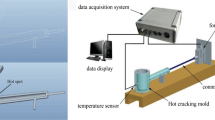
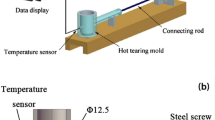
Abstract
Mg–2xY–xTM(Zn,Cu,Ni) alloys reinforced with LPSO have outstanding mechanical properties, but there is less research on Mg–2xY–xNi hot tearing sensitivity. Therefore, based on Clyne Davies Model and Newton Baseline Method, the hot tearing tendency of Mg–2xY–xNi alloys with x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 wt% was quantified, and the tendency was further verified by the tearing evaluation of “T” shaped castings. The results show that the hot tearing susceptibility (HTS) decreases with the increase in x. Especially when x ≥ 1.5 wt%, and the HTS of Mg–Y–Ni alloys is even lower than that of Mg–Y–Zn alloys. The analysis of solidification microstructure evolution reveals that with the increase in x, the grain refinement and equiaxed tendency of α-Mg increases, and the solid fraction increases when dendrites are coherent, and the feeding stage of residual liquid phase between dendrites is shortened, which is an important reason for the decrease in hot tearing tendency. The analysis of phase transformation shows that with the increase in x, the residual liquid phase between α grains increases, which has better feeding effect on solidification, while the precipitation amount of LPSO phase which has coherent relationship with α increases, and its bridging effect on inhibiting grain boundary cracking is enhanced, which is another reason for reducing the HTS.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Cao, C. Zhang, H. Cao et al., Hot-tearing susceptibility of ternary Mg–Al–Sr alloy casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41A, 706–716 (2010)
P. Gunde, A. Schiffl, P.J. Uggowitzer, Influence of yttrium additions on the hot tearing susceptibility of magnesium–zinc alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 7074–7079 (2010)
L. Zhou, Y.D. Huang, P.L. Mao et al., Influence of composition on hot tearing in binary Mg–Zn alloys. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 24, 170–176 (2011)
Y.S. Wang, Q.D. Wang, G.H. Wu et al., Hot-tearing susceptibility of Mg–9Al–xZn alloy. Mater. Lett. 57, 929–934 (2002)
J.F. Song, Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang et al., Hot tearing characteristics of Mg–2Ca–xZn alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 2687–2704 (2016)
Z.P. Luo, S.Q. Zhang, High-resolution electron microscopy on the X-Mg12ZnY phase in a high strength Mg–Zn–Zr–Y magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19(9), 813–815 (2016)
Y. Kawamura, M. Yamasaki, Formation and mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1RE2 Alloys with Long-Period Stacking Ordered structure. Mater. Trans. 48(11), 2986–2992 (2007)
D.W. Ji, C.M. Liu, Z.Y. Chen et al., Effects of Zn content on microstructures and mechanical properties of as cast Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 480–486 (2013)
J.F. Wang, P.F. Song, S. Gao et al., Influence of Y on the phase composition and mechanical properties of asextruded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 2005–2010 (2012)
Z. Liu, S.B. Zhang, P.L. Mao et al., Effects of Y on hot tearing formation mechanism of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 1214–1222 (2014)
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, Y. Peng et al., The effect of LPSO phase on hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization evolution of Mg–2.0Zn–0.3Zr–5.8Y alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 579, 209–216 (2013)
Z. Wei, Y. Wang, Z. Liu, Effects of Zn and Y on hot-tearing susceptibility of Mg–xZn–2xY alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34(16), 2001–2006 (2018)
T. Itoi, K. Takahashi, H. Moriyama, M. Hirohashi, A high-strength Mg–Ni–Y alloy sheet with a long-period ordered phase prepared by hot-rolling. Scripta Mater. 59(10), 1155–1158 (2008)
H. Liu, F. Xue, J. Bai, J. Zhou, X. Liu, Effect of substitution of 1 wt% Ni for Zn on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg94Y4Zn2, Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 585, 387–395 (2013)
S.M. Zhu, R. Lapovok, J.F. Nie, Y. Estrin, S.N. Mathaudhu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of LPSO phase dominant Mg85.8Y7.1Zn7.1 and Mg85.8Y7.1Ni7.1 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 692, 35–42 (2017)
G. Zhu, Z. Wang, W. Qiu et al., Effect of yttrium on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–6Zn–1Cu–0.6Zr Alloys. Int. Metalcast 14, 179–190 (2020)
Z.H. Huang, S.M. Liang, R.S. Chen et al., Solidification pathways and constituent phases of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 468, 170–178 (2013)
Z. Zhen, N. Hort, Y.D. Huang, N. Petri, O. Utke, K.U. Kainer, Quantitative determination on hot tearing in Mg–Al binary alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 618, 533–540 (2013)
Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan, Z. Liu, F. Beckmann, K.U. Kainer, K.N. Hort, Experimental and numerical analysis of hot tearing susceptibility for Mg–Y alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 353–362 (2013)
J.F. Song, Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang et al., Hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–Ca binary alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46(12), 6003–6017 (2015)
G. Cao, I. Haygood, S. Kou, Onset of hot tearing in ternary Mg–Al–Sr alloy casting. Metal Mater Trans A. 41, 2139–2150 (2015)
Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan, Z. Liu, F. Beckmann, K.U. Kainer, N. Hort, Hot tearing susceptibility of binary Mg–Y alloy castings. Mater. Design 47, 90–100 (2013)
L. Zhou, Z. Liu, Y.D. Huang et al., Prediction of hot tearing susceptibility for Mg–Zn–(Al) alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 509, 138–146 (2012)
Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan et al., Experimental and numerical analysis of hot tearing susceptibility for Mg–Y alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 353–362 (2014)
Y. Zhang, X. Zeng, L. Liu, C. Lu, H. Zhou, Q. Li, Y. Zhu, Effects of yttrium on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 373(1), 320–327 (2004)
Z. Zhen, N. Hort, Y.D. Huang, N. Petri, O. Utke, K.U. Kainer, Quantitative determination on hot tearing in Mg–Al binary alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 618–619, 533–540 (2009)
X. Yang, S. Wu, S. Lü, L. Hao, X. Fang, Effects of Ni levels on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Ni–Y alloy reinforced with LPSO structure. J. Alloys Compd. 726, 276–283 (2017)
M. Malekan, S.G. Shabestari, Computer-aided cooling curve thermal analysis used to predict the quality of aluminium alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 103, 453–458 (2011)
H. Cruz, C. Gonzalez, A. Juárez et al., Quantification of the microconstituents formed during solidification by newton thermal analysis method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 178, 128–134 (2006)
M.B. Djurdjevic, J.H. Sokolowski, Z. Odanovic, Determination of dendrite coherency point characteristics using first derivative curve versus temperature. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 109, 875–882 (2012)
Z.Q. Wei, S.M. Liu, Z. Liu et al., Effects of Zn content on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–7Gd–5Y–05Zr alloy. Metals 10(3), 414 (2020)
G. Cao, S. Kou, Hot tearing of ternary Mg–Al–Ca alloy castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 3647–3663 (2006)
Z. Liu, S.B. Zhang, P.L. Mao et al., Effects of Y on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Metal. Soc. China. 24, 907–914 (2014)
Z. Wang, S. Yao, G. Cao, P. Mao, F. Wang, L. Zhou, Z. Liu, Effect of yttrium addition on dynamic mechanical properties, microstructure, and fracture behavior of extrusion-shear ZC61 + xY (x = 0, 1, 2, 3) alloys. Mater. Charact. 169, 110615 (2020)
M.Z. Li, Y.Q. Wang, C. Li et al., Effects of neodymium rich rare earth elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of as cast AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27, 1138–1142 (2014)
D.K. Xu, W.N. Tang, L. Liu et al., Effect of Y concentration on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 432, 129–134 (2007)
X. Du, F. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Li, Z. Liu, P. Mao, Hot tearing susceptibility of AXJ530 alloy under low-frequency alternating magnetic field. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 33(9), 1259–1270 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from High level innovation team of Liaoning Province (XLYC1908006), Innovation Talent Program in Science and Technology for Young and Middle-aged Scientists of Shenyang (No. RC.180111), Project of Liaoning Education Department (Nos. LQGD2019002 and LJGD2019004), Liaoning nature fund guidance plan (No. 2019-ZD-0210) and Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (Nos. XLYC1807021 and 1907007), Joint Research Fund Liaoning-Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science (2019JH3/30100014), National Key R&D Project (SQ2020YFC200162-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Liu, S., Zhou, L. et al. Study on Solidification Behavior and Hot Tearing Susceptibility of Mg–2xY–xNi ALLOYS. Inter Metalcast 15, 995–1005 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00531-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00531-1