Abstract
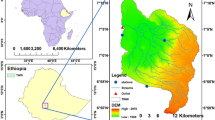
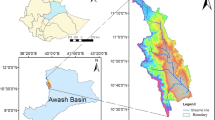
This study assesses the possible impacts of climate change (cc) on the patterns of hydro-climate variables at local scales of the Gidabo watershed in Southern Ethiopia. The Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX)-Africa data output of Hadley Global Environment Model 2-Earth System (HadGEM2-ES) was selected under the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP) scenarios. The streamflow projection by the Hydrologic Engineering Centers-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) model. The HEC-HMS model showed good agreement with the calibration and verification period in the studied four age stations. Then, the areal mean annual (ama) climate-variables trends were assessed by Mann–Kendall (MK) Sen's graphics method and Z statistics. Finally, the impact on future monthly, seasonal, and annual hydro-climate variables was quantified to the baseline period. The results revealed that the climate is successfully projected for given weather stations. The MK trend of ama minimum and maximum temperature (Tmin and Tmax), and potential-evapotranspiration (PET) show significantly increasing whereas rainfall (RF) and streamflow show insignificantly decreasing. And also, the deviation to baseline period of RF − 58.7%, − 34.5% and − 62.2%; temperature + 1.15%, + 2.2% and + 4.2%; PET + 55.5%, + 73% and + 99.9%; and streamflow − 2.63%, − 2.17% and − 3.63% in Meeso, − 0.27%, − 0.20% and − 0.40% in Kolla, + 0.40%, + 0.13% and + 0.53% in Aposto and − 0.13%, − 0.10% and − 0.03% in Bedessa under RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5, respectively. Thus, the decrement in ama and seasonal RF and the increment in temperature lead to more PET and directly affecting the streamflow negatively. Therefore, constantly monitored and updated appropriate interventions in sustainable natural resource management and development are needed in the watershed.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnell NW, Reynard NS (1996) The effects of Cc due to global warming on river flows in Great Britain. J Hydrol 183(3–4):397–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02950-8
Asaminew T, Jie Z (2019) Increase of extreme drought over Ethiopia under climate warming. Adv Meteorol 2019:18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5235429 (Article ID 5235429)
Azman BMJ (2007) Impact of climate change on water resources availability in the Komati River Basin using WEAP21 Model. MSc Thesis, WM, UNISCO IHE
Belihu MB, Abate S, Tekleab WB (2017) Hydro-meteorological trends in the Gidabo catchment of the Rift Valley Lakes Basin of Ethiopia. Phys Chem Earth. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2017.10.002
Bhattacharjee PS, Zaitchik BF (2015) Perspectives on CMIP5 model performance in the Nile River Headwaters Regions. Int J Climatol 35:4262–4275. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4284
Charron I (2014) A guidebook on climate scenarios: using climate information to guide adaptation research and decisions
Clarke L, Edmonds J, Jacoby H, Pitcher H, Reilly J, Richels R (2007) Scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric concentrations. In: Sub-report 2.1A of Synthesis and Assessment Product 2.1 by the U.S. Climate Change Science Program and the Subcommittee on Global Change Research. Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, Washington, DC
Collins WJ, Bellouin N, Doutriaux-Boucher M, Gedney N, Halloran P, Hinton T, Hughes J, Jones CD, Joshi M, Liddicoat S, Martin G, O’Connor F, Rae J, Senior C, Sitch S, Totterdell I, Wiltshire A, Woodward S (2011) Development and evaluation of an Earth-System model—HadGEM2. Geosci Model Dev 4:1051–1075. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-4-1051-2011
Degefu MA, Bewket W (2014) Variability and trends in rainfall amount and extreme event indices in the Omo-Ghibe River Basin Ethiopia. Reg Environ Change 14:799–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0538-z
Dile YT, Berndtsson R, Setegn SG (2013) Hydrological response to climate change for Gilgel Abay River, in the Lake Tana Basin—Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 8(10):e79296. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079296
Ethiopian panel on Climate Change (2015) First assessment report. Working group i physical science basis. the Ethiopian Academy of Sciences
Fekadu K (2015) Ethiopian seasonal rainfall variability and prediction using canonical correlation analysis (CCA). Earth Sci 4(3):112–119. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.earth.20150403.14
Feldman AD (2000) Hydrologic modeling system HEC-HMS. Technical Reference Manual. US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE). Hydrologic Engineering Center, HEC, Davis
Floris M, D’Alpaos A, Squarzoni C, Genevois R, Marani M (2010) Recent changes in rainfall characteristics and their influence on thresholds for debris flow triggering in the Dolomitic area of Cortina d’Ampezzo, north-eastern Italian Alps. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 10:571–580. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-10-571-2010
Gebre SL, Ludwig F (2015) hydrological response to climate change of the Upper Blue Nile River Basin: Based on IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5). J Climatol Weather Forecast 3:121. https://doi.org/10.4172/2332-2594.1000121
Gissila T, Black E, Grimes IF, Slingo JM (2004) Seasonal forecasting of the Ethiopian summer rains. Int J Climatol 24:1345–1358. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1078
Haines A (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Contribution of working group 1 to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change, JT Houghton, Y Ding, DJ Griggs, M Noguer, PJ van der Winden, X Dai. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001, pp. 881, £34.95 (HB) ISBN: 0-21-01495-6; £90.00 (HB) ISBN: 0-521-80767-0. Int J Epidemiol 32(2):321. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyg059
Hargreaves GH, Samani ZA (1985) Reference crop evapotranspiration from temperature. Appl Eng Agric 1:96–99. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.26773
Hessebo MT, Woldeamanuel T, Tadesse M (2021) Spatial and temporal climatevariability and change in the bilate catchment, central Rift Valley lakes region, Ethiopia. Phys Geogr 42(6):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723646.2019.1698094
Ho CK, Stephenson DB, Collins M, Ferro CAT, Brown SJ (2012) Calibrationstrategies: a source of additional uncertainty in climate change projections. Bull Am MeteorolSoc 93:21–26
IPCC (2001) Climate change 2001: The Third Assessment Report of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007: impacts adaptation and vulnerability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York
IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, pp. 1–30, https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part A: global and sectoral aspects. In: Field CB, Barros VR, Dokken DJ, Mach KJ, Mastrandrea MD, Bilir TE, Chatterjee M, Ebi KL, Estrada YO, Genova RC, Girma B, Kissel ES, Levy AN, MacCracken S, Mastrandrea PR, White LL (eds) Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York
Jones CD, Hughes JK, Bellouin N, Hardiman SC, Jones GS, Knight J, Liddicoat S, O’Connor FM, Andres RJ, Bell C, Boo K-O, Bozzo A, Butchart N, Cadule P, Corbin KD, Doutriaux-Boucher M, Friedlingstein P, Gornall J, Gray L, Halloran PR, Hurtt G, Ingram WJ, Lamarque J-F, Law RM, Meinshausen M, Osprey S, Palin EJ, Parsons Chini L, Raddatz T, Sanderson MG, Sellar AA, Schurer A, Valdes P, Wood N, Woodward S, Yoshioka M, Zerroukat M (2011) The HadGEM2-ES implementation of CMIP5 centennial simulations. Geosci Model Dev 4:543–570. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-4-543-2011
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods, 4th edn. Charles Grifin, London
Kiros G, Shetty A, Nandagiri L (2016) Analysis of variability and trends in rainfall over northern Ethiopia. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2471-1
Leander R, Adri Buishand T (2007) Resampling of regional climatemodel output for the simulation of extreme river flows. J Hydrol 332(3–4):487–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.08.006
Li Z (2014) Watershed modeling using arc hydro based on DEMs: a case study in Jackpine watershed. Environ Syst Res 3:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-2697-3-11
Li L, Li W, Ballard T, Sun G, Jeuland M (2016) CMIP5 model simulations of Ethiopian Kiremt-season precipitation: current climate and future changes. Clim Dyn 46(9–10):2883–2895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2737-4
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245–259. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907187
Mohammad RF, Saeid E, Zahra SS, Aboulfazl A (2014) An appropriate GCM to investigate climate change impact. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 2(1):34–47. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2012.045938
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50(3):885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Negash W, Jain MK, Goel NK (2013) Effect of climate change on runoff generation, application to Rift Valley Lakes basin of Ethiopia. J Hydrol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000647
Niguse A, Aleme A (2015) Modeling the impact of climate change on production of Sesame in western zone of Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. J Climatol Weather Forecast 3:150. https://doi.org/10.4172/2332-2594.1000150
NMA (2007) Climate change national adaptation program of action (NAPA) of Ethiopia. NMA, Oxfam International, Addis Ababa
NMSA (2001) Initial National Communication of Ethiopia to the United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). National Meteorological Services Agency, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Pettitt AN (1979) A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. Appl Stat 28:126–135. https://doi.org/10.2307/2346729
Pingale SM, Khare D, Jat MK, Adamowski J (2016) Trend analysis of climatic variables in an arid and semi-arid region of the Ajmer District, Rajasthan. India J Wat Lan Dev 28(1):3–18
Ramos-Calzado P, Gomez-Camacho J, Perez-Bernal F, Pita-Lopez MF (2008) A novel approach to precipitation series completion in climatological datasets: application to Andalusia. Int J Climatol 28:1525–1534. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1657
Riahi K, Grübler A, Nakicenovic N (2007) Scenarios of long-term socio-economic and environmental development under climate stabilization. Technol Forecast Soc Change 74(7):887–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2006.05.026
Santhi C (2001) Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37(5):1169–1188. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb03630.x
Seleshi Y, Zanke U (2004) Recent changes in RF and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 24(8):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1052
Shanka AS (2017) Evaluation of climate change impacts on run-off in the Gidabo River Basin: Southern Ethiopia. Environ Pollut Clim Change 1:129. https://doi.org/10.4172/2573-458X.1000129
Sintayehu LG (2015) Application of the HEC-HMS Model for streamflow simulation of upper Blue Nile River Basin. Hydrol Curr Res 6:199. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7587.1000199
Snyder FF (1938) Synthetic unit graphs. Trans Am Geophys Union 19(1938):447–545
Subramanya K (2009) Engineering Hydrology. Tata McGraw, 7 West Patal Nagar, New Delhi 110 008
Tabari H, Marofi S, Aeini A, Hosseinzadeh-Talaee P, Mohammadi K (2011) Trend analysis of reference evapotranspiration in the Western Half of Iran. Agric Meteorol 151:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.09.009
Tabari H, Meron TT, Willems P (2015) Statistical assessment of precipitation trends in the upper Blue Nile River basin. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1046-0
Tekleab S, Mohamed M, Uhlenbrook S (2013) Hydro-climatic trends in the Abay/Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Phys Chem Earth 61–62(2013):32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2013.04.017
Teutschbein C, Seibert J (2010) Regional climate models for hydrological impact studies at the watershed scale: a review of recent modeling strategies. Geogr Compass 4(7):834–860. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-8198.2010.00357.x
Teutschbein C, Seibert J (2012) Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: review and evaluation of different methods. J Hydrol 456–457:12–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.052
Tsvetkova O, Randhir TO (2019) Spatial and temporal uncertainty inclimatic impacts on watershed systems. Sci Total Environ 687:618–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.141
UNICEF (2015) Situation reports, news, analysis, evaluations, assessments, maps, infographics and more on Ethiopia: Floods (Southern Somali, Southern Oromia, and the lowlands in South Omo Zone in SNNPR)
Urgaya ML (2016) Modeling the impacts of climate change on chickpea production in Adaa Woreda (East Showa Zone) in the semi-arid central Rift valley of Ethiopia. J Pet Environ Biotechnol 7:288. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7463.1000288
US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) (2000) Hydrologic modeling system HEC-HMS Technical Reference Manual. Hydrologic Engineering Center, Davis
USACE (2015) Hydrological modeling system (HMS) user manual: USACE institute for water resources (CEIWR-HEC) 609 second street. Davis, CA 95616-4687
USID (2015) Climate variability and change in Ethiopia: technical report by Chemonics International for the Climate Change ATLAS Task Order No. AID-OAA-I-14-00013
van Vuuren DP, den Elzen MG, Lucas PL et al (2007) Stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations at low levels: an assessment of reduction strategies and costs. Clim Change 81:119–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9172-9
van Vuuren DP, Edmonds J, Kainuma M et al (2011) The representative concentration pathways: an overview. Clim Change 109:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0148-z
Venkatesh M (2012) Watershed and stream network delineation using arc hydro tools: School of Civil Engineering, purdel Purdue University Merwade @purdue.edu
Willems P (2008) A time-series tool to support the multi-criteria performance evaluation of rainfall-streamflow models. Environ Model Softw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2008.09.005 (Corpus ID: 31180597)
World Bank (2010) World Development Report. Development and Climate Change. World Bank, Washington, DC. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/4387 (License: CC BY 3.0 IGO)
Yilma H, Moges S (2007) Application of semi-distributed conceptual hydrological model for flow forecasting on upland catchments of Blue Nile River Basin, a case study of Gilgel Abbay catchment. Catchment and Lake Research
Yilma S, Zanke U (2004) Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 24(2004):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1052
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alehu, B.A., Desta, H.B. & Daba, B.I. Assessment of climate change impact on hydro-climatic variables and its trends over Gidabo Watershed. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 8, 3769–3791 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01327-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01327-w