Abstract
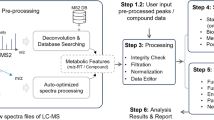
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) has enabled the detection of thousands of metabolite features from a single biological sample that produces large and complex datasets. One of the key issues in LC–MS-based metabolomics is comprehensive and accurate analysis of enormous amount of data. Many free data preprocessing tools, such as XCMS, MZmine, MAVEN, and MetaboAnalyst, as well as commercial software, have been developed to facilitate data processing. However, researchers are challenged by the inevitable and unconquerable yields of numerous false-positive peaks, and human errors while manually removing such false peaks. Even with continuous improvements of data processing tools, there can still be many mistakes generated during data preprocessing. In addition, many data preprocessing software exist, and every tool has its own advantages and disadvantages. Thereby, a researcher needs to judge what kind of software or tools to choose that most suit their vendor proprietary formats and goal of downstream analysis. Here, we provided a brief introduction of the general steps of raw MS data processing, and properties of automated data processing tools. Then, characteristics of mainly free data preprocessing software were summarized for researchers’ consideration in conducting metabolomics study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tian H, Lam SM, Shui G. Metabolomics, a powerful tool for agricultural research. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:E1871.
Shui G, Bendt AK, Jappar IA, Lim HM, Laneelle M, Hervé M, Via LE, Chua GH, Bratschi MW, Zainul Rahim SZ, Michelle AL, Hwang SH, Lee JS, Eum SY, Kwak HK, Daffé M, Dartois V, Michel G, Barry CE 3rd, Wenk MR. Mycolic acids as diagnostic markers for tuberculosis case detection in humans and drug efficacy in mice. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4:27.
Chua EC, Shui G, Lee IT, Lau P, Tan LC, Yeo SC, Lam BD, Bulchand S, Summers SA, Puvanendran K, Rozen SG, Wenk MR, Gooley JJ. Extensive diversity in circadian regulation of plasma lipids and evidence for different circadian metabolic phenotypes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:14468.
Nguyen LN, Ma D, Shui G, Wong P, Cazenave-Gassiot A, Zhang X, Wenk MR, Goh EL, Silver DL. Mfsd2a is a transporter for the essential omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid. Nature. 2014;509:503.
Jang C, Oh SF, Wada S, Rowe GC, Liu L, Chan MC, Rhee J, Hoshino A, Kim B, Ibrahim A, Baca LG, Kim E, Ghosh CC, Parikh SM, Jiang A, Chu Q, Forman DE, Lecker SH, Krishnaiah S, Rabinowitz JD, Weljie AM, Baur JA, Kasper DL, Arany Z. A branched-chain amino acid metabolite drives vascular fatty acid transport and causes insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2016;22:421.
Ouyang Q, Nakayama T, Baytas O, Davidson SM, Yang C, Schmidt M, Lizarraga SB, Mishra S, Ei-Quessny M, Niaz S, Gul Butt M, Imran Murtaza S, Javed A, Chaudhry HR, Vaughan DJ, Hill RS, Partlow JN, Yoo SY, Lam AT, Nasir R, Al-Saffar M, Barkovich AJ, Schwede M, Nagpal S, Rajab A, DeBerardinis RJ, Housman DE, Mochida GH, Morrow EM. Mutations in mitochondrial enzyme GPT2 cause metabolic dysfunction and neurological disease with developmental and progressive features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E5598.
Siskos AP, Jain P, Römisch-Margl W, Bennett M, Achaintre D, Asad Y, Marney L, Richardson L, Koulman A, Griffin JL, Raynaud F, Scalbert A, Adamski J, Prehn C, Keun HC. Interlaboratory reproducibility of a targeted metabolomics platform for analysis of human serum and plasma. Anal Chem. 2017;89:656.
Zamboni N, Saghatelian A, Patti GJ. Defining the metabolome: size, flux, and regulation. Mol Cell. 2015;58:699.
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J, Benton HP, Siuzdak G. Bioinformatics: the next frontier of metabolomics. Anal Chem. 2015;87:147.
Lam SM, Tong L, Duan X, Petznick A, Wenk MR, Shui G. Extensive characterization of human tear fluid collected using different techniques unravels the presence of novel lipid amphiphiles. J Lipid Res. 2014;55:289.
Lam SM, Wang Y, Duan X, Wenk MR, Kalaria RN, Chen CP, Lai MK, Shui G. Brain lipidomes of subcortical ischemic vascular dementia and mixed dementia. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35:2369.
Zhu ZJ, Schultz AW, Wang J, Johnson CH, Yannone SM, Patti GJ, Siuzdak G. Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by the METLIN database. Nat Protoc. 2013;8:451.
Lam SM, Chua GH, Li XJ, Su B, Shui G. Biological relevance of fatty acyl heterogeneity to the neural membrane dynamics of rhesus macaques during normative aging. Oncotarget. 2016;7:55970.
Lam SM, Wang Z, Li J, Huang X, Shui G. Sequestration of polyunsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids of Caenorhabditis elegans dauer larva attenuates eicosanoid biosynthesis for prolonged survival. Redox Biol. 2017;12:967.
Watrous JD, Henglin M, Claggett B, Lehmann KA, Larson MG, Cheng S, Jain M. Visualization, quantification, and alignment of spectral drift in population scale untargeted metabolomics data. Anal Chem. 2017;89:1399.
Melamud E, Vastag L, Rabinowitz JD. Metabolomic analysis and visualization engine for LC–MS data. Anal Chem. 2010;82:9818.
Wei X, Shi X, Kim S, Zhang L, Patrick JS, Binkley J, McClain C, Zhang X. Data preprocessing method for liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry based metabolomics. Anal Chem. 2012;84:7963.
Guan XL, He X, Ong WY, Yeo WK, Shui G, Wenk MR. Unbiased global profiling of lipids during kainite induced neuronal injury. FASEB J. 2006;20:1152.
Shui G, Bendt AK, Pethe K, Dick T, Wenk MR. Sensitive profiling of chemically diverse bioactive lipids. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:1976.
Hastings CA, Norton SM, Roy S. New algorithms for processing and peak detection in liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002;16:462.
Danielsson R, Bylund D, Markides KE. Matched filtering with background suppression for improved quality of base peak chromatograms and mass spectra in liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2002;454:167.
Johnson KJ, Wright BW, Jarman KH, Synovec RE. High-speed peak matching algorithm for retention time alignment of gas chromatographic data for chemometric analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2003;996:141.
Frenzel T, Miller A, Engel KH. A methodology for automated comparative analysis of metabolite profiling data. Eur Food Res Technol. 2003;216:335.
Lommen A. MetAlign: interface-driven, versatile metabolomics tool for hyphenated full-scan mass spectrometry data preprocessing. Anal Chem. 2009;81:3079.
Lommen A, Kools HJ. MetAlign 3.0: performance enhancement by efficient use of advances in computer hardware. Metabolomics. 2012;8:719.
Katajamaa M, Miettinen J, Oresic M. MZmine: toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:634.
Pluskal T, Castillo S, Villar-Briones A, Oresic M. MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010;11:395.
Xia J, Wishart DS. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat Protoc. 2011;6:743.
Xia J, Sinelnikov IV, Han B, Wishart DS. MetaboAnalyst 3.0—making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:W251.
Hoekman B, Breitling R, Suits F, Bischoff R, Horvatovich P. msCompare: a framework for quantitative analysis of label-free LC–MS data for comparative candidate biomarker studies. Mol Cell Proteom. 2012;11(M111):015974.
Zhang W, Chang J, Lei Z, Huhman D, Sumner LW, Zhao PX. MET-COFEA: a liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data processing platform for metabolite compound feature extraction and annotation. Anal Chem. 2014;86:6245.
Zhang W, Lei Z, Huhman D, Sumner LW, Zhao PX. MET-XAlign: a metabolite cross-alignment tool for LC/MS-based comparative metabolomics. Anal Chem. 2015;87:9114.
Smith CA, Want EJ, O’Maille G, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G. XCMS: processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal Chem. 2006;78:779.
Patti GJ, Tautenhahn R, Rinehart D, Cho K, Shriver LP, Manchester M, Nikolskiy I, Johnson CH, Mahieu NG, Siuzdak G. A view from above: cloud plots to visualize global metabolomic data. Anal Chem. 2013;85:798.
Liang YJ, Lin YT, Chen CW, Lin CW, Chao KM, Pan WH, Yang HC. SMART: statistical metabolomics analysis—an R Tool. Anal Chem. 2016;88:6334.
Zhou Z, Xiong X, Zhu ZJ. MetCCS Predictor: a web server for predicting collision cross-section values of metabolites in ion mobility-mass spectrometry based metabolomics. Bioinformatics. 2017;. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btx140.
Lam SM, Tian H, Shui G. Lipidomics, en route to accurate quantitation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1862:752.
Song X, Luo Z, Li X, Li T, Wang Z, Sun C, Huang L, Xie P, Liu X, He J, Abliz Z. In situ hydrogel conditioning of tissue samples to enhance the drug’s sensitivity in ambient mass spectrometry imaging. Anal Chem. 2017;89:6318.
Benton HP, Wong DM, Trauger SA, Siuzdak G. XCMS2: processing tandem mass spectrometry data for metabolite identification and structural characterization. Anal Chem. 2008;80:6382.
Tian H, Wang W, Zheng N, Cheng J, Li S, Zhang Y, Wang J. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers and metabolic pathway shifts of heat-stressed lactating dairy cows. J Proteom. 2015;125:17.
Griffiths WJ, Koal T, Wang Y, Kohl M, Enot DP, Deigner HP. Targeted metabolomics for biomarker discovery. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:5426.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371515, 31671226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Li, B. & Shui, G. Untargeted LC–MS Data Preprocessing in Metabolomics. J. Anal. Test. 1, 187–192 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-017-0030-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-017-0030-8