Abstract
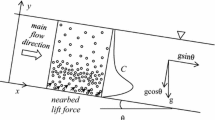
The problem dealing with the two-phase flow of particulate suspension in a converging diverging channel has been analyzed. The basic equations governing the flow are reduced to a set of ordinary differential equations by using the appropriate transformations for the velocity components. The numerical solutions are carried out using numerical technique and the results are presented graphically. The flow phenomena have been analyzed for different physical parameters, Reynolds number, cross flow Reynolds number, angle of the channel, ratios of densities fluid and particle phases and momentum inverse stokes number. The effects of parameters on the velocity of the fluid and the skin friction has been discussed.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- R:
-
Cross flow Reynolds number
- \(r,\theta \) :
-
Polar coordinates
- \(\alpha \) :
-
Angle of the channel
- \(\upsilon \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\mu \) :
-
Coefficient of viscosity
- \(\rho \) :
-
Density of the fluid
- u :
-
Fluid phase velocity
- \(u_p \) :
-
Particle phase velocity
- L :
-
Ratio of the densities of the particle and fluid phase
- \(\beta \) :
-
Momentum inverse stokes number
- S:
-
Drag coefficient of the interaction for the force exerted by one face on the other
References
Jeffery, G.B.: The two dimensional steady motion of a viscous fluid. Philos. Mag. 6, 455–465 (1915)
Hamel, G.: SpiralformigeBewgungenZaherFlussigkeiten. Jahresbericht der DeutschenMath.Vereinigung 25, 34–60 (1916)
Terril, R.M.: Slow laminar flow in a converging or diverging channel with suction at one wall and blowing at the other wall. ZAMP 16, 306 (1965)
Balmer, R.T., Kauzlarich, J.: Similarity solutionsfor converging or diverging steady flowof non-Newtonian elastic power law fluids withwall suction or injection. AICHE J. 17, 1181–1188 (1971)
Sinha Roy, J., Nayak, P.: Steady two dimensional incompressible laminar visco-elastic flow in a converging and diverging channel. Acta Mech. 43, 129–136 (1982)
Shadloo, M.S., Kimiaeifar, A.: Application of homotopy perturbation method to find an analytical solution for magnetohydrodynamic flows of viscoelastic fluids in converging/ diverging channels. In: Proceedings of the Institute of Mechanical Engineers Part C Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science 1989–1996 (vol 203-210). 2010, pp. 347–353
Umavathi, J.C., Shekar, M.: Effect of MHD on Jeffery–Hamel flow in nanofluids by differential transform method. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 3(5), 953–962 (2013)
Mustafa, T.: Extending the traditional Jeffery-Hamel flow to stretchable convergent/divergent channels. Comput. Fluids 100, 196–203 (2014)
Freidoonimehr, N., Rashidi, M.M.: Dual solutions for MHD Jeffery-Hamel nano-fluid flow in non-parallel walls using predictor homotopy analysis method. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 8(4), 911–919 (2015)
Srinivasacharya, D., Mallikarjuna, B., Bhuvanavijaya, R.: Radiation effect on mixed convection over a vertical wavy surface in darcy porous medium with variable properties. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 18(3), 265–274 (2015)
Mallikarjuna, B., Rashad, A.M., Hussein, A.K., Hariprasad Raju, S.: Transpiration and thermophoresis effects on non-Darcy convective flow over a rotating cone with thermal radiation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 4691–4700 (2016)
Mohyud-Din, S.T., Khan, U., Ahmed, N., Mohsin, B.B.: Heat and mass transfer analysis for MHD flow of nanofluid in convergent/divergent channels with stretchable walls using Buongiorno’s model. Neural Comput. Appl. (2017) (in press)
Chamkha, A.J.: Hydromagnetic two-phase flow in a channel. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 33, 437–446 (1995)
Al-Subaie, M.A., Chamkha, A.J.: Analytical solutions for hydromagnetic natural convection flow of a particulate suspension through a channel with heat generation or absorption effects. Heat Mass Transf. 39, 701–707 (2003)
Usha, R., Senthilkumar, S., Tulapurkara, E.G.: Numerical study of particulate suspension flow through wavy-walled channels. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluid 51, 235–259 (2006)
Chamkha, A.J., Al-Rashidi, S.S.: Analytical solutions for hydromagnetic natural convection flow of a particulate suspension through isoflux-isothermal channels in the presence of a heat source or sink. Energy Convers. Manag. 51, 851–858 (2010)
Rawat, S., Bhargava, R., Kapoor, S., Beg, O.A., Beg, T.A., Bansal, R.: Numerical modelling of two-phase hydromagnetic flow and heat transfer in a particle-suspension through a non-Darcian porous channel. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 7(2), 249–261 (2014)
Mallikarjuna, B., Chamkha, A.J., Bhuvanavijaya, R.: Soret and Dufour effects on Double diffusive convective flow through a non-Darcy porous medium in a cylinder annulur region in the presence of heat sources. J. Porous Media 17(7), 623–636 (2014)
Krupa Lakshmi, K.L., Gireesha, B.J., Gorla, R.S.R., Mahanthesh, B.: Effects of diffusion- thermo and thermo-diffusion on two-phase boundary layer flow past a stretching sheet with fluid particle suspension and chemical reaction: A numerical study. J. Niger. Math. Soc. 35(1), 66–81 (2016)
Yao, J., Tao, K., Huang, Z.: Flow of particulate-fluid suspension in a channel with porous walls. Transp. Porous Med. 98, 147–172 (2013)
Kamel, M.H., Eldesoky, I.M., Malur, P.M., Abumandown, R.M.: Slip effects on peristaltic transport of a particle-fluid suspension in a planar channel. Appl. Bion. Biomech. 2015, 703574 (2015). doi:10.1155/2015/703574
Eldesoky, I.M., Abdelsalam, S.I., Abumandown, M.H., Vafai, K.: Interaction between compressibility and particulate suspension on peristaltically driven flow in planar channel. Appl. Math. Mech. 38(1), 137–154 (2017)
Mallikarjuna, B., Rashad, A.M., Chamkha, A.J., Hariprasad Raju, S.: Chemical reaction effects on mhd convective heat and mass transfer flow past a rotating vertical cone embedded in a variable porosity regime. Afrika Matematika 27(3), 646–665 (2016)
Srinivasacharya, D., Mallikarjuna, B., Bhuvanavijaya, R.: Effects of thermophoresis and variable properties on mixed convection along a vertical wavy surface in a fluid saturated porous medium. Alex. Eng. J. 55, 1243–1253 (2016)
Ylimaz, O., Adil, A., Erol, S.: Slow flow of the Reiner-Rivlin fluid in a converging or diverging channel with suction or injection. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 22, 179–183 (1998)
Acknowledgements
One of the author Mallikarjuna thanks to BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-19 for giving financial assistance and support through the TECHNICAL EDUCATION QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROGRAMME [TEQIP-II] of the MHRD, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramprasad, S., Subba Bhatta, S.H.C.V., Mallikarjuna, B. et al. Two-Phase Particulate Suspension Flow in Convergent and Divergent Channels: A Numerical Model. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 3 (Suppl 1), 843–858 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0386-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0386-5