Abstract
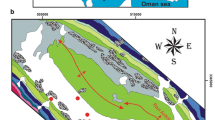
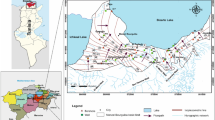
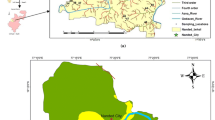
The Quaternary deposits represent the main groundwater aquifer in the study area. During the last few years, the problem of groundwater contamination has been intensified mainly due to natural and human-related factors. The present work aims to study the hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater of the Quaternary aquifer at Faquss district. To achieve that, 16 groundwater samples were collected and analyzed for major ions, trace elements, and microbiological analysis. Constructions of water level map of the Pleistocene aquifer and distribution maps for different ions in groundwater were made by surfer software. Statistical analyses for water quality parameters were carried out. Results indicate that most of the studied area is characterized by fresh water (TDS < 1000 mg/L) with low contents of K, Na, Mg, Ca, SO4, and Cl reflecting the suitability of ground water for drinking. High contents of TDS, Na, SO4, and Cl are recorded at the northeastern parts of the area; this refers to the existence of local pollution sources resulting from the infiltration of domestic, agricultural, and industrial wastes in the intensive populated area. The concentrations of trace elements (chromium, copper, cadmium, etc.) in groundwater are within the acceptable limits for drinking and domestic uses. Iron and manganese are over the acceptable limits in most of the area and the groundwater is unsuitable for drinking. Low contents of iron and manganese are recorded at the north, while aluminum contents are over the acceptable limits at the same site. The results of bacteriological analyses indicate the existence of E. coli bacteria in most of shallow wells ranges between 4 and 800 ml. So, shallow groundwater should be chemically treated before drinking. Generally, the groundwater in the studied area is suitable for irrigation, except 19% of wells suffer from sodium hazards. The ratio rNa/rCl varies between 1.012 and 1.56 in most groundwater samples and indicates the continental origin of groundwater in the study area. The ratio r (K + Na)-rCl/rSO4 reflects either Na2–SO4 water type (in 75% of groundwater samples) or NaHCO3 water type of shallow meteoric origin (in 25% of groundwater samples). The presence of Na2SO4 water type in deep meteoric water genesis at shallow depth is associated with sulfate salts (MgSO4, and CaSO4) which formed more than 25% of salt combination might reflect the influence of anthropogenic activities. The dominant process determining the water composition is evaporation.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwa AFM, Negm A, Armanuos AM (2015) Enironmental threats of an onsite sewage disposal on groundwater at Minia- Al Qamh, Sharkia Governorate, Egypt. Eighteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC18 Sharm El Sheikh, 12–14 March 2015
Abo-El-Fadl MM (2013) Possibilities of groundwater pollution in some areas, east Nile Delta. Egypt Int Environ 1:1–21
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association Inc., New York
Arnous MO, El-Rayes AE, Green DR (2015a) Hydrosalinity and environmental land degradation assessment of the East Nile Delta region. Egypt J Coast Conserv 19:491–513
Arnous MO, El Rayes AL, Green DR (2015b) Hydrosalinity and environmental land degradation assessment of the east Nile Delta region. Egypt J Coast Conserve 19:491–513
Attia FAR (1985) Management of water systems in upper Egypt. PH.D. thesis, fac. Eng., Cairo Univ., Cairo, Egypt, pp 355
Chadha DK (1999) (1999): A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrogeol J 7:431–439
Conoco (1987) Geologic map of Egypt. Egyptian general authority for petroleum (UNESCO Joint Map Project), 20 Sheets, Scale 1:500 000. Cairo
Diab MS, Khalil JB, Atta SA (1984) Hydrogeological studies on groundwater aquifers of the eastern part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Geological survey, Cairo, Egypt
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1990) Physical and chemical hydrogeology (eds) Wiley, New York
Embaby A, Afifi SY, El Atabany NM (2014) Hydrochmical evaluation of Belbies district groundwater, South El Sharkia governorate, Egypt. Life Sci J 11(12s):1074–1092
El Dairy MD 1980 Hydrogeological studies on the eastern part of Nile Delta using isotope techniques’, M.Sc. thesis, Fac. Of Sci. Zagazig Univ. pp 233
El Fayoumy IF (1968) Geology of groundwater supplies in the region east of the Nile Delta “Ph.D. thesis, Fac. Sci. Cairo Univ. pp 201
El-Fakharany MA, Mansour NM, Yehia MM, Monem M (2017) Evaluation of groundwater quality of the quaternary aquifer through multivariate statistical techniques at the southeastern part of the Nile Delta. Egypt Sustain Water Resour Manag 3(1):71–81
El Shazly EM, Abdel Hady MA, El Shazly MM, El Ghawabby MA, El Kassas LA, Salman AB, Morsi MA (1975) Geological and groundwater potential studies of El Ismailia master plan study area. In: Romate sensing research project, Academy of Scientific research and technology, Cairo, Egypt, pp 24
Eaton FM (1950) Significance of carbonate in irrigation water. Soil Sci 69(2):127–128
Forstner U, Wittman TW (1981) Metal pollution in aquatic environment. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world’s water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Gomaa MA, El Naggar IM, Ali IM, Omar JM, El Shahat MF (2014) Effect of surface water system on groundwater composition using geochemical modeling and geostatistical techniqes, East Nile Delta (case study). Int J Adv Res 2(5):475–497
Heath RC (1987) Basic Groundwater Hydrology, U.S. Geol. Surv. Water-Supply, p 2220
Hem JD (1970) Study and interpretation of chemical characteristics of natural water. Second edition- Geological survey water supply paper 1473 United States Government printing office. Wessington.
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (3eds) U.S. Geol. Surv. Water supply, paper No. 2254, pp 263
Hem JD (1991) “Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters”, book 2254, 3rd edn. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur
Hounslow AW (1995) Water quality data analysis and interpretation”. Lews Publisher, New York
Kotb, AM (1988) Geological, hydrogeological and geoelectrical studies on the Eastern portion of Delta. M.Sc. thesis, Fac. Sci., Al Azhar Univ., Cairo, Egypt, pp 120
Korany EA, Shendi EH, Abdel Tawab S (1993) Integrated detection of the problem of groundwater overflows in Abu Zaabal basalt quarries, Egypt. Fac. Of Sci., Ain Shams Univ., Cairo, Egypt
Mohamed S, El-Sabrouty MN (2014) Applications of hydrogeochemical modeling to assessment geochemical evolution of the Quaternary aquifer system in Belbies area, East Nile Delta, Egypt. J Biol Earth Sci 4(1): E34–E47
Probe IM, Bruce BW, Hansen CV (1999) Groundwater quality in Quaternary deposits of the central high plains aquifer, south central Kansas. U.S. Geol. Surv. Water recourses investigations report 00–4259
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline alkaline soils, US Department of Agriculture, Handbook 60(160)
RIGW/IWACO (1990) Vulnerability of groundwater to pollution in the Nile Valley and Delta", Technical Report No. TN/70/30/89/02, Egypt
Sallouma MKM (1983) Hydrogeological and hydrochemical assessment of the Quaternary aquifer in the eastern Nile Delta. Egypt: PhD thesis. Faculty of science, Ain Shams University, Egypt, p166
Said R, Beheri S (1961) Quantitative geomorphology of the area east of Cairo. Bull. Soc. Geographic, Egypt, pp 121–132
Said R (1991) The geology of Egypt: ABalkema, Rotterdam Pub., pp 734
Satyanarayana E, Ratnakar D, Muralidhar M (2016) Major ion chemistry of groundwater and surface water in parts of Mulugu-Venkatapur Mandal, Warangal District, Telangana State, India. Hydrol Current Res 7:253. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7587.1000253
Shata AA (1965) Geological structure of the Nile Delta. joun. engin. Cairo Egypt (in Arabic ) pp 1–3
Shata A, El Fayoumy IF (1970) Remarks on the hydrogeology of the Nile delta. In: Proc. Sym. Hydrology of Deltas.UNESCO V.II. pp 35–46
Sulin VA (1948) Oil waters in the system of natural waters. Gostoptechizdat, Moscow (in Russian)
Taha AA, Serage HM, El Din A, El Haddad IM (1997) Hyrogeological situation of the area between Ismailia canal and Cairo-Ismailia desert road, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Journal of Environment Science, vol 14
Wilocox LV (1955) Classifiction and uses of irrigation waters. US Dept. Agric. Circular (969), Washinghon D.C., pp 19
World Health Organization (WHO) (2004) Guideline for drinking water quality, 3rd edition, Vol. I recommendations, Geneva
World Health Organization (WHO) (1984) International standards for drinking water "3rd edition, vol. I, Geneva, pp 70
World Health Organization (WHO) (2017) Chemical mixtures in source water and drinking-water. World Health Organization: Bonn. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/water drink/pdf/WHO_parameter_report. (Accessed on 11 September 2017)
Zheng QL, Ma T, Wang Y, Yan Y, Liu L (2017) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in Xincai River Basin, Northern China. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 17(2017):368–371
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express their sincere appreciation to Benha University, Faculty of Science and Research institute for groundwater. Special thanks go to Prof. Mohamed El Fakharany, Head of Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Benha University who provided considerable support and encouraged me during this work and to my family who supported me.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansour, N.M. Hydrochemical studies and evaluation of groundwater quality of the Quaternary aquifer at Faquss, Al Sharqiya Governorate, Egypt. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 6, 19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00374-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00374-y