Abstract
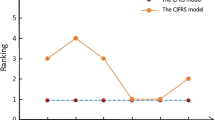
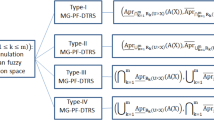
Since the classical Pawlak rough sets model only divides the domain by a single equivalence relation when dealing with uncertain information and ignores the influence of noisy data. In response to this problem, in this paper, we combine covering theory and intuitionistic fuzzy sets theory to propose variable precision multi-granulation covering rough intuitionistic fuzzy set (VPMCIFS) models. First, we construct eight different types of VPMCIFS models based on the minimum description and maximum description by setting two constraints (α, β) in variable precision and introducing them into the multi-granulation covering rough intuitionistic fuzzy set (MCIFS) models. Moreover, we discuss the properties of these models, respectively, and analyze the relationship between the proposed models and existing models. Second, based on these models, we define the approximate accuracy of the VPMCIFS models based on the minimum description and maximum description, respectively. Finally, the validity of these models was verified by the case study of dermatosis patients, and these models were analyzed and compared. By changing the values of α and β, the lower and upper approximations and approximate accuracy of each model are obtained, and the effects of different constraints on the models are analyzed and discussed. The model analyzes the problem from multiple angles and has a certain fault tolerance ability, which can effectively deal with the impact of error and noise data.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this paper as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Akram M, Adeel A (2020) Novel hybrid decision-making methods based on mF rough information. Granul Comput 5(2):185–201
Akram M, Ali G (2021) Group decision-making approach under multi (Q, N)-soft multi granulation rough model. Granul Comput 6(2):339–357
Akram M, Luqman A (2020) Granulation of ecological networks under fuzzy soft environment. Soft Comput 24(16):11867–11892
Akram M, Luqman A, Al-Kenani AN (2020) Certain models of granular computing based on rough fuzzy approximations. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 39(3):2797–2816
Akram M, Al-Kenani AN, Luqman A (2021) Degree based models of granular computing under fuzzy indiscernibility relations. Math Biosci Eng 18(6):8415–8443
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Atef M, Azzam AA (2021) Covering fuzzy rough sets via variable precision. J Math. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5525766
Barman B, Patra S (2020) Variable precision rough set based un supervised band selection technique for hyperspectral image classification. Knowl-Based Syst 193:105414
Benouini R, Batioua I, Ezghari S, Zenkouar K, Zahi A (2020) Fast feature selection algorithm for neighborhood rough set model based on Bucket and Trie structures. Granul Comput 5(3):329–347
Bonikowski Z, Wybraniec-Skardowska BE, U, (1998) Extensions and intentions in the rough set theory. Inf Sci 107(1–4):149–167
Buffett S (2021) Discretized sequential pattern mining for behaviour classification. Granul Comput 6(4):853–866
Chen YY, Chen YM (2021) Feature subset selection based on variable precision neighborhood rough sets. Int J Comput Int Syst 14(1):572–581
Chen P, Lin M, Liu J (2020) Multi-label attribute reduction based on variable precision fuzzy neighborhood rough set. IEEE Access 8:133565–133576
Han SE (2019) Roughness measures of locally finite covering rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 105:368–385
Huang YY, Li TR, Fujita LC, H, Horng SJ, (2017) Dynamic variable precision rough set approach for probabilistic set-valued information systems. Knowl-Based Syst 122:131–147
Iancu I (2014) Intuitionistic fuzzy similarity measures based on Frank t-norms family. Pattern Recogn Lett 42:128–136
Jiang HB, Zhan JM, Sun BZ, Alcantud JCR (2020) An MADM approach to covering-based variable precision fuzzy rough sets: an application to medical diagnosis. Int J Mach Learn Cyb 11(9):2181–2207
Jiang HB, Zhan JM, Chen DG (2021a) Covering-based variable precision L-fuzzy rough sets based on residuated lattices and corresponding applications. Int J Mach Learn Cyb 12(8):2407–2429
Jiang HB, Zhan JM, Chen DG (2021b) PROMETHEE II method based on variable precision fuzzy rough sets with fuzzy neighborhoods. Artif Intell Rev 54(2):1281–1319
Kong Q, Zhang X, Xu W (2019) Operation properties and algebraic properties of multi-covering rough sets. Granul Comput 4(3):377–390
Li WK, Li JJ, Huang JX, Dai WZ, Zhang XP (2021) A new rough set model based on multi-scale covering. Int J Mach Learn Cyb 12(1):243–256
Liang MS, Mi JS, Feng T (2019) Optimal granulation selection for multi-label data based on multi-granulation rough sets. Granul Comput 4(3):323–335
Liu KY, Yang XB, Fujita H, Liu D, Qian YX, YH, (2019) An efficient selector for multi-granulation attribute reduction. Inf Sci 505:457–472
Luqman A, Akram M, Koam ANA (2019) Granulation of hypernetwork models under the q-rung picture fuzzy environment. Mathematics 7(6):496
Ma JM, Zhang HY, Qian YH (2019) Three-way decisions with reflexive probabilistic rough fuzzy sets. Granul Comput 4(3):363–375
Mandal P, Ranadive AS (2019a) Multi-granulation fuzzy decision-theoretic rough sets and bipolar-valued fuzzy decision-theoretic rough sets and their applications. Granul Comput 4(3):483–509
Mandal P, Ranadive AS (2019b) Multi-granulation interval-valued fuzzy probabilistic rough sets and their corresponding three-way decisions based on interval-valued fuzzy preference relations. Granul Comput 4(1):89–108
Niu XL, Sun ZD, Kong XZ (2022) A new type of dyad fuzzy β-covering rough set models base on fuzzy information system and its practical application. Int J Approx Reason 142:13–30
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Qian YH, Liang JY, Dang CY (2010a) Incomplete multi-granulation rough set. IEEE T Syst Man Cyber Syst Hum 40(2):420–431
Qian YH, Liang JY, Yao YY, Dang CY (2010b) MGRS: a multi-granulation rough set. Inf Sci 180(6):949–970
Qian YH, Zhang H, Liang JY, Sang YL (2014) Multi-granulation decision-theoretic rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 55(1):225–237
Qian WB, Huang JT, Wang YL, Xie YH (2021) Label distribution feature selection for multi-label classification with rough set. Int J Approx Reason 128:32–55
Shi D, Zhang X (2019) Probabilistic decision making based on rough sets in interval-valued fuzzy information systems. Granul Comput 4(3):391–405
Song M, Hu L, Feng S, Wang YB et al (2022) Feature ranking based on an improved granular neural network. Granul Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-022-00324-3
Sun BZ, Ma WM, Chen XT (2019) Variable precision multi-granulation rough fuzzy set approach to multiple attribute group decision-making based on λ-similarity relation. Comput Ind Eng 127:326–343
Wang CY, Wan LJ (2021) New results on granular variable preci sion fuzzy rough sets based on fuzzy (co) implications. Fuzzy Sets and Syst 423:149–169
Wang ZH, Shu L, Ding XY (2013) Minimum description and max- imal description in covering-based rough sets. Fund Inf 128(4):503–526
Wang ZH, Wang H, Feng QR (2019) The structures and the con- nections on four types of covering rough sets. Soft Comput 23(16):6727–6741
Wang GQ, Li TR, Zhang PF, Huang QQ, Chen HM (2021) Double-local rough sets for efficient data mining. Inf Sci 571:475–498
Xue ZA, Si XM, Xue TY, Xin XW, Yuan YL (2017) Multi-granulation covering rough intuitionistic fuzzy sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(1):899–911
Xue ZA, Zhao LP, Sun L, Zhang M, Xue TY (2020) Three-way decision models based on multi-granulation support intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 124:147–172
Yang L, Zhang XY, Xu WH, Sang BB (2019) Multi-granulation rough sets and uncertainty measurement for multi-source fuzzy information system. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(6):1919–1937
Yang J, Zhou W, Li S (2021) Similarity measure for multi-granulation rough approximations of vague sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 40(1):1609–1621
Yao YY, Yao BX (2012) Covering based rough set approximations. Inf Sci 200:91–107
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zafar F, Akram M (2018) A novel decision-making method based on rough fuzzy information. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20(3):1000–1014
Zhan JM, Sun BZ (2020) Covering-based intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets and applications in multi-attribute decision-making. Artif Intell Rev 53(1):671–701
Zhan JM, Masood Malik H, Akram M (2019) Novel decision-making algorithms based on intuitionistic fuzzy rough environment. Int J Mach Learn Cyb 10(6):1459–1485
Zhan JM, Zhang XH, Yao YY (2020) Covering based multi-granulation fuzzy rough sets and corresponding applications. Artif Intell Rev 53(2):1093–1126
Zhang L, Zhu P (2022) Generalized fuzzy variable precision rough sets based on bisimulations and the corresponding decision-making. Int J Mach Learn Cyb 2022:1–32
Zhang RL, Xiong SW, Chen Z (2016) Construction method of concept lattice based on improved variable precision rough set. Neurocomputing 188:326–338
Zhang K, Zhan JM, Wu WZ, Alcantud JCR (2019a) Fuzzy β-covering based (I, T)-fuzzy rough set models and applications to multi-attribute decision-making. Comput Ind Eng 128:605–621
Zhang L, Zhan JM, Xu ZS (2019b) Covering-based generalized IF rough sets with applications to multi-attribute decision-making. Inf Sci 478:275–302
Zhang XH, Wang JQ, Zhan JM, Dai JH (2021) Fuzzy measures and coquet integrals based on fuzzy covering rough sets. IEEE T Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3081916
Zhou T, Lu HL, Hu FY, Qiu S, Cuiying W (2020) A model of high-dimensional feature reduction based on variable precision rough set and genetic algorithm in medical image. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7653946
Zhou JL, Xu FS, Guan YY, Wang HK (2021) Three types of fuzzy covering-based rough set models. Fuzzy Set Syst 423:122–148
Ziarko W (1993) Variable precision rough set model. J Comput Syst Sci 46(1):39–59
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 62076089 and 61772176, the Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province of China under Grant Nos. 182102210078 and 212102210136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MJ: data curation, investigation, resources, writing—original draft. ZX: conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, writing—review & editing. YL and YZ: project administration, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Za., Jing, Mm., Li, Yx. et al. Variable precision multi-granulation covering rough intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Granul. Comput. 8, 577–596 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-022-00342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-022-00342-1