Abstract
Laboratory dusty plasma typically refers to a collection of micron-sized solid dust particles immersed in the plasma environment, as a result, these dust particles are negatively charged to thousands of elementary charges. Due to the electrical shielding provided by free electrons and ions, the interaction between these dust particles can be modeled as the Yukawa potential. These dust particles are strongly coupled due to their high charges, so that they exhibit collective behaviors of solids and liquids. Magnetic fields are often experimentally introduced in the modulation of dusty plasmas, and later the equivalent “magnetized” dusty plasma experiment is performed, so that magnetized Yukawa systems can be experimentally achieved now. Here, we review a series of results of collective behaviors and different transport processes of magnetized two-dimensional (2D) Yukawa liquids from Langevin dynamical simulations. From the obtained spectra of the simulation results, the vibrational density of states has only one dominant peak frequency, which can be analytically expressed as a function of the cyclotron and plasma frequencies, suggesting that the cyclotron motion of dust particles has been coupled with their thermal motion. It is also found that the statistics of particle motion with a strong magnetic field tend to deviate from the classical Maxwellian distribution. When the ratio of the cyclotron and plasma frequencies for dust particles is around the order of unity, the motion of dust particles tends to be superdiffusive. As the magnetic field increases, the shear viscosity increases with the magnetic field when the Yukawa liquid is cold; however, when the Yukawa liquid is hot, the variation trend of shear viscosity is reversed. It is also found that the structural relaxation time and the diffusion coefficient can be described as a power law relationship with two distinct values of the exponent at low and high temperatures, respectively.

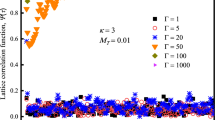
Reprinted from Feng et al. (2014)

Reprinted from Feng et al. (2014)

Reprinted from Feng et al. (2014)

Reprinted from Feng et al. (2014)

Reprinted from Wang et al. (2018)

Reprinted from Wang et al. (2018)

Reprinted from Wang et al. (2018)

Reprinted from Feng et al. (2017)

Reprinted from Feng et al. (2017)

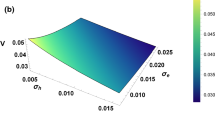
Reprinted from Lu et al. (2019)

Reprinted from Lu et al. (2019)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bonitz, Z. Donkó, T. Ott, H. Kählert, P. Hartmann, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 055002 (2010)
M. Bonitz, C. Henning, D. Block, Rep. Prog. Phys. 73, 066501 (2010)
D. Darian, W.J. Miloch, M. Mortensen, Y. Miyake, H. Usui, Phys. Plasmas 26, 043701 (2019)
Z. Donkó, G.J. Kalman, K.I. Golden, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 225001 (2002)
Z. Donkó, J. Goree, P. Hartmann, B. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 026401 (2009)
A. Einstein, Investigations on the Theory of the Brownian Movement (Dover, New York, 1956)
Y. Feng, J. Goree, B. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 205007 (2008)
Y. Feng, J. Goree, B. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 025002 (2010)
Y. Feng, J. Goree, B. Liu, Phys. Rev. E 82, 036403 (2010)
Y. Feng, J. Goree, B. Liu, E.G.D. Cohen, Phys. Rev. E 84, 046412 (2011)
Y. Feng, J. Goree, B. Liu, T. Intrator, M. Murillo, Phys. Rev. E 90, 013105 (2014)
Y. Feng, W. Lin, M.S. Murillo, Phys. Rev. E 96, 053208 (2017)
V.E. Fortov, A.V. Ivlev, S.A. Khrapak, A.G. Khrapak, G.E. Morfill, Phys. Rep. 421, 1 (2005)
S. Gonçalves, H. Bonadeo, Phys. Rev. B 46, 12019 (1992)
P. Hartmann, Z. Donkó, T. Ott, H. Kählert, M. Bonitz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 155002 (2013)
P. Hartmann, J. Reyes, E. Kostadinova, L. Matthews, T. Hyde, R. Masheyeva, K. Dzhumagulova, T. Ramazanov, T. Ott, H. Kählert, M. Bonitz, I. Korolov, Z. Donkó, Phys. Rev. E 99, 013203 (2019)
L.-J. Hou, P.K. Shukla, A. Piel, Z.L. Mišković, Phys. Plasmas 16, 073704 (2009)
H. Kählert, J. Carstensen, M. Bonitz, H. Löwen, F. Greiner, A. Piel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 155003 (2012)
G. Kalman, P. Hartmann, Z. Donkó, M. Rosenberg, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 065001 (2004)
S.A. Khrapak, G.E. Morfill, V.E. Fortov, L.G. D’yachkov, A.G. Khrapak, O.F. Petrov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 055003 (2007)
U. Konopka, G.E. Morfill, L. Ratke, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 891 (2000)
T.K. Langin, T. Strickler, N. Maksimovic, P. McQuillen, T. Pohl, D. Vrinceanu, T.C. Killian, Phys. Rev. E 93, 023201 (2016)
I. Lin, W.-T. Juan, C.H. Chiang, J.H. Chu, Science 272, 1626 (1996)
B. Liu, J. Goree, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 185002 (2005)
B. Liu, J. Goree, Phys. Rev. E 75, 016405 (2007)
B. Liu, J. Goree, Y. Feng, Phys. Rev. E 78, 046403 (2008)
S. Lu, K. Wang, Y. Feng, Phys. Plasmas 26, 053704 (2019)
A. Melzer, A. Homann, A. Piel, Phys. Rev. E 53, 2757 (1996)
R. Merlino, J. Goree, Phys. Today 57(7), 32 (2004)
G.E. Morfill, A.V. Ivlev, Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1353 (2009)
B.R.A. Nijboer, A. Rahman, Physica (Amsterdam) 32, 415 (1966)
T. Ott, H. Löwen, M. Bonitz, Phys. Rev. E 89, 013105 (2014)
A. Piel, Plasma Physics (Springer, Heidelberg, 2010)
A. Rahman, Phys. Rev. 136, A405 (1964)
T. Reichstein, J. Wilms, F. Greiner, A. Piel, A. Melzer, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 52, 813 (2012)
P. Schmidt, G. Zwicknagel, P.-G. Reinhard, C. Toepffer, Phys. Rev. E 56, 7310 (1997)
M. Schwabe, U. Konopka, P. Bandyopadhyay, G.E. Morfill, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 215004 (2011)
P.K. Shukla, A.A. Mamun, Introduction to Dusty Plasma Physics (Institute of Physics, Bristol, 2002)
A.M. Teweldeberhan, J.L. Dubois, S.A. Bonev, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 235503 (2010)
E. Thomas Jr., J.D. Williams, J. Sliver, Phys. Plasmas 11, L37 (2004)
E. Thomas Jr., R.L. Merlino, M. Rosenberg, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 54, 124034 (2012)
W. van Megen, T.C. Mortensen, S.R. Williams, J. Müller, Phys. Rev. E 58, 6073 (1998)
Q. Wang, K. Wang, Y. Feng, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 58, 269 (2018)
K. Wang, D. Huang, Y. Feng, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51, 245201 (2018)
H. Yukawa, Proc. Phys. Math. Soc. Jpn. 17, 48 (1935)
Acknowledgements
Work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 11875199, 11505124, the 1000 Youth Talents Plan, startup funds from Soochow University, and the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, K. et al. Dynamics and transport of magnetized two-dimensional Yukawa liquids. Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 3, 10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41614-019-0032-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41614-019-0032-2