Abstract
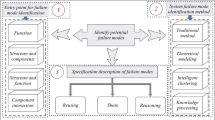
This paper purpose a structural design decision model by using service blueprint, failure mode effect analysis (FMEA), Fuzzy method, and the theory of inventive problem solving (TRIZ). In “service process analysis” stage, the service blueprint approach is used to analyze the potential service failure points in the service process. Then, FMEA is employed to diagnose the possible causes and effects of the service failure model in “service failure diagnosis” stage. The service failure models are prioritized according to the calculated integrated Risk Priority Number (RPN) and fuzzy number. In “innovative principle generation” stage, the innovative principles are generated by utilizing the TRIZ matrix. Finally, in “innovative solution conceptualization” stage, the TRIZ inventive principles are used to inspire the new solution for new service design. An empirical survey of home-care service agencies in Beijing is conducted to demonstrate the applicability of the proposed 2S2I model to improve home-care services, medical-equipment designs, and service delivery. The advantages, implications, and contributions of 2S2I model are also concluded.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboderin, I.: Changing family relationships in developing nations. In: Johnson, M.L. (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Age and Ageing, pp. 469–475. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Palmore, E.B., Whittington, F., Kunkel, S.: The International Handbook on Aging: Current Research and Developments. England, Oxford (2009)
Eiriz, V., Figueiredo, J.A.: Quality evaluation in health care services based on customer-provider relationships. Int. J. Health Care Qual. Assur. 18(6), 404–412 (2005)
Francis, J., Netten, A.: Raising the quality of home care: a study of service user’s views. Social Policy Admin. 38(3), 290–305 (2004)
Raynes, N., Temple, B., Glenister, C., Coulthard, L.: Quality at Home for Older People: Involving Service Users in Defining Home Care Specifications. Policy Press and Joseph Rowntree Foundation, York (2001)
Mitchell, J.M., Kemp, B.J.: Quality of life in assisted living homes: a multidimensional analysis. J. Gerontol. 55, 2 (2000)
Starfish, C.: The Elusive Costs of Home Care. Starfish Consulting, London (2002)
Lee, C.H., Chen, C.H., Trappey, A.J.C.: A structural service innovation approach for designing smart product service systems: case study of smart beauty service. Adv. Eng. Inform. 40, 154–167 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2019.04.006
Li, F., Chen, C.H., Lee, C.H., Khoo, L.P.: A user requirement-driven approach incorporating TRIZ and QFD for designing a smart vessel alarm system to reduce alarm fatigue. J. Navig. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0373463319000547
Dziallas, M., Blind, K.: Innovation indicators throughout the innovation process: an extensive literature analysis. Technovation 80–81, 3–29 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2018.05.005
Lee, C.H., Wang, Y.H., Trappey, A.J.C.: Service design for intelligent parking based on theory of inventive problem solving and service blueprint. Adv. Eng. Inform. 29(3), 295–306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2014.10.002
Shin, H., Perdue, R.R., Kang, J.: Front desk technology innovation in hotels: a managerial perspective. Tourism Manag. 74, 310–318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.04.004
Li, M.L., Hsu, C.H.C.: Customer participation in services and employee innovative behavior: the mediating role of interpersonal trust. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 30(4), 2112–2131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1108/ijchm-08-2016-0465
Chen, B.T.: Service innovation performance in the hospitality industry: the role of organizational training, personal-job fit and work schedule flexibility. J. Hospital. Market. Manag. 26(5), 474–488 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2017.1264344
Poppel, J., Finsterwalder, J., Laycock, R.A.: Developing a film-based service experience blueprinting technique. J. Business Res. 85, 459–466 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.10.024
Johansson, A.E., Raddats, C., Witell, L.: The role of customer knowledge development for incremental and radical service innovation in servitized manufacturers. J. Business Res. 98, 328–338 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.02.019
Yu, E., Sangiorgi, D.: Service design as an approach to implement the value cocreation perspective in new service development. J. Serv. Res. 21(1), 40–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670517709356
Beverungen, D., Luttenberg, H., Wolf, V.: Recombinant service systems engineering. Business Inform. Syst. Eng. 60(5), 377–391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12599-018-0526-4
Ma, S., Gu, H.M., Wang, Y.G., Hampson, D.P.: Opportunities and challenges of value co-creation. The role of customer involvement in hotel service development. Int. J. Contemp. Hospit. Manag. 29(12), 3023–3043 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1108/ijchm-08-2016-0479
Hsiao, Y.C.: Exploring service innovation and value creation: the critical role of network relationships. J. Manag. Organ. 25(1), 4–25 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1017/jmo.2017.40
Wang, Y.H., Lee, C.H., Trappey, A.J.C.: Modularized design-oriented systematic inventive thinking approach supporting collaborative service innovations. Adv. Eng. Inform. 33, 300–313 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2016.11.006
Weng, J.P., Wang, J.H., Yang, J.H., Yang, Y.: Root cause analysis of anomalies of multitier services in public clouds. IEEE-ACM Trans. Netw. 26(4), 1646–1659 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnet.2018.2843805
Chiu, M.C., Chu, C.Y., Chen, C.C.: An integrated product service system modelling methodology with a case study of clothing industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 56(6), 2388–2409 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1374570
Tooranloo, H.S., Ayatollah, A.S.: Pathology the internet banking service quality using failure mode and effect analysis in interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(1), 109–123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0265-y
Salazar, C., Lelah, A., Brissaud, D.: Eco-designing Product Service Systems by degrading functions while maintaining user satisfaction. J. Clean. Prod. 87, 452–462 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.031
Andriankaja, H., Boucher, X., Medini, K.: A method to design integrated product-service systems based on the extended functional analysis approach. Cirp J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 21, 120–139 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2018.02.001
Sun, R., Hu, J., Zhou, J., Chen, X.: A hesitant fuzzy linguistic projection-based MABAC method for patients’ prioritization. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(7), 2144–2160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0345-7
Dincer, H., Yuksel, S.: Comparative evaluation of BSC-based new service development competencies in Turkish banking sector with the integrated fuzzy hybrid MCDM using content analysis. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(8), 2497–2516 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0519-y
Mirghafoori, S.H., Izadi, M.R., Daei, A.: Analysis of the barriers affecting the quality of electronic services of libraries by VIKOR, FMEA and entropy combined approach in an intuitionistic-fuzzy environment. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 34(4), 2441–2451 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3233/jifs-171695
Tooranloo, H.S., Ayatollah, A.S., Marvasti, M.T.: Diagnosing the service quality improvement of university libraries in intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Malays. J. Libr. Inform. Sci. 23(3), 69–91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.22452/mjlis.vol23no3.5
Tsou, H.T., Chen, J.S., Wang, Z.Q.: Partner selection, interorganizational coordination, and new service development success in the financial service industry. Can. J. Admin. Sci. Revue Canadienne Des Sciences De L Administration 36(2), 231–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjas.1487
Johnson, S.P., Menor, L.J., Roth, A.V., Chase, R.B.: A critical evaluation of the new services development process: integrating service innovation and service design. In: Fitzsimmons, j.A., Fitzsimmons, M.J. (eds.) New Service Development, Creating Memorable Experiences. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks (2000)
Liu, C.H., Chang, A.Y.P., Horng, J.S., Chou, S.F., Huang, Y.C.: Co-competition, learning, and business strategy for new service development. Serv. Industr. J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/02642069.2019.1571045
Wu, Y.-C., Lin, G.T.R., Yu, W.-H.: How to enhance customer involvement in service innovation within service industry. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 78(6), 342–344 (2019)
Anning-Dorson, T.: Customer involvement capability and service firm performance: the mediating role of innovation. J. Busin. Res. 86, 269–280 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.07.015
Lee, Y.C., Chen, C.H., Lee, C.H.: Body anthropometric measurements of Singaporean adult and elderly population. Meas J Int Meas Confed (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.106949
Behdioğlu, S., Acar, E., Burhan, H.A.: Evaluating service quality by fuzzy SERVQUAL: a case study in a physiotherapy and rehabilitation hospital. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 30(3–4), 301–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2017.1302796
Xu, H., Fan, Z.-P., Liu, Y., Peng, W.-L., Yu, Y.-Y.: A method for evaluating service quality with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(5), 1523–1538 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0476-5
Chowdhury, M.M.H., Quaddus, M.A.: A multi-phased QFD based optimization approach to sustainable service design. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 171, 165–178 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.09.023
Haber, N., Fargnoli, M., Sakao, T.: Integrating QFD for product-service systems with the Kano model and fuzzy AHP. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2018.1470897
Ljubojevic, S., Pamucar, D., Jovanovic, D., Vesovic, V.: Outsourcing transport service: a fuzzy multi-criteria methodology for provider selection based on comparison of the real and ideal parameters of providers. Oper. Res. Int. Journal 19(2), 399–433 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-017-0293-x
de Aquino, J.T., de Melo, F.J.C., Jeronimo, T.D., de Medeiros, D.D.: Evaluation of quality in public transport services: the use of quality dimensions as an input for fuzzy TOPSIS. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(1), 176–193 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0524-1
Bhuvanesh Kumar, M., Parameshwaran, R.: Fuzzy integrated QFD, FMEA framework for the selection of lean tools in a manufacturing organisation. Prod. Plan. Contr. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2018.1434253
Lee, C.H., Chen, C.H., Li, F., Shie, A.J.: Customized and knowledge-centric service design model integrating case-based reasoning and TRIZ. Expert Syst. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.113062
Lee, Y.-C., Chen, C.-H., Lee, C.-H.: Body anthropometric measurements of Singaporean adult and elderly population. Measurement 148, 106949 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.106949
Pan, Y., Zhang, X., Tian, J., Jin, X., Luo, L., Yang, K.: Mapping asphalt pavement aging and condition using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis in Beijing, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 11, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jrs.11.016003
Chhetri, J.K., Zheng, Z., Xu, X., Ma, C., Chan, P.: The prevalence and incidence of frailty in Pre-diabetic and diabetic community-dwelling older population: results from Beijing longitudinal study of aging II (BLSA-II). BMC Geriatr. 17, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-017-0439-y
Yang, X., Chen, B., Chen, C., Wang, Y.: Dynamic model of population prediction based on Aging Chains. In: 28th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, CCDC 2016 2016, pp. 216-219. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc
Liu, X., Chen, Z., Fine, J.P., Liu, L., Wang, A., Guo, J., Tao, L., Mahara, G., Yang, K., Zhang, J., Tian, S., Li, H., Liu, K., Luo, Y., Zhang, F., Tang, Z., Guo, X.: A competing-risk-based score for predicting twenty-year risk of incident diabetes: the Beijing Longitudinal Study of Ageing study. Sci. Rep. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37248
Li, T., Horton, R.M., Bader, D.A., Zhou, M., Liang, X., Ban, J., Sun, Q., Kinney, P.L.: Aging will amplify the heat-related mortality risk under a changing climate: projection for the elderly in Beijing, China. Sci. Rep. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28161
Chen, C.K., Shie, A.J., Wang, K.M., Yu, C.H.: An ageing-in-place service innovation model by using TRIZ methodology. Hum. Fact. Ergon. Manuf. Serv. Industr. 25(2), 166–182 (2015)
Cohen-Mansfield, J., Frank, J.: Relationship between perceived needs and assessed needs for services in community-dwelling older persons. Gerontologist 48(4), 505–516 (2008)
Cutler, L.J.: Physical environments of assisted living: research needs and challenges. The Gerontologist 47 Spec No 3, 68-82 (2007)
Stone, R.I., Reinhard, S.C.: The place of assisted living in long-term care and related service systems. The Gerontologist 47 Spec No 3, 23-32 (2007)
Nakrem, S., Solbjor, M., Pettersen, I.N., Kleiven, H.H.: Care relationships at stake? Home healthcare professionals’ experiences with digital medicine dispensers—a qualitative study. Bmc Health Serv. Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-2835-1
Dwyer, T., Craswell, A., Rossi, D., Holzberger, D.: Evaluation of an aged care nurse practitioner service: quality of care within a residential aged care facility hospital avoidance service. Bmc Health Serv. Res. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-1977-x
Liu, T., Hao, X., Zhang, Z.: Identifying community healthcare supports for the elderly and the factors affecting their aging care model preference: evidence from three districts of Beijing. Bmc Health Serv. Res. 16(Suppl 7), 626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1863-y
Rizzo, A., Requejo, P., Winstein, C.J., Lange, B., Ragusa, G., Merians, A., Patton, J., Banerjee, P., Aisen, M.: Virtual reality applications for addressing the needs of those aging with disability. MMVR 163, 510–516 (2011)
Chen, S.-H., Wen, P.-C., Yang, C.-K.: Business concepts of systemic service innovations in e-Healthcare. Technovation 34(9), 513–524 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2014.03.002
Yang, H.L., Hsiao, S.L.: Mechanisms of developing innovative IT-enabled services: a case study of Taiwanese healthcare service. Technovation 29(5), 327–337 (2009)
Sun, R.X., Hu, J.H., Zhou, J.D., Chen, X.H.: A hesitant fuzzy linguistic projection-based MABAC method for patients’ prioritization. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(7), 2144–2160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0345-7
Karami, A., Gangopadhyay, A., Zhou, B., Kharrazi, H.: Fuzzy approach topic discovery in health and medical corpora. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(4), 1334–1345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0327-9
Dinçer, H., Yüksel, S.: An integrated stochastic fuzzy MCDM approach to the balanced scorecard-based service evaluation. Math. Comput. Simul. 166, 93–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2019.04.008
Dincer, H., Yuksel, S., Martinez, L.: A comparative analysis of incremental and disruptive innovation policies in the European banking sector with hybrid Interval type-2 fuzzy decision-making models. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00851-8
Del Chiappa, G., Martin, J.C., Roman, C.: Service quality of airports’ food and beverage retailers. A fuzzy approach. J. Air Transp. Manag. 53, 105–113 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2016.02.002
Hsu, W.: A fuzzy multiple-criteria decision-making system for analyzing gaps of service quality. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 17(2), 256–267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0018-3
Mishra, A.R., Jain, D., Hooda, D.S.: Exponential intuitionistic fuzzy information measure with assessment of service quality. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(3), 788–798 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0278-6
Vaziri, J., Beheshtinia, M.A.: A holistic fuzzy approach to create competitive advantage via quality management in services industry (case study: life-insurance services). Manag. Decis. 54(8), 2035–2062 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1108/md-11-2015-0535
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Social Science Fund of Jiangsu Province [Grant Number: 19SHB003]. This research was also supported by the Xi’an Jiaotong University [Grant Number: 7121192301].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shie, AJ., Lee, CH., Yu, SY. et al. A Fuzzy Design Decision Model for New Healthcare Service Conceptualization. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 23, 58–80 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00942-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00942-6