Abstract
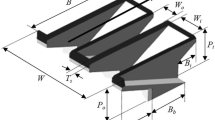
This article adopts four high-accuracy machine learning-based approaches for the prediction of discharge coefficient of a Piano Key Weir (PK-weir) under subcritical condition located on the straight open-channel flume. These approaches consist of least-square support vector machine (LS-SVM), extreme learning machine (ELM), Bayesian ELM (BELM), and logistic regression (LR). For this purpose, 70 laboratory test results are used for determining discharge coefficient of PK-weir for a wide range of discharge values. Root-mean-squared error (RMSE), Nash–Sutcliffe model efficiency coefficient (NSE), the coefficient of correlation (R), threshold statistics (TS), and scatter index (SI) are used for comparing the performance of the models. The simulation results indicate that an improvement in predictive accuracy could be achieved by the ELM approach in comparison with LS-SVM and LR (RMSE of 0.016 and NSE of 0.986), while the BELM model’s generalization capacity enhanced, with RMSE of 0.011 and NSE of 0.989 in validation dataset. The results show that BELM is a simple and efficient algorithm which exhibits good performance; hence, it can be recommended for estimating discharge coefficient.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi MA, Zahedzadeh M, Shadizadeh SR, Abbassi R (2015a) Connectionist model for predicting minimum gas miscibility pressure: application to gas injection process. Fuel 148:202–211
Ahmadi MA, Pouladi B, Javvi Y, Alfkhani S, Soleimani R (2015b) Connectionist technique estimates H2S solubility in ionic liquids through a low parameter approach. J Supercrit Fluids 97:81–87
Altun H, Bilgil A, Fidan BC (2007) Treatment of multi-dimensional data to enhance neural network estimators in regression problems. Expert Syst Appl 32(2):599–605
Anderson RM (2011) Piano key weir head discharge relationships. M.S. thesis, Utah State University, Logan, UT
Anderson RM, Tullis BP, M ASCE (2013) Piano Key Weir Hydraulics and Labyrinth Weir Comparison. J Irrig Drain Eng 139:246–253
Aqil M, Kita I, Yano A, Nishiyama S (2007) A comparative study of artificial neural networks and neuro-fuzzy in continuous modeling of the daily and hourly behaviour of runoff. J Hydrol 337:22–34
Balbay A, Avci E, Sahin O, Coteli R (2012) Modeling of drying process of bittim nuts (pistacia terebinthus) in a fixed bed dryer system by using extreme learning machine. Int J Food Eng 8:10
Berthold M, Hand DJ (2003) Intelligent data analysis: an introduction. Springer, Berlin
Bilhan O, Emiroglu ME, Kisi O (2010) Application of two different neural network techniques to lateral outflow over rectangular side weirs located on a straight channel. Adv Eng Softw 41:831–837
Bishop CM et al (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning, vol 4. Springer, New York
Cramer JS (2002) The origins of logistic regression. Tinbergen Institute, Amsterdam
Das I, Sahoo S, Van Westen C, Stein A, Hack R (2010) Landslide susceptibility assessment using logistic regression and its comparison with a rock mass classification system, along a road section in the northern Himalayas (India). Geomorphology 114:627–637
Du S, Zhang J, Deng Z, Li J (2014) A novel deformation prediction model for mine slope surface using meteorological factors based on kernel extreme learning machine. Int J Eng Res Africa 12:67–81
Dursun OF, Kaya N, Firat M (2012) Estimating discharge coefficient of semi-elliptical side weir using ANFIS. J Hydrol 426–427:55–62
Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Zaji AH, Azimi H, Sharifi A (2015) Gene expression programming to predict the discharge coefficient inrectangular side weirs. Appl Soft Comput 35:618–628
Emiroglu ME, Kisi O (2013) Prediction of discharge coefficient for trapezoidal labyrinth side weir using a neuro-fuzzy approach. Water Resour Manage 27:1473–1488
Goyal MK, Bharti B, Quilty J, Adamowski J, Pandey A (2014) Modeling of daily pan evaporation in subtropical climates using ANN, LS-SVR, Fuzzy Logic, and ANFIS. Expert Sys Appl 41:5267–5276
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (2000) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, NewYork
Huang GB, Chen L (2007) Convex incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 70:3056–3062
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2004) Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feed forward neural networks. Neural Netw 2:985–990
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Huang GB, Wang DH, Lan Y (2011) Extreme learning machines: a survey. Int J Machine Learn Cybernet 2:107–122
Jain A, Ormsbee LE (2002) Evaluation of short-term water demand forecast modeling techniques: conventional methods versus AI. J Am Water Works Assoc 94:64–72
Jain A, Varshney AK, Joshi UC (2001) Short-term water demand forecast modeling at IIT Kanpur using artificial neural networks. Water Resour Manag 15:299–321
Kabiri-Samani A, Javaheri A (2012) Discharge coefficients for free and submerged flow over piano key weirs. J Hydraulic Res 50:114–120
King G, Zeng L (2001) Explaining rare events in international relations. Int Organization 55:693–715
Kisi O, Emiroglu ME, Bilhan O, Guven A (2012) Prediction of lateral outflow over triangular labyrinth side weirs under subcritical conditions using soft computing approaches. Expert Syst Appl 39:3454–3460
Laugier F (2007) Design and construction of the first piano key weir (PKW) spillway at the Goulours dam. Int J Hydropower Dams 5:94–101
Laugier F, Lochu A, Gille C, Leite Ribeiro M, Boillat JL (2009) Design and construction of a labyrinth PKW spillway at St-Marc dam, France. Int J Hydropower Dams 5:100–107
Leite Ribeiro M, Bieri M, Boillat JL, Schleiss A, Delorme F, Laugier F (2009) Hydraulic capacity improvement of existing spillways-design of piano key weirs. In: Proc., 23rd congress of large dams. Question 90, Response 43 (CD-ROM), Int. commission on large dams (ICOLD), Paris
Lempérière F (2009) New labyrinth weirs triple the spillways discharge http://www.hydrocoop.org. Accessed 8 Feb 2010
Luk KC, Ball JE, Sharma A (2000) A study of optimal model lag and spatial inputs to artificial neural network for rainfall forecasting. J Hydrol 227:56–65
Moore DS, McCabe G, Craig B (2009) Introduction to the practice of statistics, 6th edn. Freeman, NewYork
Negnevitsky M (2005) Artificial intelligence: a guide to intelligent systems. Pearson Education, Turin
Oommen T, Baise LG, Vogel RM (2011) Sampling bias and class imbalance in maximum-likelihood logistic regression. Math Geosci 43:99–120
Parsaie A, Azamathulla HM, Haghiabi, AH (2018) Prediction of discharge coefficient of cylindrical weir–gate using GMDH-PSO. ISH J Hydraul Eng 24:116–123
Ribeiro ML, Bieri M, Boillat JL, Schleiss AJ, Singhal G, Sharma N (2012) Discharge capacity of piano key weirs. J Hydraul Eng 138:199–203
Sadri S, Burn DH (2012) Nonparametric methods for drought severity estimation at ungauged sites. Water Resour Res 48:W12505
Salmasi F, Yıldırım G, Masoodi A, Parsamehr P (2013) Predicting discharge coefficient of compound broad-crested weir by using genetic programming (GP) and artificial neural network (ANN) techniques. Arab J Geosci 6:2709–2717
Serre D (2002) Matrices: theory and applications. Springer, Berlin
Shahabi H, Khezri S, Ahmad BB, Hashim M (2014) Landslide susceptibility mapping at central Zab basin, Iran: a comparison between analytical hierarchy process, frequency ratio and logistic regression models. CATENA 115:55–70
Shu C, Ouarda TBMJ (2008) Regional flood frequency analysis at ungauged sites using the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. J Hydrol 349:31–43
Smola JA, Bernhard S (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14:199–222
Soria-Olivas E, Gomez-Sanchis J, Martin JD, Vila-Frances J, Martinez M, Magdalena JR et al (2011a) BELM: Bayesian extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22:505–509
Soria-Olivas E, Gomez-Sanchis J, Jarman I, Vila-Frances J, Martinez M, Magdalena J, Serrano A (2011b) BELM: Bayesian extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(3):505–509. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2010.2103956
Suykens JAK (2001) Support vector machines: a nonlinear modeling and control perspective. Europ J Control 7:311–327
Tayfur G (2014) Soft computing in water resources engineering: artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic and genetic algorithms. WIT Press, Southampton
Wang LJ, Sawada K, Moriguchi S (2013) Landslide susceptibility analysis with logistic regression model based on FCM sampling strategy. Comput Geosci 57:81–92
Wattimena RK, Kramadibrata S, Sidi ID, Azizi MA (2013) Developing coal pillar stability chart using logistic regression. Int J Rock Mech Min 58:55–60
Wong PK, Vong CM, Cheung CS, Wong KI (2013) Diesel engine modelling using extreme learning machine under scarce and exponential data sets. Int J Uncertainty Fuzziness Knowlege-Based Syst 21:87–98
Yu H, Shao C, Zhou D (2013) The design and simulation of networked control systems with online extreme learning machine PID. Int J Model Ident Control 20:337–343
Zaji AH, Bonakdari H, Shamshirband S, Qasem SN (2015) Potential of particle swarm optimization based radial basis function network to predict the discharge coefficient of a modified triangular side weir. Flow Meas Instrum 45:404–407
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olyaie, E., Banejad, H. & Heydari, M. Estimating Discharge Coefficient of PK-Weir Under Subcritical Conditions Based on High-Accuracy Machine Learning Approaches. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 43 (Suppl 1), 89–101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-018-0150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-018-0150-z