Abstract
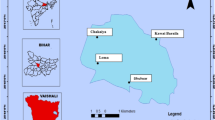
Heavy metal pollution is one of the threats to aquatic ecosystems globally and it portends a great danger to the sustenance of aquatic biodiversity in Afro-tropics, in particular. Bottom sediment samples were collected from three small African rivers, namely: Obudu river, Opa river, and Esinmirin river from Sep 2004 to July 2005. The samples were air-dried in the laboratory, digested and subsequently extracted for Ni, Fe, Zn, Cu, Pb, Cr, As, Co, Mn, and Cd using the atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Most of these metals recorded their highest values in the Esinmirin river and the lowest values in the Obudu river. However, the Kruskal–Wallis test revealed that only two metals (i.e., Cu and Pb) showed a significant difference (p < 0.05) in the variations. Geo-accumulation index, contamination factor, and enrichment factor all indicated that the bottom sediments of the rivers were highly impacted with Cd, followed by Cu and Pb. The three contamination indices suggest that the benthic fauna and the entire biota of each river system could be predisposed to pollution stress on account of these metals. Good waste management practice of Afro-tropical river basins by the local communities could contribute greatly to preserving pristine/near-pristine rivers and restoring the degraded ones.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adediji, A. (2002). Sediment delivery ratio in Opa Reservoir catchment, Southwestern Nigeria. Ph.D. Thesis, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
Adesakin, T. A., Adedeji, A. A., & Taiwo, Y. F. (2016). Temporal and spatial fluctuations of heavy metals in Opa Reservoir Ile-Ife, Nigeria. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 41(4), 435–443.
Ahmad, M. K., Islam, S., Rahman, M. S., Haque, M. R., & Islam, M. M. (2010). Heavy metals in water, sediment and some fishes of Buriganga river, Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research, 4, 321–332.
Akindele, E. O., & Adeniyi, I. F. (2013). A study of the physico-chemical water quality, hydrology and zooplankton fauna in Opa Reservoir catchment area, Ile-Ife, Nigeria. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 7(5), 192–203.
Akindele, E. O., Ehlers, S. M., & Koop, J. H. E. (2019). First empirical study of freshwater microplastics in West Africa using gastropods from Nigeria as bioindicators. Limnologica, 78, 125708.
Akindele, E. O., Ehlers, S. M., & Koop, J. H. E. (2020a). Freshwater insects of different feeding guilds ingest microplastic in two tributaries of the Gulf of Guinea in Nigeria. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08763-8.
Akindele, E. O., & Olutona, G. O. (2015). Environmental variables and benthic macroinvertebrate assemblage in the headwater streams of an Afro-tropical reservoir. Water and Environment Journal, 29(4), 541–548.
Akindele, E. O., Omisakin, O. D., Oni, O. A., Aliu, O. O., Omoniyi, G. E., & Akinpelu, O. T. (2020b). Heavy metal toxicity in the water column and benthic sediments of a degraded tropical stream. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 190, 110153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110153.
Begum, A., Ramaiah, M., Khan, I., & Veena, K. (2009). Heavy metal pollution and chemical profile of Cauvery river water. Journal of Chemistry, 6, 47–52.
Chapman, D., & Kimstach, V. (2006). Selection of water quality variables. In D. Chapman (Ed.), Water quality assessments: A guide to the use of biota, sediments and water environmental monitoring (pp. 65–122). London: Chapman and Hall.
Chen, W., Tan, S. K., & Tay, J. H. (1996). Distribution, fractional composition and release of sediment-bound heavy metals in tropical reservoirs. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 92, 273–287.
Csatorday, K., Gombos, Z., & Szalontai, B. (1984). Mn2+ and Co2+ toxicity in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Cell Biology, 81, 476–478.
Eludoyin, A. O., Ofoezie, E. I., & Ogunkoya, O. (2004). The effect of Oja-titun market effluent on the chemical quality of receiving Opa Reservoir in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Management, 72(4), 249–259.
Furse, M. T. (2000). The Application of RIVPACS procedures in headwater streams—an extensive and important national resource. In J. F. Wright, D. W. Sutcliff, & M. T. Furse (Eds.), Assessing the biological quality of freshwaters: RIVPACS and other techniques (pp. 79–91). London: Freshwater Biological Association.
Harbison, P. (1986). Mangrove muds—a sink and a source for trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17, 246–250.
Hsu, L. C., Huang, C. Y., Chuang, Y. H., Chen, H. W., Chan, Y. T., Teah, H. Y., et al. (2016). Accumulation of heavy metals and trace elements in fluvial sediments received effluents from traditional and semiconductor industries. Scientific Reports, 6, 34250.
Jaagumagi, R. (1988). The in-place pollutants program. Volume V, Part B. Benthic invertebrates studies results. Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Water Resources Branch, Aquatic Biology Section, Toronto.
Kaonga, C. C., Chiotha, S. S., Monjerezi, M., Fabiano, E., & Henry, E. M. (2008). Levels of cadmium, manganese and lead in water and algae; Spirogyra aequinoctialis. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5, 471–478.
Keay, R. W. J. (1959). An outline of Nigerian vegetation (3rd ed.). Lagos: Government Printer.
Kumwenda, S., Tsakama, M., Kalulu, K., & Kambala, C. (2012). Determination of biological, physical and chemical pollutants in Mudi river, Blantyre, Malawi. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 2, 6833–6839.
Meybeck, M., Friedrich, G., Thomas, R., & Chapman, D. (1996). Rivers. In D. Chapman (Ed.), Water quality assessment-a guide to the use of biota, sediments and water environmental monitoring, 2nd edn (pp. 227–303). UK: E and F. N. Spon, an imprint of Chapman and Hall.
Mclennan, S. M., & Taylor, S. R. (1999). Earth’s continental crust. In C. P. Marshall & R. W. Fairbridge (Eds.), Encyclopedia of geochemistry (pp. 145–150). Dordrecht-Kluwer: Academic Publishers.
Mintz, E., & Baier, K. (2000). A simple system for water purification in developing countries. Atlanta: Centre for Disease Control and Prevention Bulletin.
Mmolawa, K. B., Likuku, A. S., & Gaboutloeloe, G. K. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils along major roadside areas in Botswana. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(3), 186–196.
Mori, G. B., de Paula, F. R., de Barros Ferraz, S. F., Camargo, A. F. M., & Martinelli, L. A. (2015). Influence of landscape properties on stream water quality in agricultural catchments in South eastern Brazil. International Journal of Limnology, 51, 11–21.
Morin, S., Vivas-Nogues, M., Duong, T. T., Boudou, A., Coste, M., & Delmas, F. (2007). Dynamics of benthic diatom colonization in acadmium/zinc-polluted river (RiouMort, France). Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 168, 179–187.
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. Geological Journal, 2, 108–118.
Nasr, S. M., Okbah, M. A., & Kasem, S. M. (2006). Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution in bottom sediment of Aden Port, Yemen. International Journal of Oceanography, 1(1), 99–109.
Olabanji, I. O., & Oluyemi, E. A. (2014). Preliminary assessment of heavy metal pollution of Opa Reservoir, Ile-Ife, Southwest Nigeria using Mormyrus rume and Tilapia zillii. Ife Journal of Science, 16(1), 35–43.
Outa, J. O., Kowenje, C. O., Plessl, C., & Jirsa, F. (2020). Distribution of arsenic, silver, cadmium, lead and other trace elements in water, sediment and macrophytes in the Kenyan part of Lake Victoria: Spatial, temporal and bioindicative aspects. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 1485–1498.
Raut, R., Bajracharya, R. M., Sharma, S., Sharma, C. M., Kang, S., Zhang, Q., et al. (2017). Potentially toxic trace metals in water and lake-bed sediment panchpokhari, an alpine lake series in the central Himalaya region of Nepal. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228, 303.
Ray, G. C., & McCormick-Ray, J. (2014). Marine conservation: Science, policy and management. West Sussex: Wiley.
Rios, S. L., & Bailey, R. C. (2006). Relationship between riparian vegetation and stream benthic communities at three spatial scales. Hydrobiologia, 553, 153–160.
Rudnick, R. L., & Gao, S. (2003). Composition of the continental crust. In R. L. Rudnick (Ed.), Treatise on geochemistry (pp. 1–64). Oxford: Elsevier.
Salomons, W., & Stigliani, W. (1995). Biogeodynamics of pollutants in soils and sediments. Berlin: Springer.
Schiff, K. C., & Weisberg, S. B. (1999). Iron as a reference element for determining trace metal enrichment in southern California coastal shelf sediment. Marine Environmental Research, 48, 161–176.
Song, Y., Ji, J., Yang, Z., Yuan, X., Mao, C., Frost, R. L., et al. (2011). Geochemical behaviour assessment and apportionment of heavy metal contaminants in the bottom sediments of lower reach of Changjiang river. CATENA, 85, 73–81.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. (2012). Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In A. Luch (Ed.), Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology experientia supplementum, vol. 10. Basel: Springer.
UNEP. (2010). Final review of scientific information on cadmium. United Nations Environment Programme, Chemicals Branch.
Verry, E. S. W., Hornbeck, J. C., & Dolloff, C. A. (2000). Riparian management in forests of the Continental Eastern United States. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
White, F. (1983). The vegetation of Africa- a descriptive memoir to accompany vegetation map of Africa. Paris: UNESCO.
WHO. (2004). Manganese and its compounds: Environmental aspects. Geneva: World Health Organisation.
WHO. (2008). Cadmium. In Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd edition incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda. Vol. 1. Recommendations (pp. 317–319). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OOA collated field and laboratory data, and revised the manuscript. EOA was involved in the field work, analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. IFA made substantial contributions to conception and design of this study. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliu, O.O., Akindele, E.O. & Adeniyi, I.F. Potentially toxic metals record high contamination indices in three small African rivers. Int J Energ Water Res 5, 175–184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-020-00091-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-020-00091-4