Abstract
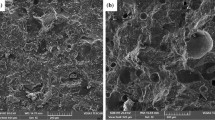
The marble processing industry produces a large volume of unmanaged waste in the form of microfine marble particles, usually referred as waste marble powder (WMP). Unregulated and open disposal of WMP has adverse effects on the environment. Marble is usually rich in calcium content, which can be used in geopolymer technology, thereby enhancing its recycling value. This research sought to determine the viability of WMP as a supplementary binder and polymerisation potential of its high calcium content (55.96%). For this purpose, WMP was used as fly ash replacement by weight (0, 5, 10, 15 and 20%) in geopolymer mortar (GPM) while other mix proportions are kept the same. The results indicated that WMP substitution adversely affected the water absorption (WA), ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV), compressive and flexural strengths of engineered GPM. The mechanical strength trends were supported by, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy tests, which revealed that the calcium content of WMP showed poor alkali activation. Marble particles remained unreacted in the GPM matrix and failed to form additional geopolymeric compounds as Ca/Si ratio was found to consistently decrease with higher WMP substitution. Accordingly, WMP can be used in geopolymers in combination with siliceous binder (fly ash) without significantly reducing the mortar mechanical properties and thus the resulting GPM can find broad applications in practice.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam J, Akhtar MN (2014) Fly ash utilization in different sectors in Indian scenario. Int J Emerg Trends Eng Dev 1:1–14
Aliabdo AA, Abd Elmoaty AEM, Auda EM (2014) Re-use of waste marble dust in the production of cement and concrete. Constr Build Mater 50:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.09.005
Anuradha R, Sreevidya V, Venkatasubramani R, Rangan BV (2012) Modified guidelines for geopolymer concrete mix design using Indian standard. Asian J Civ Eng 13(3):353–364
Arel HS (2016) Recyclability of waste marble in concrete production. J Clean Prod 131:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.052
Ashish DK (2018) Feasibility of waste marble powder in concrete as partial substitution of cement and sand amalgam for sustainable growth. J Build Eng 15:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2017.11.024
Ashish DK (2019) Concrete made with waste marble powder and supplementary cementitious material for sustainable development. J Clean Prod 211:716–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.245
ASTM C348 (2002) Flexural strength of hydraulic-cement mortars. American Society for Testing and Material 04:1–6
ASTM C597 (2016) Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity Through Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, USA, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0597-16
ASTM E1252 (2013) Standard Practice for General Techniques for Obtaining Infrared Spectra for Qualitative Analysis. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 03(Reapproved 2013), pp 1–13.https://doi.org/10.1520/E1252-98R13
ASTMC127 (2009) Standard Test Method for Density , Relative Density ( Specific Gravity ), and Absorption of Coarse Aggregate, pp 1–7
ASTMC29/C29M (1997) Standard Test Method for Bulk Density and Voids in Aggregate, pp 1–4
ASTMC535 (2009) Standard Test Method for Resistance to Degradation of Large-Size Coarse Aggregate by Abrasion and Impact in the Los Angeles Machine, pp 14–16
BS812-110 (1990) Methods for determination of aggregate crushing value (ACV). British Standard Institution
BS812-112 (2015) Determination of Aggregate Impact Value. (iv), pp 1–6
Chatterjee AK (2010) Indian fly ashes, their characteristics, and potential for mechano-chemical activation for enhanced usability. In: 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, pp 41–51
Duxson P, Fernández-Jiménez A, Provis JL, Lukey GC, Palomo A, Van Deventer JSJ (2007a) Geopolymer technology: the current state of the art. J Mater Sci 42(9):2917–2933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0637-z
Duxson P, Mallicoat SW, Lukey GC, Kriven WM, van Deventer JSJ (2007b) The effect of alkali and Si/Al ratio on the development of mechanical properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf, A 292(1):8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.05.044
Dwivedi A, Jain M (2014) Fly ash – waste management and overview: a review. Recent Res Sci Technol 6(1):30–35
Ferdous MW, Kayali O, Khennane A (2013) A detailed procedure of mix design for fly ash based geopolymer concrete. In: Proceedings of the 4th Asia-Pacific Conference on FRP in Structures, APFIS 2013, Dec, pp 11–13
Ghani A, Ali Z, Khan FA, Shah SR, Khan SW, Rashid M (2020) Experimental study on the behavior of waste marble powder as partial replacement of sand in concrete. SN Appl Sci 2(9):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03349-y
Gill P, Jangra P, Roychand R, Saberian M, Li J (2023b) Effects of various additives on the crumb rubber integrated geopolymer concrete. Clean Mater 8:100181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clema.2023.100181
Gill P, Jangra P, Ashish DK (2023) Non-destructive prediction of strength of geopolymer concrete employing lightweight recycled aggregates and copper slag. Energy Ecol Environ 8:1–14
Hadi MNS, Al-azzawi M, Yu T (2018) Effects of fly ash characteristics and alkaline activator components on compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer mortar. Constr Build Mater 175:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.092
Hardjito D, Wallah SE, Sumajouw DMJ, Rangan BV (2004) Factors influencing the compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Civ Eng 6(2):88–93
Hebhoub H, Aoun H, Belachia M, Houari H, Ghorbel E (2011) Use of waste marble aggregates in concrete. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.09.037
Hou Y, Wang D, Zhou W, Lu H, Wang L (2009) Effect of activator and curing mode on fly ash-based geopolymers. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Edit 24(5):711–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-009-5711-3
Jindal BB, Parveen S, Goyal A (2017) Predicting relationship between mechanical properties of low calcium fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Trans Indian Ceram Soc 76(4):258–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/0371750X.2017.1412837
Junaid MT, Kayali O, Khennane A, Black J (2015) A mix design procedure for low calcium alkali activated fly ash-based concretes. Constr Build Mater 79:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.01.048
Kabeer KIS, Vyas A (2018) Evaluation of strength and durability of lean concrete mixes containing marble waste as fine aggregate. Eur J Environ Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2018.1471009
Kamseu E, Akono AT, Rosa R, Mariani A, Leonelli C (2022) Valorization of marble powder wastes using rice husk ash to yield enhanced-performance inorganic polymer cements: phase evolution, microstructure, and micromechanics analyses. Clean Eng Technol 8:100461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2022.100461
Kaya M, Köksal F, Bayram M, Nodehi M, Gencel O, Ozbakkaloglu T (2022) The effect of marble powder on physico-mechanical and microstructural properties of kaolin-based geopolymer pastes. Struct Concr. https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.202201010
Khan MA, Khan B, Shahzada K, Khan SW, Wahab N, Ahmad MI (2020) Conversion of waste marble powder into a binding material. Civ Eng J (iran) 6(3):431–445. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2020-03091481
Kim W, Suh CY, Cho SW, Roh KM, Kwon H, Song K, Shon IJ (2012) A new method for the identification and quantification of magnetite–maghemite mixture using conventional X-ray diffraction technique. Talanta 94:348–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2012.03.001
Komnitsas K, Soultana A, Bartzas G (2021) Marble waste valorization through alkali activation. Minerals 11(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010046
Kumar V, Singla S, Garg R (2020) Strength and microstructure correlation of binary cement blends in presence of waste marble powder. Mater Today: Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.073
Lee WH, Lin KL, Chang TH, Ding YC, Cheng TW (2020) Sustainable development and performance evaluation of marble-waste-based geopolymer concrete. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM12091924
Lezzerini M, Luti L, Aquino A, Gallello G (2022) Effect of marble waste powder as a binder replacement on the mechanical resistance of cement mortars. Appl Sci (switzerland) 12(9):4481
Lloyd NA, Rangan BV (2010) Geopolymer concrete with fly ash. In: 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, vol 7, pp 1493–1504
Mehta A, Siddique R (2017) Properties of low-calcium fly ash based geopolymer concrete incorporating OPC as partial replacement of fly ash. Constr Build Mater 150:792–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.06.067
Mehta A, Siddique R (2018) Sustainable geopolymer concrete using ground granulated blast furnace slag and rice husk ash: strength and permeability properties. J Clean Prod 205:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.313
Nath P, Sarker PK (2015) Use of OPC to improve setting and early strength properties of low calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete cured at room temperature. Cem Concr Compos 55:205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.08.008
Nath P, Sarker PK, Rangan VB (2015) Early age properties of low-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete suitable for ambient curing. Proc Eng 125:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.11.077
Nikvar-Hassani A, Manjarrez L, Zhang L (2022) Rheology, setting time, and compressive strength of class F fly ash-based geopolymer binder containing ordinary Portland cement. J Mater Civ Eng 34(1):4021375
Palomo A, Grutzeck MW, Blanco MT (1999) Alkali-activated fly ashes: a cement for the future. Cem Concr Res 29(8):1323–1329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00243-9
Pappu A, Thakur VK, Patidar R, Asolekar SR, Saxena M (2019) Recycling marble wastes and Jarosite wastes into sustainable hybrid composite materials and validation through Response Surface Methodology. J Clean Prod 240:118249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118249
Rangan B (2014) Fly ash-based geopolymer concrete fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Geopolym Cem Concr 7982:68–106
Saloma A, Hanafiah A, Mawarni A (2016) Geopolymer mortar with fly ash. MATEC Web Conf 78:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20167801026
Saloni P, Lim YY, Pham TM, Kumar K (2021) Sustainable alkali activated concrete with fly ash and waste marble aggregates: strength and durability studies. Constr Build Mater 283:122795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122795
Seghir NT, Benaimeche O, Krzywínski K, Sadowski L (2020) Ultrasonic evaluation of cement-based building materials modified using marble powder sourced from industrial wastes. Buildings. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings10030038
Singh M, Choudhary K, Srivastava A, Singh Sangwan K, Bhunia D (2017) A study on environmental and economic impacts of using waste marble powder in concrete. J Build Eng 13:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2017.07.009
Sinsiri T, Chindaprasirt P, Jaturapitakkul C (2010) Influence of fly ash fineness and shape on the porosity and permeability of blended cement pastes. Int J Min Metallur Mater 17(6):683–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12613-010-0374-9
Surabhi. (2017) Fly ash in India: generation vis-à-vis Utilization and Global perspective. Int J Appl Chem 13(1):29–52
Temuujin J, Riessen AV, Mackenzie KJD (2010) Preparation and characterisation of fly ash based geopolymer mortars. Constr Build Mater 24(10):1906–1910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.04.012
Ushaa TG, Anuradha R, Venkatasubramani GS (2015) Performance of self-compacting geopolymer concrete containing different mineral admixtures. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 22:473–481
Vardhan K, Goyal S, Siddique R, Singh M (2015) Mechanical properties and microstructural analysis of cement mortar incorporating marble powder as partial replacement of cement. Constr Build Mater 96:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.071
Vardhan K, Siddique R, Goyal S (2019) Influence of marble waste as partial replacement of fine aggregates on strength and drying shrinkage of concrete. Constr Build Mater 228:116730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116730
Wang Q, Ding ZY, Da J, Ran K, Sui ZT (2011) Factors influencing bonding strength of geopolymer-aggregate interfacial transition zone. Adv Mater Res 224:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.224.1
Wang Y, Liu X, Zhang W, Li Z, Zhang Y, Li Y, Ren Y (2020) Effects of Si/Al ratio on the efflorescence and properties of fly ash based geopolymer. J Clean Product. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118852
Wang J, Ma B, Tan H, Du C, Chu Z, Luo Z, Wang P (2021) Hydration and mechanical properties of cement-marble powder system incorporating triisopropanolamine. Constr Build Mater 266:121068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121068
Yamanel K, Durak U, Ilkentapar S, Atabey II, Karahan O, Atiş CD (2019) Influence of waste marble powder as a replacement of cement on the properties of mortar. Revista De La Construccion 18(2):290–300. https://doi.org/10.7764/RDLC.18.2.290
Yousuf A, Manzoor SO, Youssouf M (2020) Fly ash: production and utilization in India - an overview. J Mater Environ Science 11(6):911–921
Zhao J, Tong L, Li B, Chen T, Wang C, Yang G, Zheng Y (2021) Eco-friendly geopolymer materials: a review of performance improvement, potential application and sustainability assessment. J Clean Prod 307:127085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, P., Rathanasalam, V.S., Jangra, P. et al. Mechanical and microstructural properties of fly ash-based engineered geopolymer mortar incorporating waste marble powder. Energ. Ecol. Environ. 9, 159–174 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-023-00296-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-023-00296-3