contrast and reflection coefficient are characterized by intense fracture. These areas are recommended for exploration for water at optimum yield.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullahi, N. (2014). Geoelectrical method applied to evaluation of groundwater potential and aquifer protective capacity of overburden units. British Journal of Applied Science & Technology, 4(14), 2024–2037.
Akinola, S. A. (2020). Hydrogeological characteristics of crystalline rock aquifers: implication on sustainable water supply in the basement complex terrain of Southwestern Nigeria. Sustainable Water Resources Management. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00381-z
Akinrinade, O. J., & Adesina, R. B. (2016). Hydro-geophysical investigation of groundwater potential and aquifer vulnerability prediction in Basement complex terrain – a case study from Akure, southwestern Nigeria. RMZ- Materials and Geoenvironment, 63, 55–66.
Ako, B. D. (1996). Applied geophysics. The subsurface and treasures. An inaugural lecture delivered at the Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife. Inaugural lecture series, 113, OAU Press Ltd, Ile-Ife, p. 42.
Alabi, A. A., & Makinde, V. (2016). Groundwater exploration in Igbo Ora, Ibarapa central local government area of Oyo State, Nigeria; using electrical resistivity method. Water Resources Journal, 26, 33–54.
Annor, A. E., & Freeth, S. J. (1985). Thermotectonic evolution of the basement complex around Okene, Nigeria, with special reference to deformation mechanisms. Precambrian Research, 28, 269–281.
Anomohanran, O., Ofomola, M. O., & Okocha, F. O. (2017). Investigation of groundwater in parts of Ndokwa district in Nigeria using geophysical logging and electrical resistivity methods: implications for groundwater exploration. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 129, 108–116.
Ayolabi, E. A. (2005). Geoelectric evaluation of groundwater potential: a case study of Alagbaka primary school, Akure, Southwest Nigeria. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 66, 491–495.
Badejo, A. A., Ndambuki, J. M., Kupolati, W. K., Adekunle, A. A., Taiwo, S. A., & Omole, D. O. (2015). Appraisal of access to safe drinking water in Southwest Nigeria. African Journal of Science, Technology, Innovation and Development, 7, 441–445. https://doi.org/10.1080/20421338.2015.1096669
Barker, R. D. (1989). Depth of investigation of collinear symmetrical four-electrode array. Geophysics, 54, 1031–1037.
Bayewu, O. O., Oloruntola, M. O., Mosuro, G. O., Laniyan, T. A., Ariyo, S. O., & Fatoba, J. O. (2018). Assessment of groundwater prospect and aquifer protective capacity using resistivity method in Olabisi Onabanjo University campus, Ago-Iwoye, Southwestern Nigeria. Journal of Astronomy and Geophysics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrjag.2018.05.002
Bayode, S. (2000). Geophysical characterization of the Iwo migmatite gneiss/granite complex. Its significance to groundwater potential. Unpublished M. Tech Thesis, Federal University of Technology, Akure, Nigeria, p. 213.
Emenike, C. P., Tenebe, I. T., Omole, D. O., Igene, B. U., Oniemayin, B. I., & Omeje, M. (2017). Accessing safe drinking water in sub-saharan africa: issues and challenges in South-West Nigeria. Sustainable Cities and Society, 30, 263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.01.005
George, N. J., Emah, J. B., & Ekong, U. N. (2015). Geophysical properties of hydrogeological units in parts of Niger Delta Southern Nigeria. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 105, 55–63.
Glain, D. L. (1979). Use of longitudinal conductance in vertical electrical soundings induced potential method for solving hydrogeolocial problems. Vestrik Mosk University Geology, 34, 74–100.
Graham, M. T., Dochartaigh, B. E., Ball, D. F., & MacDonald, A. M. (2009). Using transmissivity, specific capacity and borehole yield data to assess the productivity of Scottish aquifers. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 42, 227–235.
Henriet, J. P. (1976). Direct applications of the Dar Zarrouk parameters in ground water surveys. Geophysical Prospecting, 24(2), 344–353.
Ige, O. O., & Ajiboye, K. J. (2016). Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Tanke Area of Ilorin Southwestern Nigeria. Adamawa State University Journal of Scientific Research, 04(1), 41–51.
Kransy, J. (1993). Classification of transmissivity magnitude and variation. Groundwater, 31(2), 230–236.
MacDonald, A. M., Bonsor, H. C., Dochartaigh, B. E. O., & Taylor, R. G. (2012). Quantitative map of groundwater resource in Africa. Environmental Research Letters, 7, 024009.
Niwas, S., & Celik, M. (2012). Equation estimation of porosity and hydraulic conductivity of Ruhrtal Aquifer in Germany using near surface geophysics. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 84, 77–85.
Obaje, N. G. (2009). Geology and mineral resources of Nigeria. Lecture notes in earth sciences, Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 96–103
Oladapo, M. I., Mohammed, M. Z., Adeoye, O. O., & Adetola, B. A. (2004). Geoelectrical investigation of the Ondo State Housing Corporation Estate, Ijapo Akure, Southwestern Nigeria. Journal of Mining and Geology, 40(1), 41–48.
Oladunjoye, M., & Jekayinfa, S. (2015). Efficacy of Hummel (modified Schlumberger) arrays of vertical electrical sounding in groundwater exploration: case study of parts of Ibadan Metropolis, Southwestern Nigeria. International Journal of Geophysics, 2015(2):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/612303.
Olasehinde, P. I. (1989). Elucidating fracture pattern of the Nigerian basement complex using electrical resistivity method. Zangew, Geowiss, Left, pp. 109–120.
Olasehinde, P. I. (1999). An integrated geologic and geophysical exploration techniques for groundwater in the basement complex of west central part of Nigeria. Journal of Water Resources, 11, 46–49.
Olasehinde, P. I., & Raji, W. O. (2007). Geophysical studies of fractures of basement rocks at University of Ilorin, Southwestern Nigeria: application to groundwater exploration. Water Resources, 17, 3–10.
Olasunkanmi, N. K., Aina, A., Olatunji, S., & Bawalla, M. (2018). Seepage investigation on an existing dam using integrated geophysical methods. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 8(5), 7. ISSN 2224-3216.
Olatunji, J. A., Awojobi, M. O., Olasehinde, D. A., Akinrinmade, O. A., & Olasehinde, P. I. (2020). Aquifer characterization using evidences from hydro-geophysical data: a case study of Ilorin crystalline basement complex Southwestern Nigeria. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Applied Science IJRIAS, 5(1), 118–127. ISSN 2454-6194.
Olatunji, J. A., Omonona, O. V., & Odediran, O. A. (2016). Electrical resistivity investigation of the groundwater potential in parts of Kwara state Polytechnic, Ilorin, Nigeria. Global Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 23, 157–166.
Olayinka, A. I. (1996). Non-uniqueness in the interpretation of bedrock resistivity from sounding curves and its hydrogeological implication. Water Resoures, 7(12), 49–55.
Olayinka, A. I., Obere, F. O., & David, L. M., Jr. (2000). Estimation of longitudinal resistivity from Schlumberger sounding curves. Journal of Mining and Geology, 36(2), 225–242.
Olorunfemi, M. O., & Fasuyi, S. A. (1993). Aquifer types and the geoelectric/hydrogeologic characteristics of part of the central basement terrain of Nigeria (Niger State). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 16, 309–317.
Olusegun, O. A., Adeolu, O. O., & Dolapo, F. A. (2016). Geophysical investigation for groundwater potential and aquifer protective capacity around Osun State University (UNIOSUN) College of Health Sciences. American Journal of Water Resources, 4(6), 137–143.
Oluyide, P. O., Nwajide, C. S., & Oni, A. O. (1998). The geology of Ilorin with exploration on the 1:250,000 series, sheet 50 (Ilorin). Geological Survey of Nigeria Bulletin, 42, 1–84.
Oyegun, R. O., Jimoh, H. I., & Iroye, K. A. (2007). Opening up the rural area in Kwara State through the provision of water resources: the policy options. Confluence Journal of Environmental Studies, 2(1), 1–14.
Oyeyemi, K. D., Aizebeokhai, A. P., Ndambuki, J. M., Sanuade, O. A., Olofinnade, O. M., Adagunodo, T. A., Olaojo, A. A., & Adeyemi, G. A. (2018). Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surficial geophysical methods: a case study of Ota, Southwestern Nigeria. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/173/1/012028
Raji, W. O., & Abdulkadir, K. A. (2020). Evaluation of groundwater potential of bedrock aquifers in geological sheet 223, Ilorin, Nigeria using geo-electric sounding. Applied Water Science, 10, 220.
Thomas, A. H., Ushie, F. A., & Okechukwu, E. A. (2018). Hydraulic and geoelectric relationships of aquifers using vertical electrical sounding (VES) in parts of Obudu, Southern Nigeria. World Scientific News, 94(2), 261–275.
Todd, D. K. (1980). Groundwater hydrology (2nd ed., pp. 336–555). John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Vander-Velpen, B. P. A. (2004). Resist version 1.0. M.Sc. Research project ITC, Daft, The Netherlands.
WHO (World Health Organization). (1996). Guidelines for drinking water, vol. 1, Recommendation, Geneva, Switzerland.
Worthington, P. F. (1977). Influence of matrix conduction upon hydro geophysical relationships in arenaceous aquifers. Water Resources Research, 13(1), 87–92.
Wright, C. P. (1992). The hydrogeology of crystalline basement aquifers in Africa. Geological Society, London, Special Publication. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1992.066.01.01
Zohdy, A. A. R., Eaton, G. P., & Mabey, D. R. (1974). Application of surface geophysics to groundwater investigations. Techniq. Water Resources Investigations of UD Geol. Sur. Washington, p. 66.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OOI: conceptualization, methodology, validation, supervision, project administration, resources. OOA: software, formal analysis, investigation, writing original draft. IMO: writing—review and editing, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Human/animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ige, O.O., Adunbarin, O.O. & Olaleye, I.M. Groundwater potential and aquifer characterization within Unilorin campus, Ilorin, Southwestern Nigeria, using integrated electrical parameters. Int J Energ Water Res 6, 353–370 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-021-00160-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-021-00160-2