Abstract
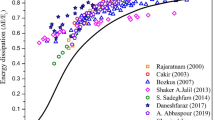
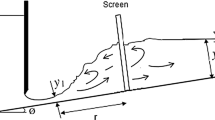
The experimental results indicate that screens with a certain porosity placed vertically in the supercritical flow direction could dissipate a considerable amount of flow energy. Unlike the former studies which have been carried out in the fixed-bed flumes, this study investigates the energy dissipation through the screen in the movable bed at the downstream of the screen. The experiments have been carried out by the screens with 40% and 50% porosities, single and double arrangements of screens and three different bed particle sizes. The supercritical Froude number varied in the range of 5–18. According to the results, double screens with 40% porosity have the highest energy dissipation. Also, the single screens with 50% porosity have the minimum bed scour for a constant amount of energy dissipation. The theoretical multivariate equations were derived based on dimensional analysis, and the related coefficients were obtained by using experimental results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslankara V (2007) Experimental investigation of tailwater effect on the energy dissipation through screens. M.S. thesis, Middle East Technical Univ., Ankara, Turkey
Azamathulla HM, Ab Ghani A, Azazi Zakaria N (2010) Prediction of scour below flip bucket using soft computing techniques. In: AIP conference proceedings, vol 1233(1), pp 1588–1593
Balkış G (2004) Experimental investigation of energy dissipation through inclined screens. M.S. thesis, Middle East Technical Univ., Ankara, Turkey
Bombardelli FA, Gioia G (2006) Scouring of granular beds by jet-driven axisymmetric turbulent cauldrons. Phys Fluids 18(8):088101
Bozkuş Z, Aslankara V (2008) Tailwater effect on the energy dissipation through screens. In: Proceedings of the 8th international congress on advances in civil engineering, Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, North Cyprus
Bozkuş Z, Çakır P, Ger M, Ozeren Y (2004) Energy dissipation through screens. In: Proceedings of the 2004 world water and environmental resources congress. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, ASCE, pp 1–8
Bozkuş Z, Balkış G, Ger M (2005) Effect of inclination of screens on energy dissipation downstream of small hydraulic structures. In: Proceedings of the 17th Canadian hydrotechnical conference, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, pp 881–890
Bozkuş Z, Gungor E, Ger M (2006) Energy dissipation by triangular screens. In: Proceedings of the 7th international congress on advances in civil engineering, Yıldız Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey
Bozkuş Z, Çakır P, Ger M (2007) Energy dissipation by vertically placed screens. Can J Civil Eng 34(4):557–564
Çakır P (2003) Experimental investigation of energy dissipation through screens. M.S. thesis, Middle East Technical Univ., Ankara, Turkey
Chanson H, Gonzalez CA (2005) Physical modelling and scale effects of air-water flows on stepped spillways. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 6(3):243–250
Daneshfaraz R, Sadeghfam S, Ghahramanzadeh A (2017) Three-dimensional numerical investigation of flow through screens as energy dissipators. Can J Civ Eng 44(10):850–859
Henderson FM (1966) Open channel flow. Macmillan, New York, pp 202–210
Lasdon LS, Fox RL, Ratner MW (1974) Nonlinear optimization using the generalized reduced gradient method. RAIRO Oper Res 8(V3):73–103
Mesbahi M, Talebbeydokhti N, Hosseini SA, Afzali SH (2017) External validation criteria and uncertainty analysis of maximum scour depth at downstream of stilling basins based on EPR and MT approaches. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 41(1):87–99
Mignot E, Moyne T, Doppler D, Rivière N (2015) Clear-water scouring process in a flow in supercritical regime. J Hydraul Eng 142(4):04015063
Mir BH, Lone MA, Rather NA (2018) Significance of shape factor of obstacle on local scour. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 43(1):323–330
Mohammadzadeh-Habili J, Heidarpour M, Samiee S (2017) Study of energy dissipation and downstream flow regime of Labyrinth Weirs. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 42(2):111–119
Parsaie A, Haghiabi AH, Saneie M, Torabi H (2017) Prediction of energy dissipation of flow over stepped spillways using data-driven models. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 42(1):39–53
Rajaratnam N, Berry B (1977) Erosion by circular turbulent wall jets. J Hydraul Res 15(3):277–289
Rajaratnam R, Chamani MR (1995) Energy loss at drops. J Hydraul Res 33(3):373–384
Rajaratnam N, Hurtig KI (2000) Screen-type energy dissipator for hydraulic structures. J Hydraul Eng 126(4):310–312
Sadeghfam S, Akhtari AA, Daneshfaraz R, Tayfur G (2014) Experimental investigation of screens as energy dissipators in submerged hydraulic jump. Turk J Eng Environ Sci 38(2):126–138
Sadeghfam S, Khatibi R, Hassanzadeh Y, Daneshfaraz R, Ghorbani MA (2017) Forced hydraulic jumps described by classic hydraulic equations reproducing cusp catastrophe features. Arab J Sci Eng 1–11
Sadeghfam S, Daneshfaraz R, Khatibi R, Minaei O (2019) Experimental studies on scour of supercritical flow jets in upstream of screens and modelling scouring dimensions using artificial intelligence to combine multiple models (AIMM). J Hydroinform. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2019.076
Taştan K, Koçak PP, Yildirim N (2016) Effect of the bed-sediment layer on the scour caused by a jet. Arab J Sci Eng 41(10):4029–4037
Wang H, Tang H, Liu Q, Wang Y (2016) Local scouring around twin bridge piers in open-channel flows. J Hydraul Eng 149(9):6016008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daneshfaraz, R., Sadeghfam, S. & Tahni, A. Experimental Investigation of Screen as Energy Dissipators in the Movable-Bed Channel. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 44, 1237–1246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-019-00306-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-019-00306-7