Abstract
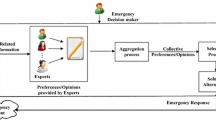
With respect to the characteristic of risk and the potential evolvement of scenarios in emergency management analysis, this study proposes an emergency decision-making method with interval probability based on cumulative prospect theory and group decision-making. Under emergency risk environment, there is a tremendous need to consider decision-maker’s psychological behavior which affects the decision results. In addition, an emergency decision generally involves joint participation among departments, which inevitably brings about group decision-making. Therefore, aiming at decision problems in emergency management, this paper provides an algorithm of emergency group decision-making considering psychological behaviors. For illustration and verification, a numerical example and two comparisons are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed method. The contribution of this study is characterized by three aspects. First, cumulative prospect theory is introduced to quantify the impact of psychological behaviors. Second, group decision-making is considered as a think tank, which makes the decision more persuasive than single-person methods. Third, this study proposes a novel intelligent optimization algorithm, plant growth simulation algorithm, to integrate the different individual evaluations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abul’Wafa AR (2011) A new heuristic approach for optimal reconfiguration in distribution systems. Electr Power Syst Res 81(2):282–289
Bell DE (1985) Disappointment in decision making under uncertainty. Oper Res 33(1):1–27
Bleichrodt H, Schmidt U, Zank H (2009) Additive utility in prospect theory. Manag Sci 55(5):863–873
Chen SM, Chang TH (2001) Finding multiple possible critical paths using fuzzy PERT. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 31(6):930–937
Chen SM, Chien CY (2011) Parallelized genetic ant colony systems for solving the traveling salesman problem. Expert Syst Appl 38(4):3873–3883
Chen SM, Chung NY (2006) Forecasting enrollments of students using fuzzy time series and genetic algorithms. Int J Inf Manage Sci 17(3):1–17
Chen SM, Kao PY (2013) TAIEX forecasting based on fuzzy time series, particle swarm optimization techniques and support vector machines. Inf Sci 247(15):62–71
Chen SM, Hong JA (2014a) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision making based on ranking interval type-2 fuzzy sets and the TOPSIS method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 44(12):1665–1673
Chen SM, Hong JA (2014b) Multicriteria linguistic decision making based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and the aggregation of fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 286:63–74
Chen SM, Wang NY, Pan JS (2009) Forecasting enrollments using automatic clustering techniques and fuzzy logical relationships. Expert Syst Appl 36(8):11070–11076
Chen SM, Lin TE, Lee LW (2014) Group decision making using incomplete fuzzy preference relations based on the additive consistency and theorder consistency. Inf Sci 259:1–15
Cui W, Blockley DI (1990) Interval probability theory for evidential support. Int J Intell Syst 5(2):183–192
Diana LY, Adam SG, Daniel BH, Eric W (2012) Decision making under time pressure, modeled in a prospect theory framework. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 118(2):179–188
Fan ZP, Liu Y, Shen RJ (2012) Risk decision analysis method for emergency response based on prospect theory. Syst Eng Theory Pract 32(5):977–984
FEMA (2015) ICS Resource Center, Federal Emergency Management Agency “FEMA Glossary”. Retrievedfrom: http://training.fema.gov/emiweb/is/icsresource/glossary.html
He DY, Zhou RX (2010) Study on methods of decision-making under interval probability. J Syst Manag 19(2):210–214
Kahneman D, Tversky A (1979) Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Economentrica 47(2):263–291
Langer T, Weber M (2001) Prospect theory, mental accounting, and differences in aggregated and segregated evaluation of lottery portfolios. Manage Sci 47(5):716–733
Lee LW, Chen SM (2008) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on the extension of TOPSIS method and interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Kunming, China 12–15. pp 3260–3265
Li T, Wang CF, Wang WB, Su WL (2005) A global optimization bionics algorithm for solving integer programming—plant growth simulation algorithm. Syst Eng Theory Pract 25(1):76–85
Liu W, Li L (2015) An approach to determining the integrated weights of decision makers based on interval number group decision matrices. Knowl Based Syst 90(C):92–98
Liu Y, Fan ZP, Zhang Y (2014) Risk decision analysis in emergency response: a method based on cumulative prospect theory. Comput Oper Res 42(2):75–82
Lu SL, Yu SZ (2014) A fuzzy k-coverage approach for RFID network planning using plant growth simulation algorithm. Int J Adv Sci Technol 30(1):43–54
Pedrycz W (2013) Granular computing-some insights and challenges. Mathw Soft Comput 20(2):15–18
Pedrycz W, Chen SM (2011) Granular computing and intelligent systems: design with information granules of high order and high type. Springer, Heidelberg
Pedrycz W, Chen SM (2015a) Granular computing and decision-making: interactive and iterative approaches. Springer, Heidelberg
Pedrycz W, Chen SM (2015b) Information granularity, big data, and computational intelligence. Springer, Heidelberg
Qiu JD, Li L (2017) A new approach for multiple attribute group decision making with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.07.008
Rajaram R, Kumar KS, Rajasekar N (2015) Power system reconfiguration in a radial distribution network for reducing losses and to improve voltage profile using modified plant growth simulation algorithm with distributed generation. Energy Rep 1(22):116–122
Rao RS, Narasimham SVL, Ramalingaraju M (2011) Optimal capacitor placement in a radial distribution system using Plant Growth Simulation Algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33(5):1133–1139
Ren PJ, Xu ZS, Hao ZN (2017) Hesitant fuzzy thermodynamic method for emergency decision making based on prospect theory. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(9):2531–2543
Sarma AK, Rafi KM (2011) Optimal selection of capacitors for radial distribution systems using plant growth simulation algorithm. Int J Adv Sci Technol 30:61–72
Tsai PW, Pan JS, Chen SM, Liao BY, Hao SP (2008) Parallel cat swarm optimization. Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Kunming, China, vol 6, pp 3328–3333
Tsai PW, Pan JS, Chen SM, Liao BY (2012) Enhanced parallel cat swarm optimization based on the Taguchi method. Expert Syst Appl 39(7):6309–6319
Tversky A, Kahneman D (1992) Advance in prospect theory: cumulative representation of uncertainty. J Risk Uncertain 5(4):297–323
Wang ZY, Li YJ (2015) Intervention mechanism of behavioral decision-making on emergency and its starting strategy of contingency plan. Syst Eng Theory Pract 35(7):2863–1870
Wang L, Wang YM (2013) Study on the emergency decision method of dynamic reference point based on prospect theory. Chin J Manag Sci 1:132–140
Wang L, Zhang ZX, Wang YM (2015) A prospect theory-based interval dynamic reference point for emergency decision making. Expert Syst Appl 42:9379–9388
Wang L, Wang YM, Martínez L (2017) A group decision method based on prospect theory for emergency situations. Inf Sci 418–419:119–135
Xu XH, Yang YS (2017) Method of dynamic emergency decision for risk type of large group based on cumulative prospect theory. Control Decision 32(11):19567–1965
Xu YJ, Zhang WC, Wang HM (2015a) A conflict-eliminating approach for emergency group decision of unconventional incidents. Knowl Based Syst 83(1):92–104
Xu XH, Du ZJ, Chen XH (2015b) Consensus model for multi-criteria large-group emergency decision making considering non-cooperative behaviors and minority opinions. Decis Support Syst 79:150–160
Yu L, Lai KK (2011) A distance-based group decision-making methodology for multi-person multi-criteria emergency decision support. Decis Support Syst 51(2):307–315
Zadeh L (1997) Towards a theory of fuzzy information granulation and its centrality in human reasoning and fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 90:111–117
Zhou L, Xu ZS, Wu XH, Fujita H (2017) Emergency decision making for natural disasters: an overview. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2017.09.037
Acknowledgements
Grateful acknowledgement is made to my supervisor Mr. Li who gave me considerable help by means of suggestion, comments and criticism. Meanwhile, the authors deeply appreciate the contribution to this paper made by editor and reviewers. Their comments are all valuable and very helpful for revising and improving our paper, as well as the important guiding significance to our researches.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Li, L. Emergency decision-making combining cumulative prospect theory and group decision-making. Granul. Comput. 4, 39–52 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-018-0086-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-018-0086-5