Abstract
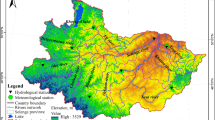
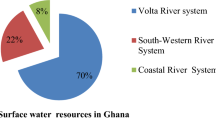
Dramatic shrinkage of the internationally registered Urmia Lake, Iran, is mainly related to the reduction in rivers flowing into the lake. This flow reduction is due to irrigation of agricultural lands upstream of the lake. The potential flows into the lake are greatly influenced by ten perennial rivers, hosting 24 large dams. Among these is the Zarine River, the largest, which contributes to 41 % of surface water flows into the lake. The river flows are controlled by the Bukan Dam, the largest reservoir in the lake basin. The riverine lives in the basin are increasingly degraded, and the recipient lake is drying up. Allocation of environmental water requirements is of main priorities for restoration of the lake. The ecological needs of the river were investigated in three different reaches, upstream and downstream of the Bukan Dam. This paper presents a framework to address the evaluation of minimum environmental flows in this river system from nine eco-hydro methods. The overall results indicate that 17 to 35 % of mean annual flow (MAF) should be allocated for maintaining an acceptable minimum environmental requirement for saving the Urmia Lake. The allocated environmental flow releases from the Bukan Dam is to be increased from currently 9 to 35 % of MAF. The contribution from major rivers surroundings the Urmia Lake is also presented.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi R, Yasi M (2015) Evaluation of environmental flow requirements using eco-hydrologic-hydraulic methods in perennial rivers. Int J Water Sci Technol 72(3):354–363
Ahmadipour Z, Yasi M (2014) Evaluation of eco-hydrology-hydraulics methods for environmental flows rivers (case study: Nazloo River, Urmia Lake Basin). J Hydraul 9(2):69–82 (in Persian)
DWAF (1997) White paper on a national water policy for South Africa. Department of Water Affairs and Forestry (DWAF), Pretoria, South Africa
Dyson M, Bergkamp G, Scanlon J (2003) The essentials of environmental flows. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK
GEFC Software (2016) http://iwmi.cgiar.org/resources/models-and-software/environmental-flow-calculators/. Accessed 14 April 2016
Hughes DA, Hannart P (2003) A desktop model used to provide an initial estimate of the ecological in stream flow requirements of rivers in South Africa. J Hydrol 270:167–181
IWMI (2004) Environmental flows. In: Environmental perspectives on river basin management in Asia, vol 1, issue 1. International Water Management Institute, Colombo
Jamab Consulting Engineers (2005) Current and future status of water resources in the Zarine River Basin and their adaptation with climate changes. West Azerbaijan Regional Water Company, Urmia, Iran (in Persian)
Jane ShK (2015) Assessment of environmental flow requirements for hydropower projects in India. Curr Sci 108(10):1815–1825
Lar Consulting Engineers (2008) Environmental issues in the Zarine River Basin. Department of Environment, West Azerbaijan District, Iran (in Persian)
McClain ME, Subalusky AL, Anderson EP et al (2014) Comparing flow regime, channel hydraulics, and biological communities to infer flow–ecology relationships in the Mara River of Kenya and Tanzania. Hydrol Sci J 59(3–4):801–819
Olden JD, Kennard MJ, Pusey BJ (2012) A framework for hydrologic classification with a review of methodologies and applications in ecohydrology. Ecohydrology 5(4):503–518
Pyrce R (2004) Hydrological low flow indices and their uses. Watershed Science Centre. WSC report no. 04, Trent University, Peterborough, Ontario
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Braun DP, Powell J (1998) A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regul Rivers Res Manag 14(4):329–340
Sadrabniro Consulting Engineers (2014) Water resources development plans on the Zarine River Basin and their consequences on the Urmia Lake. West Azerbaijan Regional Water Department, Urmia, Iran (in Persian)
Shaeri Karimi S, Yasi M, Cox JP, Eslamian S (2014) Environmental flows. In: Eslamian S (ed) Handbook of engineering hydrology. Volume 3: environmental hydrology and water management. CRC press, Taylor and Francis Group, LLC, NY 10017, USA, pp 85–104
Shokoohi A (2015) Sensitivity analysis of Hydraulic models regarding hydromorphologic data derivation methods to determine environmental water requirement. J Water Waste Water 26(3):104–115 (in Persian)
SMADA Software (2016) http://smadaonline.com/DefaultLoggedIn.aspx. Accessed 14 April 2016
Smakhtin VU, Anputhas M (2006) An assessment of environmental flow requirements of Indian river basins. IWMI research report 107. International Water Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka, pp 1–10
Smakhtin VU, Revenga C, Doll P (2004) A pilot global assessment of environmental water requirements and scarcity. Water Int 29:307–317
Smakhtin VU, Shilpakar RL, Hughes DA (2006) Hydrology-based assessment of environmental flows: an example from Nepal. Hydrol Sci 51(2):207–222
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Stensel D (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. McGraw-Hill Education, New York, pp 558–565
Tennant DL (1976) Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation and related environmental resources. J Fish 1:6–10
Tessman SA (1980) Environmental assessment, technical appendix E. In: Environmental use sector reconnaissance elements of the Western Dakotas region of South Dakota Study. Water Resources Research Institute, South Dakota State University, Brookings, USA
Tharme RE (2003) A global perspective on environmental flow assessment: emerging trends in the development and application of environmental flow methodologies for rivers. River Res Appl 19:397–442
Tharme RE, Smakhtin VU (2003) Environmental flow assessment in Asia: capitalizing on existing momentum. Proceedings of the first Southeast Asia water forum, volume 2, Chiang Mai, Thailand, November 2003. Thailand Water Resources Association, Bangkok, pp 301–313
Tsai WP, Chang FJ, Herricks EE (2016) Exploring the ecological response of fish to flow regime by soft computing techniques. J Ecol Eng 87:9–19
ULRP (2014) Urmia Lake restoration plan, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran. http://ulrp.sharif.ir/. Accessed 24 April 2016
Zhang Q, Gu X, Singh VP, Chen X (2015) Evaluation of ecological instream flow using multiple ecological indicators with consideration of hydrological alterations. J Hydrol 529:711–722
Zhang H, Singh VP, Zhang Q, Gui L, Sun W (2016) Variation in ecological flow regimes and their response to dams in the upper Yellow River basin. J Environ Earth Sci 75:938. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-5751-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Detailed work on the Zarine River is from the M.Sc. thesis of the second author, under the supervision of the first author. The results from other rivers are depicted from a number of the theses and studies focusing on ‘the Urmia Lake Restoration Plan’ conducted by the first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasi, M., Ashori, M. Environmental Flow Contributions from In-Basin Rivers and Dams for Saving Urmia Lake. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 41, 55–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-016-0040-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-016-0040-1