Abstract
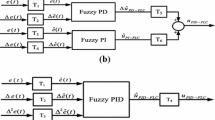
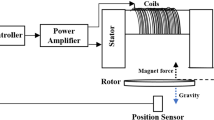
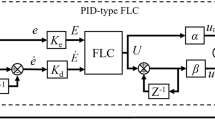
In this paper, the application of moth-flame optimization (MFO) algorithm for the optimal control of an active magnetic bearing (AMB) system is studied. Active magnetic bearings are known to be highly nonlinear multivariable systems. An AMB system is used in motors, generators, turbines and various other machineries in different industries to provide an active suspension to the rotor shafts. The comparison of controlled responses of various closed-loop systems resulting from the use of conventional proportional–integral–derivative (PID) and fuzzy logic-based intelligent control strategies is discussed. The heuristic MFO algorithm is applied to optimize the scaling factors of the fuzzy-PID controller. The proposed controller performance is superior as compared to the very famous industrial PID and fuzzy-PID controllers with respect to various time response parameters. A comparative study with other heuristic algorithms such as PSO and SA is also performed. Three performance indices, namely integral square error, integral time absolute of error (ITAE) and integral time absolute of error plus Integral time absolute of control action (ITAE + ITAU), are chosen for designing the optimization problem.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allam D, Yousri DA, Eteiba MB (2016) Parameters extraction of the three diode model for the multi-crystalline solar cell/module using moth-flame optimization algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 123:535–548
Balini HMNK, Scherer CW, Witte J (2011) Performance enhancement for AMB systems using unstable H∞ controllers. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 19(6):1479–1492
Balini HMNK, Witte J, Scherer CW (2012) Synthesis and implementation of gain-scheduling and LPV controllers for an AMB system. Automatica 48(3):521–527
Bleuler H et al (2009) Magnetic bearings: theory, design, and application to rotating machinery. Springer, Berlin
Ceylan O (2016, November) Harmonic elimination of multilevel inverters by moth-flame optimization algorithm. In: IEEE 2016 international symposium on industrial electronics (INDEL), pp 1–5
Chen SC, Nguyen VS, Le DK, Nam NTH (2014) Active magnetic bearing system equipped with a fuzzy logic controller. J Sci Eng Technol 10(2):69–80
de Queiroz MS, Dawson DM (1996) Nonlinear control of active magnetic bearings: a backstepping approach. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 4(5):545–552
Dhiman G, Kumar V (2017) Spotted hyena optimizer: a novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Adv Eng Softw 114:48–70
Du H, Zhang N, Ji JC, Gao W (2010) Robust fuzzy control of an active magnetic bearing subject to voltage saturation. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 18(1):164–169
Dussaux M (1990, June) Status of the industrial applications of the active magnetic bearings technology. In: ASME 1990 international gas turbine and aeroengine congress and exposition. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp V005T14A016–V005T14A016
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995, October) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Micro machine and human science, 1995. MHS’95. Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on. IEEE, pp 39–43
El-Fergany AA (2018) Extracting optimal parameters of PEM fuel cells using Salp Swarm Optimizer. Renew Energy 119:641–648
Fogel LJ, Owens AJ, Walsh MJ (1966) Intelligent decision making through a simulation of evolution. Syst Res Behav Sci 11(4):253–272
Gosiewski Z, Mystkowski A (2008) Robust control of active magnetic suspension: analytical and experimental results. Mech Syst Signal Process 22(6):1297–1303
Guillemin P (1996) Fuzzy logic applied to motor control. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 32(1):51–56
Hafez AI, Zawbaa HM, Emary E, Hassanien AE (2016, August) Sine cosine optimization algorithm for feature selection. In: INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications (INISTA), 2016 international symposium on. IEEE, pp 1–5
Heidari AA, Pahlavani P (2017) An efficient modified grey wolf optimizer with Lévy flight for optimization tasks. Appl Soft Comput 60:115–134
Hellendoorn H, Reinfrank M (1993) An introduction to fuzzy control. Springer, Berlin
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Sci Am 267(1):66–73
Hsu CT, Chen SL (2003) Nonlinear control of a 3-pole active magnetic bearing system. Automatica 39(2):291–298
Hu S, Zhang Y, Yin X, Du Z (2013) T–S fuzzy-model-based robust stabilization for a class of nonlinear discrete-time networked control systems. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 8:69–82
Ibrahim A, Ahmed A, Hussein S, Hassanien AE (2018, February) Fish image segmentation using Salp Swarm algorithm. In: International conference on advanced machine learning technologies and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 42–51
Jangir N, Pandya MH, Trivedi IN, Bhesdadiya RH, Jangir P, Kumar A (2016, March) Moth-flame optimization algorithm for solving real challenging constrained engineering optimization problems. In 2016 IEEE students’ conference on electrical, electronics and computer science (SCEECS), pp 1–5
Jastrzebski RP, Hynynen KM, Smirnov A (2010) H∞ control of active magnetic suspension. Mech Syst Signal Process 24(4):995–1006
Khalilpourazari S, Pasandideh SHR (2017) Multi-item EOQ model with nonlinear unit holding cost and partial backordering: moth-flame optimization algorithm. J Ind Prod Eng 34(1):42–51
Li C, Li S, Liu Y (2016) A least squares support vector machine model optimized by moth-flame optimization algorithm for annual power load forecasting. Appl Intell 45(4):1166–1178
Madni SHH, Latiff MSA, Coulibaly Y (2017) Recent advancements in resource allocation techniques for cloud computing environment: a systematic review. Clust Comput 20(3):2489–2533
Maniezzo ACMDV (1992) Distributed optimization by ant colonies. In: Toward a practice of autonomous systems: proceedings of the first European conference on artificial life. MIT Press, p 134
Mendel JM, Mouzouris GC (1997) Designing fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Analog Digital Signal Process 44(11):885–895
Meng XB, Gao XZ, Liu Y, Zhang H (2015) A novel bat algorithm with habitat selection and Doppler effect in echoes for optimization. Expert Syst Appl 42(17):6350–6364
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl Based Syst 89:228–249
Mirjalili S (2016) SCA: a sine cosine algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl Based Syst 96:120–133
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH, Mirjalili SZ, Saremi S, Faris H, Mirjalili SM (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191
Nanda SJ (2016, September) Multi-objective moth flame optimization. In: 2016 international conference on Advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI). IEEE, pp 2470–2476
Navale RL, Nelson RM (2010) Use of genetic algorithms to develop an adaptive fuzzy logic controller for a cooling coil. Energy Build 42(5):708–716
Noshadi A, Shi J, Lee WS, Shi P, Kalam A (2016a) Optimal PID-type fuzzy logic controller for a multi-input multi-output active magnetic bearing system. Neural Comput Appl 27(7):2031–2046
Noshadi A, Shi J, Lee WS, Shi P, Kalam A (2016b) System identification and robust control of multi-input multi-output active magnetic bearing systems. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 24(4):1227–1239
Rajabioun R (2011) Cuckoo optimization algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 11(8):5508–5518
Rechenberg I (1973) Evolution strategy: optimization of technical systems by means of biological evolution. Fromman-Holzboog, Stuttgart, p 104
Reddy S, Panwar LK, Panigrahi BK, Kumar R (2017) Solution to unit commitment in power system operation planning using binary coded modified moth flame optimization algorithm (BMMFOA): a flame selection based computational technique. J Comput Sci 25:298–317
Savsani V, Tawhid MA (2017) Non-dominated sorting moth flame optimization (NS-MFO) for multi-objective problems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 63:20–32
Schweitzer G (ed) (2012) Magnetic bearings: proceedings of the first international symposium. ETHG Zurich, Switzerland, June 6–8, 1988. Springer
Sobhan PV, Kumar GN, Amarnath J (2010, December) Rotor levitation by active magnetic bearings using fuzzy logic controller. In: Industrial electronics, control & robotics (IECR), 2010 international conference on. IEEE, pp 197–201
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim 11(4):341–359
Wolpert DH, Macready WG (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1(1):67–82
Xie W, Duan J (2015) The design and simulation of fuzzy PID parameter self-tuning controller. Indones J Electr Eng Comput Sci 14(2):293–297
Yang XS (2008) Nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms. Luniver Press, Beckington
Yang XS (2010) Firefly algorithm, stochastic test functions and design optimization. Int J Bio-Inspir Comput 2(2):78–84
Yao X, Liu Y, Lin G (1999) Evolutionary programming made faster. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 3(2):82–102
Yıldız BS, Yıldız AR (2017) Moth-flame optimization algorithm to determine optimal machining parameters in manufacturing processes. Mater Test 59(5):425–429
Zadeh LA (1996) Fuzzy sets. In: Fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy systems: selected papers by Lotfi A Zadeh. pp 394–432
Zawbaa HM, Emary E, Parv B, Sharawi M (2016, July) Feature selection approach based on moth-flame optimization algorithm. In: IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 4612–4617
Zhang L, Mistry K, Neoh SC, Lim CP (2016) Intelligent facial emotion recognition using moth-firefly optimization. Knowl Based Syst 111:248–267
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhyani, A., Panda, M.K. & Jha, B. Moth-Flame Optimization-Based Fuzzy-PID Controller for Optimal Control of Active Magnetic Bearing System. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Electr Eng 42, 451–463 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-018-0077-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-018-0077-1