Abstract
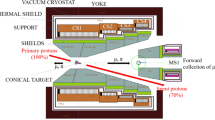
A novel surface muon capture system with a large acceptance was proposed based on the China spallation neutron source (CSNS). This system was designed using a superconducting solenoid where a long graphite target was put inside it. Firstly, the spin polarization evolution was studied in a constant uniform magnetic field. As the magnetic field can interact with the spin of the surface muon, both the spin polarization and production rate of the surface muons collected by the new capture system were calculated by the G4beamline. Simulation results showed that the surface muons could still keep a high spin polarization (>90%) with different magnetic fields (0–10 T), and the larger magnetic field is, the more surface muons can be captured. Finally, the proton phase space, Courant–Snyder parameters, and intensities of surface muons of different beam fractions were given with magnetic fields of 0 and 5 T. The solenoid capture system can focus proton and surface muon beams and collect \(\pi ^{\pm }\) and \(\mu ^{\pm }\) particles. It can also provide an intense energetic positron source.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Yaouanc, P.D. De Réotier, Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation, and Resonance: Applications to Condensed Matter (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2011)
K.M. Kojima, Advantage of musr over to other experimental techniques- Expectations to the unified facility. KEK PROCEEDINGS. High Energy Accelerator Organization 2001, 142–149 (1999)
K. Nagamine, Introductory Muon Science (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2003)
S.Q. Yang, M.A. Green, G. Barr et al., The mechanical and thermal design for the mice focusing solenoid magnet system. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 15(2), 1259–1262 (2005). doi:10.1109/TASC.2005.849556
M. Yoshida, Y. Yang, T. Ogitsu et al., Status of superconducting solenoid system for comet phase-I experiment at J-PARC. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 25(3), 1–4 (2015). doi:10.1109/TASC.2014.2382534
S. Mihara, MEG experiment at the paul scherrer institute. Nucl. Phys. A 844(1), 150c–154c (2010). doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2010.05.026
H. Miyadera, K. Nagamine, K. Shimomura et al., Design, construction and performance of dai omega, a large solid-angle axial-focusing superconducting surface-muon channel. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 569(3), 713–726 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.09.087
T. Prokscha, E. Morenzoni, K. Deiters et al., The new \(\mu \)e4 beam at psi: a hybrid-type large acceptance channel for the generation of a high-intensity surface-muon beam. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 595, 317–331 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2008.07.081
M. Yoshida, M. Fukuda, K. Hatanaka et al., Superconducting solenoid magnets for the music project. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 21(3), 1752–1755 (2011). doi:10.1109/TASC.2010.2088360
Y. Hino, K. Hatanaka, M. Lancaster et al., A new intense dc muon beam from a pion capture solenoid, MUSIC, in 36th International Conference on High Energy Physics (2012)
S. Cook, R. D’Arcy, M. Fukuda et al., First measurements of muon production rate using a novel pion capture system at MUSIC. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 408, 012079 (2013). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/408/1/012079
R. Xiao, Y.F. Liu, W.Z. Xu et al., A new muon-pion collection and transport system design using superconducting solenoids based on CSNS. Chin. Phys. C 40(5), 057004 (2016). doi:10.1088/1674-1137
R. Xiao, Y.F. Liu, W.Z. Xu et al., Study on a new large solid angle capture system for surface muon using superconducting solenoids. Nucl. Phys. Rev. 31(4), 468–474 (2014)
J. Wei, S.N. Fu, J.Y. Tang et al., China spallation neutron source-an overview of application prospects. Chin. Phys. C 33(11), 1033 (2009). doi:10.1088/1674-1137
J. Wei, H.S. Chen, Y.W. Chen et al., China spallation neutron source: design, R&D, and outlook. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 600(1), 10–13 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2008.11.017
S.N. Fu, H.S. Chen, Y.W. Chen et al., Status and challenges of the china spallation neutron source. IPAC 11, 889 (2011)
S. Agostinelli, J. Allison, K. Amako et al., Geant4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 506(3), 250–303 (2003). doi:10.12691/bb-2-4-3
J. Allison, K. Amako, J. Apostolakis et al., Geant4 developments and applications. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53(1), 270–278 (2006). doi:10.1109/TNS.2006.869826
T.J. Roberts, G4beamline-a” swiss army knife” for geant4, optimized for simulating beamline (2013)
T.J. Roberts et al., G4beamline code development (2012)
P.D. de Reotier, A. Yaouanc, Muon spin rotation and relaxation in magnetic materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 9(43), 9113 (1997). doi:10.1088/0953-8984/9/43/002
C. Yoshikawa, C. Ankenbrandt, R.P. Johnson et al., Complete muon cooling channel design and simulations. IPAC13, TUPFI060 (2013)
M. Chung, M.G. Collura, G. Flanagan et al., Pressurized h 2 rf cavities in ionizing beams and magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(18), 184802 (2013). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.184802
A. Ribon, J. Apostolakis, A. Dotti et al., Transition between hadronic models in geant4, in Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record (NSS/MIC) (IEEE, 2009), pp. 526–529. doi:10.1109/NSSMIC.2009.5401645
J.Y. Tang, G.H. Wei, C. Zhang et al., Beam preparation for the injection into CSNS RCS. in Proc. of HB2008 (2008)
H.T. Jing, C. Meng, J.Y. Tang et al., Production target and muon collection studies for an experimental muon source at CSNS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 684, 109–116 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2012.05.045
A. Bungau, R. Cywinski, C. Bungau et al., Simulations of surface muon production in graphite targets. Phys. Rev. ST-AB 16(1), 014701 (2013). doi:10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.16.014701
R. Abela, C. Baines, X. Donath et al., The \(\mu \)SR facilities at PSI. Hyperfine Interact. 87(1), 1105–1110 (1994). doi:10.1007/BF02068511
Y. Ikeda, J-parc status update. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 600(1), 1–4 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2008.11.019
M. Chung, H. Qin, R.C. Davidson, Twiss parameters and beam matrix formulation of generalized courant-snyder theory for coupled transverse beam dynamics. Phys. Plasma 17(8), 084502, 2010 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.3474930
Z.Q. Tan, W.Z. Xu, Y.F. Liu et al., A novel source of mev positron bunches driven by energetic protons for PAS application. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 763, 184–189 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2014.05.054
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Thomas Prokscha at Paul Scherrer Institute (Switzerland), Jing-Yu Tang at the Institute of High Energy Physics, and Yasuhiro Miyake at J-PARC (Japan) for their useful discussions about the muon spin polarization calculation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11527811).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, R., Liu, YF., Ni, XJ. et al. Spin polarization and production rate studies of surface muons in a novel solenoid capture system based on CSNS. NUCL SCI TECH 28, 109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0261-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0261-4