Abstract
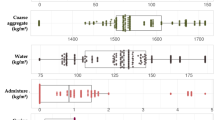
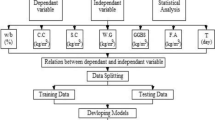
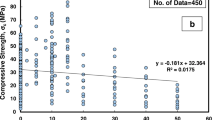
Sustainable building construction requirements demand an efficient utilization of industrial waste as alternatives to construction materials. In this work, the nano-silica (NS) has been used as a precursor to the compressive strength of mortar and multiple mixes of 107 were produced to study the effect of the nano-silica precursor (NSP). Advanced Machine Learning (AML) techniques have been used in this research work to predict the compressive strength of the NSP mortar using 75% to 25% ratio to train and validate the models. The NS precursor with a 17% degree of importance played a substantial influence with the cement due to its contribution to the pozzolanic reaction to produce C-S-H gel in mortar. The accuracies of the developed models were compared using Taylor charts, and also, the variance distribution for the developed models was conducted. The models’ performance indices, mean average error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE), root mean square error (RMSE), sum of squared error (SSE), and the coefficient of determination (R2), were used to decide the superior model. At the end of the exercise, it has been shown that the GP model showed a poorly performed model with outliers from the NS precursor mortar UCS data entries outside the ± 25% envelop. The parametric line fit of the GP is y = 0.973x, which produced MAE of 5.62 MPa, MSE of 46.71 MPa, RMSE of 6.83 MPa, and R2 of 0.680. Also, the EPR model showed a parametric line fit of y = 0.983x, which produced MAE of 4.10 MPa, MSE of 29.67 MPa, RMSE of 5.45 MPa, and R2 of 0.823, while the most superior model was produced by the ANN with a parametric line fit of 0.997x, which produced MAE of 1.47 MPa, MSE of 3.84 MPa, RMSE of 1.96 MPa, and R2 of 0.980. The outperformance of the ANN over the other AI techniques is supported by previous research work even though the ANN did not produce a closed-form parametric expression that allows a manual application of the model in the design and construction of buildings with mortar under NS precursor effect. Generally, the NSP has shown a reliable potential to improve the hardened strength of mortar, which confirms its application in the built environment as a sustainable pozzolanic construction material.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this research project have been reported in this manuscript.
References
Ahmad, A., Ahmad, W., Chaiyasarn, K., Ostrowski, K. A., Aslam, F., Zajdel, P., & Joyklad, P. (2021). Prediction of geopolymer concrete compressive strength using novel machine learning algorithms. Polymers, 13(19), 3389.
Akash, K., & Singh, G. (2018). Effect of nano silica on the fresh and hardened properties of cement 687 mortar. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 13(2018), 11183–11188.
Awoyera, P. O., Kirgiz, M. S., Viloria, A., & Ovallos-Gazabon, D. (2020). Estimating strength properties of geopolymer self-compacting concrete using machine learning techniques. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 9(4), 9016–9028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.06.008
Azim, I., Yang, J., Farjad Iqbal, M., Faisal Javed, M., Nazar, S., Wang, F., & Liu, Q. (2020). A semi-analytical model for compressive arch action capacity of RC frame structures. Structures, 27, 1231–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2020.06.011
Azim, I., Yang, J., Iqbal, M. F., Mahmood, Z., Javed, M. F., Wang, F., & Liu, Q. (2021). Prediction of catenary action capacity of RC beam-column substructures under a missing column scenario using evolutionary algorithm. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 25(3), 891–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-0431-0
Balapour, M., Joshaghani, A., & Anthony, F. (2018). Nano-SiO2 contribution to mechanical, durability, fresh and microstructural characteristics of concrete: A review. Construction and Building Materials, 181, 27–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.266
Balf, F. R., Kordkheili, H. M., & Kordkheili, A. M. (2021). A new method for predicting the ingredients of self-compacting concrete (SCC) including fly ash (FA) using data envelopment analysis (DEA). Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 46(5), 4439–4460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04927-3
Behnood, A., & Golafshani, E. M. (2018). Predicting the compressive strength of silica fume concrete using a hybrid artificial neural network with multi-objective grey wolves. Journal of Cleaner Production, 202, 54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.065
Byung-Wan, J., Chang-Hyun, K., Ghi-ho, T., & Jong-Bin, P. (2007). Characteristics of cement mortar with nano-SiO2 particles. Construction and Building Materials, 21(6), 1351–1355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.12.020
Cao, M., Khan, M., & Ahmed, S. (2020). Effectiveness of calcium carbonate whisker in cementitious composites. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering, 64(1), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.14288
Cao, M., Li, L., & Khan, M. (2018). Effect of hybrid fibers, calcium carbonate whisker, and coarse sand on mechanical properties of cement-based composites. Materiales De Construcción, 68(330 SE-Research Articles), e156. https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2018.01717
Chou, J.-S., Tsai, C.-F., Pham, A.-D., & Lu, Y.-H. (2014). Machine learning in concrete strength simulations: Multi-nation data analytics. Construction and Building Materials, 73, 771–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.054
Czarnecki, S., Shariq, M., Nikoo, M., & Sadowski, Ł. (2021). An intelligent model for the prediction of the compressive strength of cementitious composites with ground granulated blast furnace slag based on ultrasonic pulse velocity measurements. Measurement, 172, 108951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108951
de Azevedo, A. R. G., Marvila, M. T., Rocha, H. A., Cruz, L. R., & Vieira, C. M. F. (2020). Use of glass polishing waste in the development of ecological ceramic roof tiles by the polymerization process. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.13585
de Azevedo, A. R. G., Marvila, M. T., Tayeh, B. A., Cecchin, D., Pereira, A. C., & Monteiro, S. N. (2021). Technological performance of açaí natural fiber reinforced cement-based mortars. Journal of Building Engineering, 33, 101675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101675
Hoffman, F. O., & Gardner, R. H. (1983). Evaluation of uncertainties in radiological assessment models. In J. E. Till & H. R. Meyer (Eds.), Chapter 11 of Radiological Assessment: A textbook on Environmental Dose Analysis. Washington, D.C.: NRC Office of Nuclear Reactor Regulation.
Kaveh, A., Dadras, E. A., Javadi, S. M., & Geran, M. N. (2021). Machine learning regression approaches for predicting the ultimate buckling load of variable-stiffness composite cylinders. Acta Mechanica, 232, 921–931.
Kaveh, A., Gholipour, Y., & Rahami, H. (2008). Optimal design of transmission towers using genetic algorithm and neural networks. International Journal of Space Structures, 23(1), 1–19.
Kaveh, A., & Iranmanesh, A. (1998). Comparative study of backpropagation and improved counterpropagation neural nets in structural analysis and optimization. International Journal of Space Structures, 13, 177–185.
Kaveh, A., & Khalegi, A. (1998). Prediction of strength for concrete specimens using artificial neural network. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2(2), 1–13.
Kaveh, A., & Khavaninzadeh, N. (2023). Efficient training of two ANNs using four meta-heuristic algorithms for predicting the FRP strength. Structures, 52(2023), 256–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2023.03.178
Kaveh, A., & Servati, H. (2001). Design of double layer grids using backpropagation neural networks. Computers & Structures, 79(17), 1561–1568.
Khan, M., & Ali, M. (2018). Effect of superplasticizer on the properties of medium strength concrete prepared with coconut fiber. Construction and Building Materials, 182, 703–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.06.150
Khan, M., & Ali, M. (2019). Improvement in concrete behavior with fly ash, silica fume, and coconut fibers. Construction and Building Materials, 203, 174–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.103
Khan, M., Cao, M., & Ali, M. (2018). Effect of basalt fibers on mechanical properties of calcium carbonate whisker-steel fiber reinforced concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 192, 742–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.159
Khan, M., Cao, M., Hussain, A., & Chu, S. H. (2021). Effect of silica-fume content on performance of CaCO3 whisker and basalt fiber at matrix interface in cement-based composites. Construction and Building Materials, 300, 124046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124046
Li, L. G., Zhu, J., Huang, Z. H., Kwan, A. K. H., & Li, L. J. (2017). Combined effects of micro-silica and nano-silica on the durability of mortar. Construction and Building Materials, 157, 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.09.105
Musumeci, F., Rottondi, C., Nag, A., Macaluso, I., Zibar, D., Ruffini, M., & Tornatore, M. (2019). An Overview on application of machine learning techniques in optical networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 21(2), 1383–1408. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2880039
Nakkeeran, G., & Krishnaraj, L. (2023). Prediction of cement mortar strength by replacement of hydrated lime using RSM and ANN. Asian J Civ Eng, 24, 1401–1410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00577-6
Nguyen, T. P., Nguyen, V. T., Mondal, S., Pham, V. H., Vu, D. D., Kim, B.-G., & Oh, J. (2020). Improved depth-of-field photoacoustic microscopy with a multifocal point transducer for biomedical imaging. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072020
Onyelowe, K. C. & Ebid, A. M. (2023). The influence of fly ash and blast furnace slag on the compressive strength of high- performance concrete (HPC) for sustainable structures. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering.
Onyelowe, K. C., Ebid, A. M., Hanandeh, S., Moghal, A. A. B., Onuoha, I. C., Obianyo, I. I., & Ubachukwu, O. A. (2023a). The influence of fines on the hydro-mechanical behavior of sand for sustainable compacted liner and sub-base construction applications. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00800-4
Onyelowe, K. C., Ebid, A. M., Mahdi, H. A., Onyelowe, F. K. C., Shafieyoon, Y., Onyia, M. E., & Onah, H. N. (2023b). AI mix design of fly ash admixed concrete based on mechanical and environmental impact considerations. Civil Engineering Journal, 9, 27–45. https://doi.org/10.28991/CEJ-SP2023-09-03
Onyelowe, K. C., Ebid, A. M., Mahdi, H. A., Riofrio, A., Rezazadeh Eidgahee, D., Baykara, H., Soleymani, A., Kontoni, A.-P.N., Shakeri, J., & Jahangir, H. (2022c). Optimal compressive strength of RHA ultra-high-performance lightweight concrete (UHPLC) and its environmental performance using life cycle assessment. Civil Engineering Journal, 8(11), 2391–2410. https://doi.org/10.28991/CEJ-2022-08-11-03
Onyelowe, K. C., Ebid, A. M., Riofrio, A., Soleymani, A., Baykara, H., Kontoni, D.-P.N., Mahdi, H. A., & Jahangir, H. (2022e). Global warming potential-based life cycle assessment and optimization of the compressive strength of fly ash-silica fume concrete; environmental impact consideration. Frontiers in Built Environment, 8, 992552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2022.992552
Onyelowe, K. C., Iqbal, M., Jalal, F. E., Onyia, M. E., & Onuoha, I. C. (2021a). Application of 3-algorithm ANN programming to predict the strength performance of hydrated-lime activated rice husk ash treated soil. Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling, Experiments and Design, 4(4), 259–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-021-00093-7
Onyelowe, K. C., Jayabalan, J., Ebid, A. M., Samui, P., Singh, R. P., Soleymani, A., & Jahangir, H. (2022d). Evaluation of the compressive strength of CFRP-wrapped circular concrete columns using artificial intelligence techniques. Designs, 2022(6), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs6060112
Onyelowe, K. C., & Kontoni, D.-P.N. (2023). The net-zero and sustainability potential of SCC development, production and flowability in structures design. International Journal of Low Carbon Technologies, 18, 530–541. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctad033
Onyelowe, K. C., Kontoni, D.-P.N., & Ebid, A. M. (2022a). Simulation of self-compacting concrete (SCC) passing ability using the L-box model for sustainable buildings. ICED-2022a; In IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science (vol. 1123, pp. 012065, 1–8). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1123/1/012065.
Onyelowe, K. C., Kontoni, D.-P.N., & Ebid, A. M. (2022b). Flow simulation of self-consolidating concrete through V-funnel for sustainable buildings. ICED-2022b. In IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science (vol. 1123, pp. 012044, 1–9) https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1123/1/012044.
Onyelowe, K. C., Onyia, M. E., Van Bui, D., Baykara, H., & Ugwu, H. U. (2021b). Pozzolanic reaction in clayey soils for stabilization purposes: A classical overview of sustainable transport geotechnics. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 6632171. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6632171
Parashar, A. K., & Gupta, N. (2023). An investigation of micro-silica inclusion in slag-based geopolymer concrete with regression and cluster analysis. Asian J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00750-x
Parhi, S. K., & Panigrahi, S. K. (2023). Alkali–silica reaction expansion prediction in concrete using hybrid metaheuristic optimized machine learning algorithms. Asian J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00799-8
Rupasinghe, M., Mendis, P., Ngo, T., Nguyen, T. N., & Sofi, M. (2016). Compressive strength prediction of nano-silica incorporated cement systems based on a multi-scale approach. Materials & Design, 115(2017), 379–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.058
Sonebi, M., Cevik, A., Grünewald, S., & Walraven, J. (2016). Modeling the fresh properties of self-compacting concrete using the support vector machine approach. Construction and Building Materials, 106, 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.035
Sua-iam, G., & Makul, N. (2017). Incorporation of high-volume fly ash waste and high-volume recycled alumina waste in the production of self-consolidating concrete. Journal of Cleaner Production, 159, 194–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.075
Wang, Q., Hussain, A., Farooqi, M. U., & Deifalla, A. F. (2022). Artificial intelligence-based estimation of ultra-high-strength concrete’s flexural property. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 17, e01243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01243
Worden, K., & Manson, G. (2007). The application of machine learning to structural health monitoring. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 365(1851), 515–537. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2006.1938
Yu, J., Li, H., Leung, C. K. Y., Lin, X., Lam, J. Y. K., Sham, I. M. L., & Shih, K. (2017). Matrix design for waterproof Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECCs). Construction and Building Materials, 139, 438–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.076
Yu, J., Mishra, D. K., Wu, C., & Leung, C. K. Y. (2018). Very high volume fly ash green concrete for applications in India. Waste Management & Research, 36(6), 520–526. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X18770241
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.C.O. conceptualized and supervised the project. K.C.O., A.M.E. and S.H. wrote the main manuscript texts and K.C.O. and A.M.E. prepared the figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Onyelowe, K.C., Ebid, A.M. & Hanandeh, S. The influence of nano-silica precursor on the compressive strength of mortar using Advanced Machine Learning for sustainable buildings. Asian J Civ Eng 25, 1135–1148 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00832-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00832-w