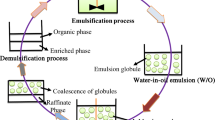
Abstract
Manganese (Mn) is one of the most widely used metals in industry, even if it is highly toxic. Thus, the accumulation of manganese-containing wastes is one of the main environmental concerns. For this reason, its recovery from aqueous solutions is of particular importance and is gaining a lot of interest. Among the water treatments, emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) presents several advantages, such as ease of use, high efficiency, and single-step extraction. Therefore, the ELM technique has a high potential to replace the conventional methods for removing heavy metal ions, particularly for its high removal efficiency. The present research aims to analyze the feasibility of manganese ions removal from the water via the ELM method. Therefore, in the first step, the physicochemical factors affecting the stability of the liquid membrane were investigated. Then, the fractional factorial design (FFD) method was used to screen and choose the pivotal, influential factors on manganese ion extraction, such as carrier concentration, emulsion-to-feed phase volume ratio, feed phase pH, water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsion stirring time and speed. Based on the collected results, the maximum extraction (> 97%) was achieved when the carrier concentration, emulsion/feed phase volume ratio, feed phase pH, W/O/W emulsion stirring time, and W/O/W emulsion stirring speed were ~ 8% v/v, ~ 3, ~ 4, ~ 17 min, and ~ 450 rpm, respectively.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecol 2011:20. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/402647
Ma H, Kökkılıç O, Waters KE (2017) The use of the emulsion liquid membrane technique to remove copper ions from aqueous systems using statistical experimental design. Miner Eng 107:88–99
Tan Z, Mei G, Li W, Zeng K, Liang R, Zeng X (2004) Metallurgy of manganese. Central South University Press, Changsha
Swain B, Jeong J, Kim S-k, Lee J-c (2010) Separation of platinum and palladium from chloride solution by solvent extraction using Alamine 300. Hydrometallurgy 104(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.03.013
Li Y, Shahbazi A, Williams K, Wan C (2008) Separate and concentrate lactic acid using combination of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 147(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8047-5
Wojtyniak B, Kołodziejczyk J, Szaniawska D (2016) Production of lactic acid by ultrafiltration of fermented whey obtained in bioreactor equipped with ZOSS membrane. Chem Eng J 305:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.048
Joglekar HG, Rahman I, Babu S, Kulkarni BD, Joshi A (2006) Comparative assessment of downstream processing options for lactic acid. Sep Purif Technol 52(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.03.015
Feng M, Wenzel M, Wang S, Du H, Zhang Y, Weigand JJ (2021) Separation of Na3VO4 and Na2CrO4 from high alkalinity solutions by solvent extraction. Sep Purif Technol 255:117282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117282
Chen K, Hao S, Lyu H, Luo G, Zhang S, Chen J (2017) Ion exchange separation for recovery of monosaccharides, organic acids and phenolic compounds from hydrolysates of lignocellulosic biomass. Sep Purif Technol 172:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.08.004
Kumar A, Thakur A, Panesar PS (2019) A review on emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) for the treatment of various industrial effluent streams. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol 18(1):153–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-019-09492-2
Salahshoori I, Nasirian D, Rashidi N, Hossain MK, Hatami A, Hassanzadeganroudsari M (2020) The effect of silica nanoparticles on polysulfone–polyethylene glycol (PSF/PEG) composite membrane on gas separation and rheological properties of nanocomposites. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03255-8
Hatami A, Salahshoori I, Rashidi N, Nasirian D (2020) The effect of ZIF-90 particle in Pebax/Psf composite membrane on the transport properties of CO2, CH4 and N2 gases by Molecular Dynamics Simulation method. Chin J Chem Eng 28(9):2267–2284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.12.011
Nasirian D, Salahshoori I, Sadeghi M, Rashidi N, Hassanzadeganroudsari M (2020) Investigation of the gas permeability properties from polysulfone/polyethylene glycol composite membrane. Polym Bull 77(10):5529–5552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03031-3
Salahshoori I, Babapoor A, Seyfaee A (2021) Elevated performance of the neat, hybrid and composite membranes by the addition of nanoparticles (ZIF-67): a molecular dynamics study. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03673-2
Salahshoori I, Seyfaee A, Babapoor A, Neville F, Moreno-Atanasio R (2021) Evaluation of the effect of silica nanoparticles, temperature and pressure on the performance of PSF/PEG/SiO2 mixed matrix membranes: a molecular dynamics simulation (MD) and design of experiments (DOE) study. J Mol Liq 333:115957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115957
San Román MF, Bringas E, Ibañez R, Ortiz I (2010) Liquid membrane technology: fundamentals and review of its applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85(1):2–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2252
Pfeiffer RM, Bunge AL (2020) Leakage and swell in emulsion liquid membrane systems: comparing continuous stirred-tank reactor and batch experiments. J Ind Eng Chem 87:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.03.013
Ahmad AL, Kusumastuti A, Derek CJC, Ooi BS (2011) Emulsion liquid membrane for heavy metal removal: an overview on emulsion stabilization and destabilization. Chem Eng J 171(3):870–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.102
Björkegren S, Karimi FR, Martinelli A, Jayakumar SN, Hashim AM (2015) A new emulsion liquid membrane based on a palm oil for the extraction of heavy metals. Membranes. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020168
Mondal S, Purkait MK, De S (2018) Emulsion Liquid Membrane. In: Mondal S, Purkait MK, De S (eds) Advances in dye removal technologies. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 313–323
Raghuraman B, Tirmizi N, Wiencek J (1994) Emulsion liquid membranes for wastewater treatment: equilibrium models for some typical metal-extractant systems. Environ Sci Technol 28(6):1090–1098. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00055a018
Kumar A, Thakur A, Panesar PS (2018) Lactic acid extraction using environmentally benign Green emulsion ionic liquid membrane. J Clean Prod 181:574–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.263
Reis MTA, de Freitas OMF, Ismael MRC, Carvalho JMR (2007) Recovery of phenol from aqueous solutions using liquid membranes with Cyanex 923. J Membr Sci 305(1):313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.08.016
Abbassian K, Kargari A (2016) Modification of membrane formulation for stabilization of emulsion liquid membrane for extraction of phenol from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 4(4):3926–3933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.08.030
Salahshoori I, Hatami A, Seyfaee A (2020) Investigation of experimental results and D-optimal design of hafnium ion extraction from aqueous system using emulsion liquid membrane technique. J Iran Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-020-02007-9
Valenzuela F, Cabrera J, Basualto C, Sapag J, Romero J, Sánchez J, Rios G (2007) Separation of zinc ions from an acidic mine drainage using a stirred transfer cell-type emulsion liquid membrane contactor. Sep Sci Technol 42(2):363–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390601069887
Shirasangi R, Kohli HP, Gupta S, Chakraborty M (2020) Separation of Methylparaben by emulsion liquid membrane: optimization, characterization, stability and multiple cycles studies. Colloids Surf A 597:124761
Davoodi-Nasab P, Rahbar-Kelishami A, Safdari J, Abolghasemi H (2017) Application of emulsion nanofluids membrane for the extraction of gadolinium using response surface methodology. J Mol Liq 244:368–373
Raji M, Abolghasemi H, Safdari J, Kargari A (2018) Response surface optimization of dysprosium extraction using an emulsion liquid membrane integrated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng Technol 41(9):1857–1870
Wagner JR, Mount EM, Giles HF (2014) 25 - Design of experiments. In: Wagner JR, Mount EM, Giles HF (eds) Extrusion, 2nd edn. William Andrew Publishing, Oxford, pp 291–308
Carley KM, Kamneva NY, Reminga J (2004) Response surface methodology. Carnegie-Mellon Univ Pittsburgh PA School of Computer Science, CASOS Technical Report, CMU-ISRI-04-136
Sahu NK, Andhare A (2018) Design of experiments applied to industrial process. Stat Approach Emphasis Des Exp Appl Chem Process 5:353–368
Kargari A, Kaghazchi T, Sohrabi M, Soleimani M (2004) Batch extraction of gold(III) ions from aqueous solutions using emulsion liquid membrane via facilitated carrier transport. J Membr Sci 233(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2003.09.027
Li N, Cahn R, Naden D, Lai R (1983) Liquid membrane processes for copper extraction. Hydrometallurgy 9(3):277–305
Patnaik P (1995) Liquid emulsion membranes: principles, problems and applications in fermentation processes. Biotechnol Adv 13(2):175–208
Laki S, Arabi Shamsabadi A, Madaeni SS, Niroomanesh M (2015) Separation of manganese from aqueous solution using an emulsion liquid membrane. RSC Adv 5(102):84195–84206. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08547K
Othman N, Mat H, Goto M (2006) Separation of silver from photographic wastes by emulsion liquid membrane system. J Membr Sci 282(1):171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.05.020
Sabry R, Hafez A, Khedr M, El-Hassanin A (2007) Removal of lead by an emulsion liquid membrane: Part I. Desalination 212(1–3):165–175
Kageyama T, Matsumiya H, Hiraide M (2004) Separation of traces of heavy metals from an iron matrix by use of an emulsion liquid membrane. Anal Bioanal Chem 379:1083–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2669-z
Fouad EA (2008) Zinc and copper separation through an emulsion liquid membrane containing Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid as a carrier. Chem Eng Technol 31(3):370–376
Gasser MS, El-Hefny NE, Daoud JA (2008) Extraction of Co(II) from aqueous solution using emulsion liquid membrane. J Hazard Mater 151(2):610–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.032
Wan Y, Zhang X (2002) Swelling determination of W/O/W emulsion liquid membranes. J Membr Sci 196(2):185–201
Chakraborty M, Bhattacharya C, Datta S (2010) Emulsion liquid membranes: Definitions and classification, theories, module design, applications, new directions and perspectives. In: Kislik VS (ed) Liquid membranes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 141–199
Basualto C, Poblete M, Marchese J, Ochoa A, Acosta A, Sapag J, Valenzuela F (2006) Extraction of cadmium from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membranes using a stirred transfer cell contactor. J Braz Chem Soc 17(7):1347–1354
Rosly MB, Jusoh N, Othman N, Rahman HA, Sulaiman RNR, Noah NFM (2020) Stability of emulsion liquid membrane using bifunctional diluent and blended nonionic surfactant for phenol removal. Chem Eng Process 148:107790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107790
Lv G, Wang F, Cai W, Zhang X (2014) Characterization of the addition of lipophilic Span 80 to the hydrophilic Tween 80-stabilized emulsions. Colloids Surf A 447:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.01.066
Gasser M, El-Hefny N, Daoud J (2008) Extraction of Co (II) from aqueous solution using emulsion liquid membrane. J Hazard Mater 151(2–3):610–615
Seyfaee A, Neville F, Moreno-Atanasio R (2015) Experimental results and theoretical modeling of the growth kinetics of polyamine-derived silica particles. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(9):2466–2475
Liu H, Zhang Y-m, Huang J, Liu T, Xue N-n, Shi Q-h (2017) Optimization of vanadium (IV) extraction from stone coal leaching solution by emulsion liquid membrane using response surface methodology. Chem Eng Res Des 123:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.05.001
Chakraborty M, Bhattacharya C, Datta S (2003) Mass transfer analysis of the extraction of nickel (II) by emulsion liquid membrane. Indian J Chem Technol 10:311–320
Peng W, Jiao H, Shi H, Xu C (2012) The application of emulsion liquid membrane process and heat-induced demulsification for removal of pyridine from aqueous solutions. Desalination 286:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.051
Peralta-Martínez MV, Arriola-Medellín A, Manzanares-Papayanopoulos E, Sánchez-Sánchez R, Palacios-Lozano EM (2004) Influence of the speed mixing-on viscosity and droplet size of oil in water emulsions. Pet Sci Technol 22(7–8):1035–1043
Nurdin S, Suli LNM, Nour AH, Rizauddin D, Gimbun J, Nurdin S (2014) Stabilization and characterization of heavy crude oil in water (o/w) emulsions. IJRET 3(2):489–496
Muschiolik G, Dickinson E (2017) Double emulsions relevant to food systems: preparation, stability, and applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16(3):532–555
Chakrabarty K, Saha P, Ghoshal AK (2010) Separation of lignosulfonate from its aqueous solution using emulsion liquid membrane. J Membr Sci 360(1):34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.04.043
Mohammed AA, Selman HM (2019) Extraction of lead ions from aqueous solution by CO-stabilization mechanisms of magnetic Fe2O3 particles and nonionic surfactants in emulsion liquid membrane. Colloids Surf A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.02.018
Mohammed AA, Selman HM, Abukhanafer G (2018) Liquid surfactant membrane for lead separation from aqueous solution: studies on emulsion stability and extraction efficiency. J Environ Chem Eng 6(6):6923–6930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.021
Kankekar PS, Wagh SJ, Mahajani VV (2010) Process intensification in extraction by liquid emulsion membrane (LEM) process: a case study; enrichment of ruthenium from lean aqueous solution. Chem Eng Process 49(4):441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2010.02.005
Roy Choudhury S, Mandal Bera A, Chkaravorty D, Gopal M, Goswami A (2013) Evaluation of physicochemical properties, and antimicrobial efficacy of monoclinic sulfur-nanocolloid. J Nanopart Res 15:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1491-y
Ludvigsson M, Lindgren J, Tegenfeldt J (2000) FTIR study of water in cast Nafion films. Electrochim Acta 45(14):2267–2271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(99)00438-7
Ahn H (2015) Central composite design for the experiments with replicate runs at factorial and axial points. In: Industrial engineering, management science and applications, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 969–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-47200-2_101.
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76(5):965–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank laboratory support for this research, which was provided by the Science and Research Branch of the Islamic Azad University (Tehran SRBIAU)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IS: Conceptualization, investigation, experimental work, gathering data, and preparing the original draft. AS: Supervision, development of the research methodology, data analyzing, and preparing the paper. AB: methodology development, writing, reviewing, and editing the manuscript. IC: Supervision, reviewing and editing the manuscript, and preparation of the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Hongmin Zhu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salahshoori, I., Seyfaee, A., Babapoor, A. et al. Recovery of Manganese Ions from Aqueous Solutions with Cyanex 272 Using Emulsion Liquid Membrane Technique: A Design of Experiment Study. J. Sustain. Metall. 7, 1074–1090 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00396-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00396-6