Abstract
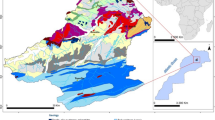
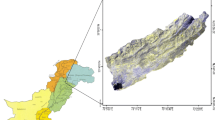
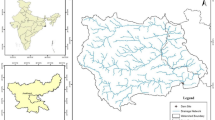
Sedimentation is a significant issue for agricultural dams in Ethiopia, as it diminishes the capacity limit and life expectancy of the repositories. The procedure of sedimentation begins from the very first moment of the seizing of water in some random supply. Even though an arrangement is made for each reservoir during anticipating a specific stockpiling limit, explicitly for silt testimony, called dead storing, a significant part of the sediments gets kept for a long time of the supply's life in zones other than the dead storing, and this pattern cannot be turned around at a simple expense. This investigation is focused on the examination of persuasive sedimentation forms in the close by many dams found in the south Gondar zone catchment situated inside the Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia and spotlights on the appraisal of yearly sedimentation rate. Spatial investigation and displaying examines were directed dependent on the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS to decide silts yield and level of effect of every store for a given scene, precipitation, and catchment heterogeneity. Field perceptions and soil testing were done to decide the components that lead to repository sedimentation. Spatial Data on the dams in south Gondar zone catchment were likewise gathered from the Ministry of Agriculture, which were utilized for ground-truthing, GIS-based computations, and model approval. The average specific sediment rate and silt delivery proportion were seen as 4059.2 t km−2 year−1 and 72.67%, individually. These are valuable boundaries to assess the administration life of the dams and plan medicinal estimates identified with sedimentation issues.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemaw BF, Majauale M, Simalenga T (2013) Assessment of sedimentation impacts on small dams—a case of small reservoirs in the lotsane catchment journal of water resource and protection, 2013, 5, 1127–1131 Published Online December 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp, https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2013.512118
CSA (2012) Summary and statistical report of the 2012 population and housing censuspopulation size by age and sex. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Erdogan EH, Erpul G, Bayramin I (2007) Use of USLE/ GIS methodology for predicting soil loss in a semiarid agricultural environment. Environ Monit Assess 131(1–3):153–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9464-6
FAO (2016) The climate of Ethiopia, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nation. Retrieved from. https://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/countries_region s/ETH/. Accessed 12 Mar 2019
Fazzini M, Bisci C, Billi P (2015) The climate of Ethiopia. In: Billi P (Ed) Landscapes and landforms of Ethiopia. World Geomorphological Landscapes, pp 65–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-8026-1_3.
Gharehkhani R (2011) Issues Problems of Sedimentation in Reservoir Siazakh Dam Case Study. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 60:1100–1102
Greig SM, Sear DA, Carling PA (2005) The impact of fine sediment accumulation on the survival of incubating salmon progeny: implications for sediment management. Sci Total Environ 344(1–3):241–258
Kim HS (2006) Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE and GIS on the Imha watershed, South Korea (Doctoral dissertation, Colorado State University).
Moges MM, Abay D, Engidayehu H (2018) Investigating reservoir sedimentation and its implications to watershed sediment yield: The case of two small dams in data-scarce upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Lakes Reserv 23:217–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12234
Morris LG, Fan J (1998) Reservoir sedimentation handbook, design, and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. McGraw-Hill Book Co, New York
Nyakatawa EZ, Reddy KC, Lemunyon JL (2001) Predicting soil erosion in conservation tillage cotton production systems using the revised universal soil loss equation. Soil Till Res 57(4):213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(00)00178-1
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). Agriculture Handbook No. 703, 1997, USDA-ARS
Sichingabula HM (1997) Problems of sedimentation in small Dams in Zambia. Human impact in erosion and sedimentation. In: Proceedings of the Rabat Symposium in April 1997. IAHS. Publ. No. 245, 1997
Walker D, Parkin G, Gowing J, Haile AT (2019) Development of a hydrogeological conceptual model for shallow aquifers in the data-scarce upper Blue Nile basin. Hydrology 6(43):1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6020043
Williams JR, Berndt HD (1972) Sediment yield computed with universal equation. J HydrDiv ASCE 98:2087–2098
Wischmeier WH, Johnson CB, Cross BV (1971) A soil erodibility nomograph for farmland and construction sites. J Soil Water Conserv 26:189–193
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation planning (No. 537). Department of Agriculture, Science, and Education Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
We (Authors) have to declare that, we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiferaw, M., Abebe, R. A spatial analysis and modeling study of sedimentation impacts on dams found in south Gondar zone, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 7, 2225–2230 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01003-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01003-5