Abstract
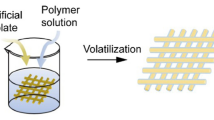
3D bioprinting provides an innovative strategy to fabricate a new composite scaffold material consisted in a porous and rough structure with using polycaprolactone (PCL), beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), and collagen as a building block for tissue engineering. We investigated the optimization of the scaffold properties based on the β-TCP concentration using 3D bioprinting method. Computer-aided drawing was applied in order to digitally design the scaffolds while instead of solid filaments, materials were prepared as a blend solution and controlled evaporation of the solvent during the bioprinting was enabled the proper solidification of the scaffolds, and they were successfully produced with well-defined porous structure. This work demonstrated the feasibility of complex PCL/β-TCP/collagen scaffolds as an alternative in the 3D bioprinting engineering to the fabrication of porous scaffolds for tissue engineering.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, S., Liu, X., Yeung, K.W.K., Liu, C.S., Yang, X.J.: Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 80, 1–36 (2014)
Karageorgiou, V., Kaplan, D.: Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 26(27), 5474–5491 (2005)
Murphy, S.V., Atala, A.: 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 773–785 (2014)
Groll, J., Boland, T., Blunk, T., Burdick, J.A., Cho, D.W., Dalton, P.D., Derby, B., Forgacs, G., Li, Q., Mironov, V.A.: Biofabrication: reappraising the definition of an evolving field. Biofabrication. 8(1), 013001 (2016)
Peltola, S.M., Melchels, F.P.W., Grijpma, D.W., Kellomaki, M.: A review of rapid prototyping techniques for tissue engineering purposes. Ann. Med. 40(4), 268–280 (2008)
Chong, E., Phan, T., Lim, I., Zhang, Y., Bay, B., Ramakrishna, S., Lim, C.: Evaluation of electrospun PCL/gelatin nanofibrous scaffold for wound healing and layered dermal reconstitution. Acta Biomater. 3(3), 321–330 (2007)
Gautam, S., Dinda, A.K., Mishra, N.C.: Fabrication and characterization of PCL/gelatin composite nanofibrous scaffold for tissue engineering applications by electrospinning method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 33(3), 1228–1235 (2013)
Woodruff, M.A., Hutmacher, D.W.: The return of a forgotten polymer—polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35(10), 1217–1256 (2010)
Holmes, R.E., Bucholz, R.W., Mooney, V.: Porous hydroxyapatite as a bone-graft substitute in metaphyseal defects. A histometric study. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 68(6), 904–911 (1986)
Mosmann, T.: Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 65(1–2), 55–63 (1983)
Lee, V.K., Dias, A., Ozturk, M.S., Chen, K., Tricomi, B., Corr, D.T., Intes, X., Dai, G.: 3D Bioprinting and 3D Imaging for Stem Cell Engineering, pp. 33–66. Springer International Publishing (2015)
Jang, D., Kim, D., Moon, J.: Influence of fluid physical properties on ink-jet printability. Langmuir. 25(5), 2629–2635 (2009)
Patlolla, A., Collins, G., Arinzeh, T.L.: Solvent-dependent properties of electrospun fibrous composites for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 6(1), 90–101 (2010)
Rosales-Leal, J.I., Rodríguez-Valverde, M.A., Mazzaglia, G., Ramón-Torregrosa, P.J., Rodriguez, L.D., Martinez, O.G., Vallecillo-Capilla, M., Ruiz, C., Cabrerizo-Vílchez, M.A.: Effects of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 365(1–3), 222–229 (2010)
Kim, J.Y., Yoon, J.J., Park, E.K., Kim, D.S., Kim, S.Y., Cho, D.W.: Cell adhesion and proliferation evaluation of SFF-based biodegradable scaffolds fabricated using a multi-head deposition system. Biofabrication. 1(1), 015002 (2009)
Davila, J.L., Freitas, M.S., Neto, P.I., Silveira, Z.C., Silva, J.V.L., d’Ávila, M.A.: Fabrication of PCL/β-TCP scaffolds by 3D mini-screw extrusion printing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 133, 43031 (2016)
Khan, S.N., Warkhedkar, R.M., Shyam, A.K.: Human bone strength evaluation through different mechanical tests. IJCET. 2, 2347–5161 (2014)
Havaldar, R., Pilli, S.C., Putti, B.B.: Insights into the effects of tensile and compressive loadings on human femur bone. Adv. Biomed. Res. 3, 101 (2014)
Aydogdu, M.O., Chou, J., Altun, E., Ekren, N., Cakmak, S., Eroglu, M., Osman, A.A., Kutlu, O., Oner, E.T., Avsar, G., Oktar, F.N., Yilmaz, I., Gunduz, O.: Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2018.1443930
Tavares, D.S., Castro, L.O., Soares, G.D.A., Alves, G.G., Granjeiro, J.M.: Synthesis and cytotoxicity evaluation of granular magnesium substituted β-tricalcium phosphate. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 21(1), 37–42 (2013)
Kim, B.S., Choi, J.S., Kim, J.D., Yoon, H.I., Choi, Y.C., Cho, Y.W.: Human collagen isolated from adipose tissue. Biotechnol. Prog. 28(4), 973–980 (2012)
Hutmacher, D. W., Schantz, T., Zein, I., Ng, K. W., Teoh, S. H., ; Tan, K.C Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 55 (2), 203–216. (2001)
Melchels, F.P.W., Tonnarelli, B., Olivares, A.L., Martin, I., Lacroix, D., Feijen, J., Wendt, D.J., Grijpm, D.W.: The influence of the scaffold design on the distribution of adhering cells after perfusion cell seeding. Biomaterials. 32, 2878–2884 (2011)
Funding
This study has been founded by BAPKO, Marmara University, grant no. FEN-C-YLP-090217-0066.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydogdu, M.O., Mutlu, B., Kurt, M. et al. Developments of 3D polycaprolactone/beta-tricalcium phosphate/collagen scaffolds for hard tissue engineering. J Aust Ceram Soc 55, 849–855 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-00299-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-00299-y