Abstract
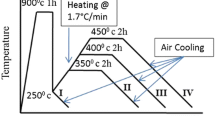
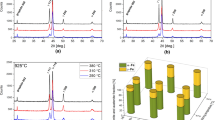
This study produced austempered ductile iron (ADI) with ausferrite structure using forced-air cooling as the quenching method. ASTM A536 65-45-12 grade of ductile iron was produced, machined into flat samples of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mm thickness, austenitised at a temperature of 820 °C for 1-h soaking period inside a muffle furnace, forced-air-cooled in an air quenching chamber to an austempering temperature (T A) of 300 °C and rapidly transferred into another muffle furnace maintained at 300 °C in order to austemper them for a fixed period of 2 h. Finally, the microstructural morphology and phase distribution of heat-treated samples were characterised using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) method. The SEM image with electron-dispersive X-ray analyses shows predominant carbon and iron peaks of high-carbon austenite and ferrite, respectively, while the XRD patterns predominantly consist of austenite (γ) and ferrite (α) phases which are the characteristic features of ADI. The study concluded that with the use of forced-air cooling as a quenching method, ADI of section thicknesses up to 25 mm with ausferrite structure is producible.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.K. Putatunda, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 315, 70–80 (2001)
K.L. Hayrynen, J.R. Keough, Austempered Ductile Iron—the State of the Industry in 2003, 2003 Keith Mills Symposium on Ductile Cast Iron
R.A. Harding, The Production, Properties and Automotive for Austempered Ductile Iron, Asia-Europe Environment Forum Conference, Jakarta, Indonesia, Nov. 23–25 (2005)
J.R. Keough, K.L. Hayrynen, Developments in the technology and engineering application of austempered ductile iron (ADI), in Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Science and Processing of Cast Iron, Beijing, China, Oct. 16–19, pp. 474–479 (2006)
D.M. James, A Design Engineer’s Digest of Ductile Iron, 8th edn. (Sorelmetal Technical Services Rio Tinto Iron & Titanium Inc, USA, 2005)
J. Zimba, D.J. Simbi, E. Navara, Cem. Concr. Compos. 25, 643–649 (2003)
T. Tun, K.T. Lwin, J. Met. Mater. Miner. 18(2), 199–205 (2008)
C. Bixler, K. Hayrynen, J. Keough, G. Pfaffmann, S. Gledhill, Locally Austempered Ductile Iron (LADI) (Society of Automotive Engineers International, 2010-01-0652, 2010)
L. Justin, J.R. Keough, Austempering Materials for Powertrain Application. Applied Process Inc. Technologies Div.—Livonia, Michigan, USA (2010)
B. Kovacs, Am. Foundry Soc. Trans. 56, 417–420 (1994)
O. Erić, D. Rajnovic, S. Zec, L. Sidjanin, M.T. Jovanovic, Mater. Charact. 57, 211–217 (2006)
J.V. Dawason, BCIRA Committee Report CT.30 (1986)
K.A.A. Mills, BCIRA Res. Cast Met. Pract. 46(3), 239–245 (1988)
J.W. Soedarsono, T.P. Soemardi, B. Suharno, R.D. Sulamet-Ariobimo, E.Z. Damanik, W.D. Haryono, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A1, 236–242 (2011)
M. Costello, BCIRA Committee Report CT.70 (1990)
M. Costello, P.A. Murrell, BCIRA Technol. Abstr. 40(6) (1992)
ASTM A 536, Am. Soc. Test. Mater. Int. 1(2), 321–325 (1998)
K.M. Pedersen, N.S. Tiedje, Mater. Charact. 59, 1111–1121 (2008)
J. Yang, S.K. Putatunda, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 382, 219–230 (2004)
S.K. Swain, R.K. Panda, J.P. Dhal, S.C. Mishra, S. Sen, Orissa J. Phys. 19(1), 73–80 (2012)
M. Górny, E. Tyrała, H. Lopez, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23(10), 3505–3510 (2014)
X.L. Guo, H.Q. Su, B.Y. Wu, Z.G. Liu, Microscopy Res. Tech. 40, 336–340 (1998)
O. Erić, T. Brdarić, N. Stojsavljević, M. Tonić, N. Nebojša Grahovac, R. Đuričić, Assoc. Metall. Eng. Serbia 16(2), 91–102 (2010)
S.L. Guang, Adv. Mater. Res. 328–330 (2011)
X.Z. Liao, Y.H. Zhao, Y.T. Zhu, J. Appl. Phys. 96(1), 636–640 (2004)
H.W. Zheng, Y.G. Zhan, Z. Chen, C. Lu, Y.W. Mai, Phys. Lett. A 373, 570–574 (2009)
R. Kumar, L. Nicola, E. Van der Giessen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 7–15 (2009)
E. Fras, M. Górny, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Science and Processing of Cast Iron, Beijing, China, Oct. 16–19 (2006)
N. Rebasa, R. Dommarco, J. Sikora, Wear 253, 885–862 (2002)
ASTM A897/897M-16, Standard Specification for Austempered Ductile Iron Castings (American Society for Testing and Materials International, 2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors hereby declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olawale, J.O., Ibitoye, S.A., Oluwasegun, K.M. et al. Forced-Air Cooling Quenching: A Novel Technique for Austempered Ductile Iron Production. Inter Metalcast 11, 568–580 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0114-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0114-7