Abstract
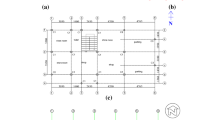
Steel is the most preferred material by designers for industrial structures because of its advantageous properties, namely, tensile strength, ductility, and durability. Industrial steel structures are commonly used for manufacturing and storage works requiring large uninterrupted dimensions. This requirement of structure is fulfilled using pre-engineered buildings (PEB). PEB is one of the widely used concepts as it optimizes steel consumption in comparison with the conventional steel building (CSB) and thus contributes to the reduction of cost and project duration without affecting the lateral stability during earthquakes. The lateral stability of the structure is ensured by providing a suitable bracing system. In this paper, the comparative behaviour of conventional and pre-engineered buildings is studied by providing different types of bracings (viz. X, V, K, and diagonal) using Staad Pro. Results indicate that PEB with diagonal bracing reduces displacement and natural time period by 17.39 and 28.02%, respectively, when compared with CSB. The study concludes that the provision of diagonal bracing contributes to improving the performance of PEB.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Alam, M., and Sakalle, R., (2020). Comparative Study of Warehouse Structure in Pre-Engineered Building with Conventional Steel Building, International Journal of Trend in Research and Development. 7(1), 116–122 http://www.ijtrd.com/papers/IJTRD21940.pdf
Arzani, H., Kaveh, A., & Kamalinejad, M. (2019). Optimal design of pitched roof rigid frames with non-prismatic members using quantum evolutionary algorithm. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.14091
Gilbile J. and Mane S.S. (2020). A review on comparative study on the structural analysis and design of pre-engineered building [PEB] with conventional steel [CSB] building, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology. 9(09), 56–58 https://rb.gy/nvbrn
IS: 800 (2007) Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi. ‘‘Indian standard general construction in steel code of practice, IS 800: 2007.
IS: 875 (Part 2) (2015) Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi. ‘‘Indian standard—code of practice for design loads (other than earthquake) for building and structures: Part 2—Live loads, IS 875 (Part 2): 2015.
IS: 875 (Part 3) (2015) Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi. ‘‘Indian standard—code of practice for design loads (other than earthquake) for building and structures: Part 3—Wind loads, IS 875 (Part 3): 2015.
IS: 875 (Part 1) (2015) Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi. ‘‘Indian standard—code of practice for design loads (other than earthquake) for building and structures: Part 1—Dead loads, IS 875 (Part 1): 2015.
Kalesha, S., Reddy, B.S.S.R., and Jagrapu, D.C.K., (2020) An analytical study on pre-engineered buildings using Staad pro, Materials today: proceedings, 296–302. https://rb.gy/gob73
Kaveh, A., & Ghafari, M. H. (2018). Geometry and sizing optimization of steel pitched roof frames with tapered members using nine metaheuristics. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology-Transactions of Civil Engineering. an. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-018-0132-1
Kaveh, A., Kabir, M. Z., & Bohlool, M. (2018). Optimal design of multi-span pitched roof frames with tapered members. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.13107
Kaveh, A., Mahdavi, V. R., & Kamalinejad, M. (2016). Optimal design of pitched roof frames with tapered members using ECBO algorithm. Smart Structures, and Systems., 19(6), 643–652. https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2017.19.6.643
Kumar, G.S., and Varghese, K.M., (2020) Comparative analysis on pre-engineered and conventional buildings with diagonal braces, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 07(06), 3668–3671 https://www.irjet.net/archives/V7/i6/IRJET-V7I6685.pdf
Sah S. K., Kangda M.Z., Sathe and Mate, (2022) A state of art review on analysis and design of pre-engineered buildings, Materials Today Proceedings. 1–7 https://rb.gy/qltew
Sharma V., Kumar R., Singh H., Ahmad W., and Pratap Y. (2017). A review study on uses of steel in construction. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(4), 1140–1142. https://www.irjet.net/archives/V4/i4/IRJET-V4I4235.pdf.
Sharma L., Taak N., and Mishra P.K. (2021). A comparative study between the pre-engineered structures and conventional structures using Staad Pro, Materials today: Proceedings. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214785320406601
Tale S. and Vasugi K. (2019). Effect of bracing under different loading for conventional and pre-engineering industrial structure. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering. https://www.ijrte.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v8i1/A2969058119.pdf
Vivek K.S. and Vyshnavi P. (2017). Pre-engineered steel building, LAMBERT Academic Publishing
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Director, of Rajarambapu Institute of Technology (RIT), Rajaramnagar, and the Head of Department, Civil Engineering, RIT for motivating and providing the required facilities in carrying out this study.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other supports were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by PPB, PDK, and KG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by PPB and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bharmal, P.P., Kumbhar, P.D. & Gumaste, K.S. Comparative study on the behaviour of conventional and pre-engineered buildings provided with different types of bracing. Asian J Civ Eng 25, 451–459 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00787-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00787-y