Abstract
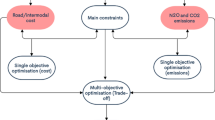
The operation of wastewater treatment facilities results in the direct emissions of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) from biological activities, which contributes to global warming. One of the objectives of this research is to investigate the issue of reducing greenhouse gas emissions during the effluent treatment process of the papermaking processes. It is also the goal of this research to minimise the cost of road and intermodal freight transportation and the greenhouse gas emissions associated with transportation. The real-world data is collected from one of Pakistan’s largest paper and board industries. Mixed integer linear programming has been used to formulate the multi-objective problem of minimising cost and greenhouse gas emissions. Using a genetic algorithm, the problem is addressed, and Pareto optimality solutions are presented to assist decision-makers in selecting the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly solutions. Intermodal freight transportation is found to be 81.1% less expensive than road, and it is also 51.1% more environmentally friendly. According to the findings of the effluent treatment study, during the manufacturing of 240,000 tons of paper and board and 210 million corrugated boxes, 3.31 tons of CO2e is emitted into the atmosphere during the water treatment process. However, looking into the emissions produced by different paper manufacturing processes, such as pulping, coating and printing, could help to understand the effect of manufacturing on global warming.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
geography LC-J of transport (2007) 2007 undefined, Chapman L. Transport and Climate Change: a Review 15:354–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2006.11.008
Kelle P, Song J, Jin M et al (2019) Evaluation of operational and environmental sustainability tradeoffs in multimodal freight transportation planning. Int J Prod Econ 209:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.08.011
Kordnejad B (2014) Intermodal transport cost model and intermodal distribution in urban freight. Procedia - Soc Behav Sci 125:358–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.1480
Liu M, Tan S, Zhang M et al (2020) Waste paper recycling decision system based on material flow analysis and life cycle assessment: a case study of waste paper recycling from China. J Environ Manage 255:109859. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2019.109859
Meng Q, Wang X (2011) Intermodal hub-and-spoke network design: incorporating multiple stakeholders and multi-type containers. Transp Res Part B Methodol 45:724–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trb.2010.11.002
Mostert M, Limbourg S (2016) External costs as competitiveness factors for freight transport — a state of the art. Routledge
Nakamura H (2000) The economic evaluation of transport infrastructure: needs for international comparisons. Transp Policy 7:3–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-070X(00)00008-1
Resat HG, Turkay M (2015) Design and operation of intermodal transportation network in the Marmara region of Turkey. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 83:16–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2015.08.006
Resat HG, Turkay M (2019) A bi-objective model for design and analysis of sustainable intermodal transportation systems: a case study of Turkey. Int J Prod Res 57:6146–6161. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1587187
Salam MA (2005) Noguchi T (2005) Impact of human activities on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions: a statistical analysis. Environ 251(25):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10669-005-3093-4
Shoukat R (2021) Modelling and analysis of intermodal freight cost and CO2emissions: application of mixed-integer linear programming and genetic algorithm. World Rev Intermodal Transp Res 10:378–399. https://doi.org/10.1504/WRITR.2021.119532
Vanelslander T, Sys C, Lam JSL et al (2019) A serving innovation typology: mapping port-related innovations. Transp Rev 39:611–629. https://doi.org/10.1080/01441647.2019.1587794
Wijeweera A, To H, Charles M (2014) An empirical analysis of Australian freight rail demand. Econ Anal Policy 44:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2014.01.001
Zhang Y, Yan Y, Hu Z (2013) Optimization model and particle swarm optimization algorithm of operation plan for scheduled freight train. Inf Technol J 12:1539–1546. https://doi.org/10.3923/itj.2013.1539.1546
Frémont A, geography PF-J of transport, 2010 undefined (2010) Hinterland transportation in Europe: combined transport versus road transport. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2010.03.009ï
Monfared MS, Monabbati SE, Kafshgar AR (2021) Pareto-optimal equilibrium points in non-cooperative multi-objective optimization problems. Expert Syst Appl 178:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114995
Pinto JT de M, Mistage O, Bilotta P, Helmers E (2018) Road-rail intermodal freight transport as a strategy for climate change mitigation. Environ Dev 25:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVDEV.2017.07.005
Chesbrough HW, Appleyard MM (2007) Open innovation and strategy. Calif. Manage. Rev. 50
Commission PP, Planning C (2014) Pakistan vision 2025
DBEIS (2021) Government conversion factors for company reporting of greenhouse gas emissions. https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/government-conversion-factors-for-company-reporting
European Commission (2011) Roadmap to a single European transport area
Giuliano G, Knatz G, Hudson N, et al (2016) Decison-making for maritime innovation investments: the significance of cost benefit and cost effectiveness analysis. Work Pap
Government of Pakistan (2020) Economic survey. Economic Advisor’s Wing, Ministry of Finance, Islamabad
Habib-ur-Rehman (2009) Pakistan Economic Survey
Heinold A, Meisel F (2020) Emission limits and emission allocation schemes in intermodal freight transportation. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 141:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2020.101963
Holland J (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence
Miettinen K (1998) Nonlinear multiobjective optimization. 12:. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5563-6
Mof (2015) Transport and communications. Pakistan Econ Surv
Shen S, Fowkes T, Whiteing T, et al (2009) Econometric modelling and forecasting of freight transport demand in Great Britain. In: In Proceedings of European Transport Conference. pp 1–21
Türkay M (2014) Environmentally conscious supply chain management. In: Process Systems Engineering. pp 87–105
Winebrake J, Corbett J, Hawker J, Korfmacher K (2008) Intermodal freight transport in the great lakes: development and application of a great lakes geographic intermodal freight transport model. Final Report. , NY, Gt Lakes 1–31
World Bank (2021) Pakistan Carbon (CO2) Emissions 1960–2019 | MacroTrends. https://www.macrotrends.net/countries/PAK/pakistan/carbon-co2-emissions. Accessed 18 Sep 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shoukat, R. Green Intermodal Transportation and Effluent Treatment Systems: Application of the Genetic Algorithm and Mixed Integer Linear Programming. Process Integr Optim Sustain 7, 329–341 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-022-00295-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-022-00295-7