Abstract
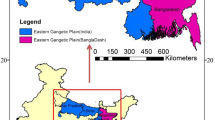
The meteorological drought is a recurring phenomenon for Bihar, a densely populated Indian state situated on the Eastern Gangetic Plain (EGP). Drought largely affects a wide population of the state since most people residing here predominantly depend on agriculture for livelihood. The linkage between Aerosol and Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall (ISMR) or southwest monsoon rainfall is a complex process affecting the hydrological cycle, which in turn may cause meteorological drought over the study area. Therefore, the relation between the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI); a metric for categorising drought intensity, and Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) are examined from 2000 to 2019. The high resolution (0.25° × 0.25°) gridded rainfall data (2000–2019) of India Meteorological Department (IMD) and AOD data (2000–2019) at a resolution of 1° × 1° at 550 nm from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectro-radiometer (MODIS) products are analysed. To understand the role of the aerosol on rainfall and to further investigate the influence on underlying cloud properties as a probable cause of meteorological drought, MODIS-derived cloud parameters namely, Cloud Top Temperature (CTT), Cloud Top Pressure (CTP), and Cloud Fraction (CF) at the resolution of 1° × 1° for the period of 2000–2019 have been examined. A strong inverse relationship between CTT/CTP and SPI whereas as a directly positive relationship between CTT/CTP and AOD is found thus a strong correlation between SPI and AOD is also well verified by cloud parameters. A possible linkage between aerosols and drought conditions through indirect and semi direct effects of aerosol cloud interactions was also found to be quite important for Bihar & EGP.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman AS, Toon OB, Stevens DE, Heymsfield AJ, Ramanathan V, Welton EJ (2000) Reduction of tropical cloudiness by soot. Science 288(5468):1042–1047
Acker JG, Leptoukh G (2007) Online analysis enhances use of NASA earth science data. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 88(2):14–17
Alam K, Iqbal MJ, Blaschke T, Qureshi S, Khan G (2010) Monitoring spatio-temporal variations in aerosols and aerosol–cloud interactions over Pakistan using MODIS data. Adv Space Res 46(9):1162–1176
Alam K, Khan R, Blaschke T, Mukhtiar A (2014) Variability of aerosol optical depth and their impact on cloud properties in Pakistan. J Atmos Solar Terr Phys 107:104–112
Albrecht BA (1989) Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 245(4923):1227–1230
Andreae MO, Rosenfeld D, Artaxo P, Costa AA, Frank GP, Longo KM, Silva-Dias MAF (2004) Smoking rain clouds over the Amazon. Science 303(5662):1337–1342
Ångström A (1929) On the atmospheric transmission of sun radiation and on dust in the air. Geogr Ann 11(2):156–166
Balakrishnaiah G, Kumar KR, Reddy BSK, Gopal KR, Reddy RR, Reddy LSS, Swamulu C, Ahammed YN, Narasimhulu K, Krishna Moorthy K, Babu SS (2012) Spatio-temporal variations in aerosol optical and cloud parameters over Southern India retrieved from MODIS satellite data. Atmos Environ 47:435–445
Bhat GS, Kumar S (2015) Vertical structure of cumulonimbus towers and intense convective clouds over the South Asian region during the summer monsoon season. J Geophys Res Atmos 120(5):1710–1722
Biswas BC, Sarkar SS (1982) Weekly rainfall probability over dry farming tract of Gujarat. Ann Arid Zone 21(3):187–194
Blain GC (2011) Standardized precipitation index based on Pearson type III distribution. Revista Brasileira De Meteorologia 26(2):167–171
Blain GC, Meschiatti MC (2015) Inadequacy of the gamma distribution to calculate the Standardized Index. Braz J Agric Environ Eng 19(12):1129–1135
Bond TC (2001) Spectral dependence of visible light absorption by carbonaceous particles emitted from coal combustion. Geophys Res Lett 28(21):4075–4078
Chen H, Jian-qi SUN, Xiao-li C (2013) Future changes of drought and flood events in China under a global warming scenario. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 6:8–13
Chung CE, Ramanathan V (2006) Weakening of North Indian SST gradients and the monsoon rainfall in India and the Sahel. J Clim 19(10):2036–2045
Cowan T, Cai W (2011) The impact of Asian and non-Asian anthropogenic aerosols on 20th century Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 38:L11703. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047268
Dey S, Di Girolamo L (2010) A climatology of aerosol optical and microphysical properties over the Indian subcontinent from 9 years (2000–2008) of Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) data. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:D15204. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013395
Fadnavis S, Sabin TP, Roy C, Rowlinson M, Rap A, Vernier J-P, Sioris CE (2019) Elevated aerosol layer over South Asia worsens the Indian droughts. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46704-9
Ganeshkumar B, Krishna GG (2016) Correlation of aerosol optical depth and spatial rainfall variability patterns for the assessment of meteorological drought. Int J Earth Sci Eng 9(1):63–67
Guhathakurta P, Rajeevan M (2008) Trends in the rainfall pattern over India. Int J Climatol 28(11):1453–1469
Guo L, Highwood E, Shaffrey L, Turner A (2013) The effect of regional changes in anthropogenic aerosols on rainfallof the East Asian Summer Monsoon. Atmosph Chem Phys 13:1521–1534
Heim RR Jr (2002) A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States. Bull Am Meteor Soc 83(8):1149–1166
India Meteorological Department (IMD) (1971) Climate Diagnostic Bulletin of India June, July, August 1971, Rep. No 88, 89 and 90. National Climate Center, IMD, Pune
Jha S, Sehgal VK, Raghava R, Sinha M (2013) Trend of standardized precipitation index during Indian summer monsoon season in agroclimatic zones of India. Earth Syst Dyn Discuss 4:429–449. https://doi.org/10.5194/esdd-4-429-2013
Jiang Y, Liu X, Yang XQ, Wang M (2013) A numerical study of the effect of different aerosol types on East Asian summer clouds and precipitation. Atmos Environ 70:51–63
Kaskaoutis DG, Kharol SK, Sinha PR, Singh RP, Kambezidis HD, Sharma AR, Badarinath KVS (2011) Extremely large anthropogenic-aerosol contribution to total aerosol load over the Bay of Bengal during winter season. Atmos Chem Phys 11(14):7097–7117
Kaufman YJ, Nakajima T (1993) Effect of Amazon smoke on cloud microphysics and albedo-analysis from satellite imagery. J Appl Meteorol 32(4):729–744
Kaufman YJ, Koren I, Remer LA, Rosenfeld D, Rudich Y (2005) The effect of smoke, dust, and pollution aerosol on shallow cloud development over the Atlantic Ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(32):11207–11212
Khain A, Rosenfeld D, Pokrovsky A (2005) Aerosol impact on the dynamics and microphysics of deep convective clouds. Q J R Meteorol Soc 131(611):2639–2663
Kharol SK, Badarinath KVS, Sharma AR, Mahalakshmi DV, Singh D, Prasad VK (2012) Black carbon aerosol variations over Patiala city, Punjab, India—a study during agriculture crop residue burning period using ground measurements and satellite data. J Atmos Solar Terr Phys 84:45–51
Kim BG, Schwartz SE, Miller MA, Min Q (2003) Effective radius of cloud droplets by ground-based remote sensing: relationship to aerosol. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD003721
Konwar M, Maheskumar RS, Kulkarni JR, Freud E, Goswami BN, Rosenfeld D (2012) Aerosol control on depth of warm rain in convective clouds. J Geophys Res 117:D13204. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD017585
Koren I, Feingold G, Remer LA (2010a) The invigoration of deep convective clouds over the Atlantic: aerosol effect, meteorology or retrieval artefact? Atmos Chem Phys 10:8855–8872
Koren I, Remer LA, Altaratz O, Martins JV, Davidi A (2010b) Aerosol-induced changes of convective cloud anvils produce strong climate warming. Atmos Chem Phys 10:5001–5010
Krishnan R, Kumar V, Sugi M, Yoshimura J (2009) Internal feedbacks from monsoon–midlatitude interactions during droughts in the Indian summer monsoon. J Atmos Sci 66(3):553–578
Krishnakumar KN, Prasada Rao GSLHV, Gopakumar CS (2009) Rainfall trends in twentieth century over Kerala. India. Atmosph Environ 43(11):1940–1944
Kumar M, Raju MP, Singh RS, Banerjee T (2017) Impact of drought and normal monsoon scenarios on aerosol induced radiative forcing and atmospheric heating in Varanasi over middle Indo-Gangetic Plain. J Aerosol Sci 113:95–107
Kumar S, Kumar P, Barat A, Sinha AK, Sarthi PP, Ranjan P, Singh KK (2019) Characteristics of observed meteorological drought and its linkage with low-level easterly wind over India. Pure Appl Geophys 176(6):2679–2696
Lau KM, Kim KM (2006) Observational relationships between aerosol and Asian monsoon rainfall, and circulation. Geophys Res Lett 33:L21810. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL027546
Lau KM, Kim MK, Kim KM (2006) Asian summer monsoon anomalies induced by aerosol direct forcing: the role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim Dyn 26(7–8):855–864
Lau KM, Tsay SC, Hsu C, Chin M, Ramanathan V, Wu GX, Li Z, Sikka R, Holben B, Lu D, Chen H, Tartari G, Koudelova P, Ma Y, Huang J, Taniguchi K, Zhang R (2008) The joint aerosol-monsoon experiment: a new challenge for monsoon climate research. Bull Am Meteor Soc 89(3):69–384
Lawrence MG, Lelieveld J (2010) Atmospheric pollutant outflow from southern Asia: a review. Atmos Chem Phys 10:11017–11096
Lewis K, Arnott WP, Moosmüller H, Wold CE (2008) Strong spectral variation of biomass smoke light absorption and single scattering albedo observed with a novel dual-wavelength photo acoustic instrument. J Geophys Res 113:D16203. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009699
Li Z, Zhao X, Kahn R, Mishchenko M, Remer L, Lee K-H, Wang M, Laszlo I, Nakajima T, Maring H (2009) Uncertainties in satellite remote sensing of aerosols and impact on monitoring its long-term trend: a review and perspective. Ann Geophys 27:2755–2770
Li Z, Niu F, Fan J, Liu Y, Rosenfeld D, Ding Y (2011) Long-term impacts of aerosols on the vertical development of clouds and precipitation. Nat Geosci 4(12):888–894
Li J, Liu C, Yin Y, Kumar KR (2016) Numerical investigation on the Ångström exponent of black carbon aerosol. J Geophys Res Atmos 121(7):3506–3518
Lohmann U, Feichter J (2005) Global indirect aerosol effects: a review. Atmos Chem Phys 5(3):715–737
Malakiya AD, Suryanarayana TMV (2016) Assessment of drought using standardized precipitation index (SPI) and reconnaissance drought index (RDI): a case study of Amreli District. Int J Sci Res 5(8):1995–2002
Manoj MG, Devara PCS, Joseph S, Sahai AK (2012) Aerosol indirect effect during the aberrant Indian Summer Monsoon breaks of 2009. Atmos Environ 60:153–163
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In: Proc. 8th conference on applied climatology, Anaheim/CA, pp 179–184
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1995) Drought monitoring with multiple time scales. In: Proc. 9th conference on applied climatology, Dallas/TX, pp 233–236
Meehl GA, Arblaster JM, Collins WD (2008) Effects of black carbon aerosols on the Indian monsoon. J Clim 21(12):2869–2882
Mishra AK, Shibata T (2012) Climatological aspects of seasonal variation of aerosol vertical distribution over central Indo-Gangetic belt (IGB) inferred by the space-borne lidar CALIOP. Atmos Environ 46:365–375
Mishra V, Aadhar S, Asoka A, Pai S, Kumar R (2016) On the frequency of the 2015 monsoon season drought in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Geophys Res Lett 43(23):12102–12112
Nair VS, Babu SS, Moorthy KK, Sharma AK, Marinoni A, Ajai (2013) Black carbon aerosols over the Himalayas: direct and surface albedo forcing. Tellus B: Chem Phys Meteorol 65:1. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v65i0.19738
Nath R, Nath D, Li Q, Chen W, Cui X (2017) Impact of drought on agriculture in the Indo-Gangetic Plain, India. Adva Atmos Sci 34(3):335–346
Pai DS, Sridhar L, Rajeevan M, Sreejith OP, Satbhai NS, Mukhopadhyay B (2014) Development of a new high spatial resolution (0.25× 0.25) long period (1901–2010) daily gridded rainfall data set over India and its comparison with existing data sets over the region. Mausam 65(1):1–18
Palchaudhuri M, Biswas S (2013) Analysis of drought using standardized precipitation index. Int J Environ Chem Ecol Geol Geophys Eng 7:119–126
Parth Sarthi P, Kumar S, Barat A, Kumar P, Sinha AK, Goswami V (2019) Linkage of aerosol optical depth with rainfall and circulation parameters over the Eastern Gangetic Plains of India. J Earth Syst Sci 128(7):128–171
Patil N, Dave P, Venkataraman C (2017) Contrasting influences of aerosols on cloud properties during deficient and abundant monsoon years. Sci Rep 7(1):1–9
Paulo AA, Pereira LS (2006) Drought concepts and characterization: comparing drought indices applied at local and regional scales. Water Int 31(1):37–49
Porch W, Chylek P, Dubey M, Massie S (2007) Trends in aerosol optical depth for cities in India. Atmos Environ 41(35):7524–7532
Prabha TV, Khain A, Maheshkumar RS, Pandithurai G, Kulkarni JR, Konwar M, Goswami BN (2011) Microphysics of pre monsoon and monsoon clouds as seen from in situ measurements during the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX). J Atmos Sci 68(9):1882–1901
Prasad AK, Singh S, Chauhan SS, Srivastava MK, Singh RP, Singh R (2007) Aerosol radiative forcing over the Indo-Gangatic plains during major dust storms. Atmos Environ 41(29):6289–6301
Prasad AK, Singh RP (2007) Changes in aerosol parameters during majordust storm events (2001–2005) over the Indo-Gangetic Plains using AERONET and MODIS data. J Geophys Res 112:D09208. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007778
Praveen D, Ramachandran A, Jaganathan R, Krishnaveni E, Palanivelu K (2016) Projecting droughts in the purview of climate change under RCP 4.5 for the Coastal Districts of South India. Indian J Sci Technol 9(6)
Rahul PRC, Salvekar PS, Devara PCS (2008) Aerosol optical depth variability over Arabian Sea during drought and normal years of Indian monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 35:L22812. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL035573
Ramanathan V, Crutzen PJ, Lelieveld J, Mitra AP, Althausen D, Anderson J, Andreae MO, Cantrell W, Cass GR, Chung CE, Clarke AD, Coakley JA, Collins WD, Conant WC, Dulac F, Heintzenberg J, Heymsfield AJ, Holben B, Howell S, HudsonShowless J, Jayaraman A, Kiehl JT, Krishnamurti TN, Lubin D, McFarquhar G, Novakov T, Ogren JA, Podgorny IA, Prather K, Priestley K, Prospero JM, Quinn PK, Rajeev K, Rasch P, Rupert S, Sadourny R, Satheesh SK, Shaw GE, Sheridan P, Valero FPJ (2001) Indian Ocean Experiment: an integrated analysis of the climate forcing and effects of the great IndoAsian haze. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D22):28371–28398
Ramanathan V, Chung C, Kim D, Bettge T, Buja L, Kiehl JT, Washington WM, Fu Q, Sikka DR, Wild M (2005) Atmospheric brown clouds: impacts on South Asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(15):5326–5333
Rolph G, Stein A, Stunder B (2017) Real-time environmental applications and display system: READY. Environ Model Softw 95:210–228
Sarangi C, Tripathi SN, Kanawade VP, Koren I, Pai DS (2017) Investigation of the aerosol–cloud–rainfall association over the Indian summer monsoon region. Atmos Chem Phys 17(8):5185–5204
Sarangi C, Kanawade VP, Tripathi SN, Thomas A, Ganguly D (2018) Aerosol-induced intensification of cooling effect of clouds during Indian summer monsoon. Nat Commun 9(1):1–9
Sarkar RP, Biswas BC, Khambete NN (1982) Probability analysis of short period rainfall in dry farming tract in India. Mausam 33(3):269–284
Sarkar S, Chokngamwong R, Cervone G, Singh RP, Kafatos M (2006) Variability of aerosol optical depth and aerosol forcing over India. Adv Space Res 37(12):2153–2159
Satheesh SK, Ramanathan V (2000) Large differences in tropical aerosol forcing at the top of the atmosphere and Earth’s surface. Nature 405(6782):60–63
Satheesh SK, Babu SS, Padmakumari B, Pandithurai G, Soni VK (2017) Variability of atmospheric aerosols over India. In observed climate variability and change over the Indian region. Springer, Singapore, pp 221–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2531-0_13
Scarnato BV, Vahidinia S, Richard DT, Kirchstetter TW (2013) Effects of internal mixing and aggregate morphology on optical properties of black carbon using a discrete dipole approximation model. Atmos Chem Phys 13:5089–5101
Schuster GL, Dubovik O, Holben BN (2006) Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J Geophys Res 111:D07207. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006328
Sharma D, Miller RL (2017) Revisiting the observed correlation between weekly averaged Indian monsoon precipitation and Arabian Sea aerosol optical depth. Geophys Res Lett 44:10006–10016. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL074373
Shrivastava S, Kar SC, Sahai AK, Sharma AR (2018) Identification of drought occurrences using ensemble predictions up to 20-days in advance. Water Resour Manage 32(6):2113–2130
Small JD, Jiang JH, Su H, Zhai C (2011) Relationship between aerosol and cloud fraction over Australia. Geophys Res Lett 38:L23802. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL049404
Solmon F, Nair VS, Mallet M (2015) Increasing Arabian dust activity and the Indian summer monsoon. Atmos Chem Phys 15(14):8051–8064
Song F, Zhou T, Qian Y (2014) Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to natural and anthropogenic forcings inthe 17 latest CMIP5 models. Geophys Res Lett 41(2):596–603
Stein AF, Draxler RR, Rolph GD, Stunder BJB, Cohen MD, Ngan F (2015) NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull Am Meteor Soc 96(12):2059–2077
Subash N, Mohan HR (2012) Evaluation of the impact of climatic trends and variability in rice–wheat system productivity using Cropping System Model DSSAT over the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Agric for Meteorol 15(164):71–81
Tang X, Chen B (2006) Cloud types associated with the Asian summer monsoons as determined from MODIS/TERRA measurements and a comparison with surface observations. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL026004
Thorn HCS (1966) Some methods of climatological analysis. WMO Technics/Note Number, (810), pp 16–22
Twomey S (1977) The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J Atmos Sci 34(7):1149–1152
Twomey SA, Piepgrass M, Wolfe TL (1984) An assessment of the impact of pollution on global cloud albedo. Tellus B 36(5):356–366
Vinoj V, Rasch PJ, Wang H, Yoon J-H, Ma P-L, Landu K, Singh B (2014) Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by West Asian dust. Nat Geosci 7(4):308–313
Vu TM, Mishra A (2016) Spatial and temporal variability of Standardized Precipitation Index over Indochina Peninsula. Cuadernos De Investigación Geográfica 42:221. https://doi.org/10.18172/cig.2928
Zhang H, Wang Z, Guo P, Wang Z (2009) A modeling study of the effects of direct radiative forcing due to carbonaceous aerosol on the climate in East Asia. Adv Atmos Sci 26(1):57–66
Zhang L, Liao H, Li J (2010) Impact of the Southeast Asian summer monsoon strength on the outflow of aerosols from South Asia. Ann Geophys 28(1):277
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Indian Meteorological Department, India, for gridded rainfall data as well as to Giovanni of NASA GES DISC, for providing datasets. “Analyses and visualizations used in this study were produced with the Giovanni online data system, developed and maintained by the NASA GES DISC”. Blue Marble Dataset (https://neo.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/view.php?datasetId=BlueMarbleNG-TB), GTOPO DEM dataset (http://clima-dods.ictp.it/regcm4/SURFACE/) and river shapefile data (https://datacatalog.worldbank.org/dataset/major-rivers-world) used in visualisation are well acknowledged. We are also thankful to the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments which significantly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
There is no funding support for the current research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PPS conceptualised the idea for this research, framed the experiments and lead authored the manuscript. SK acquired and extracted the data along with file and data handling tasks, and executed the experiments. AB contributed in plotting and visualisation of data and in manuscript. All authors contributed in modification of plots and the manuscript where deemed to be necessary.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors confirm that this research is original and has not been published in any journal (in whole or in part).
Consent for publication
All the authors have consented to publish this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parth Sarthi, P., Kumar, S. & Barat, A. A Linkage Between Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and Meteorological Drought over the Eastern Gangetic Plain of India. Aerosol Sci Eng 5, 440–450 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41810-021-00113-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41810-021-00113-6